What's New in Veeam Backup & Replication 9.0: Increase Efficiency in Creating and Storing Backup Files
In this post, I will talk about new features that you can use by upgrading your version of Veeam Backup & Replication to 9.0. Among the variety of new products, I confess, I have a few favorites - and although they may seem obscure in appearance, they are of great benefit, for which I appreciate. Of course, the whole mass in one post cannot be described, so I will immediately give a reference to the full review of the new products on the official website: What's New in Veeam Backup & Replication v9 .
Here is what awaits you under the cut:

(In the picture - an exclusive set of cakes, which we treated ourselves to on the day of release. Thanks TheRealGostev - managed to take a picture before everyone snapped up.)
In the past, the post has already been a review of this new component. I remind you that the console allows you to connect to remote servers Veeam backup; it can be set up as a separate setup, there is also an automatic installation (see the description in the User Guide ). Thus, Veeam now supports a fully distributed architecture. In previous versions, the Veeam.Backup.Service.exe and VeeamShell.exe components were exclusively coexistent, and in v9, with the efforts of our engineers, their interdependence was finally defeated - that is, as TheRealGostev put it, “split Siamese twins”.

New features have appeared in working with backup repositories.
')
First, now you can assign a connection server (mount server) to any repository. This is a Windows server that performs a specific role in the backup infrastructure — when restoring at the file level (FLR, file-level restore), such a server mounts VM files directly from the backup to its file system, as if “connecting” them to itself. The connection server can be set up in the corresponding step ( Mount Server ) of the repository setup wizard.

There are various options for activating a mount operation:
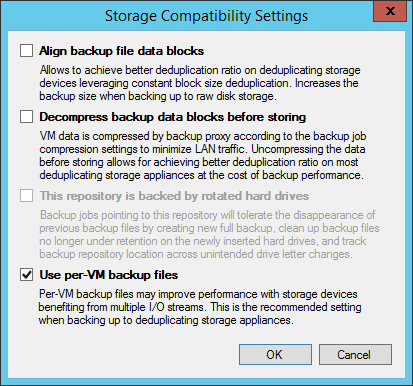
For owners of Enterprise and Enterprise Plus licenses, it is possible to create a scalable repository. This was described in some detail in an article on Habré “ about an“ infinitely ”scalable backup repository .” This repository is easier to manage (since the routine task of selecting target storage from the pool is automated), in addition, fuelconsumption of the storage space in the pool is optimized, and performance is improved, because the default is to enable per-VM backup chains.

For regular repositories, the option of storing backups “per machine” (per-VM backup files) is also offered. With this option, a write stream will be generated for each VM (and not for each job). As a result, the queue depth increases, which improves performance, since the maintenance of a single thread (queue depth = 1) is a performance limiting factor for most storage systems. Creating several threads (queue depth ~ = N, that is, the number of tasks in the repository) helps a lot.
In addition, it became possible to create larger tasks without reservations about difficulties in controlling large backups. With the release of v9, our system architects are preparing to revise the recommendations on the number of VMs included in one task - for example, bringing it to 250-300. In any case, our own testing confirmed the possibility of processing tasks containing 5,000 virtual machines.
Of course, when planning and setting up backup tasks, you need to remember that a number of operations — for example, creating a synthetic backup, Backup Copy Jobs tasks (transferring backup to a backup site), etc. — will wait for the backup of all VMs to work. For this reason, it is not recommended to create giant tasks.
Important! After you have selected the Use per VM-backup files backup storage option, you need to activate it by performing an active full backup (Active Full) operation, either manually or waiting for the schedule to be triggered.
A couple more points: remember that deduplication on the source side is not going anywhere. And second, when creating new repositories on EMC DataDomain storage systems (with DDBoost), HP StoreOnce (with Catalyst) and ExaGrid (with Accelerated Data Mover), this option is enabled by default, but it is recommended to check this, just like any other these storage settings.
After updating, new features of Veeam Backup & Replication will be disabled by default. To start using them, you should reconfigure existing backup jobs. I note that the first two options from the list below were previously available only for backup transfer jobs (Backup Copy Jobs). Now they can also be used to create other types of tasks. Here are the new features:
Defragmentation and compression. Using this option will be useful if your backup task does not include the periodic full backup (active full backup), and at the same time the data retention policy implies that the full backup file will be periodically merged with the nearest incremental copy. Such a transformation leads to the fact that the backup file becomes fragmented and “voids” are formed in it. Voids are also formed when a part of the VM has been deleted from the backup task (after removing them from the backup, the file itself does not become smaller). To reduce the file size, as well as slightly increase the speed of working with it, you can enable the Defragment and compact full backup file option. It works as follows: at the specified time, Veeam Backup & Replication will create an empty VBK file and copy there only the necessary blocks from the backup file obtained as a result of transformations. There are restrictions for this option that are described in the User Guide .
Health check and self-healing. To ensure that your backups are not damaged, in addition to SureBackup, you can activate the Perform backup files health check option. In this case, when creating each backup copy, Veeam Backup & Replication will calculate the hash and checksum of the created file. Then, before starting the next backup, Veeam Backup & Replication re-calculates the hash and checksum of the file and compares it with the previously saved values. If it is found that the file data has been damaged, Veeam Backup & Replication will replace the damaged blocks by copying the required data from the original VM or from the previous backup.

Eliminate blocks marked as deleted. Removing files in NTFS, you do not actually clear the data blocks that contain the file, but mark them as deleted. Therefore, often when creating a backup image of a VM (image-based backup), the size of the backup file can be much larger than the size displayed in the file system. Until recently, the only way to avoid copying “deleted” data was to use the sdelete utility (SysInternals) before starting a backup. In Veeam Backup & Replication v9, you can activate the BitLooker option so that before starting the backup, Veeam analyzes the MFT partition and does not copy the blocks marked as deleted.

The article “ A new version of Veeam Backup FREE Edition has been released: a brief overview ” describes in more detail how BitLooker works. This technology is currently awaiting patent.
Important! In the commercial version of Veeam Backup & Replication after the upgrade, this option is disabled by default - it is convenient to activate it using PowerShell commands:
Optimization of interaction with guest OS. In the backup infrastructure, built on the basis of Veeam Backup & Replication v9, a new component - Guest Interaction Proxy. It is intended for the interaction of the backup server with the guest OS (previously this interaction was carried out by the backup server itself, which greatly increased the load on it). If you configure automatic machine selection for the Guest Interaction Proxy role, Veeam will select a less loaded machine that is located on the same site as the VM for which you plan to back up. This approach simplifies backups in remote offices and branch offices (components interact faster when they are on the same site) and does not require the use of VMware VIX.

Exclude unnecessary files during backup. This feature is part of BitLooker technology: when backed up, Veeam also analyzes the MFT partition and creates a cache in the proxy server memory, which marks which files and folders to exclude. During the backup data is read simultaneously with the original VM and from the cache. It is important to note that the exclusion of files is possible only if you have activated the backup option taking into account the state of the application (application-aware image processing). In this case, the exclusion of many small files is processed more slowly than the exclusion of several large files of the same size, because exception handling increases the load on the proxy server. For example, to exclude 100,000 files from a backup, you need 400 MB of memory on a proxy server.

Well, one more operation is now automated - earlier, users used the PowerShell script to create a full backup to set the backup copy job, and now you can simply tick the checkbox. Target when setting up a job.
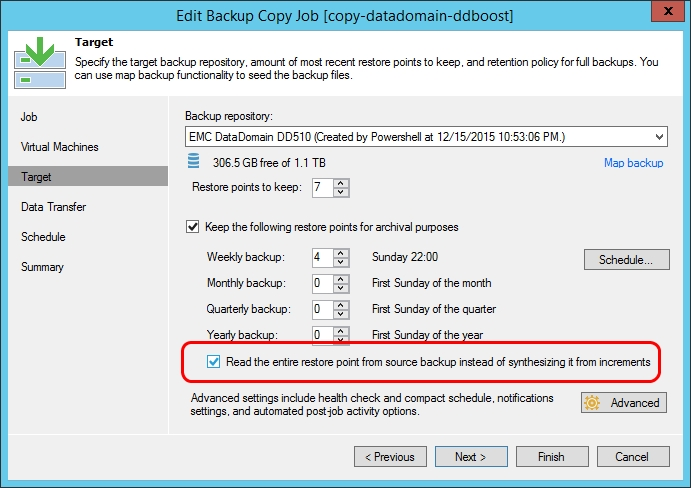
This option is useful for low-performance storage systems, on which to convert files, synthesizing a full backup from incremental ones, is inefficient, and it is much more convenient to copy a full backup.
In addition to the above links, I recommend reading (while in English. Language):
Resources in Russian:
Here is what awaits you under the cut:
- Remote Management Console
- New repository features
- New storage options
- Optimization of work with guest OS
- Setting up a full backup copy in the transfer task

(In the picture - an exclusive set of cakes, which we treated ourselves to on the day of release. Thanks TheRealGostev - managed to take a picture before everyone snapped up.)
Remote Management Console
In the past, the post has already been a review of this new component. I remind you that the console allows you to connect to remote servers Veeam backup; it can be set up as a separate setup, there is also an automatic installation (see the description in the User Guide ). Thus, Veeam now supports a fully distributed architecture. In previous versions, the Veeam.Backup.Service.exe and VeeamShell.exe components were exclusively coexistent, and in v9, with the efforts of our engineers, their interdependence was finally defeated - that is, as TheRealGostev put it, “split Siamese twins”.

New repository features
New features have appeared in working with backup repositories.
')
First, now you can assign a connection server (mount server) to any repository. This is a Windows server that performs a specific role in the backup infrastructure — when restoring at the file level (FLR, file-level restore), such a server mounts VM files directly from the backup to its file system, as if “connecting” them to itself. The connection server can be set up in the corresponding step ( Mount Server ) of the repository setup wizard.

There are various options for activating a mount operation:
- So, to restore files or objects of an application, it is first mounted on the machine where the console is running — so that the user can view the contents of the backup and select the files / objects needed for the restoration, because the browsing tools are launched from the console (whether offline or combined with the server), whether it is the Veeam Backup Browser or any of the Veeam Explorers tools.
- After the command to restore the selected files / objects (as a rule, to the machine in production) is given, the connection server will start working with the repository, and the traffic will go between it and the target machine. This will speed recovery in distributed infrastructures.
- If the recovery is performed using the Enterprise Manager and is done for the machines that have guest OS files indexed during the backup, then only one connection will be involved (both for viewing and recovery), so in this case the traffic will always go between connection server and target VM.
For owners of Enterprise and Enterprise Plus licenses, it is possible to create a scalable repository. This was described in some detail in an article on Habré “ about an“ infinitely ”scalable backup repository .” This repository is easier to manage (since the routine task of selecting target storage from the pool is automated), in addition, fuel

For regular repositories, the option of storing backups “per machine” (per-VM backup files) is also offered. With this option, a write stream will be generated for each VM (and not for each job). As a result, the queue depth increases, which improves performance, since the maintenance of a single thread (queue depth = 1) is a performance limiting factor for most storage systems. Creating several threads (queue depth ~ = N, that is, the number of tasks in the repository) helps a lot.

In addition, it became possible to create larger tasks without reservations about difficulties in controlling large backups. With the release of v9, our system architects are preparing to revise the recommendations on the number of VMs included in one task - for example, bringing it to 250-300. In any case, our own testing confirmed the possibility of processing tasks containing 5,000 virtual machines.
Of course, when planning and setting up backup tasks, you need to remember that a number of operations — for example, creating a synthetic backup, Backup Copy Jobs tasks (transferring backup to a backup site), etc. — will wait for the backup of all VMs to work. For this reason, it is not recommended to create giant tasks.
Important! After you have selected the Use per VM-backup files backup storage option, you need to activate it by performing an active full backup (Active Full) operation, either manually or waiting for the schedule to be triggered.
A couple more points: remember that deduplication on the source side is not going anywhere. And second, when creating new repositories on EMC DataDomain storage systems (with DDBoost), HP StoreOnce (with Catalyst) and ExaGrid (with Accelerated Data Mover), this option is enabled by default, but it is recommended to check this, just like any other these storage settings.
New storage options
After updating, new features of Veeam Backup & Replication will be disabled by default. To start using them, you should reconfigure existing backup jobs. I note that the first two options from the list below were previously available only for backup transfer jobs (Backup Copy Jobs). Now they can also be used to create other types of tasks. Here are the new features:
Defragmentation and compression. Using this option will be useful if your backup task does not include the periodic full backup (active full backup), and at the same time the data retention policy implies that the full backup file will be periodically merged with the nearest incremental copy. Such a transformation leads to the fact that the backup file becomes fragmented and “voids” are formed in it. Voids are also formed when a part of the VM has been deleted from the backup task (after removing them from the backup, the file itself does not become smaller). To reduce the file size, as well as slightly increase the speed of working with it, you can enable the Defragment and compact full backup file option. It works as follows: at the specified time, Veeam Backup & Replication will create an empty VBK file and copy there only the necessary blocks from the backup file obtained as a result of transformations. There are restrictions for this option that are described in the User Guide .
Health check and self-healing. To ensure that your backups are not damaged, in addition to SureBackup, you can activate the Perform backup files health check option. In this case, when creating each backup copy, Veeam Backup & Replication will calculate the hash and checksum of the created file. Then, before starting the next backup, Veeam Backup & Replication re-calculates the hash and checksum of the file and compares it with the previously saved values. If it is found that the file data has been damaged, Veeam Backup & Replication will replace the damaged blocks by copying the required data from the original VM or from the previous backup.

Eliminate blocks marked as deleted. Removing files in NTFS, you do not actually clear the data blocks that contain the file, but mark them as deleted. Therefore, often when creating a backup image of a VM (image-based backup), the size of the backup file can be much larger than the size displayed in the file system. Until recently, the only way to avoid copying “deleted” data was to use the sdelete utility (SysInternals) before starting a backup. In Veeam Backup & Replication v9, you can activate the BitLooker option so that before starting the backup, Veeam analyzes the MFT partition and does not copy the blocks marked as deleted.

The article “ A new version of Veeam Backup FREE Edition has been released: a brief overview ” describes in more detail how BitLooker works. This technology is currently awaiting patent.
Important! In the commercial version of Veeam Backup & Replication after the upgrade, this option is disabled by default - it is convenient to activate it using PowerShell commands:
asnp VeeamPSSnapin; Foreach ($job in Get-VBRJob) {
$job.Options.ViSourceOptions.DirtyBlocksNullingEnabled = $true;
$job.SetOptions($job.Options) }
New opportunities to work with guest OS
Optimization of interaction with guest OS. In the backup infrastructure, built on the basis of Veeam Backup & Replication v9, a new component - Guest Interaction Proxy. It is intended for the interaction of the backup server with the guest OS (previously this interaction was carried out by the backup server itself, which greatly increased the load on it). If you configure automatic machine selection for the Guest Interaction Proxy role, Veeam will select a less loaded machine that is located on the same site as the VM for which you plan to back up. This approach simplifies backups in remote offices and branch offices (components interact faster when they are on the same site) and does not require the use of VMware VIX.

Exclude unnecessary files during backup. This feature is part of BitLooker technology: when backed up, Veeam also analyzes the MFT partition and creates a cache in the proxy server memory, which marks which files and folders to exclude. During the backup data is read simultaneously with the original VM and from the cache. It is important to note that the exclusion of files is possible only if you have activated the backup option taking into account the state of the application (application-aware image processing). In this case, the exclusion of many small files is processed more slowly than the exclusion of several large files of the same size, because exception handling increases the load on the proxy server. For example, to exclude 100,000 files from a backup, you need 400 MB of memory on a proxy server.

Setting up a full backup copy in the transfer task
Well, one more operation is now automated - earlier, users used the PowerShell script to create a full backup to set the backup copy job, and now you can simply tick the checkbox. Target when setting up a job.

This option is useful for low-performance storage systems, on which to convert files, synthesizing a full backup from incremental ones, is inefficient, and it is much more convenient to copy a full backup.
Instead of conclusion
In addition to the above links, I recommend reading (while in English. Language):
- Description of the backup storage per VM-backup
- What is a connection server (mount server) and how it works
- About optimization of work with guest OS
Resources in Russian:
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/276815/
All Articles