27% of all recorded malware appeared in 2015

PandaLabs, the anti-virus laboratory of Panda Security , published a report for 2015.
Last year showed new records in the number of malicious programs created, exceeding 84 million variants. At the same time, both large enterprises and websites of various types were attacked in the course of the year, some of them were stolen data about users and customers. As a result, millions of users worldwide have suffered from cyber crimes. Special mention was given to the hotel chain, since they became the main target for criminals due to the huge amount of information they manage, for example, bank card data.
')
Cryptolocker struck the corporate world, but as a result of the fact that many victims are willing to pay to restore their information, we have seen a serious increase in the number of attacks against businesses. The Internet of Things (IoT) has begun to bring itself to the fore, because the safety of such devices remains in question. During 2015, we saw how different specialists managed to hack cars and remotely control them.
However, there is more than bad news. . Private companies and law enforcement are increasingly working together. Slowly but surely, they put barriers for cyber-criminals on the Internet, and although there is still a huge amount of work to be done, it’s good that their crimes will not go unpunished.
Adobe Flash is a “nightmare” for the security world due to the presence of vulnerabilities in it that are used to infect millions of users around the world. It seems that he is living the last days, because more and more systems prohibit its use.
Google is another company that has decided not to support Flash anymore in its Chrome browser, while Amazon no longer allows ads on its website to publish advertisements that use this format.
Last year, once again, was a record for the number of malicious programs created. In general, the PandaLabs anti-virus laboratory during 2015 detected and neutralized over 84 million new samples, which averages about 230,000 new threats daily.
Currently, about 304 million malware have been registered in the laboratory, which means that more than a quarter of the malware ever created was registered in 2015 (27.36%). In addition to Trojans, which are always the main type of malware, last year, notable players were also PNP and various Cryptolocker variants that wreaked havoc throughout the world and carried out information theft in exchange for a ransom payment.
Summary of new threats that emerged during 2015
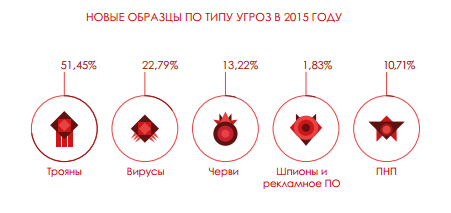
As always, the Trojans are at the top of the rankings with a share of over 50% of all the threats created in the past year.
However, the proportion of Trojans was lower than last year when compared with the other categories, especially viruses (22.79%), worms (13.22%) and PNP (10.71%). If we analyze infections caused by malware all over the world, thanks to data from the Collective Intelligence, we can see that Trojans were the cause of most infections (60.30% of all infections).
Distribution of infections
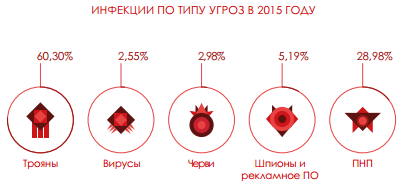
PNP ranked second, causing nearly a third of infections, bypassing spyware and adware (5.19%), worms 2.98%) and viruses (2.55%). Aggressive distribution techniques and programs used by the PNP mean that they have reached a high level of installations on users' computers.
If we look at the global level of infected computers, which is 32.13%, then we can see that it has increased over the past year mainly due to the PNP.
However, it should be noted that this number means the proportion of computers on which any type of malware is present, but this does not mean that they were infected.
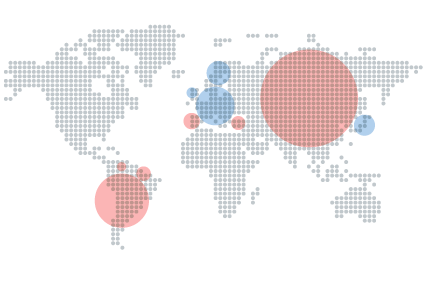
Countries with the highest level of infection: China (57.24%), Taiwan (49.15%) and Turkey (42.52%).

Asia and Latin America are the regions with the highest infection rates. Other countries that did not hit the top ten, but exceeded the world average infection rate: Colombia (33.17%), Uruguay (32.98%), Chile (32.54%) and Spain (32.15%).
If we analyze the data for the countries with the lowest infection levels, we will see that nine of the top ten countries represent Europe, and only Japan is the only non-European country in it. Scandinavian countries are at the top of the ranking: Finland (20.32%), Norway (20.51%) and Sweden (20.88%)

Other countries that did not hit the top ten, but showed an infection level below the world average: Australia (26.87%), France (27.02%), Portugal (27.74%), Austria (28.96%), Canada (29.03%), United States (29.48%), Venezuela (30.11%), Hungary (30.23%), Italy (31.84%) and Costa Rica (32.10%).
Cyber crime
If we had to single out the most dangerous cyber attacks in the first quarter of 2015, then these would certainly be cryptographers, in particular CryptoLocker . This type of attack has hurt all types of users, although companies seem to be more desirable targets, because they store valuable information for which they are willing to pay a ransom.
It is known that some companies eventually succumbed to this type of blackmail, especially those who do not have a backup system to protect their data. In February, it became known that the Illinois State Police Department paid a ransom of $ 500 to unblock a computer after being infected with a cryptographer. Cyber criminals use various types of techniques to infect systems and steal user information. One of the most common infection techniques is the use of exploits, i.e. programs that exploit vulnerabilities on the victim’s computer.
In January, it turned out that cyber fraudsters are actively exploiting a hole in Flash Player . In this case, the security hole was a zero-day vulnerability that was previously unknown, and therefore there was no patch available to it. Flash is the primary target for cyber criminals, as well as Java - other software that was most often cracked by hackers.
One of these "new" techniques (came from the past, since the first such attack was 20 years ago), used by cyber criminals to deceive users and infect them with a cryptographer, is the use of macros in Office documents (especially Word) .
Most users have a false sense of security, thinking that a text document cannot contain a threat. Knowing this, and also realizing that filters on the perimeter do not fight with such files, hackers dramatically increased the number of attacks using this method.
The weak point of such an attack is that the user must include a macro, but the cyber-criminals are well aware of this, and therefore successfully apply various ingenious techniques of social engineering. One such example, disclosed in PandaLabs, was a Word document containing a blurred image. At the top of the document, in bold capital letters, a message was written that the image was blurred for security reasons. If the user wanted to access the information, it was necessary to launch the macro by clicking on the button indicated by the arrow. After the macro was turned on, the picture became clear, but at the same time the computer was infected with one of the Cryptolocker variants.
Another cryptographer, especially popular in Australia, although he was seen in many other countries, used pictures from the hit TV series Breaking Bad. When we talk about phishing, we often think of email messages that are supposedly received from banks. Of course, phishing attacks can be performed in a similar way, and this technique is still used in many cases, but now phishers are attacking not only bank customers and payment services.
In January, a group of hackers launched a phishing attack allegedly on behalf of Apple . The malicious message came from “Apple Support” tech support and it used a common technique. The authors of the letter referred to a security issue in order to simply scare the user: “Your Apple ID has been suspended" ("Your Apple ID has been suspended").
The message warned the user that an unauthorized person tried to gain access to the user's account, and as a result, the account was disabled. The letter contained a link that led the user to a page in the design of the Apple site, where a lot of information was requested: name, postal address, phone number, bank card details, etc.
In February, the American company Anthem admitted that it was the victim of an attack, which resulted in data theft from 80 million users. In this case, the hackers managed to access one of the corporate databases using a stolen username and password. It is assumed that the attack could have cost Anthem more than $ 100 million.
In March , Slack (USA) sent a message to all its users, where they informed them that unauthorized access was found to their database where user information is stored. And although no critical information was stolen (in fact, Slack told users that there was no need to change their registration data), the company instantly turned on a two-step authorization system, forcing users to use additional security features to increase protection.
Budget airline Ryanair was the victim of an attack that caused the company losses of $ 5 million. Despite the fact that the details of the attack were not disclosed, it is known that a transfer was made to one of the Chinese banks. The company reported the crime and stated that it managed to freeze accounts with stolen money and it is going to compensate for the damage in the near future.

The medical insurer CareFirst BlueCross BlueShield has fallen victim to a cyber attack, in which it has stolen information about 1.1 million users. Every day there is a growing threat of attack from such criminals, and this is only one of hundreds of cases of theft of information occurring all over the world.
AdultFriendFinder online dating service suffered from an attack, as a result of which personal information of users was stolen. Hackers offered to sell the stolen information for 70 Bitcoins, which at that time was $ 17,000. Soon the whole database was published on the Internet.
The leading password management company LastPass has become another victim of information theft. Fortunately, it seems that hackers could not get passwords, but only hashes of master passwords of users. The complexity of these hashes (mixed and difficult to understand) makes it very difficult for hackers to get real passwords. But despite this, it was recommended to change the password if it was not very complicated.
The Hard Rock Hotel and the Casino in Las Vegas learned that their security was violated only in the eighth month since the hackers managed to start stealing customer information (their names, bank card numbers and their CVV codes).
Those customers who used their cards in restaurants, bars and shops of this complex suffered, but those who placed orders at the hotel or in the casino did not suffer. This attack resembles other attacks that we saw in the past (Target, Home Depot, UPS, Neiman Marcus), when the terminals were attacked in order to steal information about customers' bank cards.
It was rumored that Uber was the victim of an attack, because users noticed an unusual activity in their accounts. However, it seems that this was a phishing case when deceived users provided their IDs to hackers.
At the end of June, 1,400 passengers of the Polish airline LOT were detained at the Frederic Chopin Airport (Warsaw, Poland) after an attack on the systems used for flight plans.
One of the biggest attacks last year was the attack on Ashley Madison . Hackers, known as Impact Team, have posted on their website a message demanding that this dating service be closed, otherwise they will publish all the stolen information. Almost immediately after the American company failed to meet their requirements, hackers published a torrent with 10 GB of stolen information. Among the published information were data on 37 million clients: completed operations, email addresses, sexual preferences, etc. In addition, internal corporate documents were published.
In the third quarter, a number of new vulnerabilities were also used, which are used by cyber-criminals as a means of accessing their victims. In addition to the typical Flash or Java attacks, a couple of incidents occurred with the Apple Mac OS X operating system. The first incident that was detected by Stefan Esser allowed root access and was associated with adware used to attack the Mac. The second incident was discovered by MyK. It contained a vulnerability in the password management system that allowed the hacker to retrieve all stored information.
One of the methods of attack, which is rapidly gaining popularity, involves intercepting home or corporate routers. In this case, the routers remain under the control of hackers. It turned out that ASUS, DIGICOM, Observa Telecom, PLDT and ZTE routers had preset access codes . This allowed hackers to gain control over them without penetrating into the room where they were installed.
Similar examples of attacks were discovered when hackers used DDoS against Xbox Live and PSN for Christmas. Adobe Flash, known for its many security concerns, may soon disappear. iOS has banned the use of Flash in its operating system. Then Android went the same way. Now it’s Google’s turn to “drive the last nail into the coffin lid”, banning Flash in your Chrome browser. Amazon also announced that it prohibits on its website any advertising created on the basis of this technology.
The FBI detained 5 people who were involved in the 2014 JPMorgan attack . As part of this attack, hackers managed to obtain employee credentials, which were later used to access the company's 90 servers to steal information about 76 million individuals and 7 million legal entities that are customers of the company.
Microsoft decided to increase the security level of its products and solutions by doubling the remuneration for specialists capable of uncovering new critical errors in their solutions: from 50 to 100 thousand US dollars. Although this practice has become common among IT companies, it has not yet covered all sectors. However, an increasing number of companies are offering rewards in the hope that error information will reach them before they are sold “on the side”.
For example, United Airline , which offers miles as a reward, decided to offer up to 1 million miles to those who find and report errors. The FBI also decided to introduce an incentive program, although in this case it is aimed at those who will report information about hiding criminals.
The biggest reward of $ 3 million was offered to anyone who could help delay Yevgeny Mikhailovich Bogachev, the ideological inspirer of the Gameover ZeuS botnet.
Hotel chains are also becoming targets for cyber criminals. In addition to the attack on the Hard Rock Hotel and Casino in Las Vegas, there were others: the Hilton chain, the Starwood chain (Westin, Sheratin, and others.), Las Vegas Sands Casino, Trump Hotels, Mandarin Oriental, FireKeepers Casino and Hotel and others. This is a long list that will definitely grow, because hotels contain information related to millions of bank cards of their guests. As a rule, hotels offer guests to make payments using bank cards, which means that the number of attacks on POS terminals will grow (in the past they have established themselves well among cyber criminals, as in the case of Target, when hackers were able to steal information about 46 million bank cards using malware at the point of sale).
The toy maker VTech also suffered from a security hole, which resulted in the data of 4.98 million parents and 6.37 million children. A few weeks after the attack, UK police arrested those suspected of the attack.
Social networks
In January, simultaneously with the statement of President Barack Obama of the United States on the introduction of a program of measures to combat cyber-criminals, a group of individuals who introduced themselves to ISIS hacked Pentagon accounts in social networks.
Also pay attention to one of the common scams on Facebook these days: bogus posts offering gift cards from well-known companies. In January, a group of scammers launched a campaign on Facebook, within which they promised to distribute 430 Zara gift cards with a face value of $ 500. To participate, the user simply had to join this promotion, write “Thank you Zara” on his wall and invite 50 more people to do the same. The scam has spread like wildfire. In just a few hours, over 5,000 people took part, sending over 124,000 invitations.
All user connections to Facebook servers , including sent and received messages, are transmitted over secure HTTPS protocol. Once this is not enough, this social network has created a service on the Tor network, and now users can be even more confident in their online privacy. However, in addition to connections established by the user through their own service, there are other indirect forms of communication, which Facebook performs, for example, via email. We are talking about notifications that you receive in the event that your friend sent you a personal message (unless you have turned off this feature). Due to the low security of such messages, Facebook announced that now all users will receive them (if they want) protected by the popular encryption program Pretty Good Privacy (PGP). PGP hides letters from potential hackers using a system based on the public key (which should be the sender of the message) and the private key (which should only be the recipient).
WhatsApp is another popular way to attract and infect users. We found a way to deceive, by which criminals are trying to deceive users with the help of a false service called WhatsApp Trendy Blue. He presents himself as a “new version” of the application with additional functions, although in fact all he does is sign the user for an expensive service. This false program also asks you to invite at least 10 of your friends to register with their service.
Facebook has announced that this network is considering the possibility of adding a “Dislike” button on its website. As expected, the cyber criminals decided to take advantage of this opportunity. A few hours after this announcement, various types of false “Do not like” links appeared. In fact, they turned out to be traps that tricked users into sharing their personal information.
Mobile threats
We started 2015 with a threat that reminded us of old-fashioned worms in emails and “instant messengers”, upgraded for use in SMS messages. The attack begins when the victim receives an SMS message with a link to his intended image. The problem is that when you click on the link, the APK file (Android application package) is actually downloaded. If the victim establishes it, then this worm sends a similar SMS message to all contacts of the victim. Fujitsu, in collaboration with the Japanese operator NTT Docomo, released the Arrows NX F-04G, which is the first Android mobile device to offer an iris scanner as one of its security features. This method is much safer than the fingerprint scanning method, which is very popular among manufacturers such as the Apple iPhone 6 or Samsung Galaxy S6.
In June, we discovered a phishing campaign that was aimed at Android developers who published their products on Google Play, the official app store for this operating system. A message called Play Developer Support was sent from the company with the heading “Update Your Account Information” and a request to update the information in the account.
When clicking the link, the user was redirected to a page that looked like Google, where it was necessary to enter their data.
This case is different in that the hackers did not want to empty the victim’s bank account, but to use the account to spread threats through the Google Play store. What worries me most is how easily criminals can automate the whole process.
This requires:
• Create a spider or crawler (for this there are various open source projects) to download information about all applications published on Google Play.
• Analyze information to obtain email addresses of various developers.
• Run a customized phishing campaign, in which even the web page will be customized by the developer. In this case, the hype becomes even more believable, which helps to increase the “conversion rate”.
• Since the hacker has information about all the applications published by each developer, you can create a system that alerts him every time the developer of a popular application (millions of downloads) falls into the trap.
With this in mind, one of the simplest and less complex attacks will publish applications from this account. Imagine if someone tries to steal Candy Crush developer data and publishes Candy Crush 2 from the same account. If hackers are smarter and find a way to modify the application without using the private key (which cannot be obtained through the theft of registration information), they will be able to publish and update any application they want.
Returning to the previous example, imagine that hackers have created an updated version of Candy Crush, which contains a trojan: millions of people will download and install it, without even thinking about any threat.
Google has created a new program called Android Security Awards, in which it plans to pay out to those who will research and discover new flaws in Android security.
: 2000 , 1000 500 . , 38000 .
Zimperium Android 950 , . , , , . MMS, — . MMS, .. Android . , MMS.
, , . Google (Sony, LG, Motorola ) , Samsung , , , .
IBM XForce , , . Google , .
" , Android. , . : PIN- 500 . , Android PIN- - , , 500 . Apple .
Appthority Quicksand, , MDM, . Apple iOS 8.4.1.
, , — Ims0mnia. Apple , .
Apple Apple Store , XcodeGhost. iOS, , , .
Apple 225 000 iCloud. , «» , App Store, iOS.
Internet of things
HP Fortify -. , 100% , , « ». , - , .
, . Wired Jeep Cherokee, . , : , , , … , , . , .
, , BlackHat .
Land Rover 65 000 , 2013 . . BlackHat , Tesla Model S. , 6 , , . .
, , , Toyota Corolla . , , . , ( ), — - .
Cyber war
-. , Sony Pictures «», .
, . Der Spiegel , () F-35, , ..
, , , IT-. CNN , , . , , , . , , «
».
, (OPM, ), , 4 . , , . , , , , , , , .
TV5MONDE, . , «» Facebook -.
« » , .
, . , , , . , Stuxnet, . , , Stuxnet ().
Hacking Team — - - . . Hacking Team Twitter, . Hacked Team .

( , ). , Hacking Team, , , , , , . - , , Hacking Team.
« » Adobe Flash , Hacking Team.
, , , - . , , , , .
25 , . , , , .
DGI 78020 - . , , Naikon - , . , , , , , , , , , , - .
Anonymous , - .

IT- 2016
1.
- -, .. . , . , , .
2.
. PE- (https://ru.wikipedia.org/wiki/ Portable_Executable), PE-, . java-, , , Powershell, Windows 10, . , Fileless-,
, , .
3.
. , . , , .. , . , ( , .) .
4. Android
, Android, .. . . , .
5.
, 2016 , , -, .. . - « » , .
6.
, 2016 , , , , , . 2015 , , .
7.
-, - , . , Stuxnet.
8.
. , , , . , , , .
Conclusion
2015 , , 2016 . , , - 12 , , , Cryptolocker.
, .. , , - , . , , , - . , , , . , , , , , . , .
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/276301/
All Articles