Security Week 50: DDoS root DNS servers, APT Sofacy life, lots of cryptography
 Serious changes occur exactly at the moment when the percentage of people who want to change something exceeds a certain critical point. No, I'm not talking about politics now, but I am holy and holy, holy, but about IT in general and IT security. And they want, in general, everything different: companies - so that they don’t break DDoS or users, so they don’t steal passwords and steal accounts, security vendors ’new attitude to security for all concerned, regulators to regulate.
Serious changes occur exactly at the moment when the percentage of people who want to change something exceeds a certain critical point. No, I'm not talking about politics now, but I am holy and holy, holy, but about IT in general and IT security. And they want, in general, everything different: companies - so that they don’t break DDoS or users, so they don’t steal passwords and steal accounts, security vendors ’new attitude to security for all concerned, regulators to regulate.Here is a brief statement of the predictions of our experts for the next year: the evolution of APT (less technology, more mass, and generally lower costs), attacks on new financial instruments a la ApplePay and stock exchanges - closer to places of high concentration of digital money, attacks on information security agents researchers through the tools they use, hacking companies for the sake of pure damage to reputation (ak.a. hanging dirty laundry), lack of trust in any IT-tools (anything can hack), including trusted certificates, botnets from routers Ditch and other IoT, a massive crisis of cryptography.
In the predictions of this year there is not a single item “for growth”, not a single unlikely development scenario. Well, except that such attacks include computer-controlled cars, and even then we are talking about hacking the infrastructure on which they depend - cellular and satellite networks. All this, to one degree or another, will come true, the problem is that somehow I don’t want to . If possible, I would like to avoid this . And if you want not only us, but everyone in general (albeit in different ways), can 2016 also be a year of progress in collective IT security? I am never an expert, but I want to believe that yes. Go to the news of the week. Previous issues are available by tag .
Powerful attack on root DNS servers
News IANA Statement .
')
In 2007, the root DNS servers were attacked by a botnet of about five thousand computers, which led to many hours of unavailability of a pair of servers and serious overloads on others (there are 13 of them). Last week it became known that on November 30 and December 1, there were two more similar attacks. However, in 8 years, root name servers, which can be called the foundation of the Internet without serious strain, have become much more stable. Two hours of attacks did not lead to serious problems in the network (this, however, is true for the attack of 2007), the distributed server infrastructure withstood traffic of approximately five million requests per second (standard traffic to root servers amounts to hundreds of thousands of requests per second), but saturation of channels through which servers are connected, led to insignificant delays.
If you translate this story into the realities of the traditional world of bricks and cement, you get, for example, the following fantastic sketch. A large gang of criminals tried to attack the central office of the Central Bank, using a large number of automatic weapons and even grenade launchers. The armored walls and windows of the protected building survived, but due to the attack, the Bank’s office opened the next day five minutes later. The money did not disappear (they were not there, it was the Central Bank, and not a savings bank or a mint), the criminals managed to escape, they are currently being searched.

Uh If you think about it, the same thing happened to the DNS servers: they couldn’t be turned off (not one), and even if they could, it wouldn’t lead directly to the fall of the entire Internet at once. Interesting details of the attack. In 2007, it was possible to approximately localize the source, up to the country, and this time the IP addresses of the attacking computers were “evenly distributed” (thin layers all over the Internet, I suppose). Requests to the servers were quite legal, and all requested an IP address for the same domain. A repeated attack occurred in an identical scenario, only the domain name was different (which domains were not disclosed in the report). Analysis of the attack showed that the technology of DNS-amplification, when the victim's address is substituted for the address of the sender, was not used. In general, the question "what it was" has no answer yet. In the comments they write that maybe someone has tested the capabilities of his botnet, and most likely it is, but the question “why” is not answered.
Experts of "Laboratory" reveal new details of the Russian-speaking APT Sofacy (aka APT28)
News Research
A little higher, I already quoted the predictions of our experts about the evolution of APT: it is expected that next year there will be a little less advanced and persistent in these advanced persistent threats. Instead of technology, efforts will be invested in reconnaissance, and the tactic of prolonged presence in the network of victims will be replaced with prompt intervention with rapid data theft and tracing. Actually, when IB researchers uncover some kind of technically savvy operation, about the same thing happens: the organizers of the attack quickly disappear. But Sofacy is an exception. Studies of this attack have been published by many companies, but this almost never led to a change in tactics and other maneuvers. How to work since 2007, and continue.
The study of such operations as Sofacy or The Equation - really distinguished on the general background of cybercrime - helps to understand and predict the development of threats in general, since any advanced technology sooner or later becomes mass. Apparently, a powerful research department works on Sophacy: out of six exploits for 0day vulnerabilities in popular software (MS Office and Java, for example), five were found independently, another one was borrowed from the “dumping” of Hacking Team data.
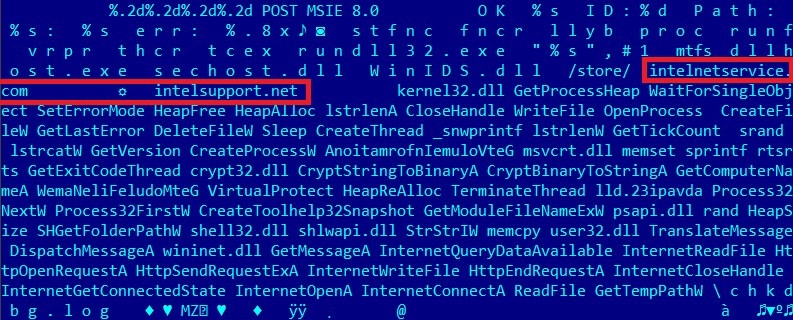
A distinctive feature of the study of threats - screenshots from Far Manager! In this case, a piece of code is shown with “stitched” domain names of C & C servers.
It does not matter whether the organizers of the attack are looking for vulnerabilities on their own or buying them on the black market, the zyrodeas are not cheap. Bringing them “to the front line” in full force means risking that they will notice the activity, they will close the vulnerabilities and generally make the task of hacking more difficult. In terms of a casino, this approach is similar to the rate of all chips for zero, and this can go either from despair or when the money is not the last and, in general, it doesn't matter whether they disappear or not. Judging by the durability of the Sofacy, we are dealing with a second option.
With Equation, this operation is related to one more thing: both there and there, the technology of “draining” data through a USB flash drive is used. This method of data exfiltration is useful if you cannot connect to the command server from a computer or a network of victims, and you really want to steal data. In details, the USBStealer module was previously investigated by ESET specialists, but what’s important here is not even the exfiltration method, but the intended status of the victims. Air-gapped networks that are completely isolated from the Internet in "ordinary companies" are rarely used.
Digest in Digest. Cryptography News: The FBI again wants backdoors in encryption . Rejecting the theoretically vulnerable algorithm SHA-1 is not so easy .
Data encryption issues are like a Pandora's box, you should open it once, and you won't be able to close it back. Once this topic was even more highly specialized than IT security, with an even higher entry threshold, if you really want to understand something about it. The entry threshold, however, remained high, but in policy discussions, encryption is becoming more and more political. Or business. This week brought a couple of examples.
Let's start with the FBI. This week, quite routine hearings took place in one of the committees of the American Congress, where FBI Director James Komi spoke (for amateurs, video appearances ). He once again confirmed what we previously already knew, for example, from Snowden’s leaks: encryption is a serious problem for law enforcement agencies when conducting investigations of illegal activities. By “activity”, different people and organizations understand completely different things, but from the point of view of clean technology, this is even good news: it means that modern methods of data protection (from anyone) generally work. Now the bad news: The FBI wants the encryption technology to work worse, specifically - so that "who needs" had access through the balcony door.

This is not necessarily about backdoors. Komi separately mentioned that this is not the only “solution”, and in general he is in favor of access to encrypted data, for example, on a smartphone, by a court decision. How exactly - let, de, the industry will understand itself. The traditional FBI opponent, the EFF Foundation, in response, recalls that any compromise of encryption systems makes them meaningless. That is, either access through the “loophole” can be obtained not only by the FBI and not only through the courts, or companies (for example, after the introduction of some new law) will be unprofitable to provide the function of data encryption, which will jeopardize all users.
I wrote about the fall in the cost of searching for collisions in SHA-1 in October . Then I finished the description of the problem on the positive: it seems that the practical implementation of the vulnerable cryptographic hashing algorithm has not yet come to an end, while refusing support in the software (for example, in browsers) is started now, and if not now, soon. So, something went wrong. Experts from Facebook and Cloudflare argue that if major websites also prohibit the use of SHA-1 on their side in the process of establishing a session, it will deny access to many users. According to Facebook, up to seven percent of their traffic. The reason is not even in the use of outdated browsers by these users, but in the use of outdated operating systems that do not support the more secure SHA256 algorithm. Specifically, it comes from Windows XP without SP3 and Android to Gingerbread. That is, about very ancient devices, the proportion of which in theory should be microscopic, but not. According to CloudFlare, a company that, in theory, is well versed in traffic of different varieties, up to 37 million users may suffer. That is why it is proposed to introduce a workaround technology that will provide a reliable protocol to those who support it, and inferior - to those for whom it is better this way than it does.
What else happened
Another massive patch from Adobe for Flash: 79 vulnerabilities are closed.
71 patches from Microsoft, including closed in-the-wild serious vulnerability in Office.
Total 150.
 Antiquities:
Antiquities:Amz Family
Non-resident very dangerous viruses infect COM- and EXE-files (or only EXE - “Amz-600”) when starting an infected file. Change the first 13h bytes of COM files to the program for switching to the virus body. Contain the short word "AMZ". Depending on the version, erase the FAT sectors of either all logical drives from A: to Z: (if they are present), or the current disk under the conditions:
“Amz-600” - if the number of the day of the week matches the number of the day of the month;
"Amz-789" - September 24 from 0:00 to 7:00 in the morning;
"Amz-801" - February 13 at 13 o'clock.
Quote from the book "Computer viruses in MS-DOS" Eugene Kaspersky. 1992 Page 23.
Disclaimer: This column reflects only the personal opinion of its author. It may coincide with the position of Kaspersky Lab, or it may not coincide. Then how lucky.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/272855/
All Articles