Turn a group of surveillance cameras into a botnet? Nothing is easier
For a long time, information security experts say that modern IoT devices and systems are poorly protected from outside interference. Some of them are not protected at all, and even a schoolboy can hack a similar gadget or a whole system. About a year ago, experts from Proofpoint discovered a botnet, the main elements of which was the home "smart" technology. As it turned out, the botnet included televisions and even one refrigerator.
The hacking in question was carried out between December 23, 2013 and January 6, 2014. The gadgets that make up the botnet, three times a day, sent letters in packages of 750 thousand at a time with 100 thousand devices (yes, it was a big botnet) to enterprises and individuals around the world. But the easiest thing for intruders, as it turned out, is to use to create a botnet not a refrigerator or a TV, but a security camera connected to the Network.
')
At the same time, security cameras are among the most common IoT devices. Reports have already been published on the Web, according to which last year around 245 million surveillance cameras operated around the world. And this is only those that are installed professionally, about which something is known. Besides them, there are still millions of other cameras installed, figuratively speaking, by housewives who know nothing about security and, accordingly, did not use security settings for their devices.
Based on the foregoing, it is not at all surprising that botnets consisting of surveillance cameras are among the most active. So, recently it became known about the attack type «HTTP flood», with a peak of 20,000 requests per second. This attack was decided to be studied by the specialists of Incapsula , who were surprised to find that the cameras installed near the company's office were part of the botnet.
After a detailed study, it also turned out that default login / password connections are used to access the settings of most cameras (which is not at all surprising, the scale of this problem is huge). One of the cameras was installed on a shopping center, five minutes drive from the company's office. Experts helped the owners of the center to set up the cameras correctly, but there were still dozens and hundreds of devices whose owners could not help with all their desire.
Some details of the attack
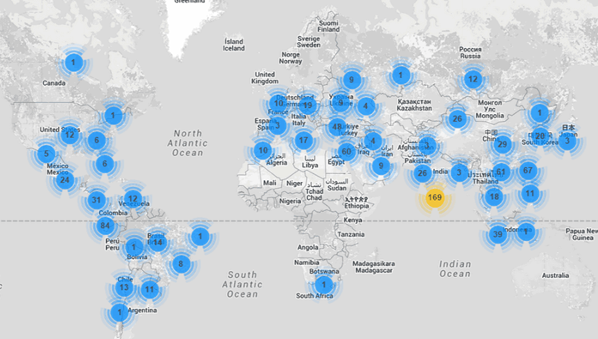
As mentioned above, the attack consisted of using HTTP GET floods with a peak of 20,000 requests. This traffic generated a total of 900 surveillance cameras from around the globe. The target of the attack is a large cloud service serving millions of users around the world.
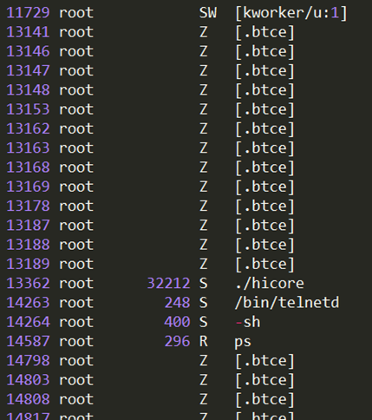
All hacked devices worked on Linux with BusyBox - a package of Unix utilities, assembled into a single package, and designed for devices with limited resources.
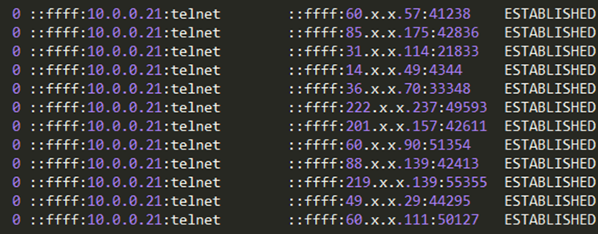
Malware turned out to be an ELF binary for ARM, one of the variants of ELF_BASHLITE . This malware scans network devices with BusyBox, looking for Telnet / SSH services that are easy to hack using dictionary brute-force.
In this case, maleware had the ability to independently launch HTTP Get flood DDoS attacks from compromised devices.
Few requests
$ strings .btce @ #! user account login login changeme 1234 12345 123456 default pass password:>% $ # 31.169.77.242 (null) / bin / sh / proc / cpuinfo BOGOMIPS PING% d.% d.% d.% d% d.% d.% d.0 ogin: assword: ncorrect / bin / busybox; echo -e '\ 147 \ 141 \ 171 \ 146 \ 147 \ 164' gayfgt multi-call REPORT% s:% s:% s REPORT % s:% s: Mozilla / 4.0 (compatible; MSIE 6.0; MSIE 5.5; Windows NT 5.0) Opera 7.02 Bork-edition [en] Mozilla / 4.0 (compatible; MSIE 6.0; Windows NT 5.1) Mozilla / 4.0 (compatible; MSIE 6.0; Windows NT 5.1; SV1) Mozilla / 4.0 (compatible; MSIE 6.0; Windows NT 5.1; SV1; FunWebProducts; .NET CLR 1.1.4322; PeoplePal 6.2) Mozilla / 4.0 (compatible; MSIE 6.0; Windows NT 5.1; SV1; MRA 5.8 (build 4157); .NET CLR 2.0.50727; AskTbPTV / 5.11.3.15590) Mozilla / 4.0 (compatible; MSIE 7.0; Windows NT 5.1; SV1; .NET CLR 2.0.50727) Mozilla / 4.0 (compatible; MSIE 7.0 ; Windows NT 5.1; Trident / 4.0; .NET CLR 1.1.4322) Mozilla / 4.0 (compatible MSIE 7.0; Windows NT 5.1; Trident / 4.0; .NET CLR 2.0.50727; .NET CLR 3.0.4506.2152; .NET CLR 3.5.30729) Mozilla / 4.0 (compatible; MSIE 8 .0; Windows NT 6.0; Trident / 4.0; Mozilla / 4.0 (compatible; MSIE 6.0; Windows NT 5.1; SV1); .NET CLR 3.5.30729) Mozilla / 5.0 (compatible; MSIE 9.0; Windows NT 6.1; Trident / 5.0) Mozilla / 5.0 (compatible; MSIE 9.0; Windows NT 6.1; WOW64; Trident / 5.0) Mozilla / 5.0 (iPad; CPU OS 5_1_1 like Mac OS X) AppleWebKit / 534.46 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version / 5.1 Mobile / 9B206 Safari / 7534.48.3 Mozilla / 5.0 (iPhone; CPU iPhone OS 5_1_1 like Mac OS X) AppleWebKit / 534.46 (KHTML, like Gecko ) Version / 5.1 Mobile / 9B206 Safari / 7534.48.3 Mozilla / 5.0 (Linux; U; Android 2.2; fr-fr; Desire_A8181 Build / FRF91) App3leWebKit / 53.1 (KHTML, Like Gecko) Version / 4.0 Mobile Safari / 533.1 Mozilla / 5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10.6; rv: 13.0) Gecko / 20100101 Firefox / 13.0.1 Mozilla / 5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10.7; rv: 13.0) Gecko / 20100101 Firefox / 13.0.1 Mozilla / 5.0 ( Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_6_8) AppleWebKit / 534.57.2 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version / 5.1.7 Safari / 534.57.2 Mozilla / 5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_6_8) AppleWebKit / 536.11 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome / 20.0.1132.47 Safari / 536.11 Mozilla / 5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac O S X 10_6_8) AppleWebKit / 536.5 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome / 19.0.1084.56 Safari / 536.5 Mozilla / 5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_7_4) AppleWebKit / 534.57.2 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version / 5.1.7 Safari / 534.57.2 Mozilla / 5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_7_4) AppleWebKit / 534.57.5 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version / 5.1.7 Safari / 534.57.4 Mozilla / 5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_7_4) AppleWebKit / 536.11 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome / 20.0.1132.47 Safari / 536.11 Mozilla / 5.0 (Macintosh; Mac OS X 10_7_4 ) AppleWebKit / 536.5 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome / 19.0.1084.56 Safari / 536.5 Mozilla / 5.0 (Windows NT 5.1) AppleWebKit / 536.11 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome / 20.0.1132.47 Safari / 536.11 Mozilla / 5.0 (Windows NT 5.1 ) AppleWebKit / 536.5 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome / 19.0.1084.56 Safari / 536.5 Mozilla / 5.0 (Windows NT 5.1; rv: 12.0) Gecko / 20100101 Firefox / 12.0 Mozilla / 5.0 (Windows NT 5.1; rv: 13.0) Gecko / 20100101 Firefox / 13.0.1 Mozilla / 5.0 (Windows NT 5.1; rv: 5.0.1) Gecko / 20100101 Firefox / 5.0.1 Mozilla / 5.0 (Windows NT 6.0) AppleWebKit / 535.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome / 13.0.782.112 Safari / 535.1 Mozilla / 5.0 (Windows NT 6.0; rv: 13.0) Gecko / 20 100101 Firefox / 13.0.1 Mozilla / 5.0 (Windows NT 6.1) AppleWebKit / 536.11 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome / 20.0.1132.47 Safari / 536.11 Mozilla / 5.0 (Windows NT 6.1) AppleWebKit / 536.5 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome / 19.0.1084.56 Safari / 536.5 Mozilla / 5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; rv: 12.0) Gecko / 20100101 Firefox / 12.0 Mozilla / 5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; rv: 13.0) Gecko / 20100101 Firefox / 13.0.1 Mozilla / 5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; rv: 2.0b7pre) Gecko / 20100921 Firefox / 4.0b7pre Mozilla / 5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; rv: 5.0) Gecko / 20100101 Firefox / 5.02 Mozilla / 5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; WOW64) AppleWebKit / 535.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome / 13.0.782.112 Safari / 535.1 Mozilla / 5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; WOW64) AppleWebKit / 536.11 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome / 20.0.1132.47 Safari / 536.11 Mozilla / 5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; WOW64) AppleWebKit / 536.11 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome / 20.0.1132.57 Safari / 536.11 Mozilla /5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; WOW64) AppleWebKit / 536.5 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome / 19.0.1084.56 Safari / 536.5 Mozilla / 5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; WOW64; rv: 12.0) Gecko / 20100101 Firefox / 12.0 Mozilla / 5.0 ( Windows NT 6.1; WOW64; rv: 13.0) Gecko / 20100101 Firefox / 13.0.1 Mozilla / 5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; WOW64; rv: 5.0) Gecko / 20100101 Firefox / 5.0 Mozilla / 5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; en-US; rv: 1.9.2) Firefox / 3.6 Mozilla / 5.0 Gecko / 20100115 (X11; Ub untu; Linux i686; rv: 13.0) Gecko / 20100101 Firefox / 13.0.1 Mozilla / 5.0 (X11; Ubuntu; Linux x86_64; rv: 13.0) Gecko / 20100101 Firefox / 13.0.1 Opera / 9.80 (Windows NT 5.1; U; en) Presto / 2.10 .229 Version / 11.60 GET /% s?% D HTTP / 1.1 Host:% s Connection: keep-alive Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate, sdch Accept: * / * Accept-Language: en-US, en; q = 0.8 User-Agent:% s Cache-Control: max-age = 0 HTTP Failed opening raw socket. Failed setting raw headers mode. Invalid flag "% s" PING PONG! GETLOCALIP My IP:% s SCANNER SCANNER ON | OFF HOLD HOLD Flooding% s:% d for% d seconds. HTTP Flooding% s:% d for% d seconds. JUNK JUNK Flooding% s:% d for% d seconds. UDP Flooding% s for% d seconds. UDP Flooding% s:% d for% d seconds. TCP Flooding% s for% d seconds. KILLATTK Killed% d. None Killed. LOLNOGTFO 8.8.8.8 / proc / net / route MAC:% 02X:% 02X:% 02X:% 02X:% 02X:% 02X BUILD% s PONG% s 2> & 1% s: __is * {_ l} (% d, % # x {locale}) / dev / null (nil) +0 - # 'I npxXoudifFeEgGaACScs hlLjztqZ CAk [S - See more at: www.incapsula.com/blog/cctv-ddos-botnet-back-yard.html# sthash.PBKyc8Hl.dpuf
Access to the hacked cameras was carried out from different places, which may indicate the work of several people.
As a conclusion
Despite the fact that this problem has been discussed more than a dozen (yes, there are a hundred) times, it remains relevant. In some even well-equipped companies, security cameras and IoT devices are treated like ordinary hardware, which you can simply install and forget.
In fact, now even irons (exaggerate, yes) are equipped with a wireless communication module. Therefore, it is better to make sure that nobody can access the conditional iron. Otherwise, then it can be painfully painful.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/269603/
All Articles