Maaaalenka PDF assembly of hardcore articles about GameDev

Hello!
I learned from publishers that from January 1 to January 10, people read more than a year. Therefore, a small gift from us - we agreed with Daniel Cook (former game designer of Epic Megagames), took and translated some of his hardcore game development materials. And stuck them in PDF on a hundred pages.
- How games are shaped by the external environment : how the market influences the plot of the game (for example, due to a decrease in the average income per game, the role of the open world decreases — it takes too long to do it) and so on. Very good analytical review from gurus with specific tips.
- Organization of gameplay in a multiplayer game - how to gather players together, how to make asynchronous interactions, and a lot more with numbers and examples. Good hardcore.
- Top 5 controversies about the development of 2014 - last year's material that discussed the trends. Everything is relevant now.
- Developer Declaration of Independence - American soul cry that "remove the dirty paw of the CFO from the plot of the game." Well approximately.
- Criticism of the criticism of games - what to do if reviews are written by amateurs, and how to stand out from ballast.
- Creating effective cause-effect relationships in games is an incredibly useful thing for all those who want to understand how the cognitive schemes of games work. It is useful not only for developers, but also for UI / UX specialists.
- Trophy tables - math picking loot from the corpses of enemies. It begins with the educational program and is rapidly accelerating to very tough decisions.
Here is a PDF and full text . Below in the post - the main points, if you are too lazy to read everything or you want to here and now.
')
How games are shaped by the external environment
This is a story about how discourse affects the development process. Here is the flesh:
- Digital distribution and low-cost toolkit: an advanced trend is the opportunity for small development teams to create and produce low-cost games.
- A huge audience, brought up on the consumption of content.
- The average income from the product falls. In fact, in the mobile gaming market, it tends to zero.
- Price per copy less than $ 0.99. As Steam develops, game kits are gaining popularity, and consoles are providing more and more free games, a further erosion of the prices of premium games is expected. We have to win a large audience and earn less money.
- Not enough clarity. Channels are flooded with games of dubious quality. During the first 30 seconds you need to show the quality - otherwise there will be no more time.
- Production cost increases: cheap tools reduce capital costs, but labor costs remain the same.
The need to achieve higher and higher quality leads to an increase in the cost schedule. Five years ago, creating a first-class mobile game could cost $ 50,000 (including paying employees for housing). Now, with lower incomes, costs range from 200 thousand to a million dollars (or higher). Such expenses arise almost exclusively as a result of the race of content and options: more art, more animation, increasing use of 3D, more and more “necessary” options.
Accordingly, the games become shorter, the options are smaller, the development time is shortened, people rely more on the development of proven mechanics. Next - predictions where all this will roll and what will pour out. Damn useful.
Here is the full text of the translation .
Organization of gameplay in a multiplayer game
Here are two schemes of the game:
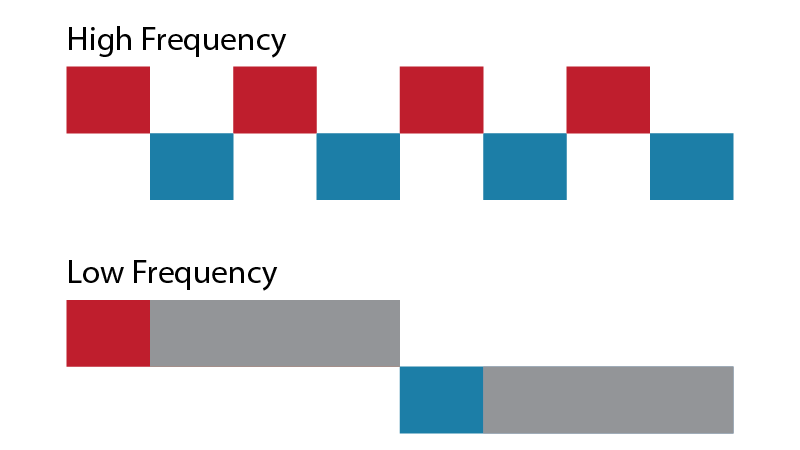
The first is a shooter, strategy or card game, when you need an answer from your opponent right away. The second is chess, step-by-step strategy or something else where you can do something before the opponent’s turn. Next is a story about how to design big games with asynchronous interaction of players. For example:
• Single player: personal skill enhancement, development, world exploration and storylines are available as development tools.
• Two players: communication, relationships, status, gifts, trade, cooperation and competition become available.
• Three or four players: alliances, politics, rumors, stereotyping, and opposition to others are becoming available.
• Small group (more than five players): interaction between groups, official leadership, role-playing specialization, official penalties.
• Medium group (more than twelve players): formation of factions, barter economy and the possibility of expulsion.
• Large groups (more than forty players): the emergence of a hierarchy (leaders and their deputies), the monetary economy, the requirements for compliance with roles. Special management systems, the consolidation of social norms in society.
• Very large groups (over two hundred players): the introduction of trading classes, market regulation of prices, fixed management systems, subclasses, the presence of celebrities, the use of propaganda. From this stage, players are not exactly familiar with all other players, and official structures are required to fulfill social norms.
• Huge groups (over a thousand players): polls, development of resources at the city level. At this level, there is a little bit of such that would not have been noted for groups of over two hundred or even forty people.
Further - about how to collect players at the same time, here's another quote:
The trap of "active player": one of the common mistakes of developers is that they believe that a high number of active players will lead to the formation of strong communities. However, in reality one should look at the real number of simultaneous users, since in many games the simultaneity factor is extremely high. There can be 1000 players in the game, but if each of them comes into the game for five minutes a day according to a sliding schedule during the week, we get that the average number of simultaneous players is 0.5. If the selection system does not cope with such a tiny, unevenly emerging number of players, the game dies.
Pro game with friends and strangers, examples of games, matches and generally a lot of hardcore. The full text is here . How to finish reading - see our example already, about how Vlaada Khvatil collected people in multiplayer , and about the history of Hive ( at the end of the tournaments ).
Top 5 controversy about the development of 2014
Short:
- Holivar "what is the game" - but do not care, most importantly, the definition does not help in the development.
- Plot-oriented games against mechanics - still not to separate one from the other. I already wrote about this, the conclusions are generally similar.
- The role of chance and the role of player skill is that it is necessary for chance that beginners have chances, but the skill at later levels solves.
- The importance of realism. “The realism of graphics and game physics is no longer the main goal for most game developers. In practice, it turned out that realism is not a prerequisite for developing a successful game. ”
- Casual vs hardcore. “The variability of the game in each case is huge. In almost every game of medium difficulty, more than half a dozen styles can be found. Each game can be compared to a city in which thousands of different people live. Thinking only about average values, you will not get a complete picture of how to improve your game qualitatively ... In my understanding, dividing players into regular and hardcore is insulting and incorrect labeling. ”
You can fully enjoy the argument in holivarah here .
Developer Declaration of Independence
- Development at the forefront - without Dev no Game.
- Vision of the game for game designer.
- Amateurs overboard.
- The developer must understand all aspects of the game.
- Do not be silent about their views.
- Need to invent new markets and trends.
- The right to make a mistake.
- The right to choose.
Apparently, someone stupidly got a strong leader. And this phenomenon is massive. Full translation here .
Criticism of the criticism of games
“We need authors with a deeper understanding of art, production and game design. Most game publications are based on information obtained from a narrow circle of players, journalists and representatives of the humanitarian academic environment. Often not offered a look from the perspective of classical science or game developers. I believe that most of these authors are just kind of illiterate in game issues. It's like taking to the jury for dancing people who watched figure skating on TV and never danced themselves. ”
In short, we see it every day at Habré, but there are also specific proposals there as well as complaints. And some who write topics with us here will find this useful:
• Justification: Does your theory have empirical evidence? No need to write something that you think.
• Awareness: have you already written about this? Look for information and be armed with it.
• Content: Does your article offer a new perspective or tool for further discussion? No need to raise the old arguments, expressing your opinion about some new chips.
• Practical focus: does your article offer a solution? Do not let your idea hang in the air. Encourage the reader to take action, building up knowledge useful for the gaming community as a whole.
The text is here .
Creating effective cause-effect relationships in games
Very cool thing with practical tools for UI, development and a whole bunch. I recommend reading in full, even if you are not a game developer. A couple of quotes:
“I'm a mechanic fixing broken black boxes. One important concept helped me a lot. It lies in the fact that when considering the relationship of the system and the response used by the game to describe the interaction with the system, these relations can be divided into "dense" and "free". In a dense system, cause and effect are clearly defined. In a free system, it is more difficult to distinguish cause-effect relationships. ”
“Skills are layered on each other. Jumping in Mario gradually develops into complex navigation skills between platforms. I believe that the stages of the game in which the player acquires basic skills should be the most dense. These systems need to be made the most obvious from the first seconds of the game, they are a kind of gateway to the game, to the rest of it, so to speak. Reduce the number of options available to use, use existing thinking patterns and make cause-effect relationships as clear and visible as possible. Then, when the player has mastered the basics, more loose connections can be introduced into the game, which will require more effort to master. ”
Here is the full text .
Trophy tables
A couple of quotes:
“This is how you can make guaranteed trophies.
• When you throw non-guaranteed items when throwing, the weight of all such items is reduced by X%
• X = 100 / maximum number of throws, until obtaining guaranteed items.
• The modified trophy table is saved for the next shot. ”
“Sometimes you want to check whether objects based on some external variable can fall out. In the game Realm of the Mad God, we wanted to avoid the players getting trophies for killing the main enemy, just without causing him the slightest damage. And for this in the trophy table, we added the conditions for obtaining trophies. When a valuable trophy comes out of the table, it is immediately checked whether the player has inflicted enough damage to the enemy to get this trophy. ”
The page is here.
From good design to excellent
And finally, an interview with Richard Garfield, telling, in particular, about prototyping. Simple and easy after all this. It is not in PDF, only the text is here .
Well, if you did not read Sirlin "Play to win" - we also translated it for a long time. Here is a post , there are links to PDF and texts.
Everything. Good holidays .
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/274077/
All Articles