Corporate Cloud: Connection Options

According to Gartner, cloud technologies are becoming increasingly popular. If in 2012 the market share of IaaS was $ 6.1 billion, in 2015 this figure increased to $ 16 billion. Moreover, the growth rate of IaaS popularity does not decrease .
IaaS allows you to solve many problems, providing flexibility and scalability, and covers the needs of various customers. Turning to IaaS, you get a cost-effective solution (compared to traditional infrastructures) with the ability to provide resources on demand and a single management system.
')
Today, more and more companies are transferring their infrastructure to the cloud. Such an approach is economically justified, profitable and convenient. One of the points that may cause questions is the choice of a suitable connection method . The following solutions are usually used to connect to cloud services: RDP client, RemoteApp, web access, Remote access VPN, VPN site-to-site, DirectAccess, VDI.
RDP client or remote desktop connection is one of the most convenient and versatile tools giving access to a workplace deployed in the cloud. It is based on the proprietary protocol RDP (Remote Desktop Protocol) - it is this one that enables the user to work remotely with a computer running the terminal access service. The user through the RDP client connects to the terminal server and sees the desktop of the remote system.
Within an established session, it can launch applications deployed on a terminal server. The security of such a connection is guaranteed by the Remote Desktop Gateway, which uses RDP over HTTPS, providing a reliable encryption method. Today, there are clients for almost all operating systems of Windows, Linux, FreeBSD, Mac OS X, iOS, Android, Symbian families.
The RemoteApp solution is a variation of the above option. However, in this case, the user sees only the launched remote application. This option will be useful if you need to restrict access to specific applications, or when the user wants to combine work on a local machine with the use of a cloud application. In this case, the launched remote Terminal Services applications will look as if they were running on the user's system.
Access to certain applications and desktops in the cloud can be organized using a browser. The user starts the browser, enters the necessary address, becomes authorized and already works with the application or remote desktop.
Another convenient, secure and frequently used tool for connecting to cloud resources is Remote access VPN. In this case, a secured tunnel is established between the application on the client’s computer and, for example, the VPN hub or router located in the cloud of the hosting provider.
To connect to a remote resource, the user launches the VPN shortcut and, upon successful authentication, gets access to the desired resources. Thus, the user's computer enters the network of a virtual remote office in the cloud and can use resources as if it is located directly at the company's office.
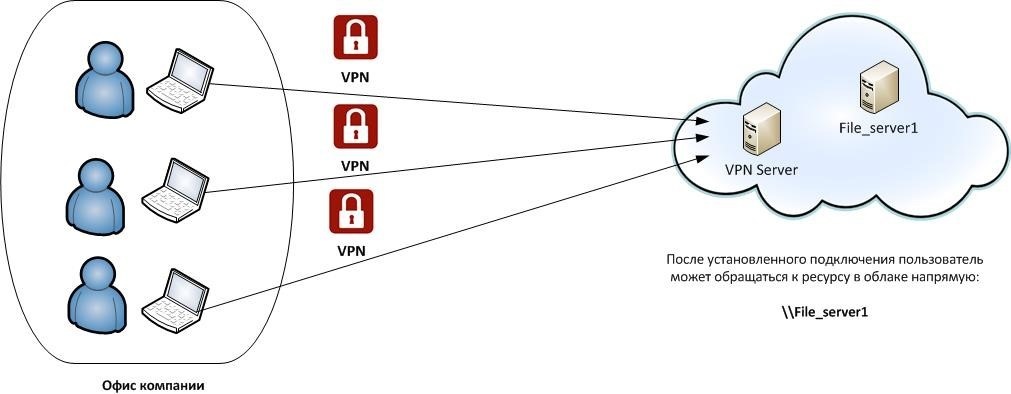
However, such a scenario is possible: employees of the company from their cloudless infrastructure need to connect to a resource in the cloud. For this there is a Site-to-site VPN, which implies the existence of two devices between which a tunnel is formed.
In this case, users are “behind devices”, so there is no need to install special software on their computers.
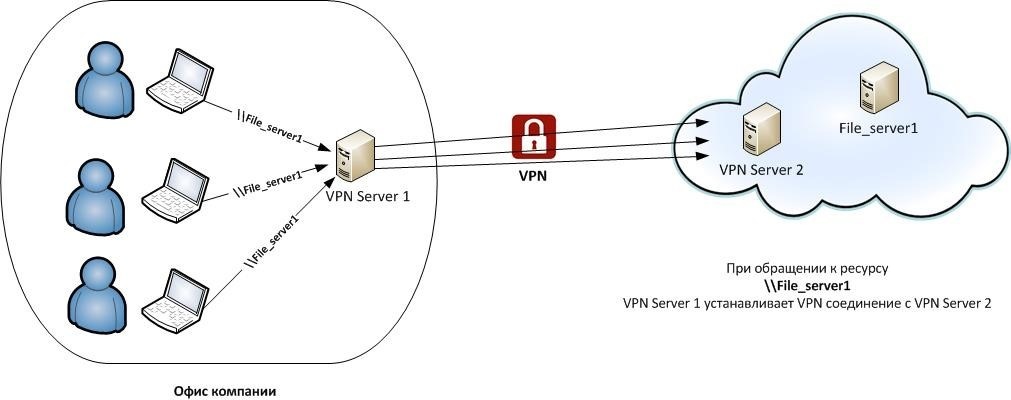
For example, here VPN Server 1 establishes a VPN connection with VPN Server 2, after which the user sees the contents of the requested resource. On the client side, there is no need to create an outgoing VPN connection.
In addition to the usual VPN implementations that can be used to remotely connect to the cloud, there is another technology — DirectAccess. In this case, as soon as the user's computer connects to the Internet, it immediately gains access to both Internet resources and the entire corporate network. That is, a user computer configured as a DirectAccess client automatically builds a reliable tunnel to the DirectAccess server and already gains access to it. At the same time, no additional actions are required from the user.
Another way is a virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI). It is implemented on many cloud platforms of corporate IaaS-providers. This technology allows you to centralize user workstations on virtualization servers, creating a single point of control, deployment and maintenance. In the provider cloud, a server with a hypervisor is allocated, on which individual VMs are deployed. The user starts the client and connects to the infrastructure.
This type of connection, at first glance, is not much different from RDP connection. But what is the difference? In the case of a RDP connection to a terminal server, this is a separate session on a shared Windows server. In the case of VDI, this is a separate, isolated container with a client operating system.
As we mentioned above, an increasing number of companies are starting to work with the cloud. A larger number ... but not all. What makes the cloud so scary business? One of the reasons is the issue of confidentiality. There is nothing wrong, and to sleep better, you just need to understand the modern nuances of working with information. Protecting the cloud environment is fundamentally no different from the traditional data center. Often it is even possible to use familiar security tools. In particular, IaaS allows you to implement any protection mechanisms and obtain the required level of confidentiality.
The second popular misconception is that, supposedly, these new technologies are still raw and not suitable for serious work. Cloud infrastructure is based on proven technologies. For example, IaaS relies almost entirely on virtualization systems like VMware vSphere. Such products have been improved for more than ten years and can already be considered a reliable solution that can increase the flexibility of the server infrastructure.
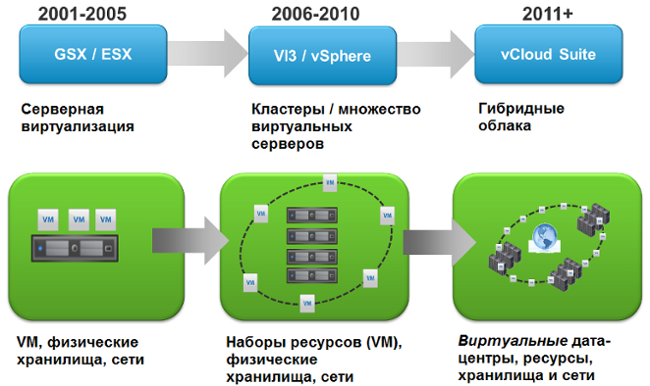
The figure above shows a brief evolution of VMware products — from the first virtualization systems to complete solutions for corporations and commercial data centers. All solutions are based on technology with more than 10 years of history - the ESXi hypervisor.
According to Gartner research , one of the popular myths about cloud computing is their inapplicability for business-critical applications. “Our application is too big and important for the cloud”, - such a phrase can be heard quite often. Cloud technologies are built on virtualization systems, so if an application can be run on a virtual server, then there should be no difficulties with the cloud.
As a real example of the work of “large” applications in a virtual and cloudy environment, one can cite the product SAP HANA. SAP has long established itself as a leading global manufacturer of automated control systems. HANA is a high-performance database engine for demanding applications. All user database information is stored in the server's RAM and is available for querying with minimal latency. The manufacturer has confirmed the full functionality of this platform in a virtual VMware environment.
The issue of data migration is most acute when moving the entire server infrastructure somewhere. We will not argue that everything is easy and simple, but if in the past you have already encountered this, you can assume that most of the difficulties have passed. However, one of the questions is still quite relevant: "How many resources do you need to allocate for a terminal server if you decide to deploy it on a remote site hosting provider?"
Since the exact calculation of resources for the terminal server is still complicated, we suggest considering techniques that will help to do this.
Piloting is perhaps the simplest method used in practice when a test virtual machine is deployed in the cloud, playing the role of a terminal server. The load on the server gradually increases, but it monitors the resources used, and compares the performance indicators for different periods of time. Based on the collected data, conclusions are drawn.
Extrapolation to the user system - this method is based on data obtained from the system used by one user. Performance aspects such as memory, processor, disk space, network are evaluated. In the future, they are used to calculate capacity in a multi-user environment.
Modeling - this method is based on the indicators already collected in the framework of the script being executed. The test server is also highlighted here, and with the help of special tools, modeling of various load levels is carried out to determine the capabilities of the server.
The latter method is one of the methods that accurately assess the potential of the system. To make it work, you first need to define a clear sequence of user actions, as well as understand how they use data (documents, files, media content, and so on).
To cope with the task help, for example, user reviews and monitoring their activity. Further, after the test environment has been deployed, the test itself is carried out - the essence of this step is to form the load on the server and determine the viability of the system. This is where a performance test is run to determine the maximum number of users a terminal server can handle.
At this stage, automation tools are used, with the help of which instances of applications that imitate the work of several users are simultaneously launched. One of the popular imitation tools is the AutoIT scripting language. Using scripts, you can simulate user input from the mouse and keyboard, work with the network, the registry and the clipboard and many more.
The WinBatch and AutoIT scripts provide the ability to automate applications, including those that do not support command line options. After modeling, it remains only to analyze the results obtained and determine an acceptable load on the system. According to the obtained results, it is determined whether it is necessary to increase additional resources, or whether they are sufficient for correct operation.
As you can see, there are various methods and tools that help calculate the required resources when deploying a terminal server in the cloud of an IaaS provider. The main thing is one thing - this is the correct use of all the considered methods.
PS Our materials on the topic on Habré:
- IaaS trends brief
- Our introduction to Cisco UCS
- Virtualization and Virtual Data Centers: Basic Questions
- IaaS for business: How Russian business moves to the “cloud”
- Data Center Experience and Problems: How to Verify Data Center Reliability
- IT infrastructure, information security and telecom: Events in 2016
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/276809/
All Articles