Migration SCCM 2007 to SCCM 2012 \ 1511
It has long been "dreamed" to write on this topic, it was all too lazy ... Stock up on cookies, this is a long time. There may be some number of errors - let me know if you find them, please. Hard to deduct ~ 35,000 characters. I deliberately do not want to divide the post into several parts, so all the information collected by me will be in one place.
Upd. you can migrate from 2007 to 1511 directly, without 2012. And in general, everything written in this article is true for migration to 1511.
1. Architecture
The SCCM 2012 hierarchy consists of three types of servers: Central Administration Site, Primary Site and Secondary Site. Creating a four-level hierarchy similar to the existing SCCM 2007 hierarchy using SCCM 2012 is impossible, because the SCCM 2012 hierarchy is three-level. The relationship between the servers in the Parent-Child hierarchy, at the head of the hierarchy is the CAS server, the Primary Site of the server is subordinate to it, and the Secondary Site of the server is subordinate to it. Starting with version 2012 SP1, stand alone Primary can be “converted” to the SCCM hierarchy, so if you have less than 90000-95000 clients in the hierarchy, there is no point in the SCCM 2012 hierarchy with the CAS server.
')
The source and destination SCCM hierarchies cannot contain the same site codes, so all site codes must be changed during migration.
Only SCCM 2007 servers with SP2 or later installed can participate in the migration.
The extension of the Active Directory directory service schema to install the SCCM 2012 hierarchy in parallel with SCCM 2007 is not necessary (in case the schema extension was made to install SCCM 2007).
1.1. Central Administration Site
The CAS server is the main SCCM hierarchy server. The SCCM 2012 hierarchy cannot contain more than one CAS server, in addition it must be installed first in the hierarchy (not relevant after 2012 SP1). CAS server does not support all roles, as it is not used to interact with clients.
The CAS server is used to manage the entire SCCM infrastructure and is the only server on which information about the entire infrastructure is available, for example, assign detection methods for the Primary Site servers or manage the access roles of administrators to the SCCM hierarchy.
The CAS server supports up to 100,000 clients in the SCCM infrastructure if the SQL server is edited as “enterprise” or “datacenter” and up to 50,000 clients if the SQL server is edited as “standard”.
1.2. Primary Site
More than 25 Primary Site servers cannot be connected to a CAS server. Primary Site server is responsible for interacting with clients and with Secondary Site servers, consolidates the data and sends them to the CAS server.
Primary Site server supports up to 10 client management points each of which supports up to 25,000 clients.
Primary Site server can manage only clients connected directly to this server or clients connected to its child servers.
Primary Site server supports up to 250 Secondary Site servers and 250 distribution points. Primary site server may transfer data to the Secondary Site server and to Distribution points according to schedule and / or may limit the bandwidth used by it.
Primary Site server supports up to 50,000 clients in case it coexists with SQL server and up to 100,000 clients if SQL server exists separately from Primary Site server. The edition of the SQL server is not important, unlike the CAS server. In addition, Secondary Site servers do not increase the limit of clients connected to the Primary Site server. If the CAS server has a database installed on the SQL server of the “standard” edition, the limit of the clients connected to the Primary Site server and its child servers is 50,000.
Primary Site server can not contain child Primary Site servers.
1.3. Secondary Site and Distribution Point
The Secondary Site servers are migrated as follows: deleting the source Secondary Site server, waiting for the next collection cycle, if the successful removal of the Secondary Site server is confirmed after collecting the information, the Distribution Point is installed and all data that was located on the source Secondary Site server is imported.
For a Distribution Point to migrate, it is necessary for the server to have an operating system supported by SCCM 2012 and the availability of free space twice the size of all the packages at the Distribution Point.
With the help of the Distribution Point and the Secondary Site server, you cannot manage the SCCM infrastructure, all administrative actions must be performed on the CAS and Primary Site servers. The main task of Distribution Points and Secondary Site servers is to reduce file traffic on the network and consolidate data from clients for transfer to the parent Primary Site server.
The Secondary Site server cannot be used to assign SCCM site code to clients. If boundary groups are used to assign sites to clients and the client is assigned a Secondary Site code, the client is assigned the code of the parent site of this Secondary Site server.
Secondary Site server supports up to 250 distribution points. Distribution point supports up to 4,000 clients.
Secondary Site server supports up to 5000 clients.
2. Ability to migrate various types of objects
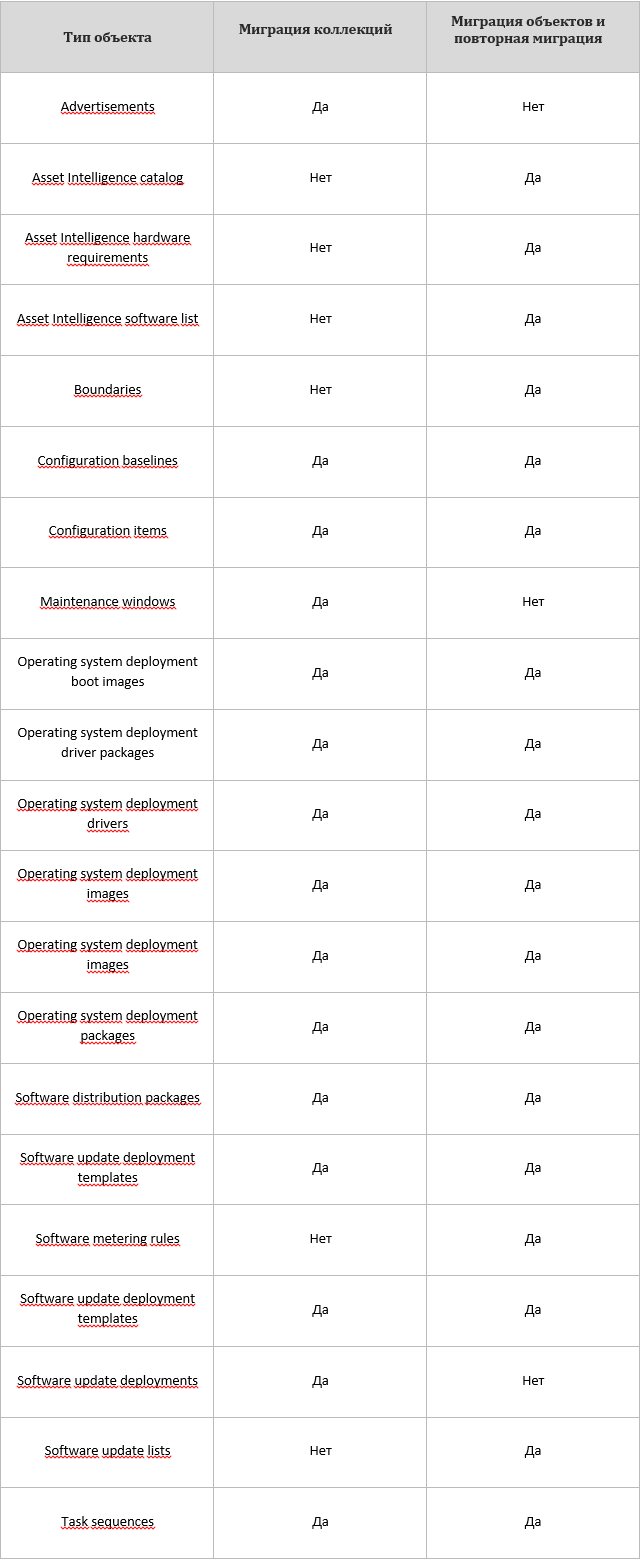
Unfortunately, I did not understand how to insert a tablet, therefore a picture.
Collection migration — when migrating collections, all objects are automatically migrated (this function can be disabled when creating a “migration job”) that are associated with this collection (except for those that cannot be migrated). Re-migration of collections is identical to the original.
Migration of objects - when performing migration of objects, it is necessary to select all objects that should participate in the migration.
However, there are some limitations. Collections must contain only users or only computers. Empty collections cannot be migrated and a folder will be created instead. If there are deployments that include all subcollections aimed at an empty collection during migration, a new collection will be created containing all subcollections and expansions will be aimed at it. Collections containing an unknown computer object will be migrated, but this item will be removed from the collection. Migration of related collections is not supported (linked collections are collections containing users and computers).
The following objects and data cannot be migrated: queries, reports, customer inventory data, Intel AMT data, modified boot images, SCCM 2007 agent cache data, client history, security settings, mof files.
Report migration is not possible using SCCM. However, you can use the SQL Server Reporting Services Report Builder utility to migrate reports. To do this, you need to convert all the reports in the source infrastructure so that they use SQL mechanisms. To do this, install the SQL Server Reporting Services role on the databases, then configure the access of the SCCM source hierarchy to this service (via the SCCM console, server management, role management), convert all reports to SQL reports (via the SCCM console, select the required reports and Click “Copy Reports to Reporting Services”). Further report migration is performed using SQL Server Reporting Services Report Builder or ReportSync utility.
Query migration is not possible using SCCM. You need to re-create the queries or export the queries as “mof” files from the SCCM 2007 hierarchy and import them into SCCM 2012, this is done by the SCCM console of the source and target hierarchies.
Mof files cannot be migrated using SCCM. You need to re-configure them in the new hierarchy. The mechanism of interaction with mof files has not changed, however, changes in existing mof files may be required for full compatibility with SCCM 2012.
3. SQL Server Requirements
For all server roles, 64-bit SQL server editions and windows authentication should be used to access the database.
The SQL Server Replication component is not used to replicate data between SCCM servers. This process is carried out by SMS Provider. If you need to generate and view reports, you need to install the SQL Server Reporting Services component on the SQL server.
For each SCCM server, a separate instance of the SQL server should be used and the “Collation” parameter of the SQL server must be the same on all servers in the SCCM hierarchy. The only supported “Collation” is SQL_Latin1_general_CP1_CI_AS.
For correct operation, the site of the servers of the SCCM 2012 hierarchy requires that the SQL server supports windows authentication. Since the mixed mode supports windows authentication, its use on SQL servers in the SCCM hierarchy is possible. Thus, it is possible to use mixed or windows authentication, “Best practice” - Windows mode.
It is necessary to use the following settings for SQL server memory consumption:
- in the case of coexistence of the installation of SQL and the SCCM server, limit the memory consumption of the SQL server to 50-80% of the RAM of the server.
- in case of separate installation of SQL and SCCM server, limit the memory consumption of the SQL server to 80-90% of the RAM of the server.
- Primary Site server and CAS server require backup of 8GB of RAM on the SQL server, and Secondary Site server requires backup of 4GB of RAM of the SQL server.
4. Network infrastructure requirements
gallery.technet.microsoft.com/SCCM-2012-R2-Network-scheme-b01fd985
This scheme without CAS role, did not find another scheme. But I think 99% of those reading this will do.
5. Preparing for migration
Since the SCCM 2012 hierarchy differs from the SCCM 2007 hierarchy, it is necessary to reorganize the existing SCCM 2007 structure and make it flatter. For the migration, you need an account with “Read” access to all objects of the SCCM 2007 hierarchy and an account with “Read” and “Write” rights to the database, in addition, you must open the following ports: 135, 445, 1433 (all TCP).
To migrate SCCM 2007 to SCCM 2012, you must select the source server in infrastructure 2007, it must be the “highest” server of the existing hierarchy, because once the source server is selected, it will not be possible to migrate all objects, servers and clients that are “above” the selected server.
Since SCCM 2012 does not support the creation of child Primary Site servers on a Primary Site server to migrate such a hierarchy, it is necessary to consolidate all the clients of all child Primary Site servers in the existing hierarchy into the corresponding parent Primary Site servers in the new hierarchy. Consolidation of clients occurs during the "migration" of the client. Prior to direct migration, clients are under the control of the SCCM 2007 hierarchy. When migrating a client, it must receive the code for the parent site of the SCCM 2012 when installing the client (via the command line key). Assigning to clients the corresponding site codes of their parent Primary Site servers and is a consolidation.
All servers in the hierarchy that will participate in the migration must be upgraded to SCCM 2007 SP2 or higher.
Secondary servers cannot be migrated, it is necessary to remove the server and install the Secondary server on it from the SCCM 2012 infrastructure (possibly along with saving data at the Distribution point).
For the uninterrupted provision of infrastructure services, SCCM can share existing Distribution Points. Setting up the sharing of existing Distribution points is done at the initial stages of the migration. To do this, you need an account with “Modify” rights to the SCCM object.
To migrate SCCM objects, you need to prepare public folders for migration, those that give access to public folders to accounts that will be responsible in the new hierarchy for access to public folders. In addition, you need to reconfigure SCCM objects so that they use the UNC path to the shared folder, this will allow you not to reconfigure objects after migration.
Collections can not be mixed, they can not contain both computers and users. All mixed collections need to be reorganized into collections that contain only users and only devices. In addition, collections that contain mixed collections and collections containing unknown computers cannot be migrated. Empty collections will be migrated as folders.
To migrate reports, you must install the SQL Server Reporting Services (SRS) role and convert all reports to SRS format. Report migration using SCCM is not possible, however it is possible using SQL.
Migration of clients allows you to avoid re-distribution of packages, this happens because during migration of packages SCCM 2012 stores in the database information about the SCCM 2007 package number, and the client, in turn, during migration saves data about installed packages.
For client migrations, it is necessary to create and distribute packages for installing SCCM 2012 clients in the SCCM 2007 hierarchy. In addition, it is possible to distribute SCCM 2012 clients in any available way, since client migration is actually impossible in place upgrade.
6. Preparing the target system for migration
The target hierarchy should be deployed from top to bottom: the central site should be deployed first, its child sites should be deployed after it, and then the lower level servers and distribution points should be deployed. If it is impossible to deploy a server from a new hierarchy at some sites, you must take advantage of the opportunity to create a content distribution point on the client system.
It is possible to transfer content according to a customized schedule, that is, without loading a channel during business hours, or using the “Prestage Content File” and transfer it to the site offline. The “Prestage Content File” is created at the central site of the hierarchy and contains all the necessary packages.
After expanding the hierarchy, it is necessary to perform testing. Check the replication of data between sites in the hierarchy, check the health of client management points and content distribution points. Check the ability of clients to connect to each client management point in the hierarchy, the ability to send and receive customer data. Test the availability of deployments and all data distribution points in the hierarchy.
The next step in preparing the target infrastructure should be the “Default Client Settings”, “Boundary”, “Boundary Group”, “Security Scope” and Administrative Accounts settings. In addition, you need to create 2 accounts to access the old hierarchy and to access the database of the old hierarchy (you may need to create more accounts if you cannot connect to different sites of the hierarchy and different database servers with the same credentials). “Security Scope” and “Boundary Group” are needed to reassign content management rights and specify the location of content in a new hierarchy.
At the beginning of the process, in the new system, the SCCM 2007 server addresses and credentials for access to them are specified, starting from the highest to the lowest server, all servers that will be involved in the migration are specified in the hierarchy. Then a selection is made of which data must be transferred from the old system to the new one.
In fact, the migration is the copying of objects from the source hierarchy to the target one. Objects are migrated using “migration jobs”. Each “migration job” can migrate any number of SCCM objects. It is possible to re-migrate SCCM objects if necessary (for example, the object has been changed). The order of migration of objects is not important. Migrating the roles or Primary Site of the SCCM servers is not possible (content distribution points and Secondary Site servers can be migrated).
To copy objects from the source hierarchy to the target, you need to collect data about the source hierarchy. The data collection process establishes a relationship between hierarchies. Data collection occurs by reading information about objects and their dependencies, collections, sites and clients from the database of the target hierarchy.
For client migration, you need to use the console of the original hierarchy or other means, since client migration occurs by “in place” client updates. The mechanisms for installing the agent on the client computer have not changed in SCCM 2012. The update can be triggered by a startup script, group policy, or installed as a package from the server of the original hierarchy. Before the client is migrated, it is under the control of the original hierarchy.
The SCCM 2007 client cannot be controlled by the SCCM 2012 hierarchy and vice versa, the SCCM 2012 client cannot be controlled by the SCCM 2007 hierarchy. In case of incorrectly configured site boundaries in the SCCM hierarchies, clients that received the wrong site code (those site code from the “other” hierarchy) will not be managed until the right site code is assigned to them. Prior to the migration, all clients are managed by the SCCM 2007 hierarchy; as the clients migrate, they become under the control of SCCM 2012.
When the migration of clients and objects is complete, you can start migrating the content distribution points. It occurs using the target hierarchy server's CAS console (the “Migrate Distribution Point” task). When migrating a content distribution point, binary files are updated and file storage is migrated. To migrate storage, it is necessary that the server has 2-2.5 times more free space than that occupied by all SCCM 2007 packages on this server, since the SCCM package storage is being rebuilt.
Migration of Secondary Site servers is not possible. Instead, there is an “in place” upgrade of the Secondary Site server only to the content distribution point of the target hierarchy (this is a technical limitation of the system introduced by Microsoft due to changes in package replication mechanisms in the hierarchy and improvements in package replication traffic control mechanisms) while maintaining all packages. 2-2.5 SCCM 2007 , SCCM.
Primary Site , Primary Site Primary Site CAS ( Primary Site ) . , «» Primary Site SCCM 2012 . , CAS .
:
ReportSync – SCCM 2007 SCCM 2012. .
RegKeytoMof – mof . .
ExtractContent – «Prestage Content» . SCCM 2012, «BIN» SCCM
CMTrace – . SCCM 2012, «Tools» SCCM.
Notepad – .
7.
Migration occurs in stages. You can proceed to the next stage of migration only after the full completion of the previous stage. In case of failure of the target hierarchy, a painless return of the IT infrastructure to the original hierarchy is possible, since migration does not imply any changes that impede the functioning of the initial hierarchy (before the client migration phase).
In the first step of the migration, you must create an SCCM target hierarchy in parallel with the existing hierarchy.
The second stage is the preparation of hierarchies and the collection of information about the original hierarchy.
At the third stage, the migration of SCCM objects takes place.
The fourth stage is the migration of SCCM clients.
The fifth step is to test the target hierarchy and decommission the source hierarchy.
7.1. SCCM 2012
1. .
2. .
3. .
4. CAS .
5. CAS .
, SCCM, ( CAS , , TCI\IP), CAS . , – .
6. CAS : CAS ( Monitoring, «Site Status» «Component Status»), .
7. Primary Site ( 2-4).
8. Install Primary Site Server.
During the installation process, you must specify the database server (the account on behalf of which the server is installed must have appropriate permissions to access the database server, in addition, TCI \ IP access must be enabled on the database server), the site code and the server should be specified which will be the parent of this Primary Site server, that is, the CAS server of the new hierarchy. To install the Primary Site server, the same distribution kit is used as for installing the CAS server.
9. Primary Site : Primary Site ( Monitoring, «Site Status» «Component Status»), , CAS (replmgr.log, rcmctrl.log Monitoring, «Site Status» «Component Status»), (mpmsi.log, mpsetup.log, smsdpmon.log Monitoring, «Site Status» «Component Status»), , .
10. Primary site ( 8 9).
11. SCCM 2012: ( Monitoring, «Site Status» «Component Status»), ( Monitoring, «Site Hierarchy»), .
12. ( , , «push» ).
13. «security scopes».
7.2.
1. . , SCCM 2007. , . , , .
2. . .
3. After that, you need to connect Primary Site with unique content to the SCCM 2012 hierarchy. Both actions are performed using the SCCM 2012 console (Migration tab, Administration tabs). To do this, select the “Specify Source Hierarchy” item and enter the necessary data for the connection. SCCM 2007 hierarchy sites are connected to a central site.
4. «Share Distribution Points» ( Migration, Administration). . , Secondary Site . ( Primary Site ).
7.3. SCCM
1. . «Create Migration Job» ( Migration, Administration). : «Collection Migration» «Object Migration». , , «Security Scope», , . SCCM. . «Collection Migration».
«Collection Migration» ( ), «Object Migration» ( ). Primary Site SCCM ( Secondary Site – ). , .
2. ( 1) . : Reporting Monitoring, Migration jobs Administration, SCCM – migmctrl.log logs.
SQL Server Reporting Services. , SQL. SQL Server Reporting Services, SCCM ( SCCM, , ), SQL ( SCCM, “Copy Reports to Reporting Services”). SQL Server Reporting Services Report Builder ReportSync.
«» sms_def.mof SCCM 2012 WMI SCCM 2012. Administration, Client Settings, ( ), «Hardware Inventory» «Set Classes». Import WMI.
3. SCCM SCCM 2012.
4. «Boundary Group» , «Boundaries» «Boundary Groups» ( Hierarchy Configuration, Administration).
5. «Prestage Content» ( SCCM). «Software Library» , «Create Prestage Content File».
6. «Prestage Content» extractcontent /p.
7.4. Migrating SCCM clients
1. Before installing the SCCM 2012 agents, it is recommended to install the SCCM 2012 software necessary for the client to work on the client machines in advance. This step is optional, but desirable because it reduces the installation time of the SCCM 2012 client and the number of installation failures. Prior to client migration, they are serviced by servers in the Source hierarchy.
2. Since the client's migration, in fact, is the agent reinstallation, it can be done in all the ways that it is possible to install the SCCM agent. Client installation methods have not changed in the new version of SCCM.
Client migration should be carried out in stages (500-1000 clients each) to reduce the load on the network infrastructure and the database server. When migrating, you need to consolidate customers. Clients of the target hierarchy may belong to one of the Primary Site servers. All clients from each Primary Site server migrate from the corresponding Primary Site server of the second level of the hierarchy of the original hierarchy and all its child sites.
To create an agent installation package for a new hierarchy in the source hierarchy, you must copy the contents of the agent installation package from the new hierarchy. The agent must be installed with the key SMSSITECODE = XXX, where XXX is the code of the parent Primary Site of the server for this client. This is necessary for the client to bind to the hierarchy.
If the installation of the SCCM 2012 agent is not made, you need to check the ccmsetup.log log on the client machine for errors. If this log is not detected on the machine, you must repeat the installation of the agent on it, since the initial attempt to install the agent was not made (perhaps the computer was turned off).
7.5. Testing the target hierarchy and decommissioning the source hierarchy
1. The content distribution points are migrated after the clients have completed their migration. To migrate content distribution points, use the “Upgrade Distribution Point” item (Migration tab, Administration tabs).
( ) SCCM SCCM . «Prestage Content» .
SCCM 2007 .
2. Primary Site SCCM 2007 (Distribution Point, Secondary Site ) . «Create Site Systems Server» «Create Secondary Site» Secondary Site .
3. : , , , . .
4. .
References :
Administrator Checklists for Migration Planning in System Center 2012 Configuration Manager
Introduction to Migration in System Center 2012 Configuration Manager
Install Sites and Create a Hierarchy for Configuration Manager
Planning for Configuration Manager Sites and Hierarchy
Supported Configurations for Configuration Manager
System Center 2012 – Configuration Manager Component Add-ons and Extensions (Tools)
Migrating from Configuration Manager 2007 to Microsoft System Center 2012 R2 Configuration Manager ()
ConfigMgr client automatic site assignment behavior in a multi site environment
Performing a side-by-side Migration from Configuration Manager 2007 (WindowsNoob)
System Center 2012 Configuration Manager Migration — Deep(ish) Dive Part 1 (troubleshooting)
System Center 2012 Configuration Manager Survival Guide
:
www.css-security.com/blog/sccm-2012-migration-made-easy-part-1
www.css-security.com/blog/sccm-2012-migration-made-easy-part-2
www.css-security.com/blog/sccm-2012-migration-made-easy-part-3
anoopcnair.com/2015/08/20/upgrading-from-sccm-2007-to-sccm-2012-with-adaptiva-onesite
activedirectory.ncsu.edu/services/sccm
Upd. you can migrate from 2007 to 1511 directly, without 2012. And in general, everything written in this article is true for migration to 1511.
1. Architecture
The SCCM 2012 hierarchy consists of three types of servers: Central Administration Site, Primary Site and Secondary Site. Creating a four-level hierarchy similar to the existing SCCM 2007 hierarchy using SCCM 2012 is impossible, because the SCCM 2012 hierarchy is three-level. The relationship between the servers in the Parent-Child hierarchy, at the head of the hierarchy is the CAS server, the Primary Site of the server is subordinate to it, and the Secondary Site of the server is subordinate to it. Starting with version 2012 SP1, stand alone Primary can be “converted” to the SCCM hierarchy, so if you have less than 90000-95000 clients in the hierarchy, there is no point in the SCCM 2012 hierarchy with the CAS server.
')
The source and destination SCCM hierarchies cannot contain the same site codes, so all site codes must be changed during migration.
Only SCCM 2007 servers with SP2 or later installed can participate in the migration.
The extension of the Active Directory directory service schema to install the SCCM 2012 hierarchy in parallel with SCCM 2007 is not necessary (in case the schema extension was made to install SCCM 2007).
1.1. Central Administration Site
The CAS server is the main SCCM hierarchy server. The SCCM 2012 hierarchy cannot contain more than one CAS server, in addition it must be installed first in the hierarchy (not relevant after 2012 SP1). CAS server does not support all roles, as it is not used to interact with clients.
The CAS server is used to manage the entire SCCM infrastructure and is the only server on which information about the entire infrastructure is available, for example, assign detection methods for the Primary Site servers or manage the access roles of administrators to the SCCM hierarchy.
The CAS server supports up to 100,000 clients in the SCCM infrastructure if the SQL server is edited as “enterprise” or “datacenter” and up to 50,000 clients if the SQL server is edited as “standard”.
1.2. Primary Site
More than 25 Primary Site servers cannot be connected to a CAS server. Primary Site server is responsible for interacting with clients and with Secondary Site servers, consolidates the data and sends them to the CAS server.
Primary Site server supports up to 10 client management points each of which supports up to 25,000 clients.
Primary Site server can manage only clients connected directly to this server or clients connected to its child servers.
Primary Site server supports up to 250 Secondary Site servers and 250 distribution points. Primary site server may transfer data to the Secondary Site server and to Distribution points according to schedule and / or may limit the bandwidth used by it.
Primary Site server supports up to 50,000 clients in case it coexists with SQL server and up to 100,000 clients if SQL server exists separately from Primary Site server. The edition of the SQL server is not important, unlike the CAS server. In addition, Secondary Site servers do not increase the limit of clients connected to the Primary Site server. If the CAS server has a database installed on the SQL server of the “standard” edition, the limit of the clients connected to the Primary Site server and its child servers is 50,000.
Primary Site server can not contain child Primary Site servers.
1.3. Secondary Site and Distribution Point
The Secondary Site servers are migrated as follows: deleting the source Secondary Site server, waiting for the next collection cycle, if the successful removal of the Secondary Site server is confirmed after collecting the information, the Distribution Point is installed and all data that was located on the source Secondary Site server is imported.
For a Distribution Point to migrate, it is necessary for the server to have an operating system supported by SCCM 2012 and the availability of free space twice the size of all the packages at the Distribution Point.
With the help of the Distribution Point and the Secondary Site server, you cannot manage the SCCM infrastructure, all administrative actions must be performed on the CAS and Primary Site servers. The main task of Distribution Points and Secondary Site servers is to reduce file traffic on the network and consolidate data from clients for transfer to the parent Primary Site server.
The Secondary Site server cannot be used to assign SCCM site code to clients. If boundary groups are used to assign sites to clients and the client is assigned a Secondary Site code, the client is assigned the code of the parent site of this Secondary Site server.
Secondary Site server supports up to 250 distribution points. Distribution point supports up to 4,000 clients.
Secondary Site server supports up to 5000 clients.
2. Ability to migrate various types of objects

Unfortunately, I did not understand how to insert a tablet, therefore a picture.
Collection migration — when migrating collections, all objects are automatically migrated (this function can be disabled when creating a “migration job”) that are associated with this collection (except for those that cannot be migrated). Re-migration of collections is identical to the original.
Migration of objects - when performing migration of objects, it is necessary to select all objects that should participate in the migration.
However, there are some limitations. Collections must contain only users or only computers. Empty collections cannot be migrated and a folder will be created instead. If there are deployments that include all subcollections aimed at an empty collection during migration, a new collection will be created containing all subcollections and expansions will be aimed at it. Collections containing an unknown computer object will be migrated, but this item will be removed from the collection. Migration of related collections is not supported (linked collections are collections containing users and computers).
The following objects and data cannot be migrated: queries, reports, customer inventory data, Intel AMT data, modified boot images, SCCM 2007 agent cache data, client history, security settings, mof files.
Report migration is not possible using SCCM. However, you can use the SQL Server Reporting Services Report Builder utility to migrate reports. To do this, you need to convert all the reports in the source infrastructure so that they use SQL mechanisms. To do this, install the SQL Server Reporting Services role on the databases, then configure the access of the SCCM source hierarchy to this service (via the SCCM console, server management, role management), convert all reports to SQL reports (via the SCCM console, select the required reports and Click “Copy Reports to Reporting Services”). Further report migration is performed using SQL Server Reporting Services Report Builder or ReportSync utility.
Query migration is not possible using SCCM. You need to re-create the queries or export the queries as “mof” files from the SCCM 2007 hierarchy and import them into SCCM 2012, this is done by the SCCM console of the source and target hierarchies.
Mof files cannot be migrated using SCCM. You need to re-configure them in the new hierarchy. The mechanism of interaction with mof files has not changed, however, changes in existing mof files may be required for full compatibility with SCCM 2012.
3. SQL Server Requirements
For all server roles, 64-bit SQL server editions and windows authentication should be used to access the database.
The SQL Server Replication component is not used to replicate data between SCCM servers. This process is carried out by SMS Provider. If you need to generate and view reports, you need to install the SQL Server Reporting Services component on the SQL server.
For each SCCM server, a separate instance of the SQL server should be used and the “Collation” parameter of the SQL server must be the same on all servers in the SCCM hierarchy. The only supported “Collation” is SQL_Latin1_general_CP1_CI_AS.
For correct operation, the site of the servers of the SCCM 2012 hierarchy requires that the SQL server supports windows authentication. Since the mixed mode supports windows authentication, its use on SQL servers in the SCCM hierarchy is possible. Thus, it is possible to use mixed or windows authentication, “Best practice” - Windows mode.
It is necessary to use the following settings for SQL server memory consumption:
- in the case of coexistence of the installation of SQL and the SCCM server, limit the memory consumption of the SQL server to 50-80% of the RAM of the server.
- in case of separate installation of SQL and SCCM server, limit the memory consumption of the SQL server to 80-90% of the RAM of the server.
- Primary Site server and CAS server require backup of 8GB of RAM on the SQL server, and Secondary Site server requires backup of 4GB of RAM of the SQL server.
4. Network infrastructure requirements
gallery.technet.microsoft.com/SCCM-2012-R2-Network-scheme-b01fd985
This scheme without CAS role, did not find another scheme. But I think 99% of those reading this will do.
5. Preparing for migration
Since the SCCM 2012 hierarchy differs from the SCCM 2007 hierarchy, it is necessary to reorganize the existing SCCM 2007 structure and make it flatter. For the migration, you need an account with “Read” access to all objects of the SCCM 2007 hierarchy and an account with “Read” and “Write” rights to the database, in addition, you must open the following ports: 135, 445, 1433 (all TCP).
To migrate SCCM 2007 to SCCM 2012, you must select the source server in infrastructure 2007, it must be the “highest” server of the existing hierarchy, because once the source server is selected, it will not be possible to migrate all objects, servers and clients that are “above” the selected server.
Since SCCM 2012 does not support the creation of child Primary Site servers on a Primary Site server to migrate such a hierarchy, it is necessary to consolidate all the clients of all child Primary Site servers in the existing hierarchy into the corresponding parent Primary Site servers in the new hierarchy. Consolidation of clients occurs during the "migration" of the client. Prior to direct migration, clients are under the control of the SCCM 2007 hierarchy. When migrating a client, it must receive the code for the parent site of the SCCM 2012 when installing the client (via the command line key). Assigning to clients the corresponding site codes of their parent Primary Site servers and is a consolidation.
All servers in the hierarchy that will participate in the migration must be upgraded to SCCM 2007 SP2 or higher.
Secondary servers cannot be migrated, it is necessary to remove the server and install the Secondary server on it from the SCCM 2012 infrastructure (possibly along with saving data at the Distribution point).
For the uninterrupted provision of infrastructure services, SCCM can share existing Distribution Points. Setting up the sharing of existing Distribution points is done at the initial stages of the migration. To do this, you need an account with “Modify” rights to the SCCM object.
To migrate SCCM objects, you need to prepare public folders for migration, those that give access to public folders to accounts that will be responsible in the new hierarchy for access to public folders. In addition, you need to reconfigure SCCM objects so that they use the UNC path to the shared folder, this will allow you not to reconfigure objects after migration.
Collections can not be mixed, they can not contain both computers and users. All mixed collections need to be reorganized into collections that contain only users and only devices. In addition, collections that contain mixed collections and collections containing unknown computers cannot be migrated. Empty collections will be migrated as folders.
To migrate reports, you must install the SQL Server Reporting Services (SRS) role and convert all reports to SRS format. Report migration using SCCM is not possible, however it is possible using SQL.
Migration of clients allows you to avoid re-distribution of packages, this happens because during migration of packages SCCM 2012 stores in the database information about the SCCM 2007 package number, and the client, in turn, during migration saves data about installed packages.
For client migrations, it is necessary to create and distribute packages for installing SCCM 2012 clients in the SCCM 2007 hierarchy. In addition, it is possible to distribute SCCM 2012 clients in any available way, since client migration is actually impossible in place upgrade.
6. Preparing the target system for migration
The target hierarchy should be deployed from top to bottom: the central site should be deployed first, its child sites should be deployed after it, and then the lower level servers and distribution points should be deployed. If it is impossible to deploy a server from a new hierarchy at some sites, you must take advantage of the opportunity to create a content distribution point on the client system.
It is possible to transfer content according to a customized schedule, that is, without loading a channel during business hours, or using the “Prestage Content File” and transfer it to the site offline. The “Prestage Content File” is created at the central site of the hierarchy and contains all the necessary packages.
After expanding the hierarchy, it is necessary to perform testing. Check the replication of data between sites in the hierarchy, check the health of client management points and content distribution points. Check the ability of clients to connect to each client management point in the hierarchy, the ability to send and receive customer data. Test the availability of deployments and all data distribution points in the hierarchy.
The next step in preparing the target infrastructure should be the “Default Client Settings”, “Boundary”, “Boundary Group”, “Security Scope” and Administrative Accounts settings. In addition, you need to create 2 accounts to access the old hierarchy and to access the database of the old hierarchy (you may need to create more accounts if you cannot connect to different sites of the hierarchy and different database servers with the same credentials). “Security Scope” and “Boundary Group” are needed to reassign content management rights and specify the location of content in a new hierarchy.
At the beginning of the process, in the new system, the SCCM 2007 server addresses and credentials for access to them are specified, starting from the highest to the lowest server, all servers that will be involved in the migration are specified in the hierarchy. Then a selection is made of which data must be transferred from the old system to the new one.
In fact, the migration is the copying of objects from the source hierarchy to the target one. Objects are migrated using “migration jobs”. Each “migration job” can migrate any number of SCCM objects. It is possible to re-migrate SCCM objects if necessary (for example, the object has been changed). The order of migration of objects is not important. Migrating the roles or Primary Site of the SCCM servers is not possible (content distribution points and Secondary Site servers can be migrated).
To copy objects from the source hierarchy to the target, you need to collect data about the source hierarchy. The data collection process establishes a relationship between hierarchies. Data collection occurs by reading information about objects and their dependencies, collections, sites and clients from the database of the target hierarchy.
For client migration, you need to use the console of the original hierarchy or other means, since client migration occurs by “in place” client updates. The mechanisms for installing the agent on the client computer have not changed in SCCM 2012. The update can be triggered by a startup script, group policy, or installed as a package from the server of the original hierarchy. Before the client is migrated, it is under the control of the original hierarchy.
The SCCM 2007 client cannot be controlled by the SCCM 2012 hierarchy and vice versa, the SCCM 2012 client cannot be controlled by the SCCM 2007 hierarchy. In case of incorrectly configured site boundaries in the SCCM hierarchies, clients that received the wrong site code (those site code from the “other” hierarchy) will not be managed until the right site code is assigned to them. Prior to the migration, all clients are managed by the SCCM 2007 hierarchy; as the clients migrate, they become under the control of SCCM 2012.
When the migration of clients and objects is complete, you can start migrating the content distribution points. It occurs using the target hierarchy server's CAS console (the “Migrate Distribution Point” task). When migrating a content distribution point, binary files are updated and file storage is migrated. To migrate storage, it is necessary that the server has 2-2.5 times more free space than that occupied by all SCCM 2007 packages on this server, since the SCCM package storage is being rebuilt.
Migration of Secondary Site servers is not possible. Instead, there is an “in place” upgrade of the Secondary Site server only to the content distribution point of the target hierarchy (this is a technical limitation of the system introduced by Microsoft due to changes in package replication mechanisms in the hierarchy and improvements in package replication traffic control mechanisms) while maintaining all packages. 2-2.5 SCCM 2007 , SCCM.
Primary Site , Primary Site Primary Site CAS ( Primary Site ) . , «» Primary Site SCCM 2012 . , CAS .
:
ReportSync – SCCM 2007 SCCM 2012. .
RegKeytoMof – mof . .
ExtractContent – «Prestage Content» . SCCM 2012, «BIN» SCCM
CMTrace – . SCCM 2012, «Tools» SCCM.
Notepad – .
7.
Migration occurs in stages. You can proceed to the next stage of migration only after the full completion of the previous stage. In case of failure of the target hierarchy, a painless return of the IT infrastructure to the original hierarchy is possible, since migration does not imply any changes that impede the functioning of the initial hierarchy (before the client migration phase).
In the first step of the migration, you must create an SCCM target hierarchy in parallel with the existing hierarchy.
The second stage is the preparation of hierarchies and the collection of information about the original hierarchy.
At the third stage, the migration of SCCM objects takes place.
The fourth stage is the migration of SCCM clients.
The fifth step is to test the target hierarchy and decommission the source hierarchy.
7.1. SCCM 2012
1. .
2. .
3. .
4. CAS .
5. CAS .
, SCCM, ( CAS , , TCI\IP), CAS . , – .
6. CAS : CAS ( Monitoring, «Site Status» «Component Status»), .
7. Primary Site ( 2-4).
8. Install Primary Site Server.
During the installation process, you must specify the database server (the account on behalf of which the server is installed must have appropriate permissions to access the database server, in addition, TCI \ IP access must be enabled on the database server), the site code and the server should be specified which will be the parent of this Primary Site server, that is, the CAS server of the new hierarchy. To install the Primary Site server, the same distribution kit is used as for installing the CAS server.
9. Primary Site : Primary Site ( Monitoring, «Site Status» «Component Status»), , CAS (replmgr.log, rcmctrl.log Monitoring, «Site Status» «Component Status»), (mpmsi.log, mpsetup.log, smsdpmon.log Monitoring, «Site Status» «Component Status»), , .
10. Primary site ( 8 9).
11. SCCM 2012: ( Monitoring, «Site Status» «Component Status»), ( Monitoring, «Site Hierarchy»), .
12. ( , , «push» ).
13. «security scopes».
7.2.
1. . , SCCM 2007. , . , , .
2. . .
3. After that, you need to connect Primary Site with unique content to the SCCM 2012 hierarchy. Both actions are performed using the SCCM 2012 console (Migration tab, Administration tabs). To do this, select the “Specify Source Hierarchy” item and enter the necessary data for the connection. SCCM 2007 hierarchy sites are connected to a central site.
4. «Share Distribution Points» ( Migration, Administration). . , Secondary Site . ( Primary Site ).
7.3. SCCM
1. . «Create Migration Job» ( Migration, Administration). : «Collection Migration» «Object Migration». , , «Security Scope», , . SCCM. . «Collection Migration».
«Collection Migration» ( ), «Object Migration» ( ). Primary Site SCCM ( Secondary Site – ). , .
2. ( 1) . : Reporting Monitoring, Migration jobs Administration, SCCM – migmctrl.log logs.
SQL Server Reporting Services. , SQL. SQL Server Reporting Services, SCCM ( SCCM, , ), SQL ( SCCM, “Copy Reports to Reporting Services”). SQL Server Reporting Services Report Builder ReportSync.
«» sms_def.mof SCCM 2012 WMI SCCM 2012. Administration, Client Settings, ( ), «Hardware Inventory» «Set Classes». Import WMI.
3. SCCM SCCM 2012.
4. «Boundary Group» , «Boundaries» «Boundary Groups» ( Hierarchy Configuration, Administration).
5. «Prestage Content» ( SCCM). «Software Library» , «Create Prestage Content File».
6. «Prestage Content» extractcontent /p.
7.4. Migrating SCCM clients
1. Before installing the SCCM 2012 agents, it is recommended to install the SCCM 2012 software necessary for the client to work on the client machines in advance. This step is optional, but desirable because it reduces the installation time of the SCCM 2012 client and the number of installation failures. Prior to client migration, they are serviced by servers in the Source hierarchy.
2. Since the client's migration, in fact, is the agent reinstallation, it can be done in all the ways that it is possible to install the SCCM agent. Client installation methods have not changed in the new version of SCCM.
Client migration should be carried out in stages (500-1000 clients each) to reduce the load on the network infrastructure and the database server. When migrating, you need to consolidate customers. Clients of the target hierarchy may belong to one of the Primary Site servers. All clients from each Primary Site server migrate from the corresponding Primary Site server of the second level of the hierarchy of the original hierarchy and all its child sites.
To create an agent installation package for a new hierarchy in the source hierarchy, you must copy the contents of the agent installation package from the new hierarchy. The agent must be installed with the key SMSSITECODE = XXX, where XXX is the code of the parent Primary Site of the server for this client. This is necessary for the client to bind to the hierarchy.
If the installation of the SCCM 2012 agent is not made, you need to check the ccmsetup.log log on the client machine for errors. If this log is not detected on the machine, you must repeat the installation of the agent on it, since the initial attempt to install the agent was not made (perhaps the computer was turned off).
7.5. Testing the target hierarchy and decommissioning the source hierarchy
1. The content distribution points are migrated after the clients have completed their migration. To migrate content distribution points, use the “Upgrade Distribution Point” item (Migration tab, Administration tabs).
( ) SCCM SCCM . «Prestage Content» .
SCCM 2007 .
2. Primary Site SCCM 2007 (Distribution Point, Secondary Site ) . «Create Site Systems Server» «Create Secondary Site» Secondary Site .
3. : , , , . .
4. .
References :
Administrator Checklists for Migration Planning in System Center 2012 Configuration Manager
Introduction to Migration in System Center 2012 Configuration Manager
Install Sites and Create a Hierarchy for Configuration Manager
Planning for Configuration Manager Sites and Hierarchy
Supported Configurations for Configuration Manager
System Center 2012 – Configuration Manager Component Add-ons and Extensions (Tools)
Migrating from Configuration Manager 2007 to Microsoft System Center 2012 R2 Configuration Manager ()
ConfigMgr client automatic site assignment behavior in a multi site environment
Performing a side-by-side Migration from Configuration Manager 2007 (WindowsNoob)
System Center 2012 Configuration Manager Migration — Deep(ish) Dive Part 1 (troubleshooting)
System Center 2012 Configuration Manager Survival Guide
:
www.css-security.com/blog/sccm-2012-migration-made-easy-part-1
www.css-security.com/blog/sccm-2012-migration-made-easy-part-2
www.css-security.com/blog/sccm-2012-migration-made-easy-part-3
anoopcnair.com/2015/08/20/upgrading-from-sccm-2007-to-sccm-2012-with-adaptiva-onesite
activedirectory.ncsu.edu/services/sccm
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/268449/
All Articles