How to detect and eliminate hidden forwarding for mobile devices
Hi, Habr! We all love it when the site works fine on any device, regardless of screen size, control methods and interaction. Often, content has to be slightly adapted to the device on which the user views it: for example, optimizing for a small smartphone screen involves changing images and other content elements. To make mobile visitors more convenient, developers often use pop-up navigation bar . If such modifications are implemented properly and their goal is to improve usability, we do not consider them as a violation of Google’s rules.
The same applies to redirects to mobile sites. It will be more convenient for users of smartphones to work not with the regular version of the site, but with the mobile one. Therefore, forwarding, for example, from example.com/url1 to m.example.com/url1 is justified. However, the hidden redirection of mobile users to extraneous pages interferes with work and violates Google’s recommendations for webmasters .
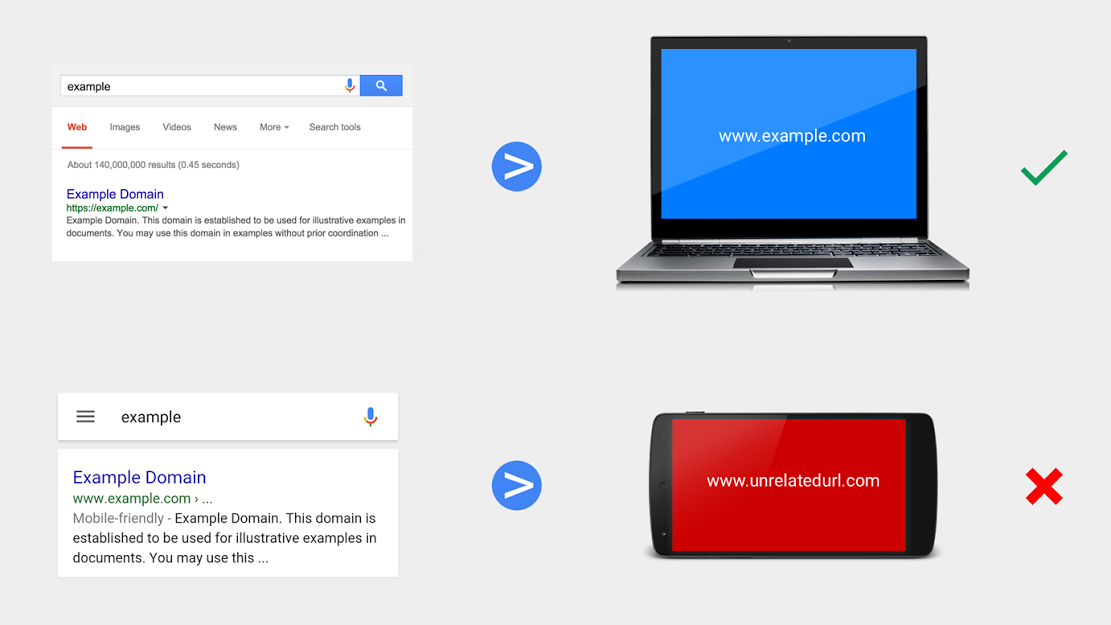
Example of a violation: the search results page on the computer and the mobile device shows the same URL. By clicking on this link, the computer user will go to the landing page, and the smartphone user will be redirected to another URL.
')
Today there are many ways to create a website. From ready-made engines, plug-ins and themes, to comfortable IDEs that require virtually no knowledge in the field of layout. Many large or old resources for a long time (at the time of ordinary phones with JAVA browsers) have a mobile version, which can be very different from the “full-featured” one. Nevertheless, we believe that the content of the site and the information provided should coincide in essence on all devices. Let's look at the main problems of redirecting mobile users.
Problem processing of mobile devices
Sometimes webmasters set up redirection of mobile visitors themselves, as a rule, in violation of our recommendations . If it hurts users, we manually take steps to solve the problem (read more about this at the end of the article). However, we are also aware of cases when hidden redirection is performed without the knowledge of the site owner .
Deliberate redirection for promotional purposes.
A script or an element placed on a site for displaying advertising or monetizing content can redirect mobile users to a different subject site without the knowledge of the webmaster. And it doesn't matter if you yourself placed the “problem” script or your site was hacked: if you don’t understand the source code of the plug-in modules, get a Trojan horse easier than ever.
Redirection of mobile users as a result of hacking the site
If your site is hacked, it can redirect mobile users to domains that spread spam, illegally collect personal data or steal money from bank cards. What to do if you are a victim of such redirects?

The general program of action is simple, just one-two-three: to determine, isolate, prevent. For the cause!
To competently deal with the problem, it must be determined. You may not even guess that someone “steals” your mobile users until someone complains or you accidentally stumble upon the results of malicious scripts.
Messages from visitors can carry little useful information and make a panic: “I opened your site, and he got me aaaaaaaaa, yyyyyyy, yyyy -y and offers rotten fruit at wholesale prices . " No problem page, no information about the device or browser.
So step one: find the problem. Tips may look obvious, but experience has shown that when it comes to real problems, many users and webmasters get lost and don’t know where to start. Start with the simplest:

Suppose you found a problem? What's next? How to deal with it? Step two: isolate the source of the problem. Sources of redirection can be two - external or internal effects.
In the first case, someone got access to your site (vulnerabilities to popular engines are regularly found and do not always close quickly). In the second, you, unwittingly, set a "time bomb" by inserting some script without checking its contents. Optionally, the site's engine could independently update items from any repository that was hacked. In any case, the algorithm is the same to eliminate such problems.
Step three: prevent repetition. Everything is simple here. You found the reason for the redirect - script, element, module, whatever. If you know where it came from - perhaps you should stop using this source of extensions. If not, check the list of known vulnerabilities for your engine or framework, a set of libraries. Perhaps the developers managed to release urgent updates.
It is not necessary to exclude the human factor. If there was no hacking and you did not place the scripts / libraries / elements, and they appeared - look at the site access history, perhaps, the initiative moderators or content administrators could intentionally or unintentionally infect the site.
Check permissions to read / write to certain folders; if writing is not required - set the read only attribute, it will prevent intruders and malware from entering through a narrow loophole to register in working folders and increase privilege levels.
If a user is redirected to other pages in order to show content other than the one shown in the search results, this is a violation of Google’s webmaster recommendations. Read more about hidden redirects here .
The Google search quality assessment team can take action on these sites, such as removing a URL from our index. If this happens, you, as the site owner, will see the corresponding alerts in the Search Console. This is just one of the reasons why we recommend that you register an account in the Search Console. The service itself is extremely flexible and allows not only to receive timely notification of problems, but also to analyze the current state of the site, as well as to send requests to Google to re-check. Fast, convenient, and most importantly - in one place.
Choose advertisers who will not direct your visitors to unexpected pages. If you are seeking to develop trust relationships in the industry - read the recommendations for working in advertising networks. You can start by looking at the IAB site quality guidelines .
There are many ways to monetize content for mobile devices, providing a high level of convenience for users and not leading to the removal of your site from search results. Use them.
If you have questions or comments on mobile redirects, leave them here or ask them on the webmaster forum or in our webmaster community on Google+ .
The same applies to redirects to mobile sites. It will be more convenient for users of smartphones to work not with the regular version of the site, but with the mobile one. Therefore, forwarding, for example, from example.com/url1 to m.example.com/url1 is justified. However, the hidden redirection of mobile users to extraneous pages interferes with work and violates Google’s recommendations for webmasters .

Example of a violation: the search results page on the computer and the mobile device shows the same URL. By clicking on this link, the computer user will go to the landing page, and the smartphone user will be redirected to another URL.
')
What where When?
Today there are many ways to create a website. From ready-made engines, plug-ins and themes, to comfortable IDEs that require virtually no knowledge in the field of layout. Many large or old resources for a long time (at the time of ordinary phones with JAVA browsers) have a mobile version, which can be very different from the “full-featured” one. Nevertheless, we believe that the content of the site and the information provided should coincide in essence on all devices. Let's look at the main problems of redirecting mobile users.
Problem processing of mobile devices
Sometimes webmasters set up redirection of mobile visitors themselves, as a rule, in violation of our recommendations . If it hurts users, we manually take steps to solve the problem (read more about this at the end of the article). However, we are also aware of cases when hidden redirection is performed without the knowledge of the site owner .
Deliberate redirection for promotional purposes.
A script or an element placed on a site for displaying advertising or monetizing content can redirect mobile users to a different subject site without the knowledge of the webmaster. And it doesn't matter if you yourself placed the “problem” script or your site was hacked: if you don’t understand the source code of the plug-in modules, get a Trojan horse easier than ever.
Redirection of mobile users as a result of hacking the site
If your site is hacked, it can redirect mobile users to domains that spread spam, illegally collect personal data or steal money from bank cards. What to do if you are a victim of such redirects?

The general program of action is simple, just one-two-three: to determine, isolate, prevent. For the cause!
How to detect hidden forwarding for mobile devices?
To competently deal with the problem, it must be determined. You may not even guess that someone “steals” your mobile users until someone complains or you accidentally stumble upon the results of malicious scripts.
Messages from visitors can carry little useful information and make a panic: “I opened your site, and he got me aaaaaaaaa, yyyyyyy, yyyy -y and offers rotten fruit at wholesale prices . " No problem page, no information about the device or browser.
So step one: find the problem. Tips may look obvious, but experience has shown that when it comes to real problems, many users and webmasters get lost and don’t know where to start. Start with the simplest:
- Open the site on your smartphone and see if you will get to another resource.
We recommend checking your site by going to it from Google search results on your smartphone. With today's diversity in the mobile device market, it is easier to debug using mobile device emulation in computer browsers. This feature is supported by Chrome , Firefox and Safari . In the latter case (Safari), you will need to open the browser settings and check the box “Show the menu“ Development ”in the menu bar”. - Read Visitor Reviews
Users may not see your site as you do. Someone has an old browser, someone has a mountain of extensions (they can also be attacked and start shoving ads / redirect users). Always read the reviews of visitors and pay attention to their complaints in order to identify problems in time. If required, ask clarifying questions, ask to send a screenshot or tell you exactly how the user got on the problem page. - Track visitors and analyze site statistics
Unusual actions of mobile users can be detected by studying web analytics data. Statistic is a powerful tool that allows you to identify problems where single checks and tests do not show anything. For example, if the average time spent on the site by the owners of mobile devices (and only them) has drastically decreased - this may be caused by the redirection.
To immediately find out about significant changes in the behavior of mobile users, you can set up special alerts in Google Analytics .
Try creating an alert about a sharp decrease in the time spent by mobile visitors to the site, or a decrease in their number. It should be remembered that significant changes in these indicators are not always the direct result of covert redirection, but a decline in attendance is still worth exploring. You didn't just do the site like that?

A hidden redirect for mobile users was found on my site. What to do?
Suppose you found a problem? What's next? How to deal with it? Step two: isolate the source of the problem. Sources of redirection can be two - external or internal effects.
In the first case, someone got access to your site (vulnerabilities to popular engines are regularly found and do not always close quickly). In the second, you, unwittingly, set a "time bomb" by inserting some script without checking its contents. Optionally, the site's engine could independently update items from any repository that was hacked. In any case, the algorithm is the same to eliminate such problems.
- Check if the site is hacked
Open the Security Issues section of the Search Console: if we detect hacking, inside you will find the corresponding alert.
In addition, it is worth exploring additional information about typical signs of hacked sites and examples from our practice . If you use any engine or framework - see the news of the corresponding community, perhaps not only you have encountered a problem. - Check if there are any other scripts and elements on the site.
If your site is not hacked, check to see if there are any third-party scripts or elements that perform redirects. To do this, follow these steps:- Attention! Before making any changes to a working site, create a backup copy of the site, check its performance.
- Find the page where users are redirected. If there are other people's scripts and elements on it, feel free to delete them one by one.
- After each deletion, check from a mobile device or via an emulator whether redirection occurs.
- After localizing the element responsible for hidden forwarding, remove it from all pages. If the element is critical and necessary for the functioning of the site - ask its supplier to help you with debugging.
- Attention! Before making any changes to a working site, create a backup copy of the site, check its performance.
We protect the site
Step three: prevent repetition. Everything is simple here. You found the reason for the redirect - script, element, module, whatever. If you know where it came from - perhaps you should stop using this source of extensions. If not, check the list of known vulnerabilities for your engine or framework, a set of libraries. Perhaps the developers managed to release urgent updates.
It is not necessary to exclude the human factor. If there was no hacking and you did not place the scripts / libraries / elements, and they appeared - look at the site access history, perhaps, the initiative moderators or content administrators could intentionally or unintentionally infect the site.
Check permissions to read / write to certain folders; if writing is not required - set the read only attribute, it will prevent intruders and malware from entering through a narrow loophole to register in working folders and increase privilege levels.
Use Search Console
If a user is redirected to other pages in order to show content other than the one shown in the search results, this is a violation of Google’s webmaster recommendations. Read more about hidden redirects here .
The Google search quality assessment team can take action on these sites, such as removing a URL from our index. If this happens, you, as the site owner, will see the corresponding alerts in the Search Console. This is just one of the reasons why we recommend that you register an account in the Search Console. The service itself is extremely flexible and allows not only to receive timely notification of problems, but also to analyze the current state of the site, as well as to send requests to Google to re-check. Fast, convenient, and most importantly - in one place.
One more thing
Choose advertisers who will not direct your visitors to unexpected pages. If you are seeking to develop trust relationships in the industry - read the recommendations for working in advertising networks. You can start by looking at the IAB site quality guidelines .
There are many ways to monetize content for mobile devices, providing a high level of convenience for users and not leading to the removal of your site from search results. Use them.
If you have questions or comments on mobile redirects, leave them here or ask them on the webmaster forum or in our webmaster community on Google+ .
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/269951/
All Articles