HPE Smart Cache: are you already speeding up?
Data caching is not new to server or storage disk subsystems. As you know, the cache is an intermediate link between the data and the disk subsystem. Considering that SSD with fast access is already fairly well established in our life, the use of All-Flash subsystems is still not available to everyone for one reason or another (mostly economic, because all theories about the low reliability of SSD are not received any serious evidence). But the desire to accelerate the speed of its storage subsystem, organized on classic HDD drives, is still present and is nowadays more of a necessity. Due to the fact that the size of the cache is of considerable importance - an increase in its volume will only benefit the high-load systems. This is where SSD cache comes to our rescue.
 Almost all manufacturers of RAID controllers have already presented models of controllers that support caching on SSDs, and today we will look at how this was implemented by HPE based on its HPE Smart Array P440ar controller .
Almost all manufacturers of RAID controllers have already presented models of controllers that support caching on SSDs, and today we will look at how this was implemented by HPE based on its HPE Smart Array P440ar controller .
And so, as an experimental system in my hands is HPE ProLiant DL380 Gen9 in the following configuration:
The hard drives were assembled in Raid10, and the tests were carried out, respectively, in two versions - with the inclusion of HPE Smart Cache and without it (using the controller cache, 2Gb).
I think that those who were interested in this topic have long been familiar with the Intel S3700 drive. He came out a relatively long time and extremely positively recommended himself. The company itself assigns them to the highest class - High Endurance and in fact recommends them to be used for high-loaded tasks like OLTP, VDI, Big Data, and for data caching less expensive - Value Endurance, but as they say - what we have. Worse, in any case, it certainly will not be, but for end users, it will naturally increase the cost of the configuration. In any case - you are free to use absolutely any SSD drives, HPE gives a recommendation only on their volume - it should be 5-10% of the capacity of your array. It is also worth making a reservation that not all controllers support HPE Smart Cache and lower-end controller models do not have this feature. Smart Cache will only work on servers of the 8th and 9th generations, i.e. improve the performance of the disk subsystem of the old servers - not work, but sorry.
')
HPE Smart Cache in the current implementation allows you to cache both read and write operations, so it does not have any limitations and can be used for any applications that are engaged in the exchange of information with the disk subsystem.
And so, let's move on to the numbers. Due to the extremely limited time for testing - they will be limited to using only iometer.
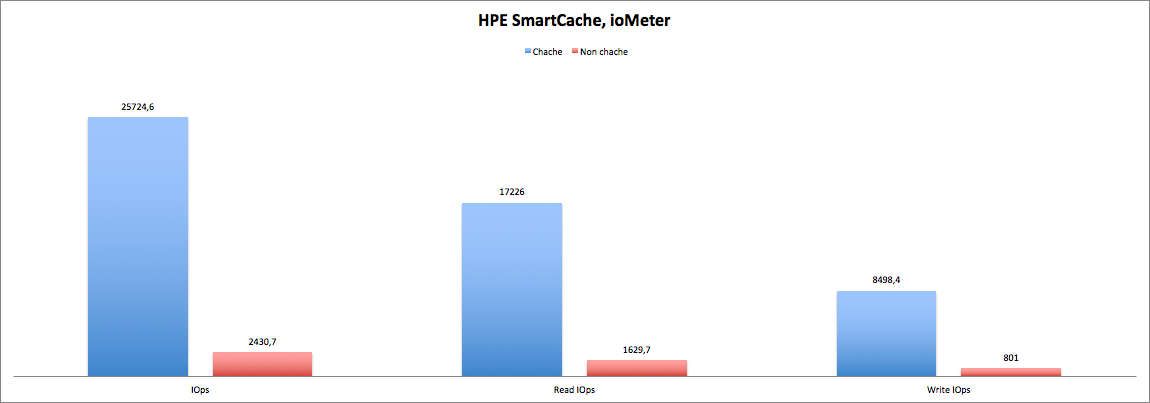
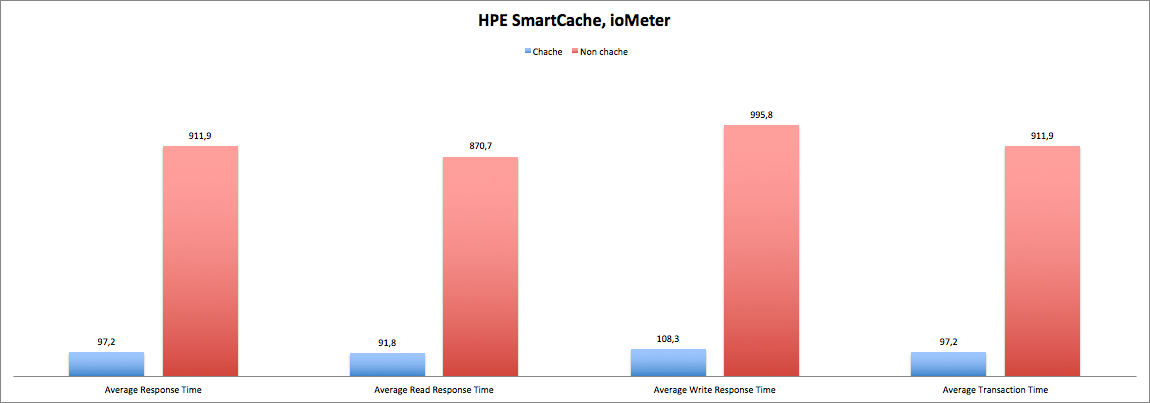
For this test, the most difficult and resource-intensive test was chosen - Database. Test configuration:
In a situation as close as possible to combat, we can see the advantage of using the cache in all respects, both in reading and writing. At the same time, the response time is also an order of magnitude lower, which is extremely important for resource-intensive OLTP applications.
As for the "classification" SSD cache in the hierarchy of performance acceleration of the disk subsystem. In principle, we have three ways to do this. The first is the theme of our material today - SSD cache, the second is the transition to All-flash, and the third is the so-called IO accelerators, which I already talked about and tested - Huawei Tecal ES3000 , Fusion-io ioDrive (which its logo offers and the company HPE), etc. These devices are able to further increase the processing speed of your data, but the cost of these solutions will be much higher than using the cache on the SSD. Perhaps it is the most profitable in terms of price / performance.
Summarizing, we can say that if you need to increase the performance of the server disk subsystem, with the lowest cost, the use of SSD-cache is quite justified. With a relatively low cost of this solution (the cost of the solution includes the SSD itself + a license for the HPE Smart Cache for the controller, and it is worth noting that if you have several RAID controllers installed in the server - the license is purchased for each of them separately), we get significant increase in speed.

And so, as an experimental system in my hands is HPE ProLiant DL380 Gen9 in the following configuration:
Processor: Intel Xeon Processor E5-2643 v3 x2
Memory: 8Gb x4
HDD: 600GB SAS 15K x4
SSD: Intel S3700 400Gb
The hard drives were assembled in Raid10, and the tests were carried out, respectively, in two versions - with the inclusion of HPE Smart Cache and without it (using the controller cache, 2Gb).
I think that those who were interested in this topic have long been familiar with the Intel S3700 drive. He came out a relatively long time and extremely positively recommended himself. The company itself assigns them to the highest class - High Endurance and in fact recommends them to be used for high-loaded tasks like OLTP, VDI, Big Data, and for data caching less expensive - Value Endurance, but as they say - what we have. Worse, in any case, it certainly will not be, but for end users, it will naturally increase the cost of the configuration. In any case - you are free to use absolutely any SSD drives, HPE gives a recommendation only on their volume - it should be 5-10% of the capacity of your array. It is also worth making a reservation that not all controllers support HPE Smart Cache and lower-end controller models do not have this feature. Smart Cache will only work on servers of the 8th and 9th generations, i.e. improve the performance of the disk subsystem of the old servers - not work, but sorry.
')
HPE Smart Cache in the current implementation allows you to cache both read and write operations, so it does not have any limitations and can be used for any applications that are engaged in the exchange of information with the disk subsystem.
And so, let's move on to the numbers. Due to the extremely limited time for testing - they will be limited to using only iometer.


For this test, the most difficult and resource-intensive test was chosen - Database. Test configuration:
Disk Size - 209,715,200 (100Gb)Database patter can be found here.
# of Outstanding IOs - 256
In a situation as close as possible to combat, we can see the advantage of using the cache in all respects, both in reading and writing. At the same time, the response time is also an order of magnitude lower, which is extremely important for resource-intensive OLTP applications.
As for the "classification" SSD cache in the hierarchy of performance acceleration of the disk subsystem. In principle, we have three ways to do this. The first is the theme of our material today - SSD cache, the second is the transition to All-flash, and the third is the so-called IO accelerators, which I already talked about and tested - Huawei Tecal ES3000 , Fusion-io ioDrive (which its logo offers and the company HPE), etc. These devices are able to further increase the processing speed of your data, but the cost of these solutions will be much higher than using the cache on the SSD. Perhaps it is the most profitable in terms of price / performance.
Summarizing, we can say that if you need to increase the performance of the server disk subsystem, with the lowest cost, the use of SSD-cache is quite justified. With a relatively low cost of this solution (the cost of the solution includes the SSD itself + a license for the HPE Smart Cache for the controller, and it is worth noting that if you have several RAID controllers installed in the server - the license is purchased for each of them separately), we get significant increase in speed.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/277285/
All Articles