Video conferencing Mind - the best choice for business
 To date, videoconferencing ( videoconferencing ) will not surprise anyone. Free video calls are available to almost everyone. Even text messaging services gradually received the functionality of first a call, and then a video chat. There are also free applications with basic functionality for joining several participants into a video conference. But there are a number of disadvantages of such communication: the quality of communication sometimes leaves much to be desired, the service is in the cloud and, therefore, confidentiality and uninterrupted negotiations are not guaranteed, the functionality is minimal and does not allow to solve most of the tasks.
To date, videoconferencing ( videoconferencing ) will not surprise anyone. Free video calls are available to almost everyone. Even text messaging services gradually received the functionality of first a call, and then a video chat. There are also free applications with basic functionality for joining several participants into a video conference. But there are a number of disadvantages of such communication: the quality of communication sometimes leaves much to be desired, the service is in the cloud and, therefore, confidentiality and uninterrupted negotiations are not guaranteed, the functionality is minimal and does not allow to solve most of the tasks.In order to provide high-quality communication and business process solutions, organizations use professional video conferencing solutions. To date, several large foreign manufacturers of video conferencing hardware solutions are on the market: Polycom, Cisco (acquired Tandberg at one time and now continues to develop video conferencing under its own brand), LifeSize, Huawei and others. All these are hardware solutions manufacturers, namely, specialized servers equipped with a Digital Signal Processor (DSP) are engaged in decoding / processing / encoding video and sound. And to equip meeting rooms, codecs are used, including the encoders themselves with DSP, as well as cameras and speakerphones.
In recent years, these brands have formed a common standard of quality and functionality of video conferencing. This includes: HD-quality video broadcasting, simultaneous holding of several independent conferences on one server, planning events and creating virtual meeting rooms. This also includes the flexible configuration of the layouts of participants' windows and voice activation - i.e. the current window is displayed in the main window.
At the beginning of the development of video conferencing, only specialized servers with expensive media cards could cope with these tasks. But in recent years, the performance of x86-processors has reached such a level that software solutions for video conferencing under the standard server architecture have begun to appear on the market.
STSS , a domestic manufacturer of server hardware together with Mind , a leading domestic developer of video conferencing software, developed a ready-made STSS Flagman MIND solution for video conferencing and webinars.
The solution not only meets all industry standards of video conferencing, but also has a number of advantages compared with the hardware implementations of the manufacturers listed above.
Cost of solution
The recommended price of a Polycom server for 10 HD (720p) subscribers is about $ 76K. A similar configuration of the STSS Flagman MIND server costs about $ 14K, including Mind Server licenses, which is 5 times less than the cost of a Polycom server.
Consider the cost of meeting room equipment: a codec, a PTZ camera with 4x optical zoom and an external Polycom microphone cost about $ 6.8K. A similar set of equipment based on STSS MIND costs no more than $ 2.5K. In this case, the role of a codec can perform any PC average performance.
Versatility and compatibility
One of the main advantages of the Mind-based solution is the support of key technologies and protocols such as:
- Stack H.323 necessary for integration with hardware solutions from leading manufacturers of professional video conferencing equipment.
- SIP for integration with IP telephony
- WebRTC for participation in conferences and webinars via a browser from anywhere in the world
')
Estimated delivery time
This criterion plays an important role in project implementation. The delivery time for VC equipment from Polycom, Cisco or Huawei is several months. And the delivery time of the STSS MIND video conferencing system does not exceed 10 days.
Scalability
The task of expanding the port capacity of the server, using the example of the same Polycom, is solved by acquiring additional connection licenses and media cards to increase performance. For example, such an upgrade to 5 HD ports will cost $ 29K, and that is not counting the cost of a media card, which costs $ 41K.
STSS MIND solution is based on standard server architecture and specialized software based on Linux. If you need to improve performance, the server can be upgraded by installing a second one or replacing the processors with more efficient ones. The flexible and convenient STSS MIND configurator allows you to choose the optimal server configuration for existing tasks or calculate a solution with a performance margin for future growth in needs. Expanding a Mind license will cost six times less than Polycom, and will not exceed $ 4.5K.
Media flow processing
In the most general terms, the process of processing a media stream is as follows:
- the rapporteur’s client computer encodes the signal from the video camera and sends it to the Mind server (in the Mind system, this process is called publishing or broadcasting).
- the server processes the media stream and sends it to all participants of the event
- the participants' computers decode the media stream and display it on the monitor screens
The load on clients, server and network depends on the quality of the video and on the number of media streams:
- In the case of a webinar with one speaker, each participant receives and decodes only one media stream.
- In the case of a conference where a lot of participants have the right to broadcast video, each client's browser receives and decodes as many streams as the participants turned on their video cameras (narrow bandwidth and weak client computers, in such a situation, can make the conference impossible
To optimize bandwidth usage, the Mind server has two broadcast modes:
- Stream mode (streams) - all video streams are transmitted to all participants of the event. The volume of traffic between the server and the client grows with an increase in the number of participants publishing their videos.
- Mixing mode (mosaic) - video streams of all participants are combined into one stream of a given quality. The volume of outgoing traffic from the server and incoming traffic to clients does not depend on the number of broadcasting participants.
For ease of management, several media profiles (performance profiles) were created in the Mind system, each of which defines the video quality and the broadcast mode.
At the start of the event, each participant is assigned a default performance profile set in the domain settings. As soon as, during the conference, the number of broadcasting participants exceeds a certain threshold value, the system automatically switches the participants to another media profile — for example, a profile with a mosaic broadcast mode and a lower broadcast quality.
Automatic switching of performance profiles reduces the load on all system components and does not interrupt ongoing activities.
The composition of the solution STSS MIND
The solution configurator allows you to quickly and accurately assess the budget of the video conferencing project and form a specification with a few clicks.
The solution includes:
1. One of the five models of the STSS Flagman MIND server , optimized to work with a certain number of participants.
STSS Flagman MIND110.4-002LF is the youngest model that supports simultaneous connection of up to 15 WebRTC clients or up to 4 SIP / H323 devices. In the webinar mode, the server will ensure participation of up to 75 participants in the WebRTC mode and up to 375 - in the Flash mode.
STSS Flagman MIND116.4-004LH - transitional model. This server is only 30% more powerful than the previous one, but has support for a dual power supply and hot-swappable disks. The model is limited to 20 connections WebRTC or 5 SIP / H323-devices.
STSS Flagman MIND216.4-004LH is a compact, high-performance 1U server with a fail-safe power supply and hot-swappable disks. Provides simultaneous connection: video conferencing: up to 50 WebRTC ports (browser) or up to 13 SIP / H323 ports (codec) / Webinar: up to 250 WebRTC participants or up to 1,250 Flash participants.
STSS Flagman MIND226.4-008LH and STSS Flagman MIND240.4-008LH have the necessary performance to support up to 150 WebRTC connections. When working through SIP or H323, the server is able to bring together nearly 4 dozen devices into a conference. With this server you can conduct HD webinars for thousands of participants. The disk subsystem of servers will allow for a long time to keep an archive of records of all events.
2. Software Mind Server with the necessary set of licenses VKS or Webinar.
VCS licenses are divided by duration (perpetual and 1 year) and by device type (port and multiport).
VCS licenses for 1 year include technical support for a period of 1 year. Perpetual licenses for video conferencing are also provided with technical support for a period of 1 year.
The license "port" - allows you to combine in a conference only WebRTC-users. The “multiport” license along with WebRTC also supports SIP / H323 devices.
It is possible to purchase both port and multiport licenses for a single server, but it is impossible to mix urgent and unlimited licenses.
Webinar licenses differ in the same way. In addition to everything, there is another difference in the number of speakers: up to 2 or up to 4 webinar speakers.
In the configurator are typical combinations of licenses. If necessary, make an individual calculation - a request is made through the configurator with the indication of the wishes.
3. In the configurator of the STSS MIND solution there is a selection of specialized equipment for completing personal workplaces, meeting rooms and conference rooms.
To equip personal jobs it is recommended:
 Practical FullHD-camera Logitech HD Pro Webcam C920.
Practical FullHD-camera Logitech HD Pro Webcam C920.As an audio headset, several Jabra models are offered:
Jabra Evolve 40 UC Stereo - wired stereo headset with a control unit and passive noise reduction.
The Jabra Pro 930 is a wireless DECT mono headset with a USB base station.
Jabra Motion UC is a wireless Bluetooth mono headset capable of connecting simultaneously to a PC and mobile phone.
For equipping small meeting rooms it is recommended:
 Prestel HD-PTZ6 video conferencing camera - USB 2.0 camera with a resolution of 1920x1080 pixels, equipped with panning electric drives: ± 180 °, tilt: from -30 ° to + 90 ° and RS-232 and RS-485 control interfaces.
Prestel HD-PTZ6 video conferencing camera - USB 2.0 camera with a resolution of 1920x1080 pixels, equipped with panning electric drives: ± 180 °, tilt: from -30 ° to + 90 ° and RS-232 and RS-485 control interfaces.As an audio system model proposed Jabra Speak 510+. This speakerphone has USB and Bluetooth connectivity. Supports up to 15 hours of battery life in talk mode on a single charge.
To equip medium meeting rooms, it is recommended:
 Prestel HD-PTZ2W video conferencing camera - swiveling Full HD camera with a wide-angle lens (overview up to 105 °), USB 3.0 and DVI-I (HDMI) interfaces, providing video transmission in 1080p30 format. 3x optical and 3x digital zoom, together with a wide viewing angle, provide full coverage of the meeting room with the ability to display video conference participants in detail.
Prestel HD-PTZ2W video conferencing camera - swiveling Full HD camera with a wide-angle lens (overview up to 105 °), USB 3.0 and DVI-I (HDMI) interfaces, providing video transmission in 1080p30 format. 3x optical and 3x digital zoom, together with a wide viewing angle, provide full coverage of the meeting room with the ability to display video conference participants in detail.As an audio system, the model proposed Jabra Speak 810 UC - this USB-speakerphone is equipped with microphones ZoomTalk. Thanks to digital signal processing, it provides crystal clear sound without echo and distortion, including at maximum volume.
For the equipment of conference rooms it is recommended:
Prestel HD-PTZ8IP video conferencing camera is a networked 1080p60 camera with support for interfaces: RJ-45, HDMI, CVBS, as well as USB 3.0 with backward compatibility with USB 2.0, equipped with a 20x optical zoom lens. The high sensitivity of the matrix (0.5 lux), high signal-to-noise ratio (> 55 dB), as well as the built-in 2D noise reduction 3D algorithms provide a clear and bright image, even in low light conditions in the meeting room.
 A 20-fold optical zoom provides an opportunity to examine in detail the videoconference participants located in the furthest corners of the vast conference rooms.
A 20-fold optical zoom provides an opportunity to examine in detail the videoconference participants located in the furthest corners of the vast conference rooms.I already introduced you to this camera in the article Video Surveillance and Analytics of Macroscop in detail , where it showed excellent abilities in zooming in and out of distant objects.
 Since conference rooms have a large area and are able to accommodate dozens of speakers, they use congress systems for high-quality sound transmission. In our case, the AVCiT solution is used with the AVCiT C3101 central module, capable of switching up to 128 consoles.
Since conference rooms have a large area and are able to accommodate dozens of speakers, they use congress systems for high-quality sound transmission. In our case, the AVCiT solution is used with the AVCiT C3101 central module, capable of switching up to 128 consoles.AVCiT D3103 - The delegate unit with a replaceable microphone allows participants to speak, apply for a speech and listen to the speaker. The microphone is equipped with a flexible leg. The console also has a headphone output that provides good audibility even with strong background noise. To prevent acoustic feedback, the built-in speaker is muted when the microphone is turned on.
AVCiT D3102 - the chairman’s console with a replaceable microphone, in addition to the functions of the delegate’s console, allows you to turn off the speakers' microphones.
Using the STSS MIND solution configurator, you can calculate the cost of the finished video conferencing solution for your needs.
Workspace service VC Mind and the available functionality in user mode
In order to create an event, select the type of event from the pop-up list on the “Start Now” tab.
There will be an automatic entry to the created event.
There are several bookmarks available in the event menu.
The tab “About the event” reflects detailed information, including direct links to the event for guests and speakers, which allow you to visit the event from anywhere with Internet access.
In the "Documents" section you can place any files that will be available for download to the participants of the event.
The “Board” mode allows you not only to use the virtual flipchart, but also to load as a substrate any text or graphic document, and to make recordings and sketches directly on it.
The “Poll” functionality is especially relevant for the webinar, when you need to get feedback from the participants after the event.
“Demonstrating the desktop” requires installing the Mind Screen Sharing extension for the browser. This functionality allows you to broadcast as a desktop as a whole, and a specific window.
Event settings include useful functionality, including the "Live broadcast" function and the creation of invitation cards.
Invitation cards can be designed for a limited number of users. This can be useful when you plan to invite a certain number of people from one organization. Thus, the link will be able to use any of the invitees, but on condition that the selected limit is not exceeded.
In addition to generating invitation links, participants can be invited in person.
To do this, enter the e-mail address or SIP-device. The invited participant receives a letter regardless of whether it is registered in the service or not. A SIP participant can receive an incoming call, and the user of the Mind Meeting mobile application, in addition to writing to the mail, will receive a notification signal to his device.
The invitation letter reflects the link to the event and, having passed through it, the participant can log in to the service under his account, register (if the functionality is not blocked by the administrator) or enter as a guest.
For each participant, you can set individual broadcasting rights. Set limits, role and layout settings.

The top pane includes the layout control buttons on the left and the session control buttons on the right.
Using them, you can turn on and off your own camera and microphone, raise a virtual hand (the moderator, seeing it, can turn on your camera or microphone - if the event takes place in the lecture mode) and change the quality of the broadcast.

The “Hardware Setup” button allows you to select a microphone and camera for use in the session.
When choosing the maximum broadcast quality, the streams pass through the server and are broadcast to all participants without changing the maximum resolution. If the capabilities of the channel or client device are limited, it is necessary to reduce the quality from maximum to high. In this mode, the server will independently combine the image, creating a single stream from all incoming. Thus, the final client will receive only one stream, including a picture from all participants. The “Permanent Presence” functionality will also be available in this mode - the server itself will determine the activity of the participant’s microphone and output the stream from its camera in an enlarged window.
For event planning, there is a convenient and intuitive form to fill out.
Rooms are created on the same principle as regular events, except that the room does not have an expiration date - it is always active. When creating a room, the participants are allowed to enter, and they can enter it anytime and for as long as they wish.
Let's take a closer look at the system architecture, technical requirements, and the details of configuration and administration.
Architecture of the video conferencing system MInd
System features
Mind is a video conferencing system (VCS) that runs on the basis of the Debian GNU / Linux operating system and provides for the exchange of real-time audio and video information between two or more remote users.
The system is focused on the creation and holding of the following types of events:
- video conferencing
- webinars
- audio conferencing
VSK Mind allows you to:
- organize mass online events
- broadcast high definition video
- quickly create events using templates
- create permanent events - online meeting rooms
- invite to events, both registered in the system of users, and participants from
- create and use address books
- flexibly manage the rights and capabilities of users during the event
- record events on the server
Clients can take part in Mind events using:
- web browsers
- mobile devices
- other software or hardware systems of video conferencing under SIP and H.323 protocol
- calls from landline or mobile phones, provided that the enterprise PBX is integrated with the Mind system via the SIP protocol
Additionally, during events, participants can use the following functions:
- electronic board
- demonstration of your desktop or part of it
- file sharing
- demonstration of documents
- chat
- creating and conducting surveys
- inviting new participants during the event
To ensure the security of data transmission, the Mind system supports:
- SSL / TLS connection
- encryption of media traffic DTLS-SRTP, AES128
- compatibility with corporate VPNs (ViPNet, S-Terra)
Terminology
Understanding the following terms is necessary for working with the system, setting it up and reading technical documentation:
Event
Any video / audio session in the Mind system. Events are one-time, scheduled or permanent. Depending on the settings of the template on which they are based, events are divided into conferences and webinars .
Webinar
An event during which only a few designated speakers can simultaneously stream a video / audio stream. The number of speakers depends on the license or subscription settings. The remaining participants act as spectators who see and hear the speakers, but not each other.
The conference
The event, all participants of which can simultaneously transmit video / audio information and receive media streams from other participants.
Room
Permanent event, performing the role of "virtual negotiation." Users can log in at any time. Designed for frequent and spontaneous meetings.
Registered user
Has an account with the Mind system. Can create events and take part in them.
a guest
He does not have an account, but can take part in the event on a special invitation sent to him. Can view event recording if allowed by event moderator .
Participants in each event can play the following roles:
Organizer
Registered user of the system who created the event. He has the maximum set of rights. The organizer automatically becomes a moderator and can appoint other moderators.
Moderator
Manages the rights of all participants and the settings of the current event, and, if necessary, appoints other moderators and speakers. Moderator can not change the rights of the organizer.
Speaker
Speaks to the participants of the event, in the same way as the speaker at a real meeting. The speaker cannot access the event settings tab, he does not assign roles.
Private member
can use the working functionality of the event. Other opportunities for ordinary participants depend on the type of event . During webinars, ordinary participants can only receive a media stream.
Licensing
License - the right to use the Mind system in accordance with the terms of the agreement between the Mind Group of Companies and the buyer of the server solution.
The license is delivered as a file with the * .key extension, which is generated by Mind specialists and transferred to the customer at the stage of solution deployment.
The license file contains the technical parameters of the Mind server solution, fixed in the contract, in particular:
- license period
- DNS name and IP address of the computer where the system is installed
- restrictions on the number of simultaneous events, the number of users, service capabilities
Users must access the Mind server only by the domain name or IP address specified in the license. Otherwise, they will be denied service.
Subscription
An object that stores individual user rights to work with the system.
The subscription is assigned to the user when creating his account and indicates:
- the maximum number of events that the user can hold simultaneously
- maximum number of participants and speakers
- the ability to record events, create polls, etc.
To use the Flash translation technology, an additional license is required for the Wowza Streaming Server, the cost of which is included in the total cost of the Mind solution.
The subscription is assigned to the user when creating his account and indicates:
- the maximum number of events that the user can hold simultaneously
- maximum number of participants and speakers
- the ability to record events, create polls, etc.
To use the Flash translation technology, an additional license is required for the Wowza Streaming Server, the cost of which is included in the total cost of the Mind solution.
Mind System Structure
The structural units of the Mind system are server , domain and company .
The Mind server is the main structural unit of the system and may contain one or more domains. The settings associated with the server affect the entire Mind system.
Domain - is a virtual video conferencing system with its unique domain name, and with its specific settings. All other objects of the system, such as users, events, templates, etc., exist within the domain.
A company is a structural unit that, if necessary, can be created within a domain. Unlike the domain, the creation of a company does not affect the technical settings of events, such as video quality, mode and technology of broadcasting, etc.
The company allows the administrator to delegate the right to create and manage user accounts to other employees of the enterprise.
Each company can have its own subscription, limiting the capabilities of users. For example, in one company there may be gathered users who are allowed to conduct a webinar with 4 speakers, and in the other, users for whom webinars are available with only one speaker.
Main features of the Company
- a company is assigned an owner who can create accounts, block and unblock them, appoint company administrators
- Company administrators, as well as the owner, can manage the accounts of their company
- all members of one company automatically see each other in the contact list
- all members of one company have the same subscription, while the total subscription opportunities are limited by the size of the company, for example, a company has no more than 10 participants - this means that in all events held by all members of the company there can be no more than 10 people in total
- The company may have its own external address book.
- Company administrators, as well as the owner, can manage the accounts of their company
- all members of one company automatically see each other in the contact list
- all members of one company have the same subscription, while the total subscription opportunities are limited by the size of the company, for example, a company has no more than 10 participants - this means that in all events held by all members of the company there can be no more than 10 people in total
- The company may have its own external address book.
Used technologies
For the transfer of video and audio streams between WEB participants, the Mind system can use two technologies - WebRTC and Flash.
WebRTC (Web Real-Time Communication) is a modern open source technology, which is a set of API functions responsible for setting up a connection and transferring media streams between a client and a server.
In this case, the client is a web browser or the Mind mobile client, the server role is played by the Mind server.
A web browser that supports WebRTC is a ready-made terminal for a video conferencing system (VCS). All the client needs to do is open a web page on the server containing correctly written java scripts.
JavaScript can access the WebRTC API functions that allow the client and server to exchange the following data:
- Signaling information (signaling), necessary for the coordination of communication parameters and connection setup. It can be transmitted via HTTP.
- Media streams transmitted via SRTP.
The process of establishing a connection using WebRTC is as follows.
— «call offer» «call answer“, HTTP(s).
— ICE (ICE IP- UDP/TCP SRTP. , ).
— NAT IP NAT. :
• Mind IP NAT. ( )
• Mind STUN (Session Traversal Utilities for NAT) /etc/xcoger/xcoder.cfg
— SRTP UDP .
— Mind ICE , ( , NAT Mind).
— restricted-cone NAT SRTP IP .
— NAT STUN IP NAT ( STUN Mind).
— SRTP .
:
- UDP 20000-30000, , TCP 20000-30000.
— TCP 20000-30000 - TURN.
— ICE (ICE IP- UDP/TCP SRTP. , ).
— NAT IP NAT. :
• Mind IP NAT. ( )
• Mind STUN (Session Traversal Utilities for NAT) /etc/xcoger/xcoder.cfg
— SRTP UDP .
— Mind ICE , ( , NAT Mind).
— restricted-cone NAT SRTP IP .
— NAT STUN IP NAT ( STUN Mind).
— SRTP .
:
- UDP 20000-30000, , TCP 20000-30000.
— TCP 20000-30000 - TURN.
In the most general terms, the idea of the STUN server can be described as follows.
— STUN NAT
— WebRTC URL STUN
— WebRTC STUN , NAT , STUN WebRTC IP
— WebRTC
— WebRTC URL STUN
— WebRTC STUN , NAT , STUN WebRTC IP
— WebRTC
TURN server (Traversal Using Relays around NAT) is used in cases where the client cannot send UDP packets to ports 20000-30000
UDP -.
SRTP HTTPS TURN .
TURN , TURN , , -.
STUN TURN SIP.
SRTP HTTPS TURN .
TURN , TURN , , -.
STUN TURN SIP.
Flash is Adobe Systems' multimedia platform for creating web applications or multimedia presentations.
Flash requires the mandatory installation of special software Adobe Flash Player on all client computers.
Real-time media streaming requires server software (for example, Adobe Media Server, Wowza Streaming Server, Red5, etc.)
Mind uses the following codecs and protocols in conjunction with Flash:
- H.264 video codec
- SPEEX audio codec
- transmission of media traffic via RTMP
As a rule, Flash does not allow to get the same high-quality video stream as when working with WebRTC, but it consumes less server resources. Using Flash makes sense when conducting large-scale events for hundreds of participants.
To ensure work through Flash, an additional component is added to the Mind server - the Wowza Streaming Server, the license cost of which is included in the total cost of the Mind solution.
The decision to use Flash is made during the implementation phase of the system, after consultation with the technical experts of Mind.
Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) is an application-level protocol designed for managing communication sessions with one or several participants for exchanging interactive traffic: voice, video, instant messages.
SIP protocol provides the exchange of signaling information:
- location of the addressee and his willingness to establish communication
- exchange of data on the functional capabilities of the participants in the session
- change of the media flow parameters of an already established communication session
- session management.
To transfer the voice and video data using other transport protocols, most often RTP.
The process of establishing a SIP connection is similar to setting up a WebRTC connection and has the same problems with NAT servers.
The SIP protocol is actively used in IP telephony, in particular, in VoIP gateways that allow telephones and office PBXs to transmit voice traffic over the Internet.
The unique user ID (SIP URI) is:
- sip: <user name> @FQDN
- sip: <phone number> @FQDN (FQDN is the name of the domain or computer where the user is registered. The phone number is used in the address if the FQDN indicates VoIP gateway).
The Mind system allows users to participate in events using the SIP protocol.
H.323 is a multimedia communication standard adopted by the main leading manufacturers of hardware solutions for video conferencing, telecommunications and multimedia equipment.
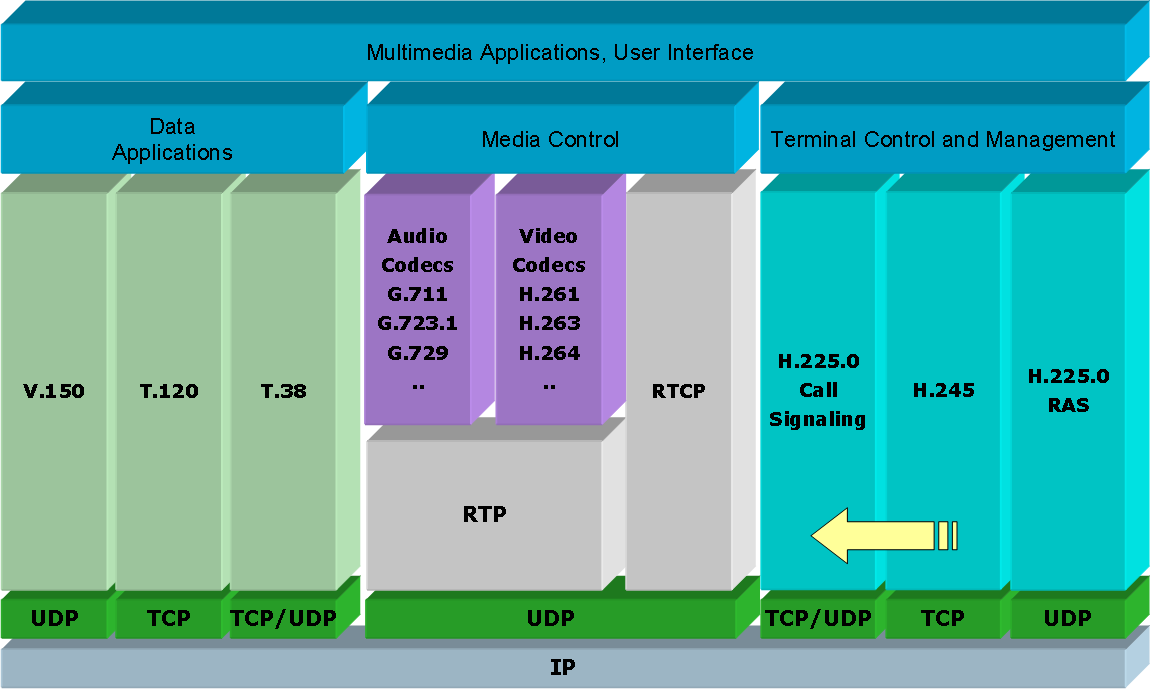
Full stack H.323 (Author ITU-T (talk) .ITU-T at en.wikipedia [Public domain], from Wikimedia Commons)
Installation Mind System
This topic is about installing a Mind server. A prerequisite for the effective use of any system is planning. It is necessary to estimate the load on the server in order to allocate the appropriate resources to the future server. It is equally important to have a clear idea of what changes need to be made in the existing infrastructure of the enterprise. For example, create DNS records or change firewall settings.
After installing the server, it is often necessary to perform its initial configuration, without which the system will not function at all. For example, setting an IP address or installing licenses.
Technical requirements
The network has a number of requirements:
Jitter - recommended value is not more than 150 ms
. Response time (ping) - recommended value is not more than 200 ms.
The following ports should be open for incoming connections to the Mind server:
TCP 22 - Access to the administrator console
TCP 80 - Web operation
TCP system interface 443 - Web-interface operation, WebRTC signaling, SRTP tunneling
TCP 1936 - Media traffic transmission for Adobe Flash
TCP, UDP 5060 - Connection of SIP client
UDP 10000-20000 - Media traffic transmission of SIP client
UDP 20000-30000 - Transmission
UDP WebRTC client media traffic 30000-40000 - Media traffic transmission in interaction with IVR
For outgoing connections from the Mind server, the following ports must be open:
TCP 25 - Send
UDP emails , TCP 53 -
TCP name service operation 80 - Optional. Check license Wowza
UDP, TCP 123 - Synchronize system time
TCP 389 - Optional. Integration with Microsoft Active Directory
TCP 443 - Push notification for Android
TCP 2195, 2196 - Push notification for iOS
TCP 2775 - Optional. Sending SMS
Customer specifications:
User PC software requirements:
Windows XP / Vista / 7/8/10 or Mac OS X 10.5-10.10
Adobe Flash Player 10.3 or later
Java Runtime Environment (JRE) version 1.6 and higher (for desktop broadcasts in browsers other than Google Chrome)
Mind Screen Sharing extension (to show your desktop in Google Chrome browser)
Recommended browsers:
Google Chrome (latest version)
Internet Explorer (starting with version 8)
Opera (latest version)
Yandex browser (latest version)
Mozilla Firefox supported, but not recommended
Recommended hardware configuration:
2-core processor with a clock frequency of 2 GHz or above
2 GB of RAM (RAM)
full duplex sound card
headset / microphone and speakers
camera with video resolution of at least 640x480 and frame rate of at least 25 frames / sec.
Network requirements:
from 512 kbps, jitter no more than 150 ms
access to server’s TCP / UDP ports according to technical documentation
in case of using a personal firewall, add server address Mind to the list of exceptions or the list of trusted hosts
Calculation of server load:
Calculation of server load is a difficult task, it requires extensive knowledge of the features of how multimedia technologies work, operating systems and equipment, and the Mind system itself.
Since this article is written about the Mind system as part of a ready-made STSS MIND software and hardware solution, I consider it more useful to tell not about the formulas for calculating the computing power of the server, but about the correct use of the STSS Flagman MIND server configurator for selecting the optimal configuration.
The configurations of processors and RAM in the solution are already calculated according to typical load criteria. But the maximum number of users is specified with the union "or" for all types of connections.
Consider an example of a typical configuration:
video conferencing: 100 WebRTC ports (browser) or 25 SIP / H323 ports (codec) / Webinar: 500 WebRTC participants or 2500 Flash participants
In this case, it is allowed: either 100 VKS connections via a browser or 25 connections via hardware codecs or 500 webinar participants via a browser or 2500 using Flash.
If the system is mixed and requires the simultaneous use of video conferencing and webinars, and with the participation of both WebRTC and SIP / H323 users, it is necessary to use a simple calculation.
It is enough just to bring all the variables to a common form - to express the values as one, for example, WebRTC VCS.
1 port SIP / H323 on load is equal to 4 ports WebRTC VCS
1 port of the participant of webinar through WebRTC on load equals 0.2 port WebRTC VCS
and so on
Knowing the planned load on the server, we calculate the performance by the maximum number of licenses purchased.
For example: we plan to simultaneously hold a video conference with up to 30 clients working through the browser. We have 4 meeting rooms with already installed hardware codecs that also need to be integrated into the system. In addition to video conferencing, the server must provide a webinar for 200 people via WebRTC with two speakers, and webinars may overlap in time with video conferencing.
It follows that we need to purchase 30 licenses of the Mind Server VCS Port, 4 licenses of the VCS Multiport, and 200 licenses of the Webinar Port for 2 speakers.
Calculate the required load: 30 + 4 * 4 + 200 * 0.2 = 86
This means that in the configurator we select the set that is as close as possible to this value of HQ connections via WebRTC.
If you need to select the configuration as accurately as possible - for this you can send a request through the form on the site and get a ready calculation from our presale.
Disk space:
~ 50 GB is enough for deployment and normal system operation, the rest is used for recording events.
Recording an event lasting 1 hour takes 700 MB - 1 GB of disk space (HD-quality video)
Load on the communication channel:
Depends on the number of participants in the event and the video stream broadcast mode (streaming or mixing mode).
Using streaming mode(video streams are transmitted to all participants of the event, the volume of outgoing traffic from the server increases with the number of participants broadcasting video) leads to the following loads on the channel:
For high-definition broadcasts, HD (1280x720 @ 30 FPS) the incoming stream will be S x 1.5Mbit / s and outgoing (P - 1) x S x 1.5 Mbit / s .
Where S (speaker) is the number of participants in the event that transmit the video, and P (participant) is the total number of participants in the event.
For example, for an HD webinar with 100 viewers and 2 speakers (publishers), the communication channel bandwidth should be at least: (100 - 1) x 2 x 1.5 = 297 Mbit / s.
Using the mix mode(video streams are combined into one stream of a given quality, which is transmitted to all participants; the amount of traffic coming from the server does not depend on the number of participants broadcasting video) leads to the following channel loads:
For high-definition broadcast, HD (1280x720 @ 30 FPS) the incoming stream will be S x 1,5 Mbit / s , but outgoing will be considered according to the formula P x 1,5 Mbit / s .
For example, for a conference in HD quality for 10 participants, the load on the channel will not exceed 10 x 1.5 = 15 Mbit / s, regardless of the number of speakers (video publishers).
Information you need to have before starting the installation of the system
Before proceeding with the installation of a working Mind system, make sure that you have all the necessary information for further configuration. It is recommended to collect all the data according to the checklist:
- IP address, network mask, gateway address
- fully qualified domain name of the server (FQDN) (end users will access it to log in)
- DNS server
addresses - NTP server addresses
- SSL certificate for the selected domain name
- the way of sending mail (direct sending or via SMTP server and the corresponding settings)
- Mind license file for the selected FQDN server
- IP addresses of computers from which system administration will be allowed
- license for Wowza media server, if Flash technology will be used
Mind System Administration
Using the video conferencing system Mind and its administration is performed using a web browser.
Initial configuration and further administration of the Mind server is performed by a user with the rights of the System Administrator using the Administration Panel.
Admin panel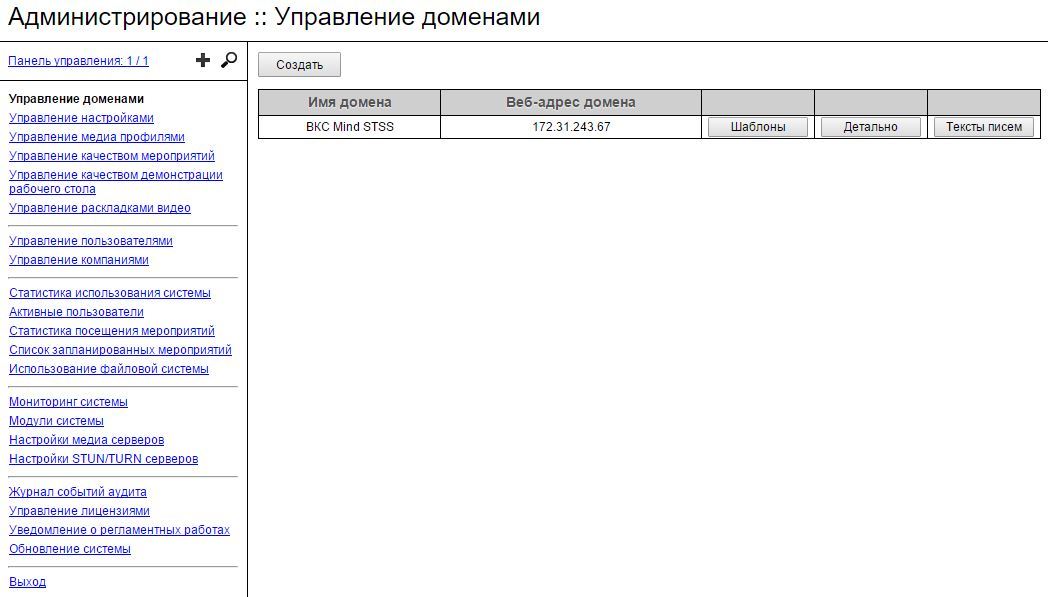
Mind :
–
–
–
. .
:
— Mind,
— ( )
—
Mind :
–
–
–
. .
:
— Mind,
— ( )
—
Initial Mind Server Setup
Mind , .
Mind :
—
— IP FQDN (IP- FQDN )
— ( Mind )
— - (- FQDN URL )
—
—
— SSL
— Email
— Email
—
— „ IP-“ ,
Mind :
—
— IP FQDN (IP- FQDN )
— ( Mind )
— - (- FQDN URL )
—
—
— SSL
—
— „ IP-“ ,
Health check
Mind .
, :
—
—
— , program is running or service is OK

Mind, :
— c Mind
— „ “ ,
— , .
, :
—
—
— , program is running or service is OK

Mind, :
— c Mind
— „ “ ,
— , .
User Account Management
There are several user roles in the Mind system that have a different set of permissions:
() — , , .
— . , .
— . .
— , .
— , Mind , , Mind API.
:
—
—
— . ( , )
SOAP API Mind .
:
—
— ( )
—
— : Email, , () .
— , .
.
:
— Email, ,
—
— Email .
() — , , .
— . , .
— . .
— , .
— , Mind , , Mind API.
:
—
—
— . ( , )
SOAP API Mind .
:
—
— ( )
—
— : Email, , () .
— , .
.
:
— Email, ,
—
— Email .
Import Accounts
, CSV- .
CSV- „ “ .
CSV- „ “ .
Editing accounts
: , , — .
:
— „ “ „ “
— ( ) „ “
— „“
— ( , Email „“
:
— ,
—
—
, , .
:
— „ “ „ “
— ( ) „ “
— „“
— ( , Email „“
:
— ,
—
—
, , .
Active Directory integration
LDAP Mind , LDAP. Active Directory (AD), LDAP .
LDAP :
— „ “, „ “
— „“
— „ LDAP“
:
LDAP url – / LDAP TCP LDAP (, ldap://dc01.vcs.ru:389)
LDAP bind DN – AD (, CN=admin,OU=Moscow,DC=domain,DC=ru)
LDAP bind credential –
LDAP base context DN – () Mind (, OU=Managers, DC=domain, DC=ru – (Organizational Unit) Managers).
LDAP base filter – . Mind AD (, mail ={0}. mail – AD. {0} , Mind. , AD Mind).
LDAP :
— „ “, „ “
— „“
— „ LDAP“
:
LDAP url – / LDAP TCP LDAP (, ldap://dc01.vcs.ru:389)
LDAP bind DN – AD (, CN=admin,OU=Moscow,DC=domain,DC=ru)
LDAP bind credential –
LDAP base context DN – () Mind (, OU=Managers, DC=domain, DC=ru – (Organizational Unit) Managers).
LDAP base filter – . Mind AD (, mail ={0}. mail – AD. {0} , Mind. , AD Mind).
Authorization process
:
— Mind
— Mind LDAP , LDAP base context DN (, Petrov, LDAP base filter sAMAccountName={0}, Mind , Active Directory Petrov)
— ,
— , Mind AD,
— , Mind , Active Directory LDAP
— ,
:
— Mind , LDAP . .
— , LDAP.
— , .
— LDAP , Mind.
— Mind
— Mind LDAP , LDAP base context DN (, Petrov, LDAP base filter sAMAccountName={0}, Mind , Active Directory Petrov)
— ,
— , Mind AD,
— , Mind , Active Directory LDAP
— ,
:
— Mind , LDAP . .
— , LDAP.
— , .
— LDAP , Mind.
Set up email and time synchronization
Mind (, ).
, Mind Exim, (Mail Transfer Agent, MTA).
:
— „ “ „ “
— „ SMTP/SMPP“
— „“ IP- SMTP
— „“ TCP
— , „ “ ( SMTP „ “, imind.
Mind :
— „ “ „ “
— ntp „“
— IP- NTP
, Mind Exim, (Mail Transfer Agent, MTA).
:
— „ “ „ “
— „ SMTP/SMPP“
— „“ IP- SMTP
— „“ TCP
— , „ “ ( SMTP „ “, imind.
Mind :
— „ “ „ “
— ntp „“
— IP- NTP
Customize templates
, , :
— , (, ), .
— .
— WebRTC Flash ( , , , ).
. . .
.
:
—
—
:
—
—
, .
:
— „ “ „ “
— „“
— „“
— „“
— „“ ( )
— „“
, , . .
Mind. , , , , , 2 , . .
Mind.
— , (, ), .
— .
— WebRTC Flash ( , , , ).
. . .
.
:
—
—
:
—
—
, .
:
— „ “ „ “
— „“
— „“
— „“
— „“ ( )
— „“
, , . .
Mind. , , , , , 2 , . .
Mind.
User work with templates
, Mind, :
—
—
—
, , . . .
, . , .
—
—
—
, , . . .
, . , .
Basic template settings
, .
, .
, :
— -
— -
— , — , -, .
, . , , .
:
. , / ( ).
. . , , , ( ).
. , ( ). .
, .
, :
— -
— -
— , — , -, .
, . , , .
:
. , / ( ).
. . , , , ( ).
. , ( ). .
The choice of broadcast technology
Mind : WebRTC Flash ( rtmp)
. Mind :
WebRTC ( ).
Flash .
Mind, , WebRTC, Flash.
.
:
— —
— —
— — , .
. Mind :
WebRTC ( ).
Flash .
Mind, , WebRTC, Flash.
.
:
— —
— —
— — , .
Setting broadcast quality
.
(WebRTC Flash) :
—
—
—
—
—
, :
—
— (fps)
—
„ “ „ “. . „“ „ “ .
, , .
(WebRTC Flash) :
—
—
—
—
—
, :
—
— (fps)
—
„ “ „ “. . „“ „ “ .
, , .
Media profiles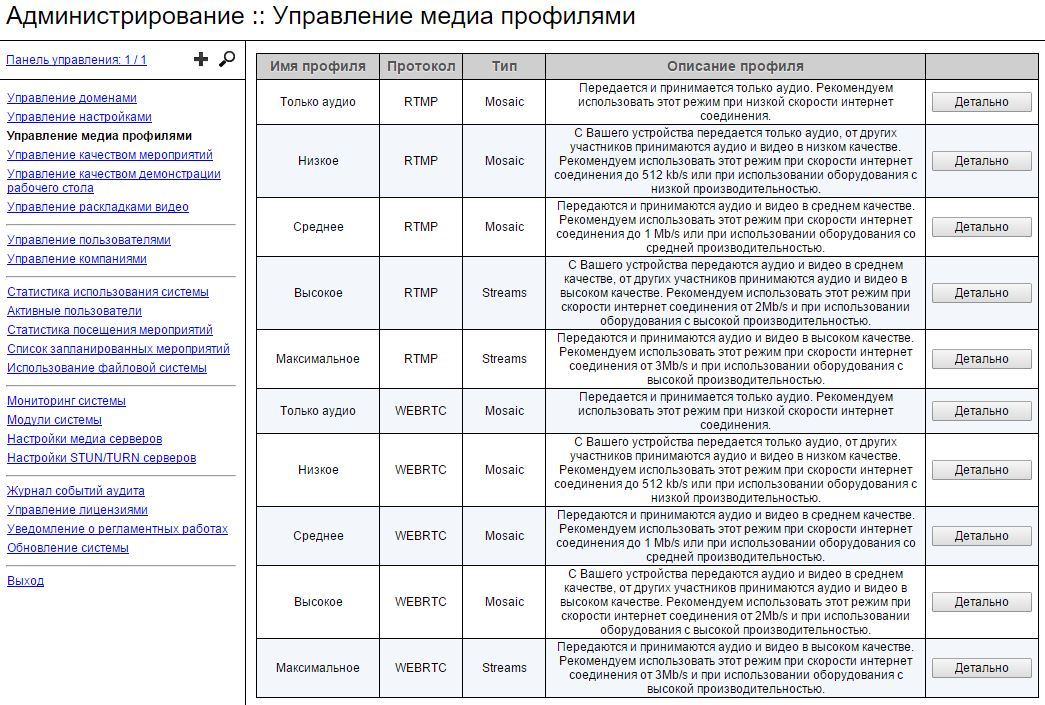
( ) .
, WebRTC Flash, :
—
—
—
—
—
„ “ „ “.
. „ “ „ “ „ “.
, :
— , „ “ .
— „“.
— , , , .
, – , , .
( ) .
, WebRTC Flash, :
—
—
—
—
—
„ “ „ “.
. „ “ „ “ „ “.
, :
— , „ “ .
— „“.
— , , , .
, – , , .
Media Profile Settings
( ) , , .
:
– . (streams) (mosaic)
– ,
.
:
— , , , . .
— , , .
— „ -“ , .
WebRTC, , . ,
Flash, . , .
():
— , .
— . , mosaic . selector , , ( voice detection).
( ) , , .
:
– . (streams) (mosaic)
– ,
.
:
— , , , . .
— , , .
— „ -“ , .
WebRTC, , . ,
Flash, . , .
():
— , .
— . , mosaic . selector , , ( voice detection).
Mobile client setup
iOS Android Mind Mind Meeting.
Mind ( Mind Meeting, ).
Mind.
-- Mind SaaS ( „“ ) InHouse ( ). .
Mind Mind, .. Mind. .
SaaS- vcs.imind.ru App Store Google Play.
Mind :
—
— push-
Mind ( Mind Meeting, ).
Mind.
-- Mind SaaS ( „“ ) InHouse ( ). .
Mind Mind, .. Mind. .
SaaS- vcs.imind.ru App Store Google Play.
Mind :
—
— push-
Integration with SIP clients
Mind. Mind . „Sip“, „ “ – 1000.
, , (IVR) Mind ID . ID . „ “ .
ID . , (softswitch), IP- Mind.
IP SIP URI sip:<_>@<IP__Mind>. , sip:1000@10.0.3.94 — sip:390326798@10.0.3.94 – ( ID 390-326-798).
(softswitch IP ) Mind SIP-. , SIP-.
Mind:
— „ “ „ “
— „“
— SIP
— „ sip-“ IP- (, sip:192.168.0.123:5060, SIP- IP- Mind )
— „ “
— „SIP “ ( , , , 1000, sip:1000@domain.ru)
— , „“
SIP Mind:
— Mind TLS SIP-.
— Mind NAT SIP- .
— Mind IP-, SIP-.
— Mind SIP- . Mind , Mind SIP-trunk.
Mind. Mind . „Sip“, „ “ – 1000.
, , (IVR) Mind ID . ID . „ “ .
ID . , (softswitch), IP- Mind.
IP SIP URI sip:<_>@<IP__Mind>. , sip:1000@10.0.3.94 — sip:390326798@10.0.3.94 – ( ID 390-326-798).
(softswitch IP ) Mind SIP-. , SIP-.
Mind:
— „ “ „ “
— „“
— SIP
— „ sip-“ IP- (, sip:192.168.0.123:5060, SIP- IP- Mind )
— „ “
— „SIP “ ( , , , 1000, sip:1000@domain.ru)
— , „“
SIP Mind:
— Mind TLS SIP-.
— Mind NAT SIP- .
— Mind IP-, SIP-.
— Mind SIP- . Mind , Mind SIP-trunk.
Media Server Settings
Mind NAT, , WebRTC IP . Mind, , :
— Mind IP- NAT
— Mind STUN
, IP- :
— „ “ „ “
— „“
— „ “
— NAT „ “ „ “ ( HTTPS )
URL STUN /etc/xcoger/xcoder.cfg
— Mind IP- NAT
— Mind STUN
, IP- :
— „ “ „ “
— „“
— „ “
— NAT „ “ „ “ ( HTTPS )
URL STUN /etc/xcoger/xcoder.cfg
.
:
—
—
— iPad
— : , / , SMS .. ( )
, Mind, .
:
— „ “ „ “
— „“
— „ “
— ,
—
— , „“
„ “ „ “

, :
— „ “ .
— „ “
— „ ID“
Mind . , ..
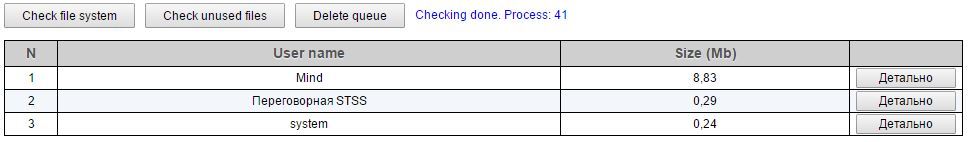
, , .
„Check file system“ . „Check unused files“ , .
, :
— „ “ .
— „ “
— „ ID“
Mind . , ..
, , .
„Check file system“ . „Check unused files“ , .

Mind , .
:
—
—
—
—
, . , 10 .
:
— „ “
— „ “
—
— .
, .
, „ “, Mind .
Conclusions and Conclusion
STSS Flagman MIND is a domestic video conferencing solution for businesses of any scale. The number of companies that have evaluated all the advantages of Mind VCS over hardware solutions of foreign manufacturers is growing every day.
You can evaluate the performance of the VC system Mind yourself right now:
1. The fastest way: you need to register with the imind.ru cloud service and check the functionality of the system. The functionality of the cloud service has been cut, but the overall presentation will appear.
2. To test a full-fledged local version, you need to come to our central office located in Moscow on Berezhkovskaya Embankment. In our demo zone, the entire solution is presented: server, cameras and audio peripherals.
3. You can download the image of the demo version and try to raise the system yourself.
Waiting for your comments!
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/277013/
All Articles