Why do you need best practices in IT infrastructure management?
How do you work: on a whim or science? Probably no one will give a definite answer: work in the IT field involves a combination of experience and technology, precise instructions, standards, and beautiful, even talented, engineering finds. In any case, experience decides. What about someone else's experience? The world has created a lot of codes and rules for the work of IT services, which combines the concept with a marketing touch - “best practices”. This is an experience formed by a multitude of companies that makes it quite easy to solve standard problems.

In the post we will tell what ITIL, ITSM, CobiT, DevOps are, how they are connected and why even the system administrators of small companies need to know something about these abbreviations.
ITIL (IT Infrastructure Library) is a set of publications (library) containing the best practices in IT service management. ITIL provides guidance on the provision of quality IT services, processes, functions, and other tools necessary to support them. The structure of ITIL is based on the service life cycle, which consists of five stages (strategy, design, transformation, operation, and continuous improvement). There are also additional publications that are included in ITIL and contain specific recommendations on industries, types of companies, work models and technological architectures. This is the canonical definition of ITIL.
In fact, this library has created a whole paradigm for managing the company's IT infrastructure, based on SLA (compliance of the service provider’s promises to customer expectations) and ITSM (IT Service Management, IT service management). ITSM is the concept of organizing the work of an IT department and its interaction with an external or internal customer, as well as external contractors.
')
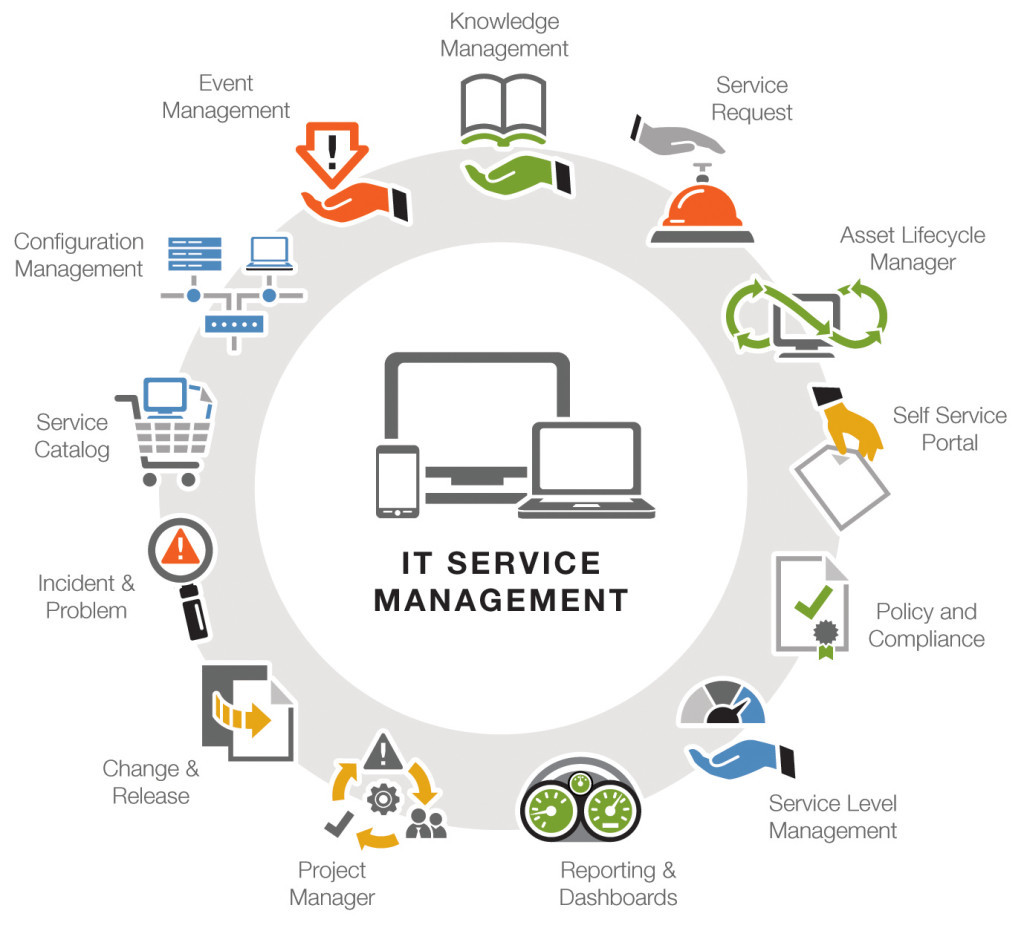
ITSM itself is an IT project, so, like all other projects, it has its advantages and disadvantages. Using ITSM methods makes it possible to make the service cheaper and faster, and the work of the IT department is more transparent, which is especially valuable in multi-branch and holding organizations. There is also another point that in the age of startups and literally lightning growth of new types of business went beyond the interests of large organizations - this is the possibility of certification according to ISO 20000, the international standard for managing and maintaining IT services. Useful thing if you are applying for a piece of the market and looking for an investor.
Now about the risks. It is clear that the ITSM standards and the ITIL library describe the best practices, and when reading them it seems that everything is logical and should work in exactly this way.
As a matter of fact, it is ITIL that we owe to the creation and development of convenient ticket systems, incident management and the Service Desk. Most of the developers of this software (and Alloy Software is no exception) in the development of modules relied precisely on the recommendations of ITIL.
CobiT (Control Objectives for Information and Related Technologies , management tasks for information and related technologies) - collection of standards and guidelines for IT audit management and security; guide and a collection of practices for managing IT processes. ITIL-related tool that is continuously updated and is designed to ensure that peace and understanding prevail between the company's management, IT specialists and auditors (external and internal). Simply put, the managing manager must understand all the IT risks, including those associated with inaction in situations that require correction, as well as the potential risks associated with using a particular element of the company's IT infrastructure.
Consider two common situations.
Situation one. The company's management may not have an understanding of what is happening in the IT space, but at the same time be a complete understanding of the goals and mission of the business, processes, product and services. Conversely, a CIO can fanatically build an ideal IT infrastructure, with little or no interest in how it fits into the company's development strategy. And this happens quite often in the most vulnerable layer - medium-sized business, which has not yet reached a new level of management (as a giant), but has already experienced the growth of services and the rupture of simple and intelligible intra-company communications inherent in small business. Meanwhile, this state of affairs does not relieve the head of responsibility for absolutely all processes in the company, including those taking place in IT.
 Situation two , peculiar to companies of any level: from microbusiness to transnational corporations, is an inadequate assessment of risks. Almost every one of us has met at least once with risks of an oversized scale: for example, the fear of DDoS in a small company or the well-known “problem 2000” that has never become a reality. These are risks that are given great importance and which do not carry an objective threat. On the other hand, there are underestimated risks to which no one pays attention, but they are able to put the entire workflow or cause commercial damage: unlimited validity of user accounts and user passwords from work PCs and corporate information systems, client banks; transfer of commercially significant data over unsecured channels; lack of antiviruses and so on. In order to classify risks and correctly evaluate them, it is necessary to conduct an internal and / or external IT audit. He, in turn, should not be a verification of compliance with the rules and not an impetus for compliance with the rules, namely compliance with the rules. Therefore, the audit should be regular and associated with the monitoring system process of obtaining and evaluating objective data on the current state of the information system, actions and events occurring inside it.
Situation two , peculiar to companies of any level: from microbusiness to transnational corporations, is an inadequate assessment of risks. Almost every one of us has met at least once with risks of an oversized scale: for example, the fear of DDoS in a small company or the well-known “problem 2000” that has never become a reality. These are risks that are given great importance and which do not carry an objective threat. On the other hand, there are underestimated risks to which no one pays attention, but they are able to put the entire workflow or cause commercial damage: unlimited validity of user accounts and user passwords from work PCs and corporate information systems, client banks; transfer of commercially significant data over unsecured channels; lack of antiviruses and so on. In order to classify risks and correctly evaluate them, it is necessary to conduct an internal and / or external IT audit. He, in turn, should not be a verification of compliance with the rules and not an impetus for compliance with the rules, namely compliance with the rules. Therefore, the audit should be regular and associated with the monitoring system process of obtaining and evaluating objective data on the current state of the information system, actions and events occurring inside it.
In light of these situations, let us return to CobiT. It describes the goals, objectives and principles of management, objects of management, IT processes, tools for working with IT infrastructure, as well as IT security issues. The current version of CobiT and articles on it can be read on the ISACA website (there are free and paid materials). CobiT can be defined as an IT corporate governance methodology that:
In addition, CobiT complies with ISO 9000 and ISO / IEC 17799 standards, information security and information security management standards. Using CobiT principles, you can minimize risks and control the return on IT investment. What we like about CobiT is that it is well structured and the field of view of this set of rules includes planning, organization, acquisition, implementation, operation and maintenance, as well as monitoring and evaluation of the five most important elements of each company (according to the definition of CobiT, IT resources ).
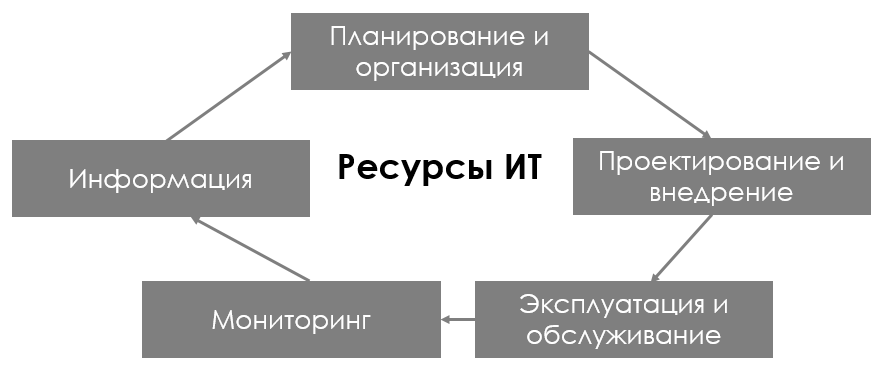
That is, in fact, CobiT proceeds from the understanding that IT infrastructure is information management, and according to the code, information is evaluated according to several criteria:
So how do CobiT and ITIL compare? ITIL is a library of best practices in the provision of IT services, and CobiT is more about IT management and auditing. Accordingly, all processes described in ITIL can be controlled and audited by the CobiT standard.
Associated with ITIL (in some sources it is considered a direct consequence), CobiT is covered, but has a completely different paradigm approach to DevOps system administration. However, the very decoding of the name indicates that it is a hybrid at the junction of administration and development (development and operations). The DevOps methodology combines the work of developers and IT engineers (these can be formed teams, individuals or even one person), thereby ensuring rapid deployment rates, reliability and security of the production environment (including testing). Simply put, this methodology ruled out a common phrase that became a meme: “The problem is on the hardware / software side”.

DevOps fits perfectly into the Agile methodology with frequent builds and releases, works well in the case of the development and testing of cloud services, as well as continuously developing user applications (corporate systems, games, schedulers, aggregators, etc.), which is why since 2009 He developed well and got accustomed in many teams as a peculiar type of IT cooperation. An additional advantage of the DevOps methodology is felt when developers and test engineers use virtual machines, configuration files, integration and continuous testing. For example, when testing IP telephony services, the tester writes and uses automatic tests, he himself sets up the scheme, virtual machines, database replication - in fact, this is DevOps.
As a DevOps methodology, there are many advantages, including:
As you can see, DevOps is not an approach purely to system administration, respectively, its use is mainly in developer companies.
Indeed, ITIL and CobiT affect and describe several dozen IT processes, many of which are not found in most organizations. However, this is not a reason to abandon the basics of methodologies in order to introduce some ideas into the life of your IT infrastructure. Here is an approximate list of what makes use of some of the principles of the listed methodologies.
The management of the company has its own benefit from the use of the principles of the listed methodologies. First of all, this is an aspect of economy and planning.
In principle, almost every system administrator came across individual elements of methodologies and actively used them in his practice. However, an integrated approach and the gradual introduction of new practices will certainly have their effect, regardless of the size of the company. We experienced this on ourselves - both in the process of developing our systems and in the process of managing the company. We always repeat to our customers: yes, our systems are designed taking into account the principles of ITIL, but their use and implementation does not at all oblige blindly to obey the principles. On the contrary, we always note that Alloy Software programs are flexibly configured for almost any infrastructure:
Alloy Navigator - a comprehensive tool for managing the work of the IT infrastructure of the enterprise. The product is a simple and multifunctional Service Desk system, with extensive asset management capabilities and support for the entire range of tasks of the IT department. Aimed at the need of medium and large businesses. For small businesses there is Alloy Navigator Express.
Alloy Discovery is a system for collecting and processing information about computer hardware and software of a company. The product is designed specifically for network administrators and service providers, suitable for small and medium businesses. For a very small business there is Alloy Discovery Express.
The new year is coming. Undoubtedly, like any other, it will bring new challenges and successes to companies and the entire IT industry. Therefore, the Alloy Software team wishes everyone success and development. Do not let your reliable and controlled IT infrastructure fail you. Holiday greetings!

In the post we will tell what ITIL, ITSM, CobiT, DevOps are, how they are connected and why even the system administrators of small companies need to know something about these abbreviations.
Zoo Methodologies: a very brief overview
ITIL and ITSM
ITIL (IT Infrastructure Library) is a set of publications (library) containing the best practices in IT service management. ITIL provides guidance on the provision of quality IT services, processes, functions, and other tools necessary to support them. The structure of ITIL is based on the service life cycle, which consists of five stages (strategy, design, transformation, operation, and continuous improvement). There are also additional publications that are included in ITIL and contain specific recommendations on industries, types of companies, work models and technological architectures. This is the canonical definition of ITIL.
In fact, this library has created a whole paradigm for managing the company's IT infrastructure, based on SLA (compliance of the service provider’s promises to customer expectations) and ITSM (IT Service Management, IT service management). ITSM is the concept of organizing the work of an IT department and its interaction with an external or internal customer, as well as external contractors.
')

ITSM itself is an IT project, so, like all other projects, it has its advantages and disadvantages. Using ITSM methods makes it possible to make the service cheaper and faster, and the work of the IT department is more transparent, which is especially valuable in multi-branch and holding organizations. There is also another point that in the age of startups and literally lightning growth of new types of business went beyond the interests of large organizations - this is the possibility of certification according to ISO 20000, the international standard for managing and maintaining IT services. Useful thing if you are applying for a piece of the market and looking for an investor.
Now about the risks. It is clear that the ITSM standards and the ITIL library describe the best practices, and when reading them it seems that everything is logical and should work in exactly this way.
- If you take all the provisions as they are, without reference to the current state of affairs in business in general and in the IT service in particular, you can come to an excessive formalization and significant disruption of work. The process of implementing the principles of ITIL should be selective and adaptive.
- Again, before changing the management approach, an in-depth analysis of the processes occurring within the IT infrastructure should be carried out - if everything works and there are no obvious ways and needs for improvement, it is better to approach ITSM selectively and implement the most valuable and necessary principles: license management (SAM), configuration management or just set up monitoring.
- If there is no clear purpose to use the principles of ITIL, then it is better to abandon the idea. Clear objectives are, for example, changing the license management policy or solving the problem of employees using pirated software. The unintelligible goal is to introduce and apply what was imposed from above, because it was heard at the conference.
As a matter of fact, it is ITIL that we owe to the creation and development of convenient ticket systems, incident management and the Service Desk. Most of the developers of this software (and Alloy Software is no exception) in the development of modules relied precisely on the recommendations of ITIL.
CobiT
CobiT (Control Objectives for Information and Related Technologies , management tasks for information and related technologies) - collection of standards and guidelines for IT audit management and security; guide and a collection of practices for managing IT processes. ITIL-related tool that is continuously updated and is designed to ensure that peace and understanding prevail between the company's management, IT specialists and auditors (external and internal). Simply put, the managing manager must understand all the IT risks, including those associated with inaction in situations that require correction, as well as the potential risks associated with using a particular element of the company's IT infrastructure.
Consider two common situations.
Situation one. The company's management may not have an understanding of what is happening in the IT space, but at the same time be a complete understanding of the goals and mission of the business, processes, product and services. Conversely, a CIO can fanatically build an ideal IT infrastructure, with little or no interest in how it fits into the company's development strategy. And this happens quite often in the most vulnerable layer - medium-sized business, which has not yet reached a new level of management (as a giant), but has already experienced the growth of services and the rupture of simple and intelligible intra-company communications inherent in small business. Meanwhile, this state of affairs does not relieve the head of responsibility for absolutely all processes in the company, including those taking place in IT.
 Situation two , peculiar to companies of any level: from microbusiness to transnational corporations, is an inadequate assessment of risks. Almost every one of us has met at least once with risks of an oversized scale: for example, the fear of DDoS in a small company or the well-known “problem 2000” that has never become a reality. These are risks that are given great importance and which do not carry an objective threat. On the other hand, there are underestimated risks to which no one pays attention, but they are able to put the entire workflow or cause commercial damage: unlimited validity of user accounts and user passwords from work PCs and corporate information systems, client banks; transfer of commercially significant data over unsecured channels; lack of antiviruses and so on. In order to classify risks and correctly evaluate them, it is necessary to conduct an internal and / or external IT audit. He, in turn, should not be a verification of compliance with the rules and not an impetus for compliance with the rules, namely compliance with the rules. Therefore, the audit should be regular and associated with the monitoring system process of obtaining and evaluating objective data on the current state of the information system, actions and events occurring inside it.
Situation two , peculiar to companies of any level: from microbusiness to transnational corporations, is an inadequate assessment of risks. Almost every one of us has met at least once with risks of an oversized scale: for example, the fear of DDoS in a small company or the well-known “problem 2000” that has never become a reality. These are risks that are given great importance and which do not carry an objective threat. On the other hand, there are underestimated risks to which no one pays attention, but they are able to put the entire workflow or cause commercial damage: unlimited validity of user accounts and user passwords from work PCs and corporate information systems, client banks; transfer of commercially significant data over unsecured channels; lack of antiviruses and so on. In order to classify risks and correctly evaluate them, it is necessary to conduct an internal and / or external IT audit. He, in turn, should not be a verification of compliance with the rules and not an impetus for compliance with the rules, namely compliance with the rules. Therefore, the audit should be regular and associated with the monitoring system process of obtaining and evaluating objective data on the current state of the information system, actions and events occurring inside it.In light of these situations, let us return to CobiT. It describes the goals, objectives and principles of management, objects of management, IT processes, tools for working with IT infrastructure, as well as IT security issues. The current version of CobiT and articles on it can be read on the ISACA website (there are free and paid materials). CobiT can be defined as an IT corporate governance methodology that:
- focused on real business requirements;
- supports the process approach to IT infrastructure management and controls the processes;
- evaluates the effectiveness of IT in the company.
In addition, CobiT complies with ISO 9000 and ISO / IEC 17799 standards, information security and information security management standards. Using CobiT principles, you can minimize risks and control the return on IT investment. What we like about CobiT is that it is well structured and the field of view of this set of rules includes planning, organization, acquisition, implementation, operation and maintenance, as well as monitoring and evaluation of the five most important elements of each company (according to the definition of CobiT, IT resources ).
- Data - information within the company in any form, media files, external information.
- Applications - many automated and manual procedures.
- Technology - software, hardware, DBMS, SU networks, OS.
- Equipment - resources that support technology.
- People are personnel with skills and abilities, including control and monitoring.

That is, in fact, CobiT proceeds from the understanding that IT infrastructure is information management, and according to the code, information is evaluated according to several criteria:
- productivity - ensuring the availability of information through the most economical and productive use of resources
- efficiency - relevance and timeliness of information
- confidentiality - ensuring the protection of information from unauthorized access
- integrity - accuracy, completeness and accuracy of information
- consistency - compliance with laws, regulations and local regulations (decrees, contracts, articles of association, etc.)
- availability and ease of access - the ability to obtain and use information for managing business processes
- reliability - the property of information to reflect the real state of affairs necessary for making managerial (including financial) decisions.
So how do CobiT and ITIL compare? ITIL is a library of best practices in the provision of IT services, and CobiT is more about IT management and auditing. Accordingly, all processes described in ITIL can be controlled and audited by the CobiT standard.
Devops
Associated with ITIL (in some sources it is considered a direct consequence), CobiT is covered, but has a completely different paradigm approach to DevOps system administration. However, the very decoding of the name indicates that it is a hybrid at the junction of administration and development (development and operations). The DevOps methodology combines the work of developers and IT engineers (these can be formed teams, individuals or even one person), thereby ensuring rapid deployment rates, reliability and security of the production environment (including testing). Simply put, this methodology ruled out a common phrase that became a meme: “The problem is on the hardware / software side”.

DevOps fits perfectly into the Agile methodology with frequent builds and releases, works well in the case of the development and testing of cloud services, as well as continuously developing user applications (corporate systems, games, schedulers, aggregators, etc.), which is why since 2009 He developed well and got accustomed in many teams as a peculiar type of IT cooperation. An additional advantage of the DevOps methodology is felt when developers and test engineers use virtual machines, configuration files, integration and continuous testing. For example, when testing IP telephony services, the tester writes and uses automatic tests, he himself sets up the scheme, virtual machines, database replication - in fact, this is DevOps.
As a DevOps methodology, there are many advantages, including:
- standardization and automation of the environment
- high speed development, deployment and testing
- opportunity to release updates frequently
- minimization of problems with customer implementation, etc.
As you can see, DevOps is not an approach purely to system administration, respectively, its use is mainly in developer companies.
Visible Ops Warning
You can hear the term Visible Ops. It is not directly related to DevOps, but it is related to ITIL, namely, this is the book (with the development of technology turned into a series of books) Visible Ops Handbook, which is an excellent step-by-step guide to using ITIL in the company. The books have interesting practical examples of large corporations. The first book, which has become a classic, reveals IT problems in a company and the goals of change in simple English. In any case, at least look through the PDF-ku worth.
Ok, my company is not in the top 100 of the world, what should I do with this information?
Indeed, ITIL and CobiT affect and describe several dozen IT processes, many of which are not found in most organizations. However, this is not a reason to abandon the basics of methodologies in order to introduce some ideas into the life of your IT infrastructure. Here is an approximate list of what makes use of some of the principles of the listed methodologies.
- Distribution of responsibility in a team and understanding of interrelations of all divisions. For example, the sales department cannot live separately from the IT service, because it is a user of services and information provided by IT. This is especially noticeable in those companies where data is collected in a centralized database, and then distributed on request (for example, companies with billing information from which is unloaded using special reports according to access rights). Plus, within the IT service team itself, it is also necessary to clearly assign responsibilities - this will ensure coordinated action.
- The growth of attentiveness and responsibility. In case the staff is aware of continuous monitoring and periodic IT audit, many incidents can be avoided, since it becomes obvious to the user that any tricks will be revealed.
- Increased reaction rate to problems. If the company has a system of tickets and requests, then the efficiency of servicing internal customers is greatly enhanced, and the speed of solving the problem is controlled by the initiator of the application.
- Simplicity and transparency in identifying problems. The incident handling system in conjunction with the network monitoring software helps you quickly determine the cause of the problem and the objects involved in the problem. And, therefore, to obtain reliable information to find a solution.
- Simplify resource utilization. System administrators and engineers with the help of special programs can remotely install physically and morally outdated software and hardware and either update it or replace it with a new one. At the same time, it is possible to plan the replacement of IT infrastructure elements, and this is a guarantee of stable work of employees without sudden downtime.
The management of the company has its own benefit from the use of the principles of the listed methodologies. First of all, this is an aspect of economy and planning.
- Managing software licenses, checking for free licenses is one of the tangible savings on IT infrastructure. Establishing a license usage profile helps to adjust the volume of purchased or leased products, redistribute the software according to real needs. A classic example: the sales department of 7 people, three of whom are constantly “in the fields”, and another one - unloads the data once a month for analysis. In the department there are seven licenses for CRM, and it would be possible to do with five. The same story is repeated in the departments of logistics and design, where expensive software is installed and often stands idle.
- Regulated work within the IT service reduces the number of deadlines and unrealized projects.
- Understanding the current slice of hardware and software in the company allows you to reasonably budget for the purchase of IT assets, quickly and accurately assess the company's needs in upgrading the IT infrastructure.
- An accurate understanding of the organization of the IT infrastructure helps to optimize the ratio of capital and operating expenses. For example, making a choice in favor of renting software on a SaaS model or using virtual computing power in the cloud.
In principle, almost every system administrator came across individual elements of methodologies and actively used them in his practice. However, an integrated approach and the gradual introduction of new practices will certainly have their effect, regardless of the size of the company. We experienced this on ourselves - both in the process of developing our systems and in the process of managing the company. We always repeat to our customers: yes, our systems are designed taking into account the principles of ITIL, but their use and implementation does not at all oblige blindly to obey the principles. On the contrary, we always note that Alloy Software programs are flexibly configured for almost any infrastructure:
Alloy Navigator - a comprehensive tool for managing the work of the IT infrastructure of the enterprise. The product is a simple and multifunctional Service Desk system, with extensive asset management capabilities and support for the entire range of tasks of the IT department. Aimed at the need of medium and large businesses. For small businesses there is Alloy Navigator Express.
Alloy Discovery is a system for collecting and processing information about computer hardware and software of a company. The product is designed specifically for network administrators and service providers, suitable for small and medium businesses. For a very small business there is Alloy Discovery Express.
Remembering the previous comments on Habré, let's highlight the prices of products right in the post:
Alloy navigator
Alloy Navigator Express - from 20 000 rub. / user, from 150 rubles. / host
Alloy Navigator Enterprise - from 83,000 rubles. / user, from 150 rubles. / host
Details here
The post about Alloy Navigator on Habré lives here .
Alloy discovery
Alloy Discovery Express - from 12 000 rub. / user, from 150 rubles. / host
Alloy Discovery Enterprise - from 19 000 rub. / user, from 150 rubles. / host
Details here
The post about Alloy Discovery on Habré lives here .
Alloy Navigator Express - from 20 000 rub. / user, from 150 rubles. / host
Alloy Navigator Enterprise - from 83,000 rubles. / user, from 150 rubles. / host
Details here
The post about Alloy Navigator on Habré lives here .
Alloy discovery
Alloy Discovery Express - from 12 000 rub. / user, from 150 rubles. / host
Alloy Discovery Enterprise - from 19 000 rub. / user, from 150 rubles. / host
Details here
The post about Alloy Discovery on Habré lives here .
The new year is coming. Undoubtedly, like any other, it will bring new challenges and successes to companies and the entire IT industry. Therefore, the Alloy Software team wishes everyone success and development. Do not let your reliable and controlled IT infrastructure fail you. Holiday greetings!
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/274167/
All Articles