Email and Security: Is it possible to protect email correspondence?

In our blog on Habré we write a lot about creating mailing lists and working with e-mail. Today we will talk about an infrequently touched upon, but important topic - how safe are such communications, and how to protect yourself when using email? This is the question that Quora users asked . We present to your attention the best answer given by Bill Franklin, a former employee of the secure mail service Lavaboom (the project was closed in the summer of 2015).
Are there any secure mail services, and how are popular mailers different in this regard?
Email is inherently insecure. It was created for personal correspondence, but in reality emails are not much safer than postcards.
Franklin says that when he sends from Oxford via Gmail a letter to Yahoo! Mail to a friend in San Francisco, the message can be intercepted at least 7 times: on the sender's computer, when sent to the Gmail server, on the Gmail server, when transferred from Gmail to Yahoo !, on the Yahoo! Mail, when transferred to a friend's computer and, finally, on the recipient's computer. Everyone knows that the chain is as strong as its weak link, so even if both correspondents do everything they can to secure their computers, they still have to rely on the protection of Gmail and Yahoo!
')
Who may need to break the mailbox
Who may be interested in accessing someone else's mailbox? First of all, these are government organizations, a postal provider and cybercriminals. Of course, it is impossible to hide the correspondence from the postal service, an ordinary user is also unlikely to be able to resist hackers. At the same time, if Gmail has access to your account, then the US National Security Agency (NSA) also has it. And if the NSA builds a backdoor into the mail service, then attackers will also be able to use it. Thus, the user needs to protect his account from all three groups of “interceptors” because if one of them gets access, then the others can get it.
The reasons why they may want to crack the email box:
- Government agencies: mass tracking and obtaining data about individuals;
- Gmail: scanning letters by keywords to advertise;
- Hackers: sending spam, stealing bank data, stealing personal information - the list is limited only by the ingenuity of hackers who find new ways to get money with the help of stolen personal data.
Below is a diagram of information security researcher Brian Krebs - it clearly shows that the average user's mailbox has far more value than is commonly thought.
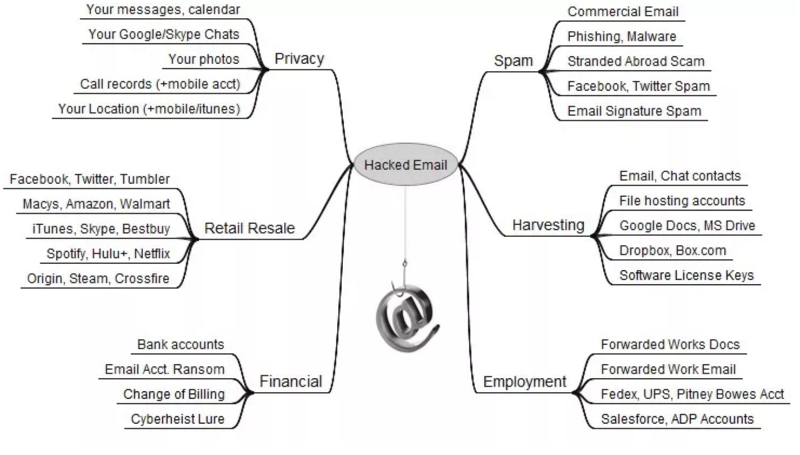
Weak spots
There are many ways to intercept email at the seven access points listed above. Franklin talked about how this can be done in his example. The quickest way (this method takes about an hour) is to break into the base in Cardiff, where the transatlantic telephone cable originates, install a node to intercept the email and wait for it to be sent.
The US National Security Agency has the ability to access the email in all seven access points. And, according to the articles by Jacob Appelbaum and Glen Greenwald, the NSA’s collection efforts are not limited to this.
Here, for example, one of the slides of the presentation of the PRISM program from the NSA:
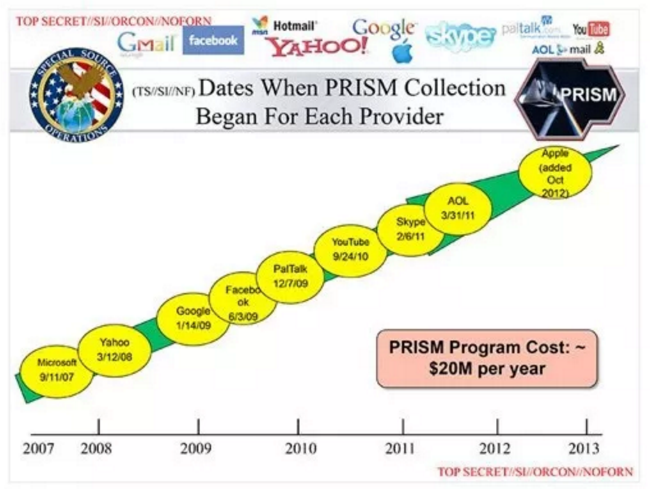
The cost of the program is about $ 20 million per year.
PRISM is a surveillance program launched by the US National Security Agency (with the participation of the UK Government Communications Center), which is also used to intercept emails. At the same time, the largest email providers Microsoft, Yahoo! and Google was among the first to take part in it. And, nevertheless, e-mail remains a more popular means of online communication than Facebook or any other service. Therefore, its importance for the special services is obvious. So, sending a mail message, you must assume that it will be on the servers of PRISM or other similar programs, where the "employees" can read them.
In addition to technical flaws in email security, we can also consider laws protecting the privacy of its users. A huge number of users send emails from US mail services - for example, Gmail.
- After 180 days, your emails on the servers of US mail providers become US property.
- The study showed that 55% of American employers read e-mails of their employees.
- It is worthwhile to read the story of Lavabit service, which has now ceased its work, which was used by Edward Snowden. It can be concluded that it is impossible to conceal any email while it is on the server of an American company.
- Read the Glen Greenwald report series “Nowhere to Hide”.
Metadata, or simple data about the data, are important. For example, the matadata of this response to Quora is the time of its publication, the data about the author, the duration of his stay on the site, the location, the browser he uses, the data on his computer, the local time ... in general, the list is quite long. In the emails, the metadata is even greater. The entire Internet is full of them, probably they are even more valuable than the data itself. In her stunning presentation on the topic “ How the NSA betrayed the trust of the entire world - time to act ”, Mikko Hyppönen explores the importance of metadata.
When you send an email, all the metadata is sent with it. When you reply or forward an email, you automatically forward all the metadata from the previous letter. For example, if several people communicate by e-mail, using any of the aforementioned methods of interception, any interested person can easily access the location data of all the participants in the correspondence, and also find out the topic of discussion without even reading the contents of the letters. You can read more about this in the article entitled “What the metadata of your emails can tell the NSA”.
It is also worth mentioning that by sending an email to a Gmail email address, even if you are not his client, you automatically provide Google with all the information - and you do not need to accept its terms of service (which means reading your emails). The same applies to other US postal services.
How to secure your mailbox
So, all of the above, in fact, suggests that e-mail is insecure, data and metadata can tell a lot about you, and it’s impossible to save yourself from invasion of privacy. But all is not so hopeless. As Edward Snowden said: “The times when the protection of citizens' privacy was completely dependent on the state remained in the past. We are no longer obliged to ask the government for privacy; this is our right . ”
“All intelligence services — absolutely everything — fear simple and secure communication tools,” says Jacob Applebaum .
Asymmetric encryption is the most secure and easy solution, but something else can be done. It is enough to perform several simple steps in order to significantly increase the level of security of email communications.
Step 1. Encryption
Pretty Good Privacy (PGP) is a program that allows you to turn the content of letters into nonsense for everyone except the sender and the recipient. Suitable for some very easy to use email clients. More details about it can be read here .
Step 2. Do not use American postal service
When choosing a postal service, it is necessary to take into account the geographical factor, but you should not rely entirely on it. For example, in Germany and Switzerland, laws protecting the privacy of citizens are more effective than in the United States or the United Kingdom. Therefore, it is safer to use e-mail clients of other countries, for example, Korean Naver.
Step 3. Do not trust the mail provider
Refusal of US mail services is a good start, but ideally you should use email providers with zero information disclosure. Zero disclosure means that the server does not have access to the source text of the data. More information about this is presented here .
Step 4. Mail on your server (it's not that difficult)
Starting your own mail server is not as difficult as it seems. Thus, you can reduce the risk of hacking email-account. This means that the user himself will administer his mailbox, and if someone needs to get its contents, they will have to create a backdoor for this particular server. The likelihood that someone needs you is not particularly great.
Finally, several solutions to improve email security:
- Mozilla thunderbird with the Enigmail extension;
- Mailpile mail client;
- A list of other relatively safe services with an estimate of their parameters is compiled by reference .
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/276761/
All Articles