Disaster corporate data center as a service
There are many solutions for building disaster-tolerant systems using the technologies of consolidation and virtualization of computing resources, cluster systems, technologies of replication and continuous data protection, and the customer can build a disaster-resistant data center either independently or using sites of commercial data centers and service providers.
Today, almost every company that actively uses IT to support a business has its own data processing center (DPC). Increasing data center reliability requirements is one of the market trends. Since the data center is often a key element of the company's business, experts have long been looking for cost-effective ways to increase its reliability. And sooner or later there is a need to ensure not only the hardware reliability of the data center, but also its disaster recovery .

According to an EMC study , 82% of organizations in the world are not fully confident that they can restore their systems and data. Unplanned downtime and data loss cost organizations around the world more than $ 1.7 billion annually. According to an Acronis study, in Russia only 2% of the surveyed companies are absolutely sure that their IT infrastructure will pass any test. 49% of Russian specialists expect long interruptions in its work in the event of a disaster or accident.
')
According to foreign statistics, the most frequent causes of accidents are equipment failures (24%), power supply systems (16%), hurricanes (16%) and floods (15%).

Accidents are unavoidable in any technically complex systems, but they can be made not critical for business. To prevent such situations, disaster-resistant systems are being created — reserve capacity is being deployed at a geographically remote site. But first, let's define the terms describing high reliability systems.

Disaster Recovery (DR) is the ability to recover from a disaster, that is, resistance to the effects of natural disasters and terrorist acts. Fault tolerance (Fault-Tolerance, FT) - the property of the system to maintain operability after the failure of one or several components. High availability (HA) is indicated when the systems are able to perform the required function under the given conditions at a given time or within a given time interval. Business Continuity (BC) is the processes, methods and equipment for non-stop performance of critical business functions. And finally, RTO (Recovery Time Objective) - the time during which it is possible to restore the IT system, RPO (Recovery Point Objective) - how much data will be lost during disaster recovery, RCO (Recovery Capacity Objective) - how much of the load should be provided by the backup system .
To protect against natural, man-made disasters or terrorist attacks and ensure business continuity, it is necessary to back up basic data storage and processing systems. In the event of a catastrophe, the data center building may suffer, therefore it is necessary to create a geographically remote site - a backup data center. When the Tier III reliability level is not enough, a geographically distributed disaster-resistant data center infrastructure can guarantee the availability of four and even five nines.
Distribution of data centers across multiple sites requires the organization of redundant communication channels, data replication between storage facilities, backup planning and system recovery. We need a data synchronization mechanism to ensure that they are up-to-date if one of the nodes fails and to support the work of those information systems that need such synchronization. A critical parameter, in addition to bandwidth, is the delay in data transfer.

There are two main strategies for using distributed data centers - “active / active”, when infrastructure applications and services are distributed between sites, and users work with the nearest data center, or “active / passive”, in which applications are centralized, and users work with the primary node. In the event of a system failure, the load automatically switches to the backup data center. The ability to apply a strategy depends on the application.
Often at the heart of disaster-resistant data center - geographically distributed cluster configuration of servers with connection to a common storage area network (SAN). The nodes of the separated cluster are located on the main and backup sites, forming a single system. This ensures continuous availability of services even in the event of loss of the primary data center. Using clustering, you can automatically switch the load between sites of a distributed data center in the event of an accident. An economical modification of the solution is also possible, in which the remote data center operates in standby mode and in the event of a failure in the main data center supports a limited set of services.

Depending on the distance and architecture of the solution, inter-site communications can use Ethernet, MPLS or IP protocols. The distance between the data center with synchronous replication can be up to 80-100 km - it is limited by the application-related latency in the network. With synchronous replication, the application receives confirmation of the completion of an I / O operation after its execution on both sides. Using FCIP technology through individual switches, you can also organize asynchronous communication between data centers that are thousands of kilometers apart, and use traffic hardware compression. Compared with the Fiber Channel (FC) protocol, FCIP is faster at a distance of more than 100 km. When using FCIP, Fiber Channel packets are encapsulated in TCP / IP and then transmitted through an IP tunnel. FCIP is the main practically working method of data center communication when FC transmission over dark optics or via xWDM is impossible or impractical. It supports both direct connection of FCIP devices to each other, and connection via WAN.
A key element of a disaster-proof solution is a geographically distributed data storage system. Modern storage systems provide built-in tools for building disaster-proof solutions. For example, data storage systems at specified sites can completely duplicate each other, and the sites themselves link redundant high-speed communication channels, which allows to implement projects with the highest demands on the reliability of data transmission and their availability, including synchronous data replication. Alternatively, data can be backed up asynchronously.
Some storage systems have the ability to “stretch” volumes between sites with the help of the disk array itself. As a result, an inexpensive, disaster-proof solution is created that does not require reorganization of the data storage architecture. Another option is to use Microsoft Azure cloud infrastructure for backing up data.

A typical scenario is a backup data center in another city within the region (distance - 300-400 km). For LAN communication, IP or MPLS / VPLS, DWDM is used; for SAN communication - FCIP, DWDM. In this case, you can use a number of "metrocluster" technologies, use asynchronous replication. Synchronous replication at such a distance requires limitations and additional tools. With the separation of sites thousands of kilometers speak already about the "geocluster".
Clustering methods are offered by suppliers of operating systems, virtualization environments , application developers, manufacturers of IT systems and network equipment. For example, the basis of a VMware vSphere-based metrocluster is duplication of storage systems at two geographically separated sites with possible load balancing at the data center network level. When one of the data centers is unavailable, the virtual machines will be automatically launched on the second platform. In this case, the recovery speed of the virtual environment (RTO) is usually a few minutes.
Do not forget that the implementation of the DR strategy requires a serious investment. Implementation of such a project is usually associated with large financial costs. To substantiate and decide on the construction of such a class of systems is very difficult. Moreover, it is likely that you will never use the backup recovery plan. However, in an emergency, a good recovery plan will save time and money and help minimize losses due to downtime. A serious accident can lead to the loss of a data center, and this is a serious problem for a business. According to world statistics, 93% of companies that have lost their data center for only 10 days are ruined during the year.
It is necessary to find a balance between the costs of maintaining disaster recovery and business losses in the event of a disaster, taking into account the time of full recovery of all business processes. The illustrations below will help to get some idea of the costs of implementing a distributed data center in a company, more accurately estimate the amount of unavoidable costs and avoid possible misunderstanding of managers. In general, the dependence is as follows: the shorter the recovery time required, the more expensive the data protection methods are (according to Gartner information):
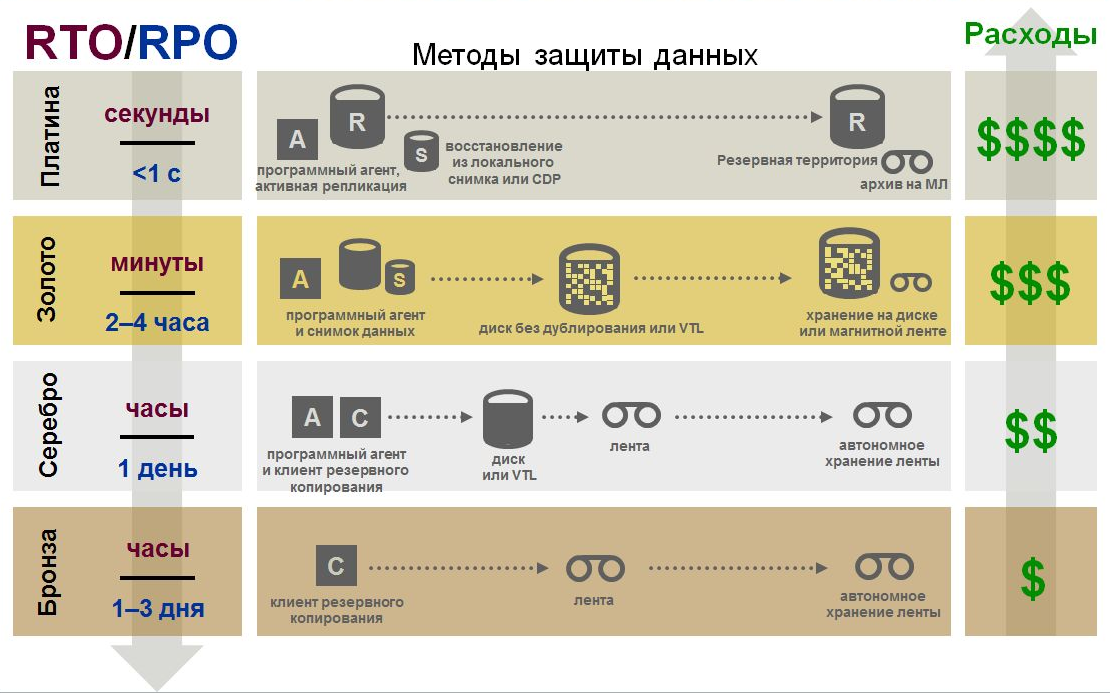
If we are talking not only about backup and recovery of systems and data, but about disaster recovery, then choosing the optimal solution for some parameters is also always a compromise (according to Compulink ).

Zero performance RTO / RPO has only a high availability system. Of course, this is the most expensive option (according to Cisco ).
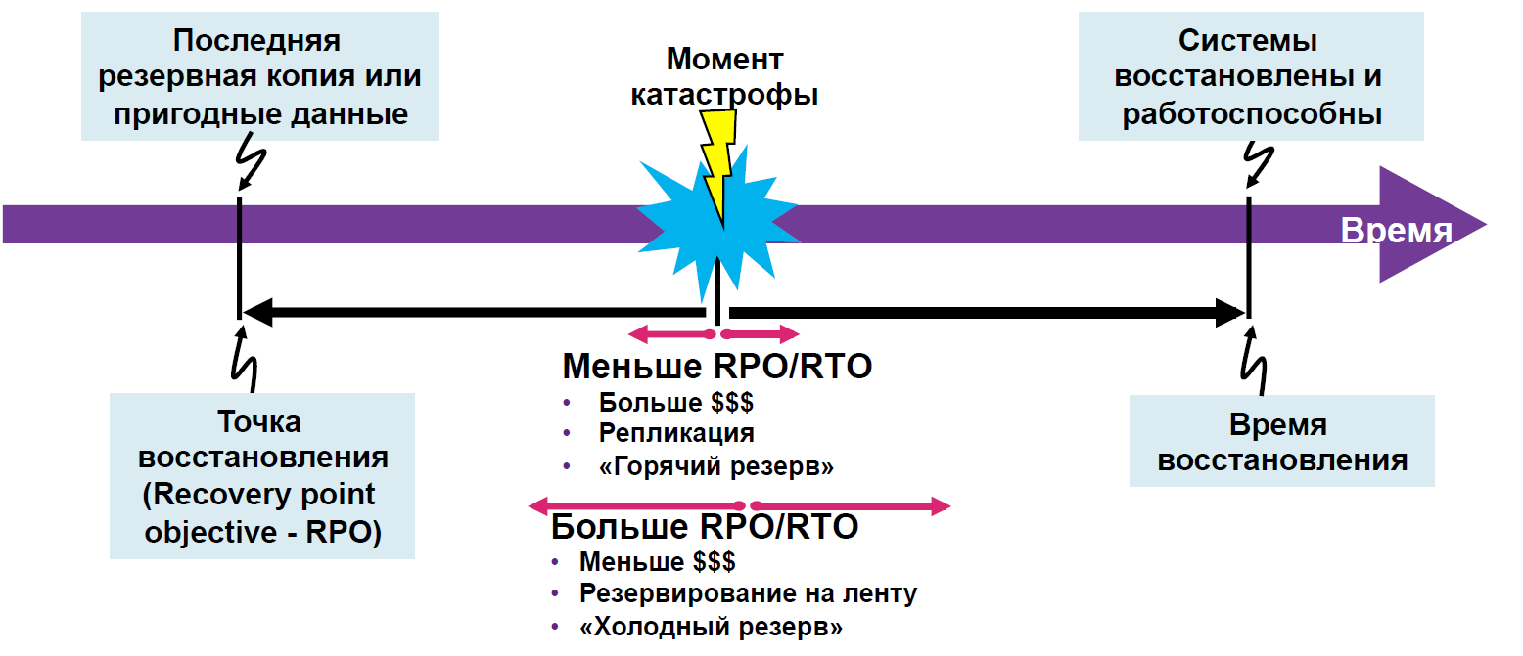
Ensuring disaster resilience has always required substantial costs, time and financial. It is necessary to have two spaced sites, a fast communication channel between them, a data transmission network, data storage systems with replication support, computing power and engineering equipment for uninterrupted power supply and data center cooling. It will take a staff of highly qualified IT professionals who can customize and support all this. It is required to pay attention to the design of systems for their implementation and testing. However, this task has solutions without major capital investments.
With the spread of virtualization and cloud technologies, new ways to protect against disasters have appeared:

According to EMC, which conducted a survey of Russian companies in 2014, only 6% of respondents rely on the active / active mode. These companies are less likely to experience data loss than those who rely on backup: 13% vs. 24%.
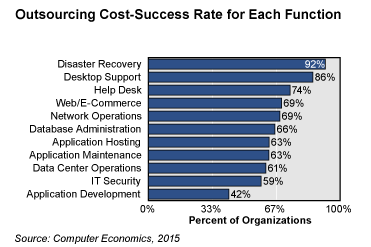
If a company does not have the capacity to build DR infrastructure, outsourcing can be a reasonable solution. Such services are quite accessible today. Interestingly, according to a recently published Computer Economics IT Outsourcing Statistics 2015/2016 study, disaster recovery has the highest potential for cost savings for customers among the most common types of outsourcing. It was noted by 92% of surveyed organizations.
 Instead of creating your own backup site, an organization can use a virtual (cloud) data center of the provider or completely abandon its own data center and switch to a cloud model. This option is suitable for many organizations. This modern approach to disaster recovery is called the “backup data center as a service” (Disaster Recovery as a Service, DRaaS). DRaaS eliminates the impact of accidents on business processes, ensures smooth operation, and removes many logistical and organizational issues from the client.
Instead of creating your own backup site, an organization can use a virtual (cloud) data center of the provider or completely abandon its own data center and switch to a cloud model. This option is suitable for many organizations. This modern approach to disaster recovery is called the “backup data center as a service” (Disaster Recovery as a Service, DRaaS). DRaaS eliminates the impact of accidents on business processes, ensures smooth operation, and removes many logistical and organizational issues from the client.
The reliability of the service provider is provided by two (or more) geographically remote data centers, which are specialized buildings with a high level of reliability. In the case of a fully virtual data center, each of them has a copy of a client's virtual data center — primary and backup. All changes in the main instance in real time are reflected in the backup. Failure of any of the copies will not affect the work of the organization. When an accident happens, instead of the main data center, the backup is instantly connected, and all employees and customers continue to work as usual. According to the OSP Data survey, more than half (54%) of Russian respondents consider it important that the service provider has several geographically distant data centers to ensure disaster recovery.

One example of the above approach is the Backup Data Center (BDC) or the SAFEDATA backup data center service package. In fact, it is not limited to the DRaaS framework. This is a whole range of design services and the creation of a backup site for the main data center of the customer. The main data center of the customer can be either a physical infrastructure located on the customer’s site or a virtual IT infrastructure.
SAFEDATA has its own distributed data center network in Moscow, connected by its own fiber-optic communication lines. This allows us to provide customers with not only the creation and placement of a backup site, but also the placement of the main data center, distributed between two remote sites.
BDC services can include the placement of equipment and virtual computing resources, the provision of fiber-optic communication lines and L2 channels, data synchronization between two sites, the provision of Internet channels with guaranteed bandwidth, protection against DDoS attacks and backup.
Choosing the SAFEDATA data center as a platform for creating a backup data center, the customer gets access to expertise in the field of design, construction and maintenance of data centers, dedicated round the clock technical support. It is also possible to rent office and warehouse premises.
Disaster-resistant solutions and services today are offered a lot. Please share in the comments that you are using, how these decisions have helped you.
Today, almost every company that actively uses IT to support a business has its own data processing center (DPC). Increasing data center reliability requirements is one of the market trends. Since the data center is often a key element of the company's business, experts have long been looking for cost-effective ways to increase its reliability. And sooner or later there is a need to ensure not only the hardware reliability of the data center, but also its disaster recovery .

According to an EMC study , 82% of organizations in the world are not fully confident that they can restore their systems and data. Unplanned downtime and data loss cost organizations around the world more than $ 1.7 billion annually. According to an Acronis study, in Russia only 2% of the surveyed companies are absolutely sure that their IT infrastructure will pass any test. 49% of Russian specialists expect long interruptions in its work in the event of a disaster or accident.
')
According to foreign statistics, the most frequent causes of accidents are equipment failures (24%), power supply systems (16%), hurricanes (16%) and floods (15%).

Accidents are unavoidable in any technically complex systems, but they can be made not critical for business. To prevent such situations, disaster-resistant systems are being created — reserve capacity is being deployed at a geographically remote site. But first, let's define the terms describing high reliability systems.

Disaster Recovery (DR) is the ability to recover from a disaster, that is, resistance to the effects of natural disasters and terrorist acts. Fault tolerance (Fault-Tolerance, FT) - the property of the system to maintain operability after the failure of one or several components. High availability (HA) is indicated when the systems are able to perform the required function under the given conditions at a given time or within a given time interval. Business Continuity (BC) is the processes, methods and equipment for non-stop performance of critical business functions. And finally, RTO (Recovery Time Objective) - the time during which it is possible to restore the IT system, RPO (Recovery Point Objective) - how much data will be lost during disaster recovery, RCO (Recovery Capacity Objective) - how much of the load should be provided by the backup system .
Disaster resistant data center
To protect against natural, man-made disasters or terrorist attacks and ensure business continuity, it is necessary to back up basic data storage and processing systems. In the event of a catastrophe, the data center building may suffer, therefore it is necessary to create a geographically remote site - a backup data center. When the Tier III reliability level is not enough, a geographically distributed disaster-resistant data center infrastructure can guarantee the availability of four and even five nines.
Distribution of data centers across multiple sites requires the organization of redundant communication channels, data replication between storage facilities, backup planning and system recovery. We need a data synchronization mechanism to ensure that they are up-to-date if one of the nodes fails and to support the work of those information systems that need such synchronization. A critical parameter, in addition to bandwidth, is the delay in data transfer.

There are two main strategies for using distributed data centers - “active / active”, when infrastructure applications and services are distributed between sites, and users work with the nearest data center, or “active / passive”, in which applications are centralized, and users work with the primary node. In the event of a system failure, the load automatically switches to the backup data center. The ability to apply a strategy depends on the application.
Often at the heart of disaster-resistant data center - geographically distributed cluster configuration of servers with connection to a common storage area network (SAN). The nodes of the separated cluster are located on the main and backup sites, forming a single system. This ensures continuous availability of services even in the event of loss of the primary data center. Using clustering, you can automatically switch the load between sites of a distributed data center in the event of an accident. An economical modification of the solution is also possible, in which the remote data center operates in standby mode and in the event of a failure in the main data center supports a limited set of services.

Depending on the distance and architecture of the solution, inter-site communications can use Ethernet, MPLS or IP protocols. The distance between the data center with synchronous replication can be up to 80-100 km - it is limited by the application-related latency in the network. With synchronous replication, the application receives confirmation of the completion of an I / O operation after its execution on both sides. Using FCIP technology through individual switches, you can also organize asynchronous communication between data centers that are thousands of kilometers apart, and use traffic hardware compression. Compared with the Fiber Channel (FC) protocol, FCIP is faster at a distance of more than 100 km. When using FCIP, Fiber Channel packets are encapsulated in TCP / IP and then transmitted through an IP tunnel. FCIP is the main practically working method of data center communication when FC transmission over dark optics or via xWDM is impossible or impractical. It supports both direct connection of FCIP devices to each other, and connection via WAN.
A key element of a disaster-proof solution is a geographically distributed data storage system. Modern storage systems provide built-in tools for building disaster-proof solutions. For example, data storage systems at specified sites can completely duplicate each other, and the sites themselves link redundant high-speed communication channels, which allows to implement projects with the highest demands on the reliability of data transmission and their availability, including synchronous data replication. Alternatively, data can be backed up asynchronously.
Some storage systems have the ability to “stretch” volumes between sites with the help of the disk array itself. As a result, an inexpensive, disaster-proof solution is created that does not require reorganization of the data storage architecture. Another option is to use Microsoft Azure cloud infrastructure for backing up data.

A typical scenario is a backup data center in another city within the region (distance - 300-400 km). For LAN communication, IP or MPLS / VPLS, DWDM is used; for SAN communication - FCIP, DWDM. In this case, you can use a number of "metrocluster" technologies, use asynchronous replication. Synchronous replication at such a distance requires limitations and additional tools. With the separation of sites thousands of kilometers speak already about the "geocluster".
Clustering methods are offered by suppliers of operating systems, virtualization environments , application developers, manufacturers of IT systems and network equipment. For example, the basis of a VMware vSphere-based metrocluster is duplication of storage systems at two geographically separated sites with possible load balancing at the data center network level. When one of the data centers is unavailable, the virtual machines will be automatically launched on the second platform. In this case, the recovery speed of the virtual environment (RTO) is usually a few minutes.
Resilience Economics
Do not forget that the implementation of the DR strategy requires a serious investment. Implementation of such a project is usually associated with large financial costs. To substantiate and decide on the construction of such a class of systems is very difficult. Moreover, it is likely that you will never use the backup recovery plan. However, in an emergency, a good recovery plan will save time and money and help minimize losses due to downtime. A serious accident can lead to the loss of a data center, and this is a serious problem for a business. According to world statistics, 93% of companies that have lost their data center for only 10 days are ruined during the year.
It is necessary to find a balance between the costs of maintaining disaster recovery and business losses in the event of a disaster, taking into account the time of full recovery of all business processes. The illustrations below will help to get some idea of the costs of implementing a distributed data center in a company, more accurately estimate the amount of unavoidable costs and avoid possible misunderstanding of managers. In general, the dependence is as follows: the shorter the recovery time required, the more expensive the data protection methods are (according to Gartner information):

If we are talking not only about backup and recovery of systems and data, but about disaster recovery, then choosing the optimal solution for some parameters is also always a compromise (according to Compulink ).

Zero performance RTO / RPO has only a high availability system. Of course, this is the most expensive option (according to Cisco ).

Ensuring disaster resilience has always required substantial costs, time and financial. It is necessary to have two spaced sites, a fast communication channel between them, a data transmission network, data storage systems with replication support, computing power and engineering equipment for uninterrupted power supply and data center cooling. It will take a staff of highly qualified IT professionals who can customize and support all this. It is required to pay attention to the design of systems for their implementation and testing. However, this task has solutions without major capital investments.
Virtualization, clouds and disaster recovery
With the spread of virtualization and cloud technologies, new ways to protect against disasters have appeared:
- Replication to the cloud. Private and public cloud technologies have simplified replication between sites. The replication process can span all virtual machines, specific databases, or snapshots of data. In addition, cloud technologies help organizations choose the DR option that is most suitable for financial terms — there is the flexibility to choose acceptable downtime. That is, you can often choose an acceptable downtime and at the same time fit into the budget.
- Virtualization as a backup / restore mechanism. Here the idea is simple: it is much easier to restore a virtual machine than a physical server. You can save VM Status Snapshots to the backup data center or mirror virtual machines. In the latter case, the “active / active” configuration is obtained — in the event of a failure on the main site of a VM that performs critical tasks, it switches to the same VM on the reserve site.
- The use of software configuration technologies (Software Defined, SD). In essence, this is the development of virtualization. Software-configured platforms (network equipment, storage systems, security devices, load balancers, etc.) provide a flexible, fault-tolerant environment with “virtual devices” for various purposes, functioning as virtual machines on standard servers. For example, if you enable load balancing mechanisms (Global Server Load Balancing, GSLB) for DR, you can automatically switch users to the backup site when the primary fails. For users, the process will be transparent.
- IaaS (infrastructure on demand). Cloud platforms and virtualization environments allow you to quickly allocate the necessary IT resources. For DR, the ability to quickly recover virtual machines and data is important. Cloud technologies and virtualization are great for this purpose. You can create very economical IaaS solutions — either active / active or active / passive. For example, a regular backup of VM and data in the data center of the provider is set. In the event of a crash, a new environment is deployed — VMs are started with their backup data. The process is not instant, but fast enough. In IaaS, the main thing is flexibility. When implementing the DR strategy, the provider will help the customer to extract the maximum from this flexibility.

According to EMC, which conducted a survey of Russian companies in 2014, only 6% of respondents rely on the active / active mode. These companies are less likely to experience data loss than those who rely on backup: 13% vs. 24%.
If a company does not have the capacity to build DR infrastructure, outsourcing can be a reasonable solution. Such services are quite accessible today. Interestingly, according to a recently published Computer Economics IT Outsourcing Statistics 2015/2016 study, disaster recovery has the highest potential for cost savings for customers among the most common types of outsourcing. It was noted by 92% of surveyed organizations.

Backup data center as a service
 Instead of creating your own backup site, an organization can use a virtual (cloud) data center of the provider or completely abandon its own data center and switch to a cloud model. This option is suitable for many organizations. This modern approach to disaster recovery is called the “backup data center as a service” (Disaster Recovery as a Service, DRaaS). DRaaS eliminates the impact of accidents on business processes, ensures smooth operation, and removes many logistical and organizational issues from the client.
Instead of creating your own backup site, an organization can use a virtual (cloud) data center of the provider or completely abandon its own data center and switch to a cloud model. This option is suitable for many organizations. This modern approach to disaster recovery is called the “backup data center as a service” (Disaster Recovery as a Service, DRaaS). DRaaS eliminates the impact of accidents on business processes, ensures smooth operation, and removes many logistical and organizational issues from the client.The reliability of the service provider is provided by two (or more) geographically remote data centers, which are specialized buildings with a high level of reliability. In the case of a fully virtual data center, each of them has a copy of a client's virtual data center — primary and backup. All changes in the main instance in real time are reflected in the backup. Failure of any of the copies will not affect the work of the organization. When an accident happens, instead of the main data center, the backup is instantly connected, and all employees and customers continue to work as usual. According to the OSP Data survey, more than half (54%) of Russian respondents consider it important that the service provider has several geographically distant data centers to ensure disaster recovery.

One example of the above approach is the Backup Data Center (BDC) or the SAFEDATA backup data center service package. In fact, it is not limited to the DRaaS framework. This is a whole range of design services and the creation of a backup site for the main data center of the customer. The main data center of the customer can be either a physical infrastructure located on the customer’s site or a virtual IT infrastructure.
SAFEDATA has its own distributed data center network in Moscow, connected by its own fiber-optic communication lines. This allows us to provide customers with not only the creation and placement of a backup site, but also the placement of the main data center, distributed between two remote sites.
BDC services can include the placement of equipment and virtual computing resources, the provision of fiber-optic communication lines and L2 channels, data synchronization between two sites, the provision of Internet channels with guaranteed bandwidth, protection against DDoS attacks and backup.
Choosing the SAFEDATA data center as a platform for creating a backup data center, the customer gets access to expertise in the field of design, construction and maintenance of data centers, dedicated round the clock technical support. It is also possible to rent office and warehouse premises.
Disaster-resistant solutions and services today are offered a lot. Please share in the comments that you are using, how these decisions have helped you.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/273947/
All Articles