Installing a white certificate on a Microsoft VDI farm

Many companies use VDI infrastructure to organize remote work with unmanaged company personal stations. When publishing a VDI farm on the Internet, external users are faced with the problem of mistrust of the certificate that was issued by the corporate certificate authority. In consequence of this, security warnings appear when setting up a remote connection.
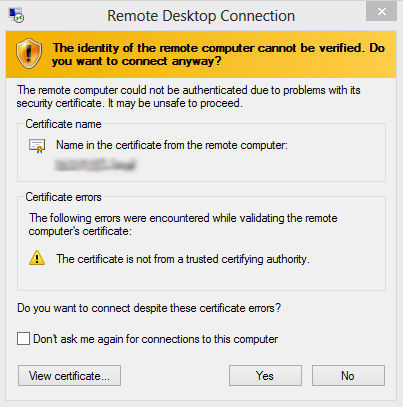
In this case, the warning appears twice: the first time the Connection Broker server is not trusted, and the second is the virtual machine of the VDI farm.
')
Many system administrators come out of this situation either by prompting users to ignore this message by checking the “Do not ask again” box, or by installing the root certificate in the trusted user’s remote computer and publishing the corporate CA CRL. However, these methods do not work if the user connects every time from different places, or connects to different virtual machines.
To solve this problem, you must use the "white" certificate issued by a trusted Certificate Authority for the VDI farm. The name of this external certificate and the names of the VDI computers must match.
SOLUTION TO THE PROBLEM
First we need a wildcard certificate of the type * .yourcompany.com, purchased from a trusted certificate authority.
Adding a new DNS Suffix in the domain:
Add a new Active Directory Integrated zone yourcompany.com to the DNS on the domain controller, which will serve internal requests for new server names and virtual machines of the VDI farm.
To maintain an additional domain suffix in the domain, it is necessary to make changes to the msDS-AllowedDNSSuffixes attribute at the domain level. You must add the internal and external domain names as attribute values, for example, yourcompany.local and yourcompany.com. At the domain level, we create a new group policy to specify the DNS suffixes that will be added to the short machine names for DNS queries.
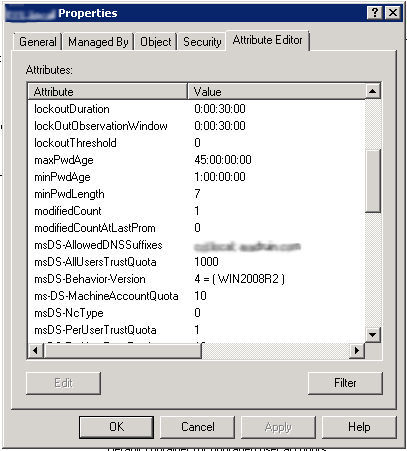
The following policy must be enabled and comma-separated values of the internal domain name and external domain name: Computer Configuration \ Policies \ Administrative Templates \ Network \ DNS Client \ DNS suffix search list.

Installing the certificate on the RD server
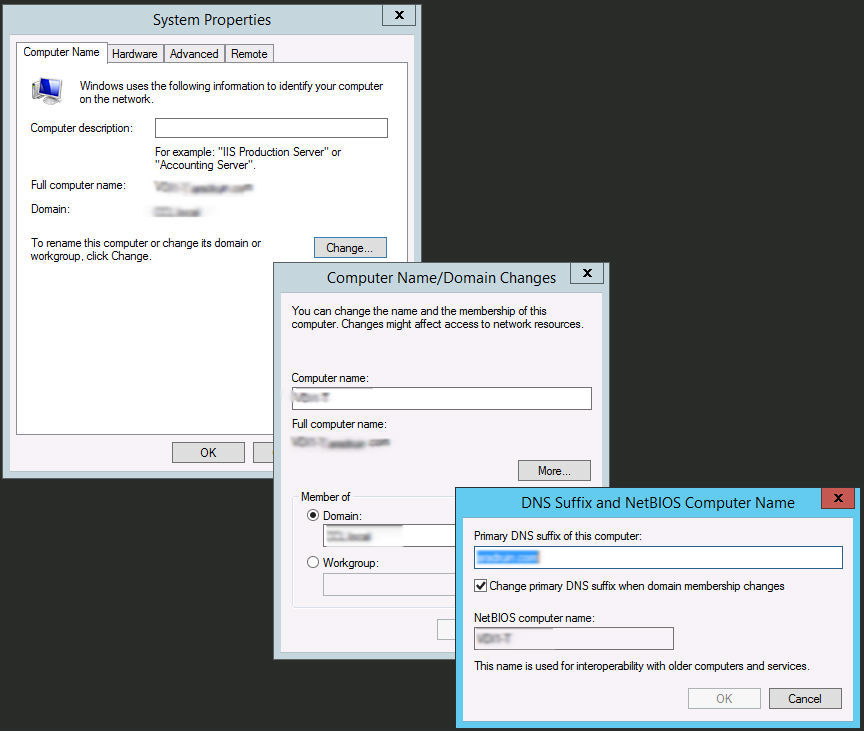
Before creating a VDI farm, you must change the DNS suffix of the planned RD servers to an external domain name. To do this, go to the properties of the computer and choose to change the name of the computer. In the window for changing the computer name, click the More ... button and specify a new primary DNS suffix for the computer - yourcompany.com.
Next, create a new VDI farm based on selected Microsoft Windows Server 2012 R2 servers. Information on this procedure can be easily found on the net.
After the pfx certificate file is in your hands, you can start installing it on a new VDI farm. On the RD Connection Broker server, go to Server Manager -> Remote Desktop Services -> Overview. In the Deployment Overview field in the TASKS drop-down list, select Edit Deployment Properties.
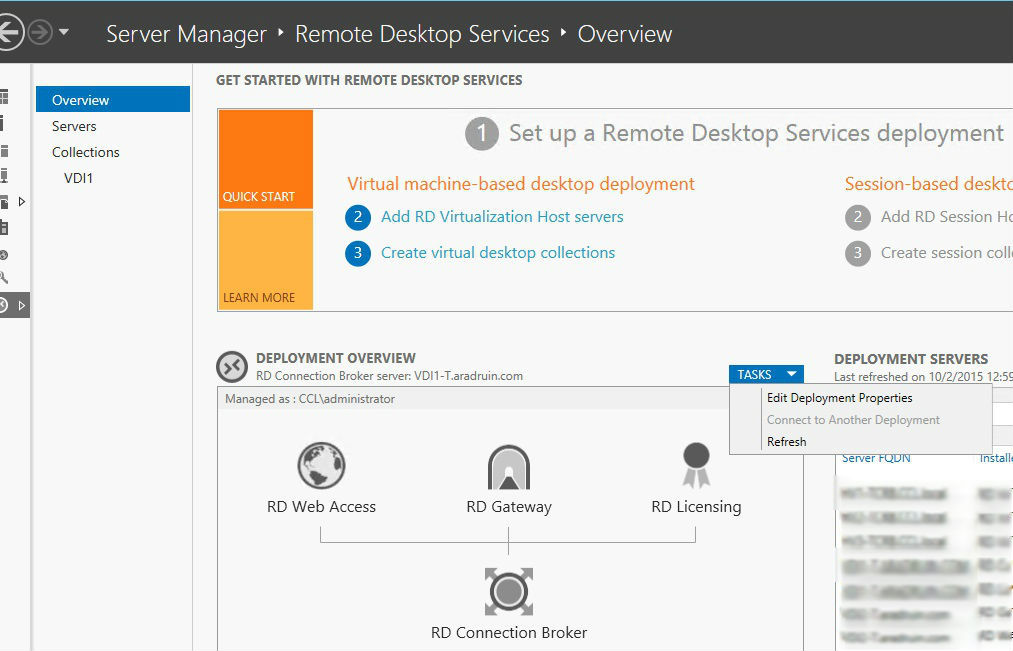
Open the Certificates tab and install the required certificate * .yourcompany.com for all farm services. Adding is done one by one. Select the existing certificate, specify its path on the file system and password.

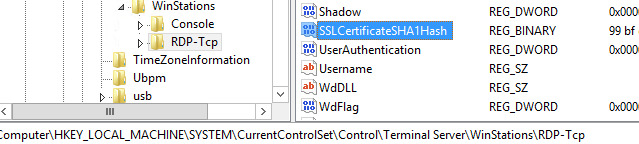
After that, these certificates will be installed on the VDI servers, but not on the virtual machines. In the registry on the Connection Broker server, the SSLCertificateSHA1Hash REG_BINARY parameter appears with the thumbprint value of the certificate at the following address:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE \ SYSTEM \ CurrentControlSet \ Control \ Terminal Server \ WinStations \ RDP-Tcp.
This parameter is responsible for selecting the certificate that will be used when setting up the RDP session. This option will need to be installed on client machines.
Installing a certificate on virtual machines
To use a white certificate on virtual machines, you must:
- Install the certificate on all machines in the personal certificate store of the computer.
- Set permissions to read the certificate key for the Network Service of each machine.
- Have SSLCertificateSHA1Hash REG_BINARY parameter with thumbprint certificate value.
- Virtual machine names must match the certificate name, i.e. have yourcompany.com suffix
Let's create a new group policy at the level of the Organizational Unit, dedicated to computer accounts of virtual machines of the VDI farm.
This policy must run Startup Script ExportVDICert.bat on virtual machines.
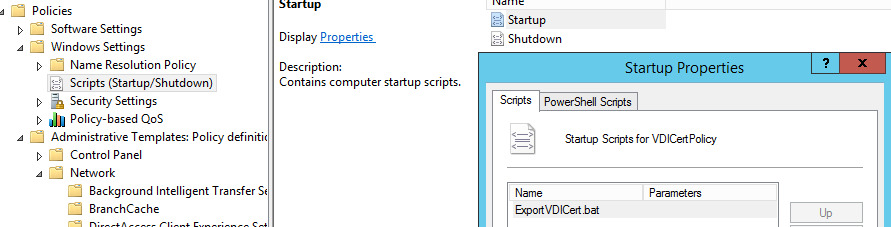
The specified script uses the certutil and FindPrivateKey utilities from Microsoft. Certutil is a built-in utility, FindPrivateKey is provided as a Samle tool for developers and can be compiled independently. The script must be located inside the policy.
The certificate and utility FindPrivateKey must be placed in a network folder, from where the script will pick up files for installation. Script text:
certutil -f -p "<certificate password>" -importpfx "<Path to pfx>" NoExport c: mkdir "c:\TempCertSecurity" cd "c:\TempCertSecurity" xcopy "<Path to FindPrivateKey.exe>" "c:\TempCertSecurity" FindPrivateKey.exe My LocalMachine -t "<thumbprint of certificate>" -a > tmp.txt set /p myvar= < tmp.txt del tmp.txt del FindPrivateKey.exe cd \ rd "c:\TempCertSecurity" cacls.exe %myvar% /E /G "NETWORK SERVICE":R" Using this script after rebooting the virtual machine, a new certificate will be installed and rights will be configured for it.
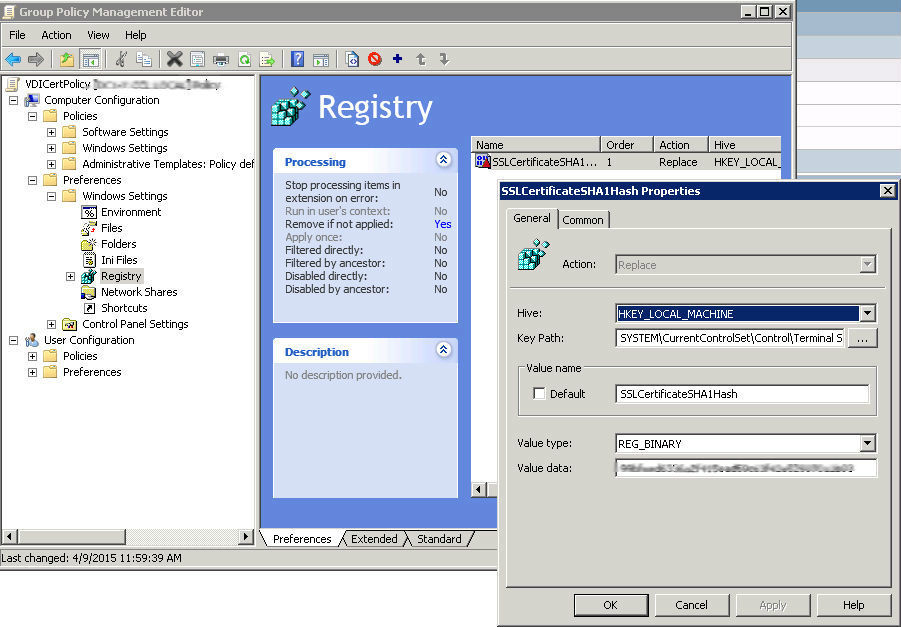
The next part of the policy concerns setting the SSLCertificateSHA1Hash parameter. The required key is configured via Preferences \ Windows Settings \ Registry
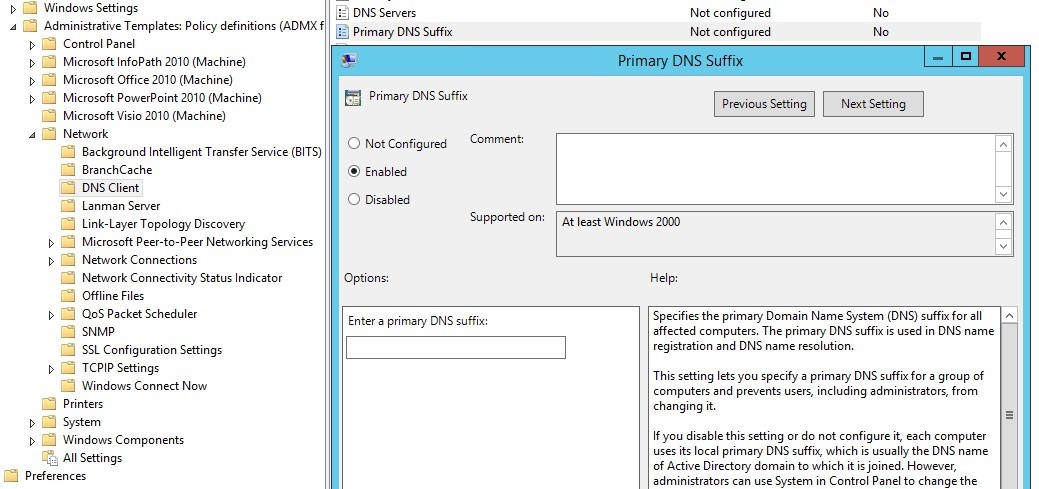
To centrally change the Primary DNS suffix of virtual machines in a policy, you must enable Primary DNS suffix and set it as the external domain name of yourcompany.com.
After rebooting, the machine will receive a new FQDN corresponding to the white certificate. After performing these operations, users will no longer see annoying security warnings.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/268785/
All Articles