A fake base station for $ 1400 allows you to accurately determine the location of the phone in the 4G / LTE network
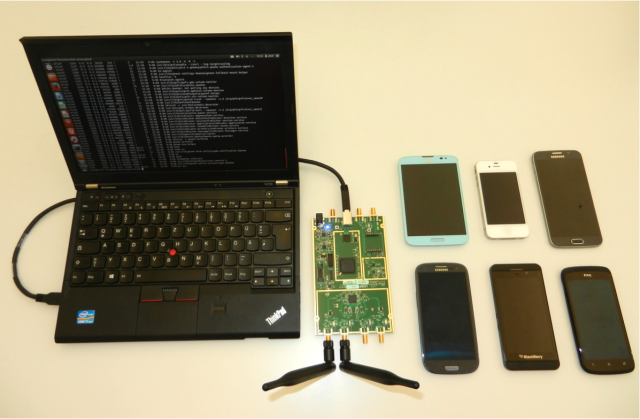

Researchers have developed an inexpensive way to detect the exact location of a smartphone operating on an LTE / 4G cellular network. This development makes it clear that mobile networks of new generations are just as vulnerable to certain types of attacks, as are networks operating according to the old, already outdated communication standards and specifications.
A new attack exploits a vulnerability in the LTE protocol . This standard by the end of the year will provide communications for 1.37 billion subscribers. To conduct an attack, it is required to assemble a system of elements whose total value is about $ 1,400. The software uses Open Source software. The system, node NodeB, allows you to determine the location of phones that are compatible with the LTE standard, with an accuracy of up to 10-20 meters. In some cases, this equipment allows you to find out the GPS coordinates of devices, although an attack of this type can be detected by a smartphone user. Another method of determining the coordinates of smartphones has been developed, and the attack is almost impossible to detect. This method allows you to determine the location of a given device within a couple of square kilometers.
The same group of specialists has developed a new type of attack that allows disconnecting phones from the LTE network, which provokes the transition of devices to work with 2G and 3G, that is, more vulnerable protocols. And here the intruders have already untied their hands. So, in the 2G network you can find out the location of the phone within 1 km2 , in the 3G network the situation is approximately the same. According to experts, the discovered methods of hacking refute the axiom about the invulnerability of new generation networks.
')
“The LTE standard provides for the use of a multi-layer security system that helps prevent subscriber localization and be sure that network services are always available. We have shown that new vulnerabilities jeopardize the security of LTE network subscribers, ”the researchers noted in their report.
As in the case of networks of previous generations, the LTE network prevents the subscriber (his terminal) from localizing by assigning a temporary mobile subscriber number (TMSI). This identifier exists for a short time. When a network interacts with a device, it usually uses TMSI, rather than a phone number or some other permanent identifier, which helps prevent intruders from monitoring network traffic, with the further localization of a specific user. In 2G networks, such security measures are bypassed by sending a hidden message to the user, or by calling the subscriber’s phone, which ensures that the location of the device is determined by the mobile network.
The information security team, which discovered these vulnerabilities, determined that a series of requests could be initiated by social networking applications and instant messengers, such as Facebook, WatsApp, Viber, and the owner of the tracking device could not be detected. An attacker using this feature of the instant messengers can identify the user by linking the Facebook profile to the TMSI. And already TMSI, in turn, can be used to determine the coordinates of the phone.
You can also conduct much more accurate attacks using fake base stations, eNodeB communication nodes. To create such a station, researchers used Universal Software Radio Peripheral with OpenLTE. The total cost of the equipment was about $ 1,400.
In the active mode, this communication node identifies itself as the base station of the operator, which ensures the connection of LTE phones to this communication center. After that, attackers can get a certain kind of information transmitted by smartphones that have connected to the station. This is, for example, a list of nearby base stations and a signal strength for each of them. After that, the attacker, using triangulation, can easily determine the coordinates of the device (as mentioned above, in some cases it is possible to determine the GPS coordinates).
At the same time, an attack in the semi-passive mode allows you to remain unnoticed, although the location data of the smartphone obtained during such an attack will be less accurate than in the case of an active attack.
As for the research team, its members are doctoral students at Berlin Technical University Altaf Shaik (Altaf Shaik), N.Asoukan (N. Asokan) from the University of Helsinki, Waltteri Niemi (Valtteri Niemi) from the University of Helsinki, and Jean-Pierre Seifert (Jean- Pierre Seifert), professor at the Technical University of Berlin.
In order to help telecom operators avoid attacks on their networks by intruders, experts provided telecommunications companies with their ideas on how to improve network security.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/269953/
All Articles