Data ONTAP 8.3 ADP: FlashPool StoragePools
OS Data ONTAP 8.3 cDOT is one of the largest releases of NetApp. One of the key features of the release is the Advanced Drive Partitioning (ADP) technology, in a previous article I considered the application of this technology for Root-Data Partitioning , in this very same I propose to consider the internal StoragePools device. Read more about what 's new in cDOT 8.3 here .
StoragePools is similar to Root-Data Partitioning, which also uses partitioning, providing a new way to distribute SSD cache for hybrid aggregates.
StoragePool technology was developed specifically for hybrid units in order to more efficiently distribute SSD cache between them. For example, you have only 4 SSDs installed in your system, and you want to make a cache for 2, 3 or even 4 units, ADP will help you here.
')
So, first you need to create a StoragePool and add a set of SSD disks there.
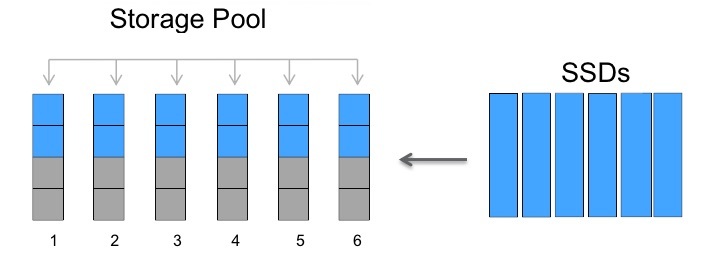
All disks in StoragePool will be split into even 4 pieces. This is not configurable anywhere, the system will always split them into even four parts. You can have multiple storagepools. By creating a StoragePool, by default, the partitions will be equally divided between the two nodes of the HA system, but this can be changed.
The set of the first (P1), second (P2), third (P3) and fourth (P4) partitions of the StoragePool drive is called the Allocation Unit, respectively (AU1, AU2, AU3, AU4).


you can build RAID4 (and lose 1 Parity disk) or collect RAID-DP (and lose 2 Parity disks)
Since there are very few disks, in the case of RAID-DP it is allowed not to have a Spare disk.
For RAID-4, you must have one Spare disk
Hot-Spare drive is always highly recommended in all configurations.
When choosing between RAID4 (with a spare disk) and RAID-DP (without a spare disk), NetApp prefers RAID4.
In production systems with four SSDs, as a rule, it is RAID4 with a Spare disk that is used (we lose two disks out of four) . It is also possible to assemble a RAID-DP with a Spare disk on four disks and lose 3 disks out of 4x.
It is important to note that if any one (whole) RAID4 or RAID-DP group fails in the unit (whether it is SSD, AU or HDD), the whole unit will go to the Degraded and Offline state. In this connection, NetApp always recommends using Spare disks and the security level appropriate for your expectations for redaction groups.
Before buying SSD drives for FlashPool, you can estimate how many drives and which capacity can increase throughput and response speed, based on the number of hit hits that could be in the case of a cache.
When an SSD disk fails, all raid groups (AU) that use its partitions will be affected, as a result all units that use these AUs. In this connection, it is recommended to always have a Spare disk, in other, this recommendation has always been.
StoragePools is another technology under the hood of cDOT that is designed to be as simple as possible. Just like Root-Data Partitioning, it just is and just works. In general, the technology copes with its task perfectly - to distribute SSD cache for hybrid units more flexibly. It indirectly allows you to save on SSD drives, so before it was necessary to buy at least 4x SSD for each hybrid unit, now you can use one set of 4x SSDs for 4 units. Understanding the subtleties of the StoragePool, you can more rationally distribute the cache by allocating it in portions to aggregates: for example, you can start with one AU for an agragat, and then add it if necessary.
An ADP FAQ is available at Fieldportal .
I ask to send messages on errors in the text to the LAN .
Comments, additions and questions on the article on the contrary, please in the comments .
StoragePools is similar to Root-Data Partitioning, which also uses partitioning, providing a new way to distribute SSD cache for hybrid aggregates.
Hybrid unit
StoragePool technology was developed specifically for hybrid units in order to more efficiently distribute SSD cache between them. For example, you have only 4 SSDs installed in your system, and you want to make a cache for 2, 3 or even 4 units, ADP will help you here.
')
So, first you need to create a StoragePool and add a set of SSD disks there.

All disks in StoragePool will be split into even 4 pieces. This is not configurable anywhere, the system will always split them into even four parts. You can have multiple storagepools. By creating a StoragePool, by default, the partitions will be equally divided between the two nodes of the HA system, but this can be changed.
The set of the first (P1), second (P2), third (P3) and fourth (P4) partitions of the StoragePool drive is called the Allocation Unit, respectively (AU1, AU2, AU3, AU4).

- Now we can assemble individual Raid Groups (RG) from the Allocation Unit (AU).
- Allocation Unit'y are created only from SSD.
- A raid group that already contains an AU can consist of only one AU.
- Several raid groups consisting of AU can coexist in one unit or live in several different units, units can live on the first and / or second node.
- AU is used entirely to create a raid group.
- You can use any available number of AU or not to use.
- As long as the RAID group is no larger than 14 drives, it can be converted to RAID-RAID and back on the go.
- As an exception to the rules, an SSD can be added to the aggregate consisting of HDDs as a cache (a hybrid aggregate, it is also called FlashPool). As a rule, NetApp does not allow merging disks of the same type in one unit.
- As an exception to the rule, for SSD raid groups it is allowed to have an excellent type of security (RAID4 or RAID-DP) from the one that is configured for the HDD. As a rule, all raid groups should have the same type of security. In our case, the recommendation is as follows: all raid groups consisting of HDD must have the same type of security, and raid groups consisting of SSD / AU may have an excellent type of protection from the HDD, but must have the same type of protection in SSD / AU raid groups .

RAID and Spare Disk Recommendations
If you have only 4 disks
you can build RAID4 (and lose 1 Parity disk) or collect RAID-DP (and lose 2 Parity disks)
Since there are very few disks, in the case of RAID-DP it is allowed not to have a Spare disk.
For RAID-4, you must have one Spare disk
Hot-Spare drive is always highly recommended in all configurations.
When choosing between RAID4 (with a spare disk) and RAID-DP (without a spare disk), NetApp prefers RAID4.
The preference of RAID4 on a small number of SSDs is due to several reasons:
- SSD drives are actually more reliable than regular drives; therefore, on small quantities, SSD RAID4 is more reliable than HDD in the same RAID
- SSD drives are much faster restored because of what the output of the second drive in the process of reconstruction is much less likely due to HDD
- Since SSD disks have a limited number of rewrite cycles, the Spare disk will not be used at all (and will not wipe the rewrite cycles)
- If the number of SSDs exceeds 7 disks, it is recommended to use (convert the group into) RAID-DP
In production systems with four SSDs, as a rule, it is RAID4 with a Spare disk that is used (we lose two disks out of four) . It is also possible to assemble a RAID-DP with a Spare disk on four disks and lose 3 disks out of 4x.
It is important to note that if any one (whole) RAID4 or RAID-DP group fails in the unit (whether it is SSD, AU or HDD), the whole unit will go to the Degraded and Offline state. In this connection, NetApp always recommends using Spare disks and the security level appropriate for your expectations for redaction groups.
Example of converting RAID-DP to RAID4 for SSD Cache (AU)
storage aggregate modify -aggregate aggr_name -hybrid-enabled true storage pool show-available-capacity storage aggregate add aggr_name -storage-pool sp_name -allocation-units number_of_units storage aggregate modify -aggregate aggr_name -raidtype raid4 -disktype SSD storage aggregate show-status test Aggregate test (online, mixed_raid_type, hybrid) (block checksums) Plex /test/plex0 (online, normal, active, pool0) RAID Group /test/plex0/rg0 (normal, block checksums, raid-dp) Usable Physical Position Disk Pool Type RPM Size Size Status -------- --------------------------- ---- ----- ------ -------- -------- ---------- dparity 1.2.3 0 BSAS 7200 827.7GB 828.0GB (normal) parity 1.2.4 0 BSAS 7200 827.7GB 828.0GB (normal) data 1.2.5 0 BSAS 7200 827.7GB 828.0GB (normal) data 1.2.6 0 BSAS 7200 827.7GB 828.0GB (normal) data 1.2.8 0 BSAS 7200 827.7GB 828.0GB (normal) RAID Group /test/plex0/rg1 (normal, block checksums, raid4) Usable Physical Position Disk Pool Type RPM Size Size Status -------- --------------------------- ---- ----- ------ -------- -------- ---------- parity 1.3.3 0 SSD - 82.59GB 82.81GB (normal) data 1.4.0 0 SSD - 82.59GB 82.81GB (normal) data 1.4.1 0 SSD - 82.59GB 82.81GB (normal) data 1.4.2 0 SSD - 82.59GB 82.81GB (normal) Advanced Workload Analyzer (AWA)
Before buying SSD drives for FlashPool, you can estimate how many drives and which capacity can increase throughput and response speed, based on the number of hit hits that could be in the case of a cache.
AWA sample output
### FP AWA Stats ### Host lada66a Memory 93788 MB ONTAP Version NetApp Release Rfullsteam_awarc_2662016_1501071654: Wed Jan 7 17:43:42 PST 2015 Basic Information Aggregate lada66a_aggr1 Current-time Fri Jan 9 16:14:29 PST 2015 Start-time Fri Jan 9 12:30:16 PST 2015 Total runtime (sec) 13452 Interval length (sec) 600 Total intervals 24 In-core Intervals 1024 Summary of the past 20 intervals max ------------ Read Throughput (MB/s): 134.059 Write Throughput (MB/s): 1333.279 Cacheable Read (%): 27 Cacheable Write (%): 22 Max Projected Cache Size (GiB): 216.755 Summary Cache Hit Rate vs. Cache Size Referenced Cache Size (GiB): 216.755 Referenced Interval: ID 22 starting at Fri Jan 9 16:04:38 PST 2015 Size 20% 40% 60% 80% 100% Read Hit (%) 1 3 6 11 21 Write Hit (%) 5 11 13 14 23 AWA Summary for top 8 volumes Vol interval len (sec) 19200 In-core volume intervals 8 Volume #1 lada66a_vol8 Summary of the past 32 intervals max ------------ Read Throughput (MB/s): 1.751 Write Throughput (MB/s): 18.802 Cacheable Read (%): 11 Cacheable Write (%): 16 Max Projected Cache Size (GiB): 29.963 Projected Read Hit (%): 31 Projected Write Hit (%): 16 Volume #2 lada66a_vol7 Summary of the past 32 intervals max ------------ Read Throughput (MB/s): 1.640 Write Throughput (MB/s): 17.691 Cacheable Read (%): 14 Cacheable Write (%): 13 Max Projected Cache Size (GiB): 28.687 Projected Read Hit (%): 29 Projected Write Hit (%): 13 disadvantages
When an SSD disk fails, all raid groups (AU) that use its partitions will be affected, as a result all units that use these AUs. In this connection, it is recommended to always have a Spare disk, in other, this recommendation has always been.
findings
StoragePools is another technology under the hood of cDOT that is designed to be as simple as possible. Just like Root-Data Partitioning, it just is and just works. In general, the technology copes with its task perfectly - to distribute SSD cache for hybrid units more flexibly. It indirectly allows you to save on SSD drives, so before it was necessary to buy at least 4x SSD for each hybrid unit, now you can use one set of 4x SSDs for 4 units. Understanding the subtleties of the StoragePool, you can more rationally distribute the cache by allocating it in portions to aggregates: for example, you can start with one AU for an agragat, and then add it if necessary.
An ADP FAQ is available at Fieldportal .
I ask to send messages on errors in the text to the LAN .
Comments, additions and questions on the article on the contrary, please in the comments .
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/270169/
All Articles