Cybergroup Buhtrap uses for its purposes attacks Watering Hole
In late October, our analysts noticed malicious activity on the Ammy website, which specializes in developing Ammyy Admin remote access tools. The attackers managed to upload to the server of this company's website a malicious modification of the distribution of the above program, which contained the malicious software of the buhtrap cybergroup .

Despite the fact that Ammyy Admin is legitimate software, it has already been used by attackers in its malicious campaigns and, therefore, some anti-virus products, including ESET, detect it as a potentially unwanted application (PUA). However, it is still widely used, in particular, in Russia.
Fig. Appearance of the website ammyy.com.
')
As we noted in our previous study on operation buhtrap, this cyber group actively specialized in cyber attacks of Russian business. For this phishing email was used. Since various tools for remote access to computers are actively used by corporate users, there is definitely a meaning in the compromise of the Ammy website. It should be noted that the company's customers are listed on Ammyy’s website, including Russian banks, as well as companies from the 500 Fortune list.
Currently, this website has already been cleared of malware and distributes legitimate distributions of Ammyy Admin, but within a week, users downloaded from there a fake distribution that contains the installer of the program, as well as an executable file of malware. An investigation by our specialists revealed that during the specified period of time, the website distributed several families of malware. Below is the timeline for site distribution by various malware families.
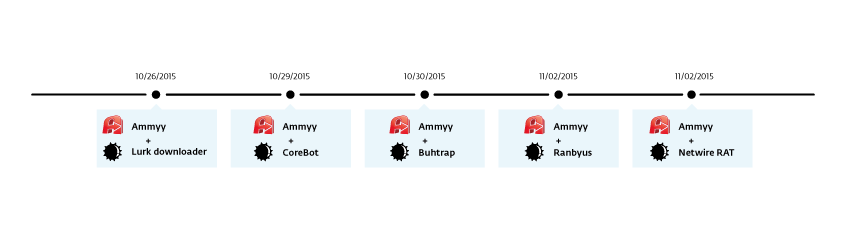
Fig. The timeline for the distribution of various types of malware compromised website Ammyy (Lurk, CoreBot, Buhtrap, Ranbyus, Netwire RAT).
The first malware we saw on the website was the lurk trojan downloader. It was distributed on October 26th. After that, on October 29th, we observed CoreBot, and on the 30th, the malicious program of the Buhtrap cybergroup. In early November, we observed Ranbyus, a distributed banking Trojan, and Netwire RAT, a remote access tool.
Although the above malware families are not related to each other, the fake distributions of Ammyy Admin performed the same actions: they installed the remote administration program itself, and also launched a file called AmmyyService.exe or AmmyySvc.exe, which was malicious software. It can be assumed that the attackers who hacked the website provided their services in distributing malicious content to various attackers.
In the case of Buhtrap, the malware was a bootloader (daunloader) and its behavior is similar to the similar malware from the campaign we described earlier . The loader receives a list of software installed on the system, as well as a list of URLs visited by the user. If he finds the system he has compromised is suitable for attackers, he downloads the necessary trojan for her. The file of the loader itself was signed by the following digital certificate. As in the previous case of the Buhtrap operation, the loader specializes in downloading not the executable file itself, but the installation package (archive), which also includes the dropper of the malicious program.
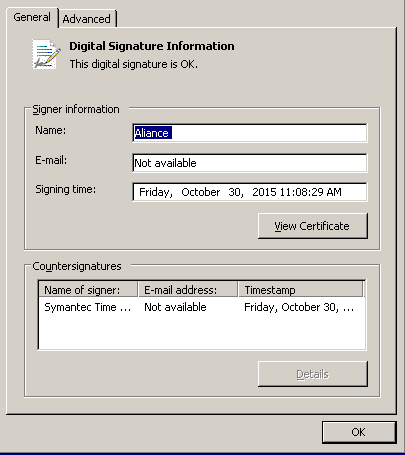
Fig. A valid digital certificate that signed the Buhtrap loader.
The downloaded package contains the necessary files that are necessary for attackers to carry out cyber espionage operations. Malicious code specializes in receiving keystrokes on the keyboard (keylogger), enumerating smart cards and interacting with a remote C & C server. The capabilities of the malware are identical to those we considered in the case of the malware used in the previous malicious campaign; they both use the DLL Side-Loading mechanism for their loading. The main difference is that this time not Yandex Punto was selected as the legitimate application for Side-Loading DLLs, but the software called The Guide .
Conclusion
Cybergroup Buhtrap continues to be active and uses new methods to compromise corporate users. Like the cybercriminals behind the Carbanak banking trojan, the Buhtrap cyber group uses the methods of compromising users that we are used to seeing in targeted cyber attacks. Using the Watering Hole allows you to retrain the Buhtrap from the category of simple cyber group to the APT group.

Despite the fact that Ammyy Admin is legitimate software, it has already been used by attackers in its malicious campaigns and, therefore, some anti-virus products, including ESET, detect it as a potentially unwanted application (PUA). However, it is still widely used, in particular, in Russia.

Fig. Appearance of the website ammyy.com.
')
As we noted in our previous study on operation buhtrap, this cyber group actively specialized in cyber attacks of Russian business. For this phishing email was used. Since various tools for remote access to computers are actively used by corporate users, there is definitely a meaning in the compromise of the Ammy website. It should be noted that the company's customers are listed on Ammyy’s website, including Russian banks, as well as companies from the 500 Fortune list.
Currently, this website has already been cleared of malware and distributes legitimate distributions of Ammyy Admin, but within a week, users downloaded from there a fake distribution that contains the installer of the program, as well as an executable file of malware. An investigation by our specialists revealed that during the specified period of time, the website distributed several families of malware. Below is the timeline for site distribution by various malware families.

Fig. The timeline for the distribution of various types of malware compromised website Ammyy (Lurk, CoreBot, Buhtrap, Ranbyus, Netwire RAT).
The first malware we saw on the website was the lurk trojan downloader. It was distributed on October 26th. After that, on October 29th, we observed CoreBot, and on the 30th, the malicious program of the Buhtrap cybergroup. In early November, we observed Ranbyus, a distributed banking Trojan, and Netwire RAT, a remote access tool.
Although the above malware families are not related to each other, the fake distributions of Ammyy Admin performed the same actions: they installed the remote administration program itself, and also launched a file called AmmyyService.exe or AmmyySvc.exe, which was malicious software. It can be assumed that the attackers who hacked the website provided their services in distributing malicious content to various attackers.
In the case of Buhtrap, the malware was a bootloader (daunloader) and its behavior is similar to the similar malware from the campaign we described earlier . The loader receives a list of software installed on the system, as well as a list of URLs visited by the user. If he finds the system he has compromised is suitable for attackers, he downloads the necessary trojan for her. The file of the loader itself was signed by the following digital certificate. As in the previous case of the Buhtrap operation, the loader specializes in downloading not the executable file itself, but the installation package (archive), which also includes the dropper of the malicious program.

Fig. A valid digital certificate that signed the Buhtrap loader.
The downloaded package contains the necessary files that are necessary for attackers to carry out cyber espionage operations. Malicious code specializes in receiving keystrokes on the keyboard (keylogger), enumerating smart cards and interacting with a remote C & C server. The capabilities of the malware are identical to those we considered in the case of the malware used in the previous malicious campaign; they both use the DLL Side-Loading mechanism for their loading. The main difference is that this time not Yandex Punto was selected as the legitimate application for Side-Loading DLLs, but the software called The Guide .
Conclusion
Cybergroup Buhtrap continues to be active and uses new methods to compromise corporate users. Like the cybercriminals behind the Carbanak banking trojan, the Buhtrap cyber group uses the methods of compromising users that we are used to seeing in targeted cyber attacks. Using the Watering Hole allows you to retrain the Buhtrap from the category of simple cyber group to the APT group.

Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/270643/
All Articles