Digest: What we taught the search for this summer
Hi, Habr! Chickens are known to count in the fall. Autumn is in full swing, let's see what we have taught Google search for this summer.

Search development takes place in two directions. One of them you do not see - it is an internal change, a secret sealed, the holy of holies and all that. It is there that magic is created, words are recognized , voice requests are processed, pictures, videos and music are searched for and located.
')
The second direction is that you can personally observe user interfaces and interaction tools with the Google search service. Today we will talk about these improvements, what if someone missed?
140 characters per post can hold surprisingly a lot of information. Extremely simple and minimalist at the start, the service is now overgrown with features and unites the whole world, is one of the fastest "news agencies", helps people in the most unexpected situations (including warning of emergencies). Google search allows you to receive results directly from this social network directly in the search results in the form of cards.
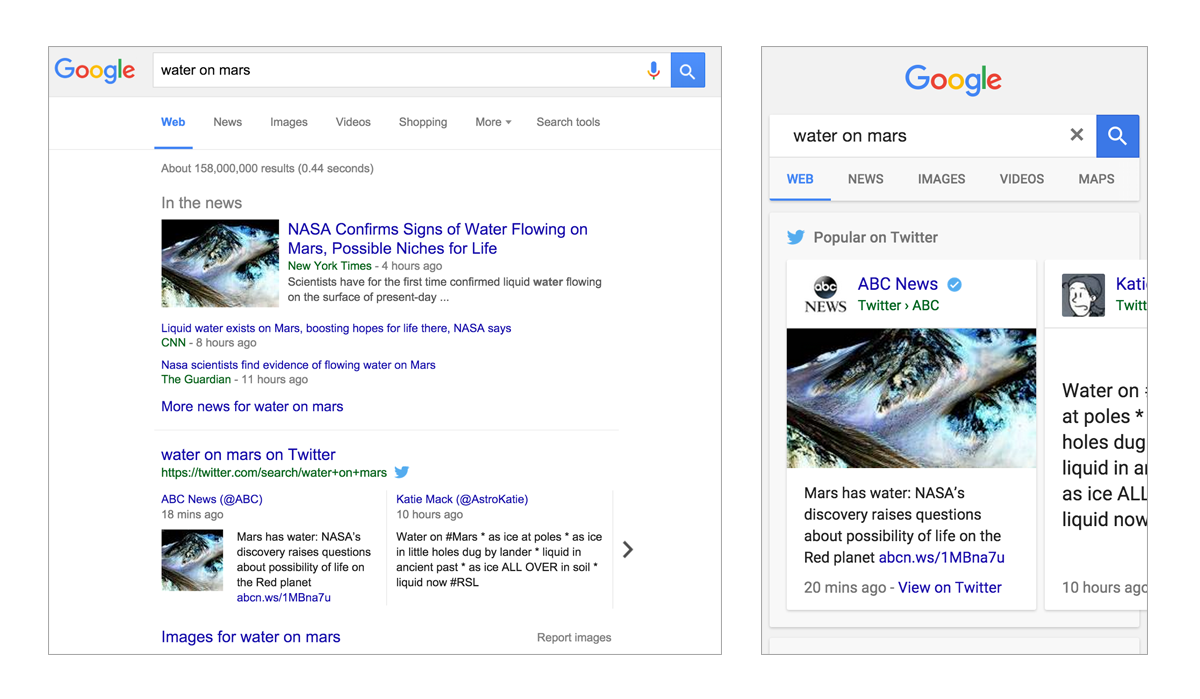
Requests like% interest_ object% Twitter result in the latest entries from the corresponding account, if one exists. And requests for popular hashtags allow you to view the latest entries, without going to the web version of Twitter or to the corresponding applications.
Introduced at the end of May for some languages. While the Russian language is not among them.
And again, mobile platforms. Convenience of working on a small diagonal (and even without a physical keyboard, with one hand, on the go or in conditions that are clearly far from “sit back and work calmly”) has always been a hot issue. Multitasking is good, and convenient and contextual multitasking is even better.
With Google Now on Tap, you can not switch between applications, but call a mobile search from any screen and on top of almost any task. The application will be paused and you will not lose the entered information, current status and position on the screen.
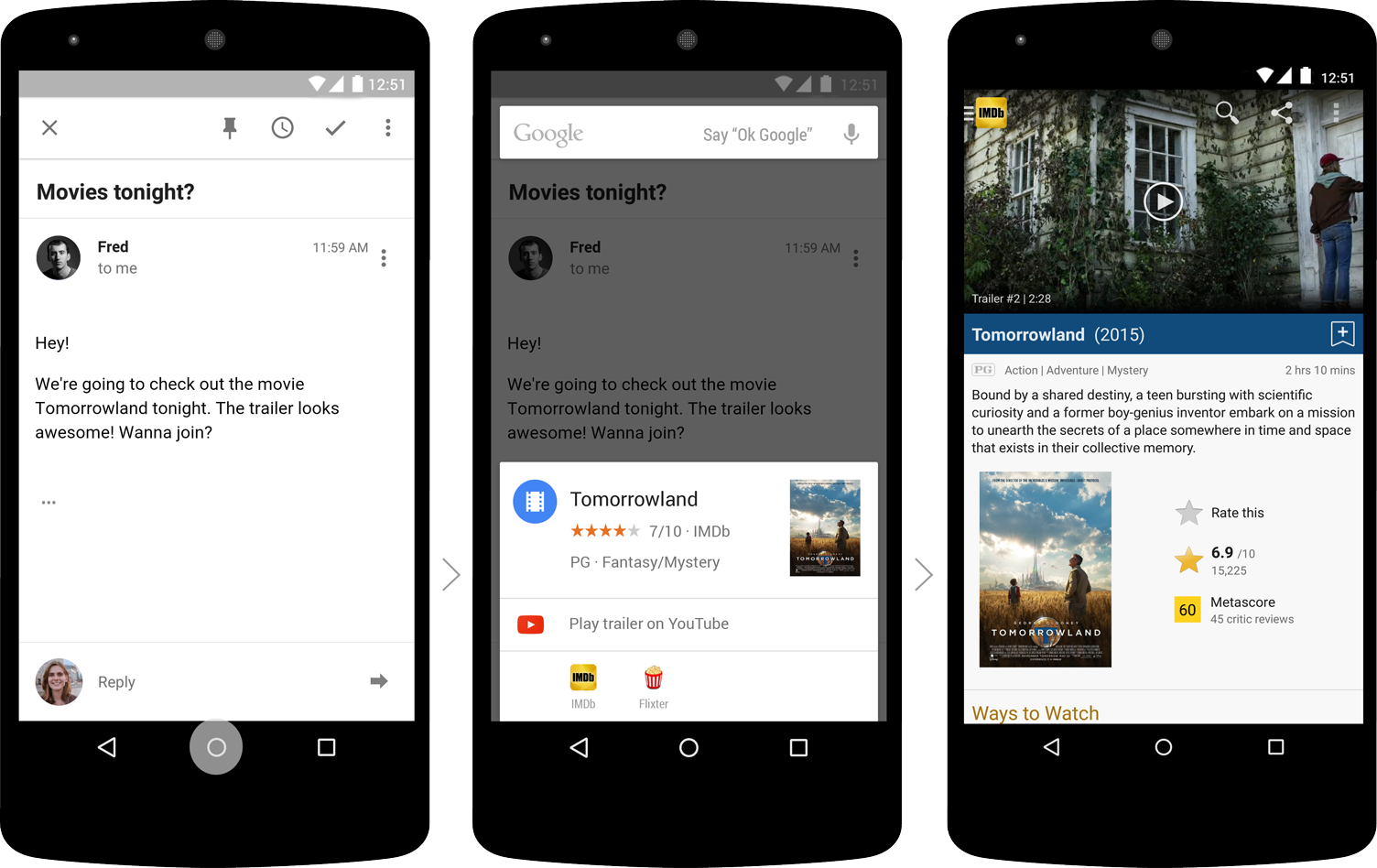
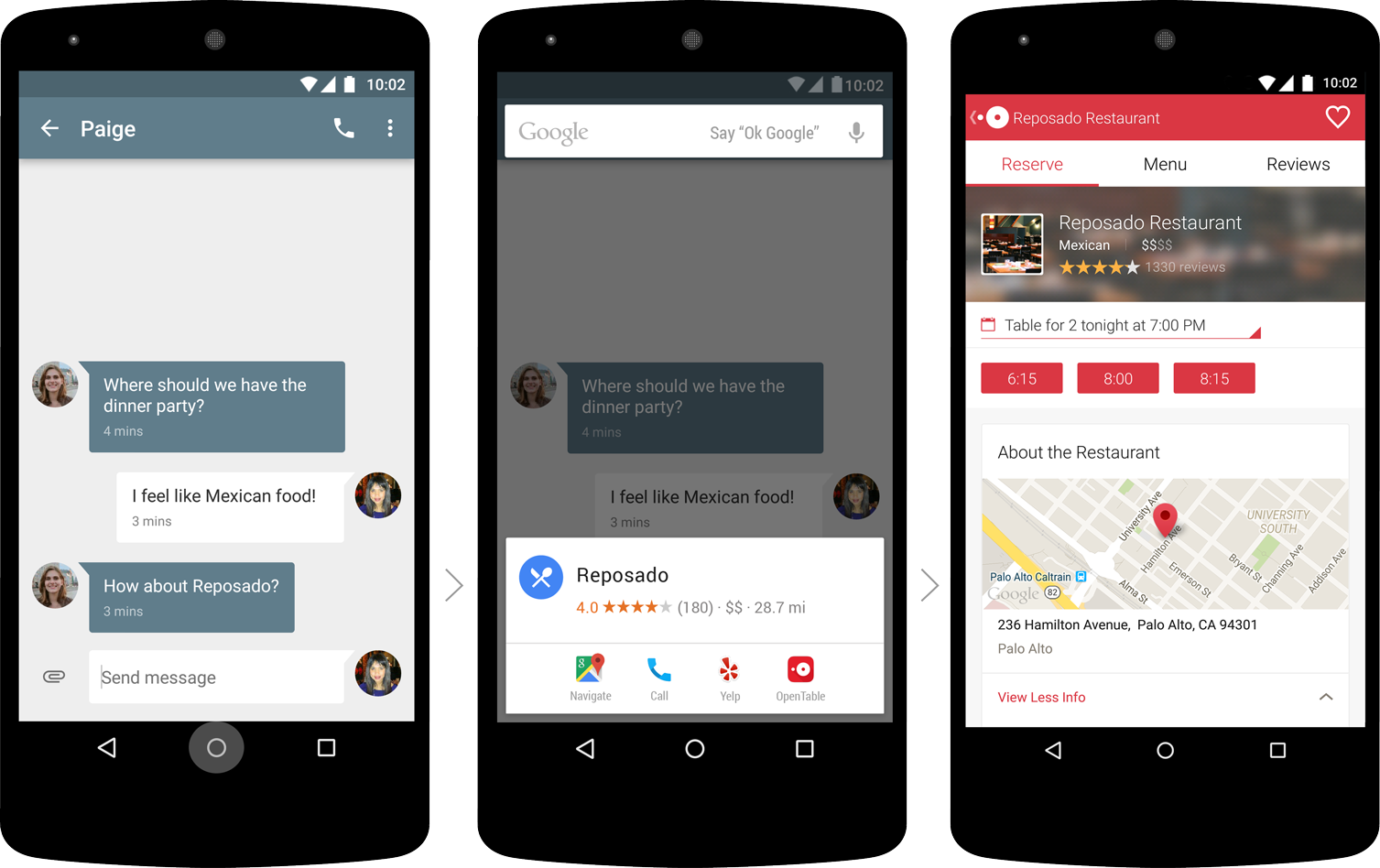
The context from Now knows how to interact with applications installed on your smartphone. For example, you “paused” correspondence with friends, using Now on Tap, found a restaurant in which you want to meet in the evening. If you have applications that can book tables, and search results can interact with them, you can still use them without leaving the “main” screen.
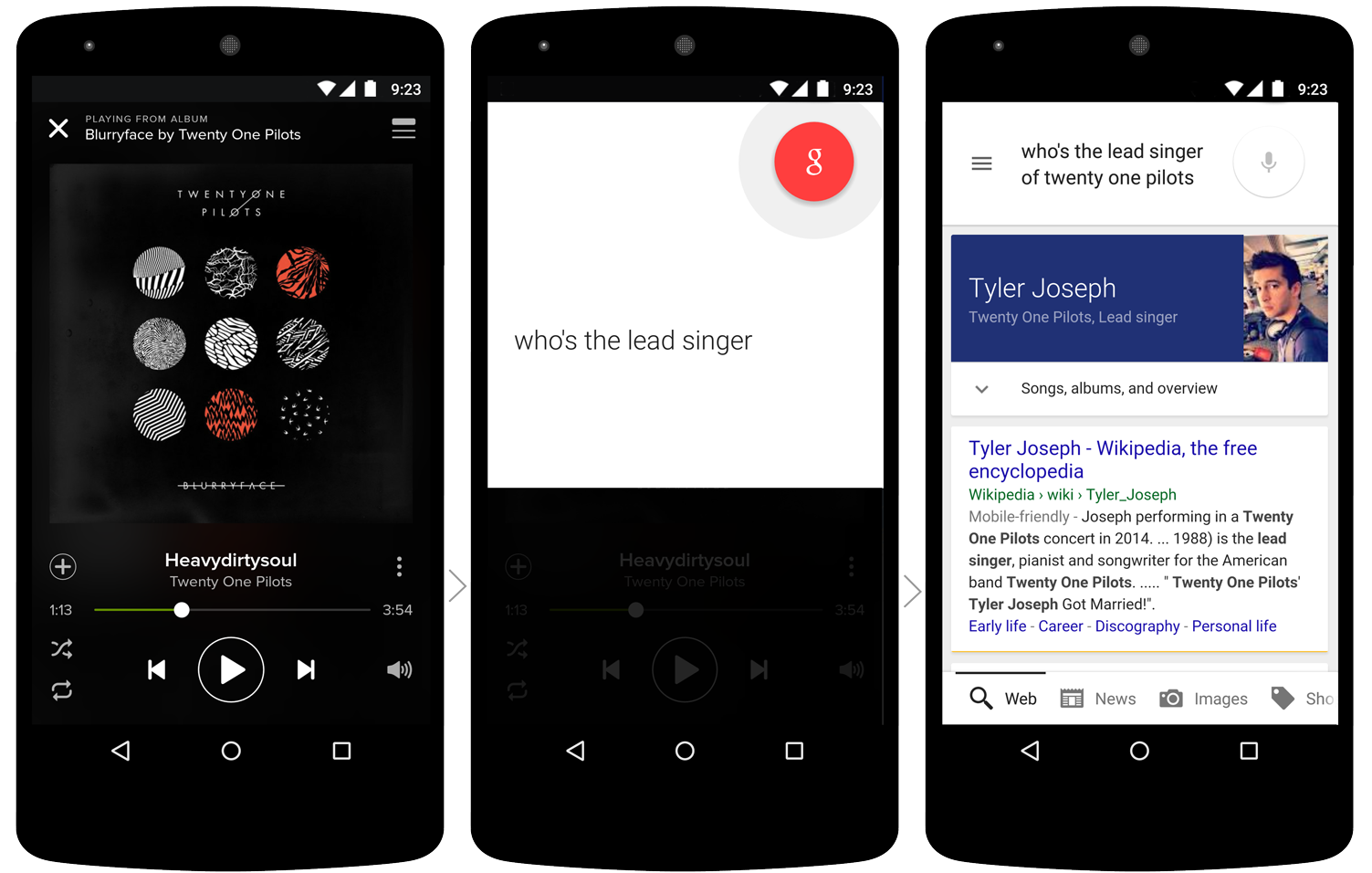
Another example is working with the Spotify streaming player. Do you have any composition, and you want to know more about the vocalist of the group? Just use the context from Google Now. Ask "Who is the vocalist of the group". He will independently take the rest of the information from the launch context: in this case, from the Spotify player.
A small change to make your smartphone smarter.It will be available for English with the release of Android M.
We have not forgotten about iOS users. Call Now on Tap on the iPhone will not work, but we have taught Google search to work with the data of iOS applications. This feature is present for more than two years on Android devices, but it only came out with iOS with the release of the eighth version of the Apple OS.
At the time of launch (early June), a search within the application content was available for a variety of reasons in a limited number of applications. In the US, Google Search can interact with Eat24, Free Dictionary, Huffington Post, OpenTable, Pinterest, SeatGeek, Slideshare, Tapatalk, Yellow Pages, YouTube and Zillow, some applications are also supported in Brazil, Germany, Japan and Australia. In addition, dozens of other (most popular and useful) applications are on the way, including in other countries. If you are an iOS application developer and want to implement a similar feature in your homepage - at the end of this post on our blog there is a brief guide on how to integrate Google search on iOS.
The interaction between applications in Android is much freer, so we were able to teach Google Now (which perfectly recognizes simple human speech) to send text messages in the most popular messengers. Just tell me who and what to send, and the rest of the Google application will do for you:
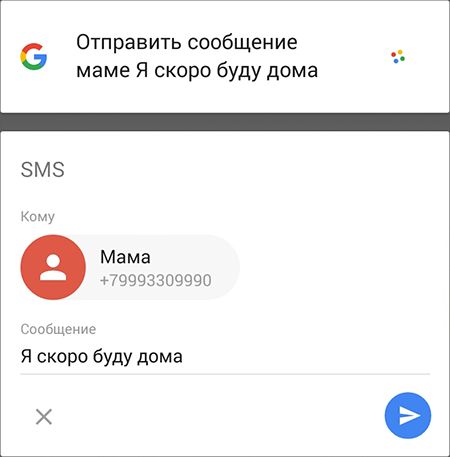
Currently WhatsApp, Viber, Telegram, NextPlus and WeChat are supported. At the time of launch (end of July), this feature worked only with the English language, now Vk and GetTaxi work for the Russian language 100%. The list of partners is gradually expanding, we will definitely tell about the possibilities of these interactions separately.
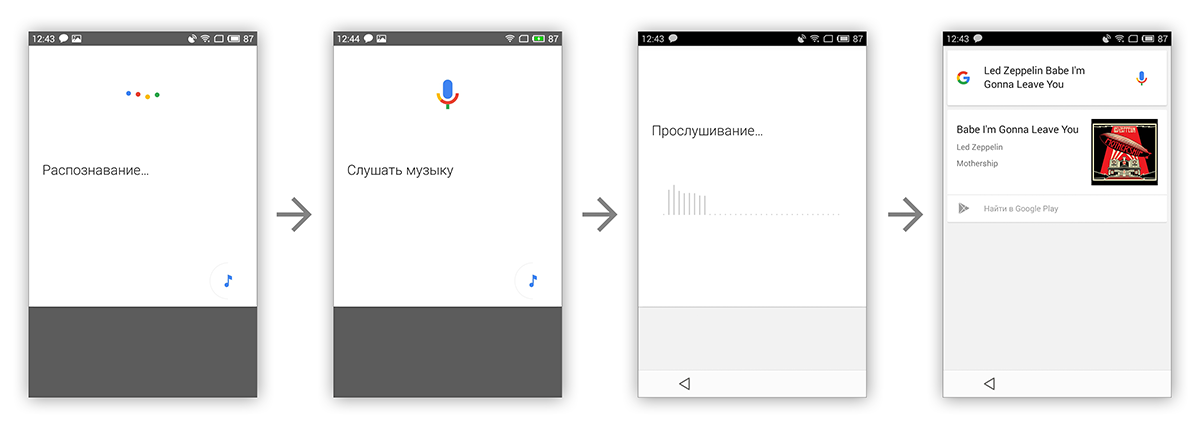
PS: And even earlier, in the spring, we taught the application cards to interact with voice search at the query level. For example, “shazam this song” will launch the automatic recognition of music using the Shazam service, of course, if you consider the availability of the corresponding application and the latest version of Google Search on your smartphone * .
* - To work correctly, you need to switch the Google Voice Search to English as the main language. If you don’t have Shazam, you have chosen Russian as the main language, and a great unfamiliar composition is playing around, just say “Ok, Google!”. Google search itself will understand that there is music somewhere. All you have left is to click on the “note” in the lower-right corner.
Update our service to reduce links Goo.gl. to complete the beautiful picture of the integration of search and mobile applications. We added support for cross-platform application integration. For example, you want to share your location using Google Maps. You click the Share button, special APIs generate an abbreviated link, and when the recipient clicks on it, the magic will begin. The Goo.gl service will determine the user's platform, whether the corresponding application is installed on the device, and, if so, will open the result in it. Simple, convenient, in one click.
As you all have noticed, the Google logo, which has remained virtually unchanged since 1999, was fully updated on September 1, 2015 . A new, clean and simple visual style should fit organically into the Material Design concept, and our key product, Google Search, should be in line with the modern corporate style. We updated Google Now so that it not only conforms to the Material Design in spirit, but also fully reflects all the modern features of both the search engine and the visual language, on the basis of which Android 5.0 and 6.0 are built.
If you, as a Google Search user, welcome new features, then you shouldn’t forget about those who implement pleasing features in applications using our technologies: about developers. There are a number of complex tasks that are not corrected in a minute, they require the preparation of new standards or a complete revision of current algorithms of work. However, on the street "boring technologies" today is a holiday.
The development of localized domains required the appropriate adaptation of various non-Unicode elements of the Internet, and work within Google itself. Now more and more new gTLDs are being introduced (generic Top-Level Domain - Common Top Level Domain), and we made sure that Google search responded to them adequately.
For example, new gTLDs do not affect the ranking of search results. It makes no difference whether you are looking for a site in the domain zone .com, .org or some new type of .BRAND. Keywords within the domain itself will not affect the results and order of issue.
We also took care of the support of the Japanese and Chinese national alphabets. You can verify this by specifying the search query [site: み ん な]. Unfortunately, there are a number of restrictions imposed on the site owners themselves (for example, all links must be set in Unicode, so that the search engine can interpret them normally as links).
By the way, there is no difference in the format in which the links will be (nationally, using Unicode, or given to ASCII via Punycode ), and the results, again, will not affect the format of the links.
All other gTLD issues (mainly related to geographically-related domains (for example,. London)) either do not affect or affect the search results slightly. We try not to use information from the domain name, but to bind the results to geotarget, if possible. Questions on multilingual and multiregional sites are addressed in our Help Center .
Transferring a site to a new TLD is no different from transferring it to another domain, and these issues are also discussed in detail in our Help Center . Most importantly, do not forget that the processing of such results takes some time, and your old email addresses may be on business cards given to someone, so ensure appropriate measures for sending mail to new domains.
Google search is famous for its auto-completion queries. How many internet memes and funny pictures in the past have generated strange requests from people who have become available to the public through auto substitution?
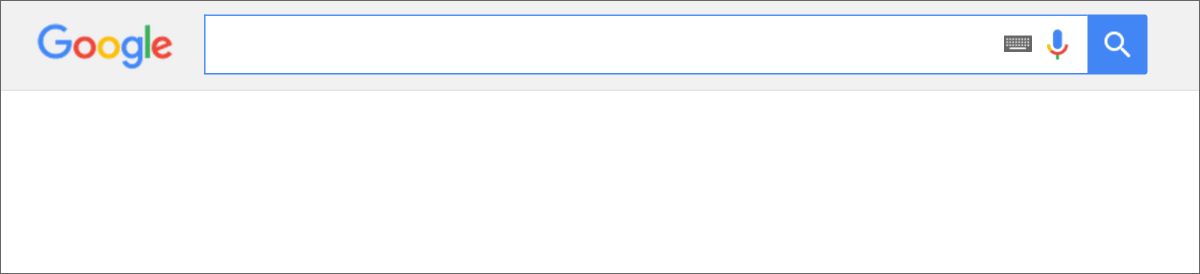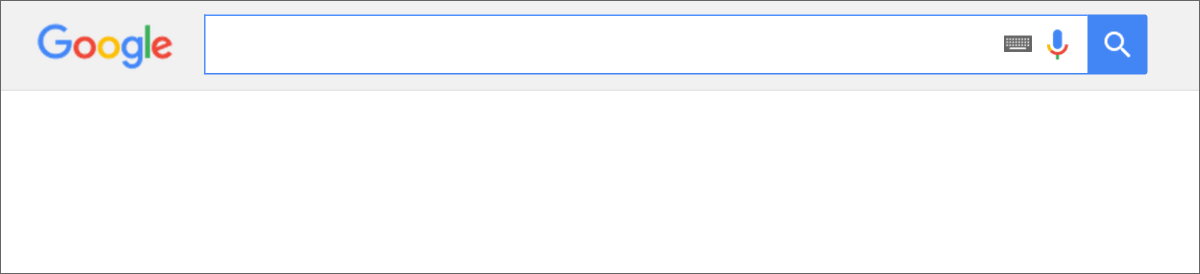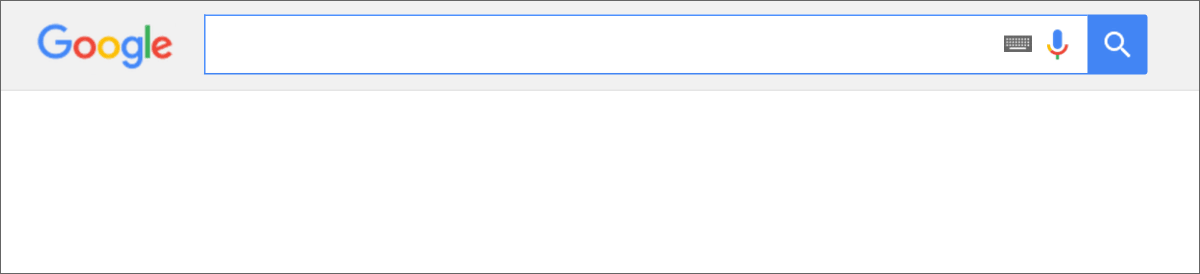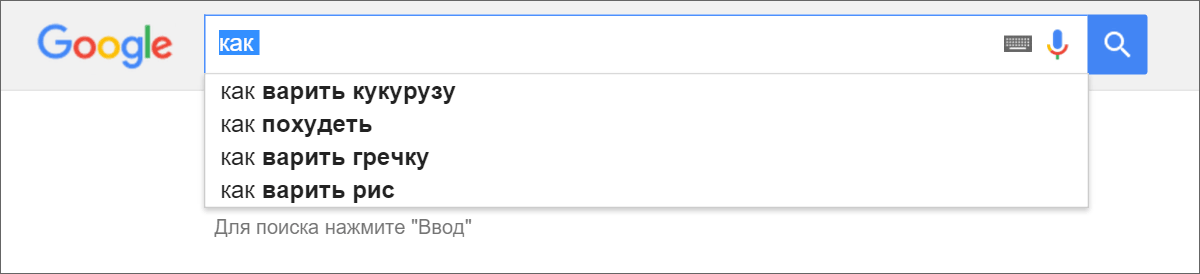
In fact, of course, the auto-completion algorithms are not designed for entertainment purposes, but to simplify our life with you.
For years, this feature had closed internal APIs, which some third-party developers used through unofficial tools developed by reverse engineering. They allowed the use of search substitution, regardless of Google Search itself.
At times, this use of undocumented APIs led to interesting results and made it possible to create really convenient links between services. A vivid example of how resourceful programmers use our technologies have pushed for the opening of some internal APIs for interacting with third-party applications (for example, as happened with the Google Maps API after we saw amazing results on connecting Google Maps data and other sources).
Nevertheless, all users of the "unofficial" API bear the risks due to the fact that the API can be changed or disabled without warning, and now it is one of these cases.
We created autocompletion as an element of search, and never meant to use it in isolation from search queries. The main value of auto-completion data is that they (the data) are related to search queries, and do not exist by themselves.
Since August 10, we have restricted unauthorized access to internal auto-completion APIs. For those developers and site owners who want to use auto-completion, we are ready to offer an alternative solution. Our Google Custom Search Engine service allows you to use all the features of auto-completion queries along with site search. For everyone who is already using Google CSE, no changes will occur, and everyone who wants to join this technology will be welcome here .
Users are looking for information, not a site. The more information on your site is correct for the user, the higher is your site in search results. Relevance of information, the relevance of search results - something that we are really proud of in Google, but we do not forget about webmasters.
In August, we updated Google Search Analytics in the Search Console, adding the ability to access data through new APIs . We hope this helps webmasters to collect important statistics in a convenient way for them. If you have already used any Google APIs, then working with the Search Analytics API is easy for you. If you are new to this plan, then especially for you we have a page with a brief guide on how to use the API and examples in Python.
For example, you can find out how much fresh data from your site is seen by Google Search, the top 10 pages of a site, the top 10 of all requests limited by platform and / or region, and much more.
We are curious about what will come out of this small experiment, perhaps, new services will be born, or the ranking of the largest sites that have optimized their work due to detailed and easily accessible statistics will change. Most importantly, remember that search engine optimization should lead to an improvement in users finding information, and not to a meaningless increase in the mention of keywords and geotagging. After all, we are trying for the sake of users, and not for the sake of increasing entropy? ;)
As you can see, the main achievements of this summer relate to improving the user experience on mobile platforms and facilitating access to search services on them. Direct integration with applications, contextual multitasking and intelligent interaction with content - everything so that the search is easier and more accessible.
In addition, we solved a number of important issues in the area of supporting other languages, and, of course, provided new APIs for collecting statistics.

Search development takes place in two directions. One of them you do not see - it is an internal change, a secret sealed, the holy of holies and all that. It is there that magic is created, words are recognized , voice requests are processed, pictures, videos and music are searched for and located.
')
The second direction is that you can personally observe user interfaces and interaction tools with the Google search service. Today we will talk about these improvements, what if someone missed?
Mobile search and results from Twitter
140 characters per post can hold surprisingly a lot of information. Extremely simple and minimalist at the start, the service is now overgrown with features and unites the whole world, is one of the fastest "news agencies", helps people in the most unexpected situations (including warning of emergencies). Google search allows you to receive results directly from this social network directly in the search results in the form of cards.

Requests like% interest_ object% Twitter result in the latest entries from the corresponding account, if one exists. And requests for popular hashtags allow you to view the latest entries, without going to the web version of Twitter or to the corresponding applications.
Introduced at the end of May for some languages. While the Russian language is not among them.
Google Now on Tap aka Context from Google Now
And again, mobile platforms. Convenience of working on a small diagonal (and even without a physical keyboard, with one hand, on the go or in conditions that are clearly far from “sit back and work calmly”) has always been a hot issue. Multitasking is good, and convenient and contextual multitasking is even better.
With Google Now on Tap, you can not switch between applications, but call a mobile search from any screen and on top of almost any task. The application will be paused and you will not lose the entered information, current status and position on the screen.

The context from Now knows how to interact with applications installed on your smartphone. For example, you “paused” correspondence with friends, using Now on Tap, found a restaurant in which you want to meet in the evening. If you have applications that can book tables, and search results can interact with them, you can still use them without leaving the “main” screen.

Another example is working with the Spotify streaming player. Do you have any composition, and you want to know more about the vocalist of the group? Just use the context from Google Now. Ask "Who is the vocalist of the group". He will independently take the rest of the information from the launch context: in this case, from the Spotify player.

A small change to make your smartphone smarter.
Search within iDevice applications
We have not forgotten about iOS users. Call Now on Tap on the iPhone will not work, but we have taught Google search to work with the data of iOS applications. This feature is present for more than two years on Android devices, but it only came out with iOS with the release of the eighth version of the Apple OS.
At the time of launch (early June), a search within the application content was available for a variety of reasons in a limited number of applications. In the US, Google Search can interact with Eat24, Free Dictionary, Huffington Post, OpenTable, Pinterest, SeatGeek, Slideshare, Tapatalk, Yellow Pages, YouTube and Zillow, some applications are also supported in Brazil, Germany, Japan and Australia. In addition, dozens of other (most popular and useful) applications are on the way, including in other countries. If you are an iOS application developer and want to implement a similar feature in your homepage - at the end of this post on our blog there is a brief guide on how to integrate Google search on iOS.
Send messages using voice in Google search
The interaction between applications in Android is much freer, so we were able to teach Google Now (which perfectly recognizes simple human speech) to send text messages in the most popular messengers. Just tell me who and what to send, and the rest of the Google application will do for you:

Currently WhatsApp, Viber, Telegram, NextPlus and WeChat are supported. At the time of launch (end of July), this feature worked only with the English language, now Vk and GetTaxi work for the Russian language 100%. The list of partners is gradually expanding, we will definitely tell about the possibilities of these interactions separately.
PS: And even earlier, in the spring, we taught the application cards to interact with voice search at the query level. For example, “shazam this song” will launch the automatic recognition of music using the Shazam service, of course, if you consider the availability of the corresponding application and the latest version of Google Search on your smartphone * .
* - To work correctly, you need to switch the Google Voice Search to English as the main language. If you don’t have Shazam, you have chosen Russian as the main language, and a great unfamiliar composition is playing around, just say “Ok, Google!”. Google search itself will understand that there is music somewhere. All you have left is to click on the “note” in the lower-right corner.

Short links goo.gl and mobile apps
Update our service to reduce links Goo.gl. to complete the beautiful picture of the integration of search and mobile applications. We added support for cross-platform application integration. For example, you want to share your location using Google Maps. You click the Share button, special APIs generate an abbreviated link, and when the recipient clicks on it, the magic will begin. The Goo.gl service will determine the user's platform, whether the corresponding application is installed on the device, and, if so, will open the result in it. Simple, convenient, in one click.
New design of google app
As you all have noticed, the Google logo, which has remained virtually unchanged since 1999, was fully updated on September 1, 2015 . A new, clean and simple visual style should fit organically into the Material Design concept, and our key product, Google Search, should be in line with the modern corporate style. We updated Google Now so that it not only conforms to the Material Design in spirit, but also fully reflects all the modern features of both the search engine and the visual language, on the basis of which Android 5.0 and 6.0 are built.
Boring things
If you, as a Google Search user, welcome new features, then you shouldn’t forget about those who implement pleasing features in applications using our technologies: about developers. There are a number of complex tasks that are not corrected in a minute, they require the preparation of new standards or a complete revision of current algorithms of work. However, on the street "boring technologies" today is a holiday.
Support for new top-level domains
The development of localized domains required the appropriate adaptation of various non-Unicode elements of the Internet, and work within Google itself. Now more and more new gTLDs are being introduced (generic Top-Level Domain - Common Top Level Domain), and we made sure that Google search responded to them adequately.
For example, new gTLDs do not affect the ranking of search results. It makes no difference whether you are looking for a site in the domain zone .com, .org or some new type of .BRAND. Keywords within the domain itself will not affect the results and order of issue.
We also took care of the support of the Japanese and Chinese national alphabets. You can verify this by specifying the search query [site: み ん な]. Unfortunately, there are a number of restrictions imposed on the site owners themselves (for example, all links must be set in Unicode, so that the search engine can interpret them normally as links).
By the way, there is no difference in the format in which the links will be (nationally, using Unicode, or given to ASCII via Punycode ), and the results, again, will not affect the format of the links.
All other gTLD issues (mainly related to geographically-related domains (for example,. London)) either do not affect or affect the search results slightly. We try not to use information from the domain name, but to bind the results to geotarget, if possible. Questions on multilingual and multiregional sites are addressed in our Help Center .
Transferring a site to a new TLD is no different from transferring it to another domain, and these issues are also discussed in detail in our Help Center . Most importantly, do not forget that the processing of such results takes some time, and your old email addresses may be on business cards given to someone, so ensure appropriate measures for sending mail to new domains.
Changes to the autocomplete API
Google search is famous for its auto-completion queries. How many internet memes and funny pictures in the past have generated strange requests from people who have become available to the public through auto substitution?
Hidden text
Search line type ~ 2004

Search line type ~ 2004

In fact, of course, the auto-completion algorithms are not designed for entertainment purposes, but to simplify our life with you.
For years, this feature had closed internal APIs, which some third-party developers used through unofficial tools developed by reverse engineering. They allowed the use of search substitution, regardless of Google Search itself.
At times, this use of undocumented APIs led to interesting results and made it possible to create really convenient links between services. A vivid example of how resourceful programmers use our technologies have pushed for the opening of some internal APIs for interacting with third-party applications (for example, as happened with the Google Maps API after we saw amazing results on connecting Google Maps data and other sources).
Nevertheless, all users of the "unofficial" API bear the risks due to the fact that the API can be changed or disabled without warning, and now it is one of these cases.
We created autocompletion as an element of search, and never meant to use it in isolation from search queries. The main value of auto-completion data is that they (the data) are related to search queries, and do not exist by themselves.
Since August 10, we have restricted unauthorized access to internal auto-completion APIs. For those developers and site owners who want to use auto-completion, we are ready to offer an alternative solution. Our Google Custom Search Engine service allows you to use all the features of auto-completion queries along with site search. For everyone who is already using Google CSE, no changes will occur, and everyone who wants to join this technology will be welcome here .
New Google Search Analytics
Users are looking for information, not a site. The more information on your site is correct for the user, the higher is your site in search results. Relevance of information, the relevance of search results - something that we are really proud of in Google, but we do not forget about webmasters.
In August, we updated Google Search Analytics in the Search Console, adding the ability to access data through new APIs . We hope this helps webmasters to collect important statistics in a convenient way for them. If you have already used any Google APIs, then working with the Search Analytics API is easy for you. If you are new to this plan, then especially for you we have a page with a brief guide on how to use the API and examples in Python.
For example, you can find out how much fresh data from your site is seen by Google Search, the top 10 pages of a site, the top 10 of all requests limited by platform and / or region, and much more.
We are curious about what will come out of this small experiment, perhaps, new services will be born, or the ranking of the largest sites that have optimized their work due to detailed and easily accessible statistics will change. Most importantly, remember that search engine optimization should lead to an improvement in users finding information, and not to a meaningless increase in the mention of keywords and geotagging. After all, we are trying for the sake of users, and not for the sake of increasing entropy? ;)
Summing up
As you can see, the main achievements of this summer relate to improving the user experience on mobile platforms and facilitating access to search services on them. Direct integration with applications, contextual multitasking and intelligent interaction with content - everything so that the search is easier and more accessible.
In addition, we solved a number of important issues in the area of supporting other languages, and, of course, provided new APIs for collecting statistics.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/269873/
All Articles