Corporate phishing

Phishing emails in a corporate environment usually mark a targeted attack , well thought out and implemented. Unlike ordinary users, employees of companies can be instructed properly about the existing threats to information security. For e-mail messages, one or another control may be established by the IT / IB staff of the departments.
Prelude
Phishing emails aimed at ordinary users are usually little “personalized”; only the user's email can be substituted for attracting attention. In the area of attacks on corporate systems, phishing is preceded by a thorough collection and analysis of information about the object and subjects of attack, horizontal communications, possible areas of responsibility and authority. This is necessary for the development of a well-thought-out sociotechnical scenario and the addition of details that make it possible to put down the vigilance of the recipients of the letter.
')
Currently, the percentage of targeted phishing attacks that are organized through emails is growing, in which a particular organization or group of individuals can be identified. Target users receive carefully crafted phishing emails that force a person to enter more sensitive personal information — such as a username and password, that give access to corporate networks or databases with critical information. In addition to requesting credentials, targeted phishing emails can also contain malware. For example, when you press a certain key, programs can be loaded to track everything that the victim will enter using the keyboard.
Under the usual scenario, the penetration into the system began with a phishing mailing. Since here we are dealing with a targeted attack, the phishing mailing was as much as possible adapted for a specific recipient. As Bruce Schneier noted , this is not just phishing, but phishing with a “laser sight”.
In this case, the letters were intended for US officials who were sent to Copenhagen for a conference on climate change. They received malicious files in the mail. Characteristically, the letters were titled "China and Climate Change", and the return address was a fake address of the famous journalist National Journal who specializes in articles on the international economy. This fact alone indicates that the attackers carefully thought out the attack and calculated that the addressees must necessarily open the attached file.
Additionally, the body of the letter contained comments that create the impression that the document is directly related to the work duties of the officials.
Targeting phishing campaigns requires more time and money from cybercriminals than with traditional phishing campaigns. Fraudsters must access or steal lists of valid email addresses for the target organization or group of individuals, and then create believable letters that are highly likely to attract recipients and they will provide their personal data. However, if successful, the financial return on targeted phishing can be much higher, so the investment pays off.
What is common in high-profile stories about data leakage from leading retailer systems Target and Neiman Marcus, the health insurance giant Anthem and Sony Pictures? They all began with a carefully planned targeted phishing attack using emails. Documents infected with malware were attached to the letters. However, they all looked quite normal and were addressed to specific employees within the organization.
Acupuncture phishing has become the most common type of targeted attack for one simple reason: this technique really works, misleading even those users who are serious about security. It creates for hackers a strong point for penetrating the corporate network. According to a Check Point survey conducted among more than 10,000 organizations worldwide, 84% of them have downloaded at least one infected document in the past 12 months. This happens because an attacker simply needs to get an idea of the company or its specific employees on the Internet, and then write a letter that will cause even the most vigilant employee to open a malicious attachment and thereby initiate a hacker attack.
Collection of information
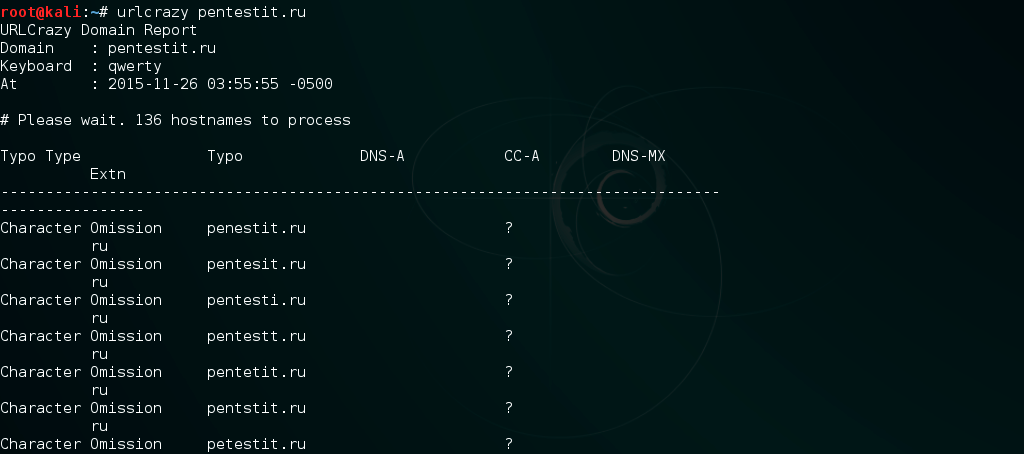
Information is collected from public sources using specialized tools , queries in search engines , specialized services , analysis of company profiles in social networks and on job sites. Such a collection of information can be correlated with the OSINT methodology (Open Source Intelligence - intelligence based on an analysis of open sources of information). The larger, more accurate (at least two or three sources) and more relevant information - the higher the success of the attack.
Use theHarvester utility to collect domain and postal address information:
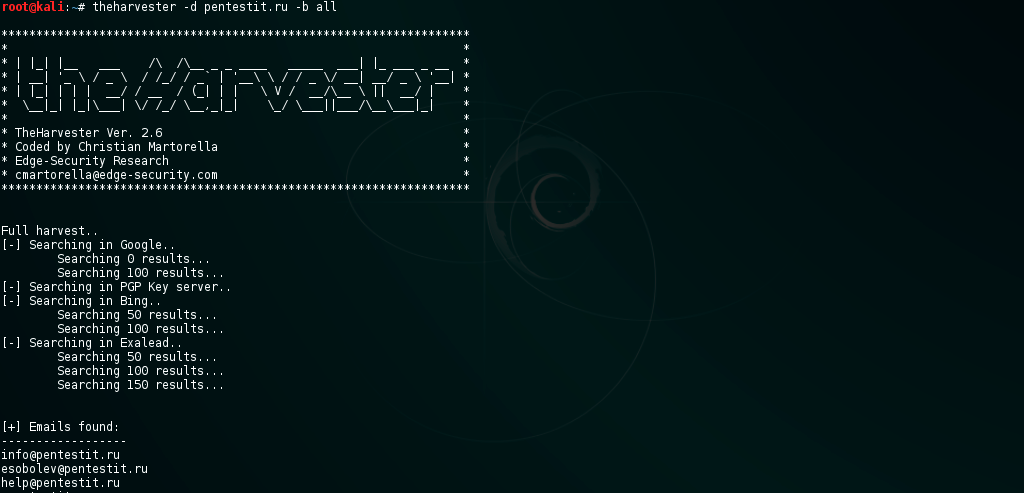
Using the recon-ng utility to collect information from social networks:
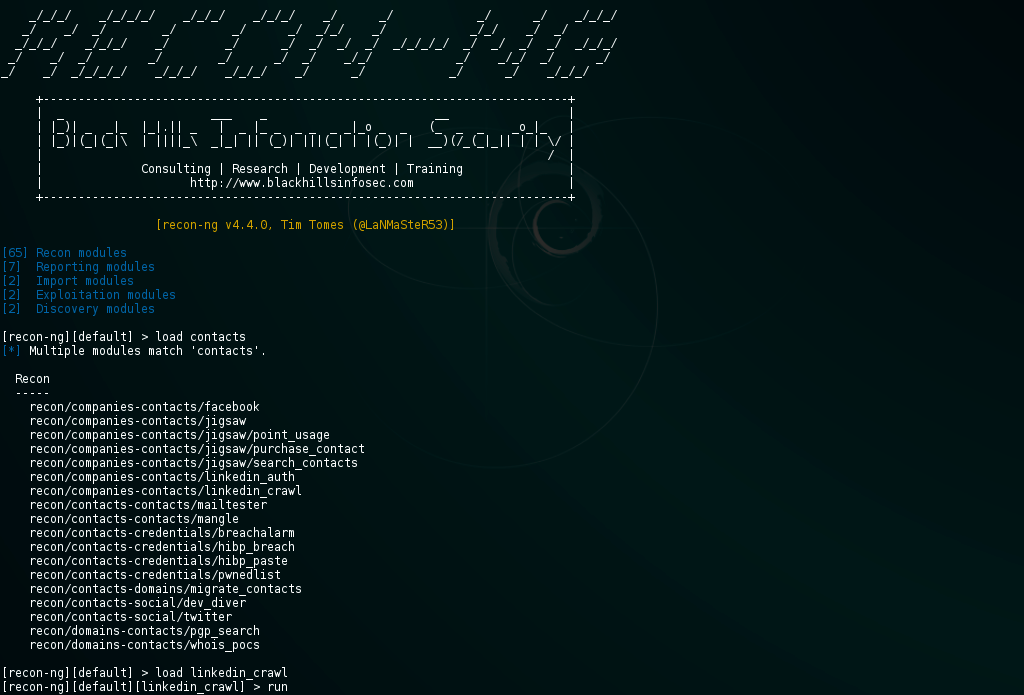
Using specialized services to obtain information:
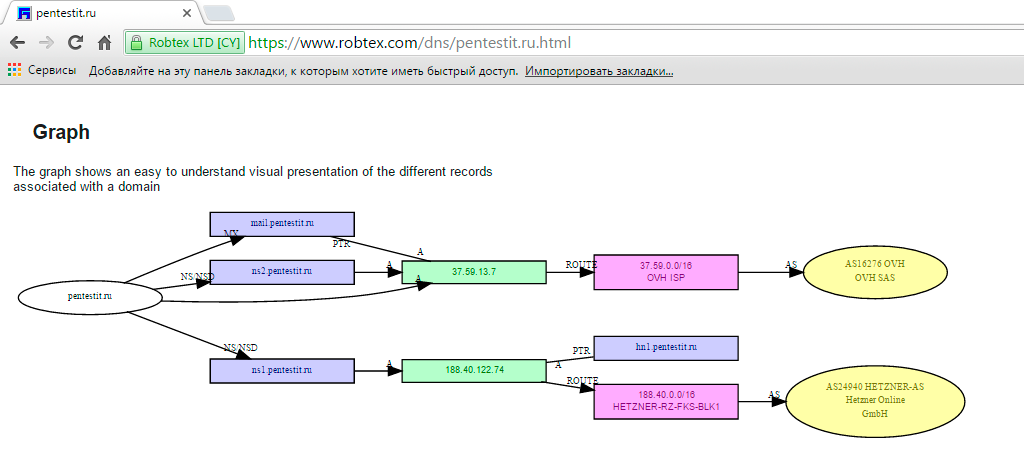
Analysis of the information received
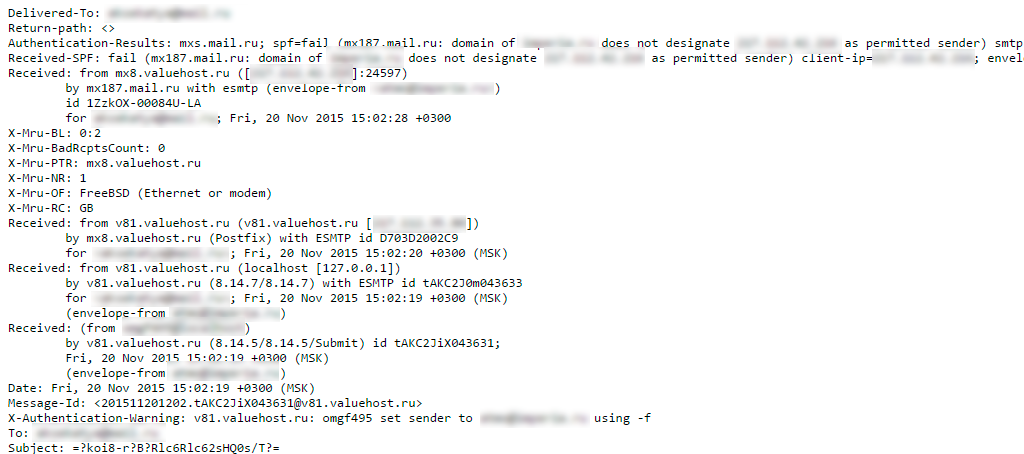
After intelligence and information gathering, attackers verify the information obtained. This may be a phone call, sending an e-mail message - to confirm the accuracy. Also, the detected services (subdomain mail.example.site) are checked for the formation of phishing login forms.
With the victim, you can enter into correspondence to find out the version of the possible software, IP addresses, antivirus software - all this can be extracted from the service headers and the body of the letter:
Attack script formation
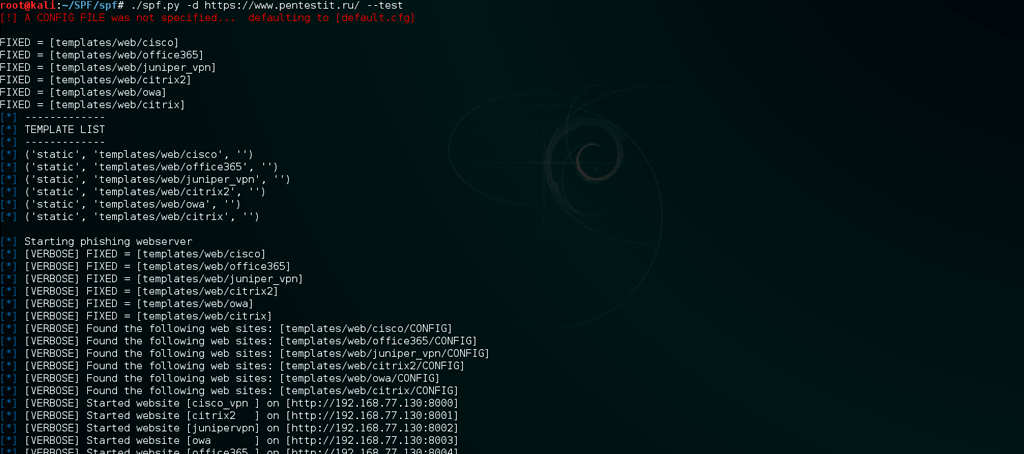
To form a phishing script, attackers can register a fake domain:
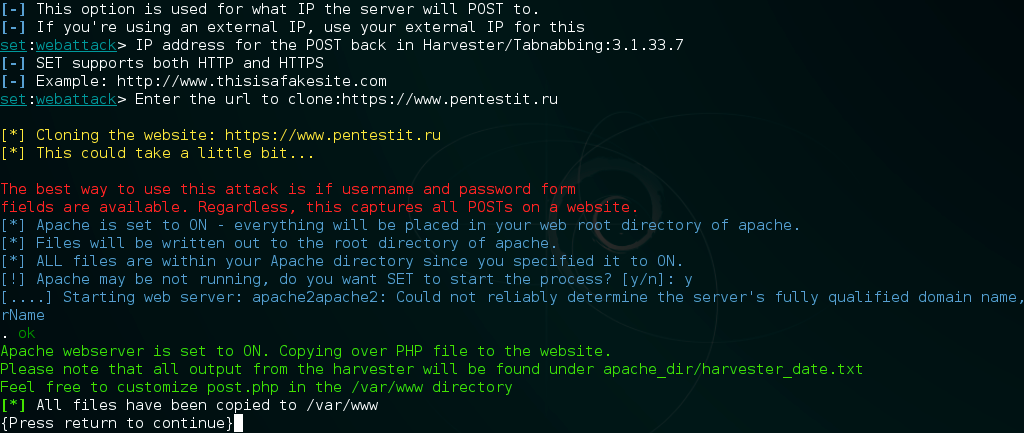
Attackers can create a fake login page at:
- Corporate website;
- mail subdomain (or folder);
- corporate portal;
- CRM system;
- technical services (bugtracker, etc.)
Attack implementation
Phishing emails sent to large lists of addresses are developed taking into account social engineering methods. For example, this could be content that requires a specific action from the recipient, as well as the inclusion of links to websites that look plausible (say, fraudulent online banking services websites). However, in the e-mail messages of this type, personal data is very rarely used. At the same time, thanks to targeted phishing emails, social engineering has taken a new level. By addressing the recipient by name and sending the letter directly to his or her address, the attackers inevitably increase the degree of trust in the malicious email and the fake websites that the victim is redirected to.
For the attack, a targeted email is created containing personalized information and a link to the phishing site. Mailing can be made from a fake website or using available (unclosed) smtp realy to fake the sender's address.
Basic vectors:
- mail delivery error;
- a technical error;
- a message containing a link to a large amount of attachment / invalid format, etc .;
- messages from legislative / executive authorities;
- court decisions.
Errors of displaying the content and links in the letter are made in order to force the user to leave the mail program (if he uses it). Also, these messages can lead to a known user, but a compromised resource - attacks of this class are called watering hole .
But the lion's share of phishing messages is made up of malicious files (the user may not know his password, or authorization on resources occurs through LDAP , etc.), modified RAT and office documents containing macros with this or that functionality.
An example of forming a back-connect shell using the macros of an office suite and powershell:
Cases from practice
Examples and types of attacks depend directly on the target chosen by the attackers, it is quite difficult to give specifics, therefore, as a dessert, a couple of examples from the practice of our company and our colleagues.
Phishing mailing was made to one of the financial organizations. Employees' addresses were extracted using SQL injection from the developed CRM in one of the subdomains. Corporate mail has been set up for gmail. The phishing message contained a link to a similar resource and the gmail login form. Cherry on the cake was embedded in this page iframe - the code of one of the known bundles of exploits . Those. in addition to the exploitation of the sociotechnical vector, an additional vector was implemented in the form of exploiting browser vulnerabilities and their components. The attack allowed attackers to gain control on some accounts.
An email containing a malicious program in the form of a .scr file was sent to one organization. The zero patient who downloaded and launched the malware did not see any obvious signs of its work and tried to do it several more times. After that, he sent this investment to his colleagues with the remark “I can’t open it, try it, can it open?” The victim himself initiated a pandemic of viral activity in the corporate environment.
Protection
Nowadays, more and more sophisticated methods are being used to force the victim to follow links to certain websites, where people unwittingly leave malicious information to attackers or download malicious software onto their computer. Most spam emails now contain URLs to which recipients navigate to malicious websites. At the same time, fraudulent websites where victims are sent look exactly the same as their legally valid counterparts.
According to a study conducted at the University of California at Berkeley, even those who have long and often use the Internet sometimes fall for scammers and go to their websites. To protect themselves against phishing websites, users should use a comprehensive verification strategy for the likely level of confidence in the content, monitor the address bar and security settings in it, pay attention to the image of the lock in the browser window and the security certificate of each website to which the user is redirected.
As measures of protection, it is necessary to establish control over email attachments and links, conduct trainings with personnel about the presence of new threats , observe precautions and notify all suspicious cases to technical personnel.
Previous article: phishing email examples .
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/271597/
All Articles