The practice of reducing the cost of electricity data center
Some issues of energy saving in data centers

One of the most important cost items at the stage of operation of the data processing center (DPC) is the payment for consumed electricity. This is not surprising - all data center systems, starting with IT equipment, for the sake of the normal functioning of which the data center is created, and ending with alarm systems and surveillance systems, consume electricity. Therefore, the most reliable way to save on electricity is to sell computing and telecommunication devices, and close the data center. Unfortunately, without a working computing and communication technology, doing business in modern conditions is unimaginable, so the option of completely eliminating the data center in this article will not be considered.
')
The power consumption of the data center as a single system consists of the consumption of individual systems, both information and telecommunications, and engineering infrastructure systems, including the inevitable unproductive losses. To achieve energy savings in general, it is necessary to explore the possibilities of reducing the consumption of each subsystem.
The main consumers of energy are, of course, computing and telecommunication systems. However, for the normal functioning of computing and telecommunications equipment, work, as a rule - continuous, of a number of auxiliary, service systems is necessary. These auxiliary systems form the engineering infrastructure of the data center.
For a stable, normal operation of the most important IT equipment, it is necessary to ensure comfortable conditions: first of all, remove the heat generated by IT equipment, ensure relative humidity of air within 50 ± 10%, create conditions for the operation of security systems, and conditions for the work of the service personnel .
In general, in order to find ways to reduce energy costs, it is necessary to determine the numerical criteria for evaluating energy efficiency and analyze each of the energy-consuming systems from the point of view of reducing consumption.
There are several methods for assessing energy efficiency in a data center, differing mainly in the degree of accounting for changes in consumption (as a function of time, computational load, etc.). We use the simplest.
The simplest and most visual assessment method is to calculate the energy efficiency ratio of PUE (Power Usage Effectiveness), and its inverse DCE (Datacenter Efficiency, in fact, the efficiency). In this case, the “beneficial effect” is considered to be the consumption of IT equipment, and the DCE coefficient (data center efficiency) is calculated as the ratio of the consumption of IT equipment to the total energy consumption of the data center; PUE ratio - the ratio of total data center consumption to IT equipment consumption. The PUE value can be in the range from 1.0 to infinity. A PUE value close to 1.0 will indicate 100% efficiency — all energy is used only by IT equipment. True, this indicator is practically unattainable - in connection with the above.

In practice, it is more convenient and clearer to operate with PUE. This is confirmed by international practice.
To assess the situation with us, it is useful to know the world statistics on energy efficiency. Thus, the “LAN Network Solutions Journal” http://www.osp.ru/lan/2014/05/13041191/ "> confirms that
According to experts , a detailed measurement of PUE is quite expensive, although for a rough assessment of large efforts it is not required: “With typical PUE data for PUE values of 1.8–2.5, there is no need for high precision measurements — it’s enough to measure the power at the electrical installation input and UPS outputs that feed the payload. The minimum program is to install meters for commercial metering of electricity. ”
In our data centers, just about this technique is used: the power consumption of the entire data center is determined using data from commercial metering devices and / or direct measurements of currents on the input lines of the input switchgear (ASU) using current tongs (unfortunately, no projects were installed in the technological control of currents and voltages; savings ...); IT equipment consumption is determined by direct measurements of the currents at the output of the UPS by current clamps and / or by the indications of the UPS; The total consumption of engineering infrastructure systems is determined using data from commercial metering devices and / or direct measurements of currents on the input lines of the input switchgear using current clamps, since in a normal situation the UPS / IT equipment and engineering infrastructure systems are powered from separate input lines - for the main data center ; for backup data center data is taken from the system of commercial accounting, and from the testimony of the current load of the UPS.
We are well aware that the measurement accuracy leaves much to be desired: neither the current clamp nor the UPS monitoring system can serve as a measuring tool. However, for a rough assessment of them is enough. In order to assess the reliability of the measured power consumption, the “theoretical” consumption of IT systems and components of the engineering infrastructure is calculated using passport data of computing and telecommunications equipment. The difference between the measured and calculated values allows us to draw some interesting conclusions: about the measurement accuracy, and the accuracy of the data provided in the documentation, the level of loading of IT equipment and engineering infrastructure, and unregistered consumers (in our case, for example, data centers turned out to be unaccounted consumers of data center electricity) places of monitoring group employees connected to the main data center UPS).
Each system (subsystem) of IT and engineering infrastructure of the data center is characterized by its own capabilities and methods for reducing energy consumption. Consider the basic systems and possible methods to reduce their power consumption.
The main consumer of energy, as has been repeatedly stated above, is IT equipment. Methods to reduce its consumption are given in the recommendations of , for example, Eaton specialists:
A detailed description of the methods and reasons for reducing the power consumption of IT equipment due to their use is left to system administrators; However, all this is quite obvious.
The application of these measures, including the replacement of IT equipment with more energy efficient ones, gives the most significant result for reducing the overall power consumption of the data center, since the contribution of IT systems to the overall consumption is the main one, and decreasing the power consumption of other critical systems decreases: the cost of cooling, own consumption of UPS, the loss of energy transportation.
The own consumption of the UPS is due to the operation of the inverter-inverters that make up them, electronics, automation, and heat losses. The efficiency of the UPS is determined by the efficiency factor, which is calculated as the ratio of the total system power, including the UPS, to the power consumed by the load. Modern UPSs provide an efficiency of 0.75-0.98, while the best performance is achieved at the UPS load level within 0.8-0.95 of the maximum nameplate capacity. Methods to reduce their own consumption of UPS are as follows:
A separate item I would like to indicate the uniform distribution of the load across the phases of the supply voltage. Modern UPSs, of course, allow 100% phase imbalance on the load, but this does not add efficiency to them.
Energy losses in communication lines and distribution equipment are due to the following reasons:
These losses depend on the following factors:
Methods to minimize energy losses in transmission lines and distribution systems:
By the efficiency of the air conditioning system we mean the ratio of the cost of electricity for the operation of the system to the amount of heat removed from the cooled equipment. The efficiency of the heat removal system from IT equipment (air conditioning, air-conditioning) is determined by many factors, including the ones listed above with respect to power transmission lines. In addition, the overall efficiency of the data center cooling system is significantly curled by the following factors:
Methods to reduce the energy consumption of the air-conditioning system are aimed at improving the efficiency of cooling and reducing heat losses (we are talking about freon systems).
Energy saving opportunities in ventilation and gas removal systems are limited. The ventilation system in the data center is designed primarily to ensure the normal operation of staff, it does not affect the functioning of IT systems, and, conversely, can reduce the efficiency of cooling systems. Therefore, it is recommended to start the ventilation system only for the time when the personnel work in the data center premises. As for the gas removal system, in normal condition it should not work, and it starts only after the automatic fire extinguishing systems have triggered.
Judging by experience, the continuous operation of the steam humidification system (air humidification in the data center rooms) is not always necessary.Observations carried out in the premises of one of our data centers show, for example, that it is advisable to start the steam humidification system only in the winter, when the air humidity in the street is lowered due to frost (freezing moisture); ). In the warm season, due to the architectural features of the premises of our data center, humidity "itself" is maintained at 40-55%. However, before giving recommendations for a specific site, it is necessary to study the characteristics of its location, consideration of the climatic zone and long-term observations.
In general, it is impractical to look for ways to reduce the power consumption of a number of auxiliary systems of the data center engineering infrastructure, since these systems
These systems include:
In general, lowering the power consumption of these systems is not possible. In addition, the last two of these systems consume electricity only in case of emergency.
During the operation of several computing sites (data centers, server and telecommunications nodes), a number of ways to reduce the cost of electricity supply, from those listed above, have been tested and introduced. Some did not lead to a significant reduction in power consumption, others showed decent results.
For systems and sites, you can bring the following data.
Replacing IT equipment with more energy efficient is the most costly, but also the most effective solution. An illustrative example is the process of replacing heavy-class servers, storage systems and blades at our Novosibirsk main site. For 8 months, from July 2014 to February 2015, due to the replacement of IT equipment, the power of the machine room (IT load) was reduced from 120 to 84 kW. Accordingly, energy costs for cooling equipment in the machine room, the load on the UPS system and its own consumption have decreased; the power consumed by the engineering infrastructure systems decreased from 56 to 37 kW; Total data center consumption fell from 180 to 120 kW:
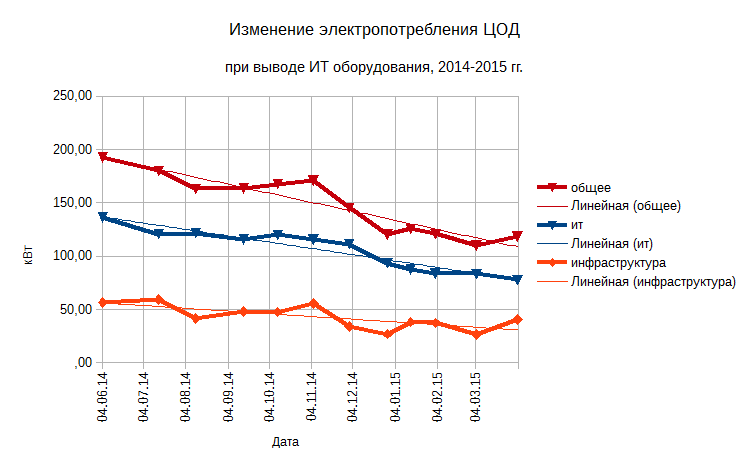
And all this despite the fact that until July 2014, the general trend was a gradual increase in power consumption; peak values reached 160 kW of IT equipment capacity, and 228 kW of total power consumption:
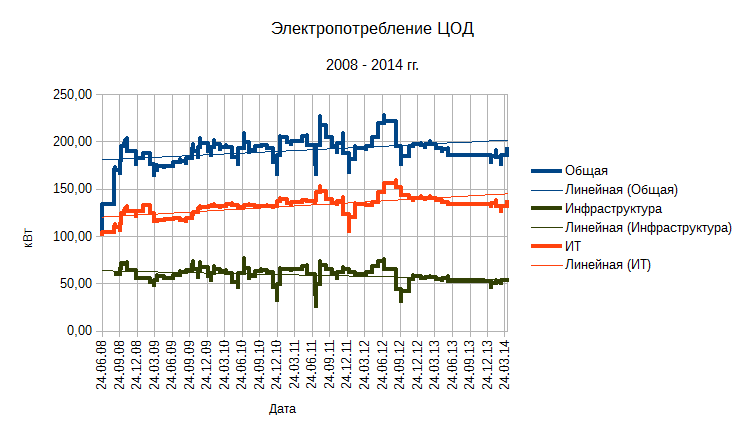
Actually, practice confirmed the thesis cited at the beginning of the article: the best way to save electricity in the data center is to turn off IT equipment.
High-performance UPSs Newave ConceptPower Upgrade are used at Novosibirsk sites, in Moscow, in the main data center - APC Galaxy UPSs. All UPSs have decent characteristics, for example, the efficiency of double conversion of Newave UPSs with loads at 75-100% of the maximum is 96%; even at a load level of 25% of the maximum, the manufacturer promises an efficiency of at least 92%.
The UPSs are installed in air-conditioned premises, the climatic conditions for them are optimal.
Regulation of the UPS load level, unfortunately, is not possible due to the adopted redundancy schemes.
The question of leveling the load in phases was done from the moment the data center was put into operation: the installation of any new IT equipment — or the movement of the existing one — was carried out taking this factor into account.
In general, all measures to reduce losses in power transmission lines and switching and distribution systems were taken at the construction stage of our data centers.
Due to the adopted backup schemes and technical and operational features, part of the checks aimed at identifying losses is performed according to the situation, and not on a regular basis: insulation resistance measurement, for example, is carried out only when the power supply lines are disconnected; the same applies to the bolting and screw connections in panel equipment. Surveys of power and distribution boards are regularly carried out using pyrometers to identify unreliable connections. However, the quality of the materials and equipment used and the operating conditions of cable lines and switching equipment (protection from external influences, constant temperature and humidity) guarantee the absence of significant electricity losses during transportation, at least within the territory of the data center.
In the framework of solving the problem of optimizing and improving the efficiency of air conditioning systems, quite a lot of activities were carried out.
During the design and construction of data centers, modern and energy-efficient models of air conditioners were selected. So, in the main data center in Novosibirsk installed precision air conditioners Stulz, in the backup data center channel conditioners Daikin; In the main data center in Moscow, HiRef precision systems are installed. The efficiency of these systems lies in the zone of 0.22-0.27 kW of consumed electric power per 1 kW of cooling capacity.
Concluded long-term contracts with service companies for regular maintenance of air conditioning systems. During operation, malfunctions that led to increased power consumption were identified and eliminated: for example, the data center in Novosibirsk, for example, replaced the fan motors twice (winding damage, increased heat generation), the bearings in the fans were replaced in three air conditioners.
; , (2008-2010), . / ; , .
In the first years of operation, there was an acute problem of uneven cooling of IT equipment after switching air conditioners as part of the adopted redundancy scheme: temperatures were set in different areas of the machine rooms with a significant difference, for example, the temperature on the left side of the cabinet rows was 3-5 ° C lower than nominal, on the right side 3-5º above. The problem was solved by transferring the inlet air temperature sensors from the air conditioners closer to the IT equipment. This not only ensured uniform cooling of IT equipment, but also equalized the load on air conditioners, and, ultimately, reduced energy consumption.
Much attention is paid to optimizing air flow, mainly cold, to ensure sufficient and uniform cooling of IT equipment. This is achieved by replacing perforated raised floor plates and using “active floor” modules (for main data centers), and direct adjustment of air flow using adjustable grilles and deflectors on air ducts (backup data center in Novosibirsk, see photo) when moving or changing the composition of the cooled equipment .

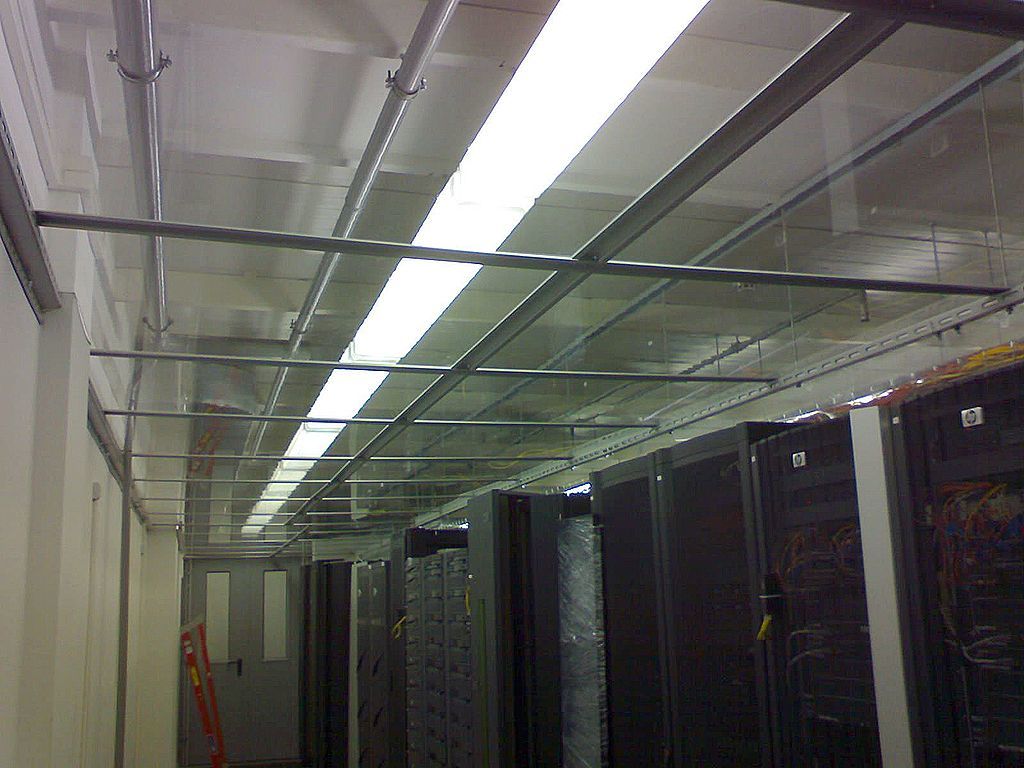
During the design and construction of data processing centers, the possibility of separating machine rooms into “cold” and “hot” corridors was foreseen. This opportunity was implemented on the Novosibirsk sites, first in the backup data center (October 2010, photo above, panels from the roofs of the cabinets to the ceiling are visible), then mainly in the data center (May 2011):

After the corridors were divided, the Novosibirsk data center system consumed electricity conditioning decreased by 9-17% depending on the time of year.
In the backup data center, separate cold air ducts were replaced with manifolds with deflectors and adjustable grilles; at a rough estimate, this reduced the power consumption of air conditioners by 4-7%.
The above recommendations are practically applied: for the warm season, the steam humidification systems of air conditioners are turned off, the water mains overlap; continuous monitoring of the relative humidity in the data center premises is carried out according to the data of climate monitoring systems. If necessary (the fall of the relative humidity to 30-35%), the systems are switched on for a short time. The level of efficiency (energy savings) of this event is difficult to assess.
The most complete, and therefore indicative data are available on the main data center in Novosibirsk.
The general reduction in power consumption due to the replacement and reduction of the IT equipment fleet was discussed above. Reducing the power consumption of the data center by 60 kW - the result is more than worthy. However, in addition to absolute indicators, relative values characterizing overall energy efficiency are also of great importance.
As the main indicator, we use the PUE coefficient, which describes the overall energy efficiency of the data center as a single system.
The history of the struggle for kilowatts is approximately as follows:
1. 2008–2009. The stage of final data center commissioning, "grinding"; energy efficiency was practically not thought at that time, since there were enough other various problems: “stuffing” the data center with equipment that was moved, including from other platforms, optimization of equipment placement in the hall, debugging of engineering infrastructure systems, in particular, air conditioning, etc. . And, by the way, the elimination of continuous accidents in engineering systems. Therefore, PUE in 2008 was at the level of 1.55-1.56, and in 2009 it is quite stable at the level of 1.49.
2. 2010 Special measures to reduce consumption were not carried out, PUE ranged from 1.58 in winter to 1.402 in summer, with an average annual value of 1.44.
3. In 2011, work began on improving the efficiency and reliability of the air conditioning system. The ways of supplying air to the condensers of air conditioners were expanded, the IT equipment was moved in the engine room for uniform cooling, the above-mentioned transfer of temperature sensors for incoming air, and a number of other measures. The average value of PUE for the year is 1.44. Despite the fact that by the end of the year it grew to 1.55, because of the increase in the total capacity of IT equipment in the data center, the UPS system was expanded.
4. In 2012, the corridors in the engine room were finally divided, the process of upgrading IT equipment began. Optimized air flow, to improve the cooling of heavy systems used plates "active floor". The working conditions of air conditioners condensers have been improved, the “windows” for the inflow and outflow of outside air have been expanded. Result: PUE average 1.4 per year.
5. 2013. No special measures were taken to improve PUE; by the end of the year, a number of coolant leaks in the mains had been eliminated, which, it must be assumed, led to a certain decrease in PUE.
6. 2014. The decrease in PUE is mainly due to the modernization and replacement of IT equipment, and, accordingly, the change in the redundancy scheme of air conditioners from 4 + 1 to 3 + 2.
7. 2015. The data for the first three months of the current, 2015.
In general, the dynamics is positive, the PUE ratio was reduced from an average of 1.55-1.57 at the beginning of the data center operation to 1.32 (as of March 4, 2015).
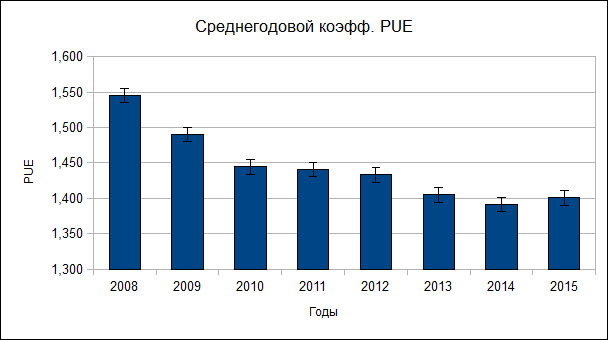
The result is good, given the high complexity and cost of energy efficiency measures, and given that for many data centers, the value of PUE 1.6 is an unattainable dream ( Efficiency of the infrastructure of the data center ):
Over the years of operation (2008-2015), the data center of medium size in general with elementary, generally accepted means was able to reduce the total energy consumption from an average level of 200 kW to 110-120 kW. The cost of electricity, therefore, decreased by about 40-54%, which, you see, is not the worst result.
It should be borne in mind that there are fewer opportunities to reduce PUE values; it is simply not possible to reach a value of 1.0 - for purely physical reasons.
, , -, , . , . , , PUE 1,39-1,43.
PS , , .

Introduction
One of the most important cost items at the stage of operation of the data processing center (DPC) is the payment for consumed electricity. This is not surprising - all data center systems, starting with IT equipment, for the sake of the normal functioning of which the data center is created, and ending with alarm systems and surveillance systems, consume electricity. Therefore, the most reliable way to save on electricity is to sell computing and telecommunication devices, and close the data center. Unfortunately, without a working computing and communication technology, doing business in modern conditions is unimaginable, so the option of completely eliminating the data center in this article will not be considered.
')
The power consumption of the data center as a single system consists of the consumption of individual systems, both information and telecommunications, and engineering infrastructure systems, including the inevitable unproductive losses. To achieve energy savings in general, it is necessary to explore the possibilities of reducing the consumption of each subsystem.
The main consumers of energy are, of course, computing and telecommunication systems. However, for the normal functioning of computing and telecommunications equipment, work, as a rule - continuous, of a number of auxiliary, service systems is necessary. These auxiliary systems form the engineering infrastructure of the data center.
The main consumers of energy. Energy Consumption Structure
For a stable, normal operation of the most important IT equipment, it is necessary to ensure comfortable conditions: first of all, remove the heat generated by IT equipment, ensure relative humidity of air within 50 ± 10%, create conditions for the operation of security systems, and conditions for the work of the service personnel .
So, the main consumers:
- IT equipment.
- The system of maintaining climate parameters (air conditioning, humidification / dehumidification).
- Ventilation and gas removal system.
- Lighting.
- Security systems (fire extinguishing, fire alarm, drainage, access control system, video surveillance, etc.).
In addition to the above, energy is consumed:
- The system of guaranteed power supply (maintaining the DGU in standby mode - heating, recharging batteries, automation work).
- Uninterruptible power supply system (own consumption - work of inverters, electronics, automation, etc.).
- Losses during transportation and distribution of energy (heating of cables, losses in interconnects - in switchboards, PDUs, etc.).
Virtually all of the electricity that goes to the data center is ultimately converted to heat.
Electrical Efficiency Measurement for Data Centers, White Paper 154 by Neil Rasmussen, APC by Schneider Electric
In general, in order to find ways to reduce energy costs, it is necessary to determine the numerical criteria for evaluating energy efficiency and analyze each of the energy-consuming systems from the point of view of reducing consumption.
Data Center Energy Efficiency Assessment Method
There are several methods for assessing energy efficiency in a data center, differing mainly in the degree of accounting for changes in consumption (as a function of time, computational load, etc.). We use the simplest.
PUE / DCE
The simplest and most visual assessment method is to calculate the energy efficiency ratio of PUE (Power Usage Effectiveness), and its inverse DCE (Datacenter Efficiency, in fact, the efficiency). In this case, the “beneficial effect” is considered to be the consumption of IT equipment, and the DCE coefficient (data center efficiency) is calculated as the ratio of the consumption of IT equipment to the total energy consumption of the data center; PUE ratio - the ratio of total data center consumption to IT equipment consumption. The PUE value can be in the range from 1.0 to infinity. A PUE value close to 1.0 will indicate 100% efficiency — all energy is used only by IT equipment. True, this indicator is practically unattainable - in connection with the above.

In practice, it is more convenient and clearer to operate with PUE. This is confirmed by international practice.
To assess the situation with us, it is useful to know the world statistics on energy efficiency. Thus, the “LAN Network Solutions Journal” http://www.osp.ru/lan/2014/05/13041191/ "> confirms that
“The average value of PUE dropped from 2.5 in 2007 to 1.65 at present”(May 2014). A joint study by T-Systems and Intel of 2010 “DataCenter 2020: hot aisle and cold aisle containment efficiencies reveal no significant differences” predicted a decrease in PUE by 2020 for new data centers from 1.8 to 1.4. That is, today PUE can be considered typical in the range of 1.8-1.5. I note that for popular now “green” data centers, PUE values within 1.1–1.02 are, according to experts, speculation, since they simply do not take into account their own energy sources (wind turbines, solar panels, etc.).
Energy Measurement Techniques
According to experts , a detailed measurement of PUE is quite expensive, although for a rough assessment of large efforts it is not required: “With typical PUE data for PUE values of 1.8–2.5, there is no need for high precision measurements — it’s enough to measure the power at the electrical installation input and UPS outputs that feed the payload. The minimum program is to install meters for commercial metering of electricity. ”
In our data centers, just about this technique is used: the power consumption of the entire data center is determined using data from commercial metering devices and / or direct measurements of currents on the input lines of the input switchgear (ASU) using current tongs (unfortunately, no projects were installed in the technological control of currents and voltages; savings ...); IT equipment consumption is determined by direct measurements of the currents at the output of the UPS by current clamps and / or by the indications of the UPS; The total consumption of engineering infrastructure systems is determined using data from commercial metering devices and / or direct measurements of currents on the input lines of the input switchgear using current clamps, since in a normal situation the UPS / IT equipment and engineering infrastructure systems are powered from separate input lines - for the main data center ; for backup data center data is taken from the system of commercial accounting, and from the testimony of the current load of the UPS.
We are well aware that the measurement accuracy leaves much to be desired: neither the current clamp nor the UPS monitoring system can serve as a measuring tool. However, for a rough assessment of them is enough. In order to assess the reliability of the measured power consumption, the “theoretical” consumption of IT systems and components of the engineering infrastructure is calculated using passport data of computing and telecommunications equipment. The difference between the measured and calculated values allows us to draw some interesting conclusions: about the measurement accuracy, and the accuracy of the data provided in the documentation, the level of loading of IT equipment and engineering infrastructure, and unregistered consumers (in our case, for example, data centers turned out to be unaccounted consumers of data center electricity) places of monitoring group employees connected to the main data center UPS).
Ways to reduce power consumption by system
Each system (subsystem) of IT and engineering infrastructure of the data center is characterized by its own capabilities and methods for reducing energy consumption. Consider the basic systems and possible methods to reduce their power consumption.
IT equipment
The main consumer of energy, as has been repeatedly stated above, is IT equipment. Methods to reduce its consumption are given in the recommendations of , for example, Eaton specialists:
- Disconnect power from inactive equipment.
- Server virtualization, load balancing.
- Combining servers and data centers, using blades.
- Enhance server power management features.
- Use IT equipment with high-performance power supplies.
A detailed description of the methods and reasons for reducing the power consumption of IT equipment due to their use is left to system administrators; However, all this is quite obvious.
The application of these measures, including the replacement of IT equipment with more energy efficient ones, gives the most significant result for reducing the overall power consumption of the data center, since the contribution of IT systems to the overall consumption is the main one, and decreasing the power consumption of other critical systems decreases: the cost of cooling, own consumption of UPS, the loss of energy transportation.
Uninterruptible Power Supply
The own consumption of the UPS is due to the operation of the inverter-inverters that make up them, electronics, automation, and heat losses. The efficiency of the UPS is determined by the efficiency factor, which is calculated as the ratio of the total system power, including the UPS, to the power consumed by the load. Modern UPSs provide an efficiency of 0.75-0.98, while the best performance is achieved at the UPS load level within 0.8-0.95 of the maximum nameplate capacity. Methods to reduce their own consumption of UPS are as follows:
- The main method - the use of UPS with high efficiency.
- Maintain the UPS load level at 0.8-0.9 of the maximum (maximum efficiency, see above).
- The use of modular UPS, allowing to regulate the rated power by switching on / off individual power modules.
- Maintain optimal climatic conditions of the UPS (UPS efficiency decreases with increasing ambient temperature).
A separate item I would like to indicate the uniform distribution of the load across the phases of the supply voltage. Modern UPSs, of course, allow 100% phase imbalance on the load, but this does not add efficiency to them.
Power Transmission Lines, Power Distribution Systems
Energy losses in communication lines and distribution equipment are due to the following reasons:
- heat loss during energy transfer;
- leakage currents.
These losses depend on the following factors:
- own electrical resistance of power transmission lines;
- length of power transmission lines;
- geometry of power transmission lines;
- insulation resistance and reliability;
- quality of connections and contacts.
Methods to minimize energy losses in transmission lines and distribution systems:
- Minimization of cable lengths.
- The use of cables with conductors of materials with high electrical conductivity (low resistance), for example, copper instead of aluminum.
- Using tires instead of cables.
- Reliable insulation, minimizing leakage currents.
- Reliable connections:
- minimizing the number of compounds;
- careful drawing of mechanical connections;
- regularly checking the quality of connections, including with a pyrometer or thermal imager, to determine the increased heat generation, which may indicate a poor connection quality;
- use welding or brazing instead of mechanical (threaded) connections.
- Regular check of insulation resistance of power cables.
- The use of electrical and wiring products only high quality.
Air conditioning systems
By the efficiency of the air conditioning system we mean the ratio of the cost of electricity for the operation of the system to the amount of heat removed from the cooled equipment. The efficiency of the heat removal system from IT equipment (air conditioning, air-conditioning) is determined by many factors, including the ones listed above with respect to power transmission lines. In addition, the overall efficiency of the data center cooling system is significantly curled by the following factors:
- The efficiency of air conditioners is the ratio of cooling capacity to energy consumed.
- Heat losses in the main coolant.
- Heat loss during the delivery of cold to IT equipment.
- The level of thermal insulation of the cooled rooms (machine rooms, UPS rooms, panel rooms, etc.).
- Efficiency of distribution of cold and hot air streams in cooling rooms and near cooled equipment, elimination of cold losses.
Methods to reduce the energy consumption of the air-conditioning system are aimed at improving the efficiency of cooling and reducing heat losses (we are talking about freon systems).
- The use of modern energy-efficient air conditioners. For the "classic" domestic air conditioners to generate 1 kW of cooling capacity (more precisely, to remove 1 kW of heat) 0.33-0.4 kW of electricity is required; for industrial precision air conditioners, this figure can now be 0.2-0.25 kW of electricity per 1 kW of cooling capacity.
- Timely maintenance of refrigeration units: contamination of heat exchangers of air conditioners can reduce the efficiency by 7-12% due to a decrease in the heat transfer coefficient; polluted air filters reduce cooling efficiency by increasing airflow resistance by 5–8%. For example, there have been cases of complete loss of air conditioners when the heat exchangers of the condensers were covered with a layer of poplar fluff; heat exchange (heat removal from the heat carrier) was completely blocked, the freon mixture did not condense from the gaseous to the liquid state.
- Timely preventive maintenance: faulty components, including the motors of the fan drives, increase the power consumption of the systems and the own heat generation of the units. “Broken” bearings or “sagging” drive belts, for example, in pressure fans, due to increased friction losses, reduce the efficiency of both the fan and the unit as a whole; in addition, as in the previous case, the heat generation of the installation increases.
- Choosing the right backup scheme for air conditioners, based on the requirements of the reliability of the system and its efficiency. The most efficient air conditioners operate at 80-85% of the load from the maximum passport; at high levels of load, the lifetime of the units decreases, while at lower levels, the energy efficiency of the system decreases.
- Fine tuning of the parameters of the refrigeration units.
- Proper placement of temperature sensors input and output air (relevant for complex systems of precision and ducted air conditioners).
- Minimizing the loss of cold in refrigerated rooms, thermal insulation of walls, ceilings and building structures of refrigerated rooms to prevent heat exchange through them.
- Minimizing refrigerant lines.
- Maintaining the integrity of the thermal insulation of highways and coolant pipelines (coolant).
- Minimization of the length of the path of delivery of cold air to the equipment; Here, however, there are some peculiarities: for example, in the case of cooling IT equipment out of the raised floor, it is desirable to have as much storage space as possible - as a cold accumulator, despite the lengthening of the air supply paths.
- Providing cold air from air conditioners directly to the front panels of enclosures with installed IT equipment, using air ducts to supply cooled air, and to remove hot air.
- In the case of cooling from the raised floor - adjusting the flow of cold air to the IT equipment by installing / removing perforated plates (gratings), selecting gratings with different percentages of holes, using “active floor” plates (with built-in fans, temperature sensors and fan speed controllers ).
- Prevent mixing of cold and hot air streams; in practice, the separation of data center machine halls (and other technological rooms, where appropriate) into “cold” and “hot” corridors, isolation of corridors, organization of isolated “cold” and / or “hot” rooms.
Ventilation and gas removal system
Energy saving opportunities in ventilation and gas removal systems are limited. The ventilation system in the data center is designed primarily to ensure the normal operation of staff, it does not affect the functioning of IT systems, and, conversely, can reduce the efficiency of cooling systems. Therefore, it is recommended to start the ventilation system only for the time when the personnel work in the data center premises. As for the gas removal system, in normal condition it should not work, and it starts only after the automatic fire extinguishing systems have triggered.
Steam humidification systems
Judging by experience, the continuous operation of the steam humidification system (air humidification in the data center rooms) is not always necessary.Observations carried out in the premises of one of our data centers show, for example, that it is advisable to start the steam humidification system only in the winter, when the air humidity in the street is lowered due to frost (freezing moisture); ). In the warm season, due to the architectural features of the premises of our data center, humidity "itself" is maintained at 40-55%. However, before giving recommendations for a specific site, it is necessary to study the characteristics of its location, consideration of the climatic zone and long-term observations.
Systems in which the reduction of power consumption is impossible or impractical
In general, it is impractical to look for ways to reduce the power consumption of a number of auxiliary systems of the data center engineering infrastructure, since these systems
- as a rule, they already have low own electricity consumption, and its reduction is a complex engineering task;
- the power consumption of these systems is minimal within the data center, and its reduction will not have any noticeable effect on the overall situation.
These systems include:
- Components of the guaranteed power supply system - own consumption of diesel generator sets in standby mode. As a rule, electric power is consumed from an external source for the operation of automation, the control system, recharging of batteries, and maintaining the temperature of process fluids to ensure quick and reliable start of a diesel generator set in the event of a break in external power supply.
- Climate parameters monitoring system.
- Access Control System (ACS).
- The system of video surveillance and video registration.
- Security and fire alarm system.
- Automatic fire extinguishing system.
- Flood protection system (drainage system).
In general, lowering the power consumption of these systems is not possible. In addition, the last two of these systems consume electricity only in case of emergency.
Practical application of methods for reducing power consumption of the data center
During the operation of several computing sites (data centers, server and telecommunications nodes), a number of ways to reduce the cost of electricity supply, from those listed above, have been tested and introduced. Some did not lead to a significant reduction in power consumption, others showed decent results.
For systems and sites, you can bring the following data.
IT equipment
Replacing IT equipment with more energy efficient is the most costly, but also the most effective solution. An illustrative example is the process of replacing heavy-class servers, storage systems and blades at our Novosibirsk main site. For 8 months, from July 2014 to February 2015, due to the replacement of IT equipment, the power of the machine room (IT load) was reduced from 120 to 84 kW. Accordingly, energy costs for cooling equipment in the machine room, the load on the UPS system and its own consumption have decreased; the power consumed by the engineering infrastructure systems decreased from 56 to 37 kW; Total data center consumption fell from 180 to 120 kW:

And all this despite the fact that until July 2014, the general trend was a gradual increase in power consumption; peak values reached 160 kW of IT equipment capacity, and 228 kW of total power consumption:

Actually, practice confirmed the thesis cited at the beginning of the article: the best way to save electricity in the data center is to turn off IT equipment.
Uninterruptible Power Supply
High-performance UPSs Newave ConceptPower Upgrade are used at Novosibirsk sites, in Moscow, in the main data center - APC Galaxy UPSs. All UPSs have decent characteristics, for example, the efficiency of double conversion of Newave UPSs with loads at 75-100% of the maximum is 96%; even at a load level of 25% of the maximum, the manufacturer promises an efficiency of at least 92%.
The UPSs are installed in air-conditioned premises, the climatic conditions for them are optimal.
Regulation of the UPS load level, unfortunately, is not possible due to the adopted redundancy schemes.
The question of leveling the load in phases was done from the moment the data center was put into operation: the installation of any new IT equipment — or the movement of the existing one — was carried out taking this factor into account.
Power Transmission Lines, Power Distribution Systems
In general, all measures to reduce losses in power transmission lines and switching and distribution systems were taken at the construction stage of our data centers.
Due to the adopted backup schemes and technical and operational features, part of the checks aimed at identifying losses is performed according to the situation, and not on a regular basis: insulation resistance measurement, for example, is carried out only when the power supply lines are disconnected; the same applies to the bolting and screw connections in panel equipment. Surveys of power and distribution boards are regularly carried out using pyrometers to identify unreliable connections. However, the quality of the materials and equipment used and the operating conditions of cable lines and switching equipment (protection from external influences, constant temperature and humidity) guarantee the absence of significant electricity losses during transportation, at least within the territory of the data center.
Air conditioning systems
In the framework of solving the problem of optimizing and improving the efficiency of air conditioning systems, quite a lot of activities were carried out.
During the design and construction of data centers, modern and energy-efficient models of air conditioners were selected. So, in the main data center in Novosibirsk installed precision air conditioners Stulz, in the backup data center channel conditioners Daikin; In the main data center in Moscow, HiRef precision systems are installed. The efficiency of these systems lies in the zone of 0.22-0.27 kW of consumed electric power per 1 kW of cooling capacity.
Concluded long-term contracts with service companies for regular maintenance of air conditioning systems. During operation, malfunctions that led to increased power consumption were identified and eliminated: for example, the data center in Novosibirsk, for example, replaced the fan motors twice (winding damage, increased heat generation), the bearings in the fans were replaced in three air conditioners.
; , (2008-2010), . / ; , .
In the first years of operation, there was an acute problem of uneven cooling of IT equipment after switching air conditioners as part of the adopted redundancy scheme: temperatures were set in different areas of the machine rooms with a significant difference, for example, the temperature on the left side of the cabinet rows was 3-5 ° C lower than nominal, on the right side 3-5º above. The problem was solved by transferring the inlet air temperature sensors from the air conditioners closer to the IT equipment. This not only ensured uniform cooling of IT equipment, but also equalized the load on air conditioners, and, ultimately, reduced energy consumption.
Much attention is paid to optimizing air flow, mainly cold, to ensure sufficient and uniform cooling of IT equipment. This is achieved by replacing perforated raised floor plates and using “active floor” modules (for main data centers), and direct adjustment of air flow using adjustable grilles and deflectors on air ducts (backup data center in Novosibirsk, see photo) when moving or changing the composition of the cooled equipment .

During the design and construction of data processing centers, the possibility of separating machine rooms into “cold” and “hot” corridors was foreseen. This opportunity was implemented on the Novosibirsk sites, first in the backup data center (October 2010, photo above, panels from the roofs of the cabinets to the ceiling are visible), then mainly in the data center (May 2011):

After the corridors were divided, the Novosibirsk data center system consumed electricity conditioning decreased by 9-17% depending on the time of year.
In the backup data center, separate cold air ducts were replaced with manifolds with deflectors and adjustable grilles; at a rough estimate, this reduced the power consumption of air conditioners by 4-7%.
Steam humidification systems
The above recommendations are practically applied: for the warm season, the steam humidification systems of air conditioners are turned off, the water mains overlap; continuous monitoring of the relative humidity in the data center premises is carried out according to the data of climate monitoring systems. If necessary (the fall of the relative humidity to 30-35%), the systems are switched on for a short time. The level of efficiency (energy savings) of this event is difficult to assess.
The results of the measures to reduce power consumption
The most complete, and therefore indicative data are available on the main data center in Novosibirsk.
The general reduction in power consumption due to the replacement and reduction of the IT equipment fleet was discussed above. Reducing the power consumption of the data center by 60 kW - the result is more than worthy. However, in addition to absolute indicators, relative values characterizing overall energy efficiency are also of great importance.
As the main indicator, we use the PUE coefficient, which describes the overall energy efficiency of the data center as a single system.
The history of the struggle for kilowatts is approximately as follows:
1. 2008–2009. The stage of final data center commissioning, "grinding"; energy efficiency was practically not thought at that time, since there were enough other various problems: “stuffing” the data center with equipment that was moved, including from other platforms, optimization of equipment placement in the hall, debugging of engineering infrastructure systems, in particular, air conditioning, etc. . And, by the way, the elimination of continuous accidents in engineering systems. Therefore, PUE in 2008 was at the level of 1.55-1.56, and in 2009 it is quite stable at the level of 1.49.
2. 2010 Special measures to reduce consumption were not carried out, PUE ranged from 1.58 in winter to 1.402 in summer, with an average annual value of 1.44.
3. In 2011, work began on improving the efficiency and reliability of the air conditioning system. The ways of supplying air to the condensers of air conditioners were expanded, the IT equipment was moved in the engine room for uniform cooling, the above-mentioned transfer of temperature sensors for incoming air, and a number of other measures. The average value of PUE for the year is 1.44. Despite the fact that by the end of the year it grew to 1.55, because of the increase in the total capacity of IT equipment in the data center, the UPS system was expanded.
4. In 2012, the corridors in the engine room were finally divided, the process of upgrading IT equipment began. Optimized air flow, to improve the cooling of heavy systems used plates "active floor". The working conditions of air conditioners condensers have been improved, the “windows” for the inflow and outflow of outside air have been expanded. Result: PUE average 1.4 per year.
5. 2013. No special measures were taken to improve PUE; by the end of the year, a number of coolant leaks in the mains had been eliminated, which, it must be assumed, led to a certain decrease in PUE.
6. 2014. The decrease in PUE is mainly due to the modernization and replacement of IT equipment, and, accordingly, the change in the redundancy scheme of air conditioners from 4 + 1 to 3 + 2.
7. 2015. The data for the first three months of the current, 2015.
In general, the dynamics is positive, the PUE ratio was reduced from an average of 1.55-1.57 at the beginning of the data center operation to 1.32 (as of March 4, 2015).

The result is good, given the high complexity and cost of energy efficiency measures, and given that for many data centers, the value of PUE 1.6 is an unattainable dream ( Efficiency of the infrastructure of the data center ):
“According to research by the Uptime Institute, a standard data center has an average value of PUE 2.5. This means that for every "incoming" 2.5 watts only one watt comes to the server racks. Most facilities could achieve a PUE = 1.6 using equipment more efficiently and introducing advanced working methods. ”
Conclusion
Over the years of operation (2008-2015), the data center of medium size in general with elementary, generally accepted means was able to reduce the total energy consumption from an average level of 200 kW to 110-120 kW. The cost of electricity, therefore, decreased by about 40-54%, which, you see, is not the worst result.
It should be borne in mind that there are fewer opportunities to reduce PUE values; it is simply not possible to reach a value of 1.0 - for purely physical reasons.
, , -, , . , . , , PUE 1,39-1,43.
PS , , .
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/271873/
All Articles