Let's Encrypt Announces IdenTrust Cross Certification
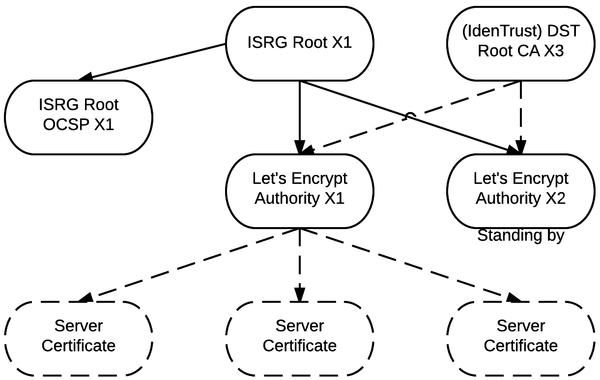
On the site of the project Let's Encrypt it was reported that on October 19, 2015, the certificate authorities “Let's Encrypt Authority X1” and “Let's Encrypt Authority X2” received cross-signatures from IdenTrust. Now certificates issued by Let's Encrypt have become trusted for all major browsers. You can verify this by accessing the page protected by Let's Encrypt's first certificate: helloworld.letsencrypt.org . If your browser does not issue a warning, then it considers the certificate of this domain to be trusted.
about cross certificates
Cross-certificate - CA certificate where the values of the “Subject” and “Publisher” fields are different. Simply put, if the CA certificate is not self-signed, then this is a cross-certificate. Cross certification is needed to build hierarchical and distributed trust models. In a hierarchical trust model, only the root CA is self-signed. He signs the CA certificates of the next level of the hierarchy, those - even one level lower, and so on. The distributed trust model implies that all CAs have self-signed certificates and are additionally cross-certified with all other CAs included in the list of this distributed trust.
The root CA “Let's Encrypt - ISRG Root X1” will be added to the trusted certification centers of browsers later, but reaching relevant agreements does not detract from the significance of the cross-certification. After all, users' browsers must be updated to update their trust lists. Without this, users for some time would still receive warnings about an untrusted certificate when visiting all sites protected by Let's Encrypt certificates.
“Let's Encrypt Authority X1” is the main one, and “Let's Encrypt Authority X2” is a backup CA in case of a catastrophe and the impossibility of using X1. Thus, the fault tolerance of the issuing CA was provided.
The private keys of the root and CA issuing CAs are stored on the HSM, which guarantees a high level of protection against theft of keys or unauthorized access to them.
about HSM
The HSM or Hardware Security Module, or Hardware Security Module , is a device that is protected from tampering, both hardware and software. If an unauthorized access attempt is detected, the HSM may permanently destroy the data stored on it. Inside the HSM, a key pair is generated and stored and all necessary cryptographic operations are performed. For example, the end-user certificate is signed directly inside the HSM using the appropriate command received from the CA. To access the settings or, for example, launch the HSM, simultaneous authentication of several employees who hold the keys is required. There are both locally installed HSM modules with USB or PCI-X interfaces, as well as network HSM with Ethernet interface.
Let's Encrypt supports Certificate Transparency technology, so all issued certificates can be viewed on the CT log . From the log it is clear that certificates are issued for a period of 3 months.
About Certificate Transparency
Certificate Transparency technology is designed to make a "transparent" issue of certificates by Certification Authorities. To do this, information about all issued certificates gets into the log file. This log is only available for adding information and is cryptographically protected from unauthorized intervention or deletion of individual records. Information about the certificate to be issued enters the log before the actual release of the certificate. This prevents the possibility to issue a certificate without leaving any traces.
A full launch of the project is scheduled for a week from November 16. I think the guys from Let's Encrypt should be well prepared for a potentially large load in the first hours and days after launch.
')
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/269213/
All Articles