Vulnerability in Platius: access to any account
Last week we received a letter inviting me to interview the Platius company. The position was written as if under me, and after the phone rang, an interview was arranged. I had an evening of preparation and I decided to study what the company was doing all the same.
It turned out that the “provision” of free access to the accounts of its users.
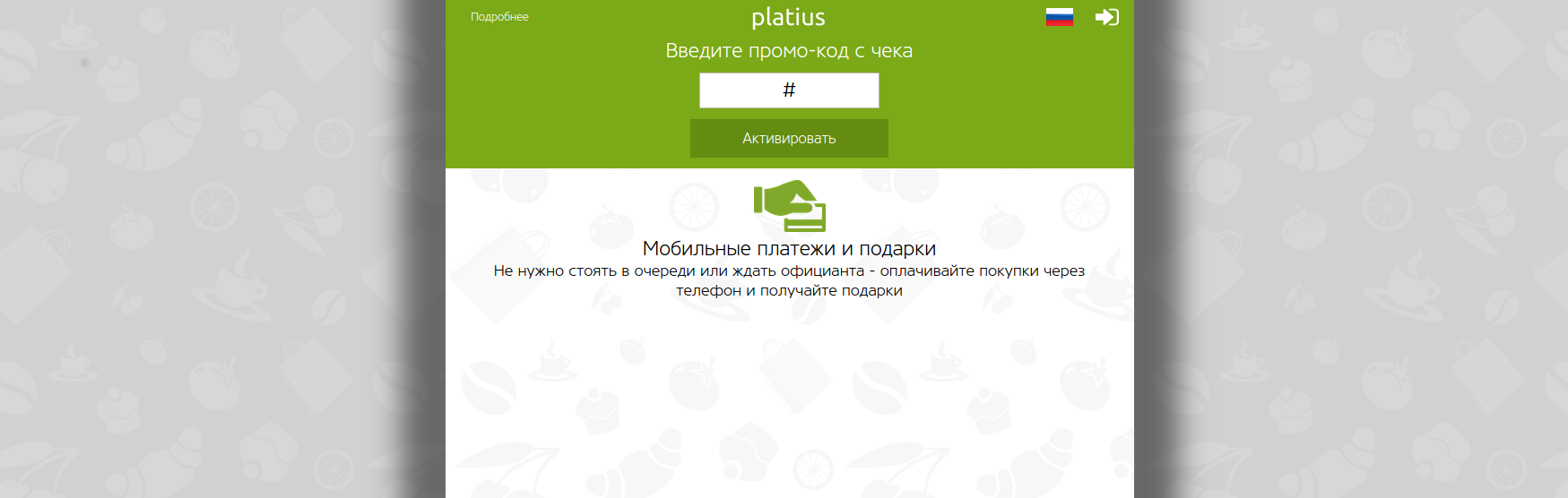
After 5 minutes, Google found out:
')
Played with the promotional code, did not find anything interesting. I decided to see how the authorization and registration takes place. After entering the phone number are asked to enter the captcha. Behind his back was the experience of automatically passing some captchas. In this case, you could not even look at the insides of the implementation of a captcha, and even heavy OCR algorithms are not needed. The numbers on the image are always:

Typical captcha
That is, we have enough of checking a pair of control points for the passage of a captcha. Here is the first weak point. But as it turned out, you can not even pass the captcha.
After checking the captcha, an SMS with a password to enter the account comes to the specified number. But apparently a bunch of captcha-session is not marked passed, and we can send new passwords to any phone number in unlimited quantities. Thereby, it is possible to arrange an attack on the sending module.
Signature "If the SMS did not come, ask for the password again. This can be done in 10 minutes ”is just a fiction, there is no time limit for requesting a new password, as well as the functionality for requesting it.
Go to the cherry on the cake: the password for authorization in the office. The password is 4 decimal digits. I tried to drive a couple of invalid - I received an invitation to try again. I tried: the limit on the number of attempts and does not smell like my own and the lifetime of such a password. Quickly dashed script for "hacking" your account:
The experiment showed that my three-day password was still valid for login. As you can guess, the password is not marked used after successful authorization, which gives an attacker the ability to log into any account without even disturbing the owner of the SMS.
Access to the account allows you to access various personal data and it is possible to pay, which passes through a bank card attached to the account. I did not dare to test this part, because it is terrible to bind my hard-earned money to such unreliable things.
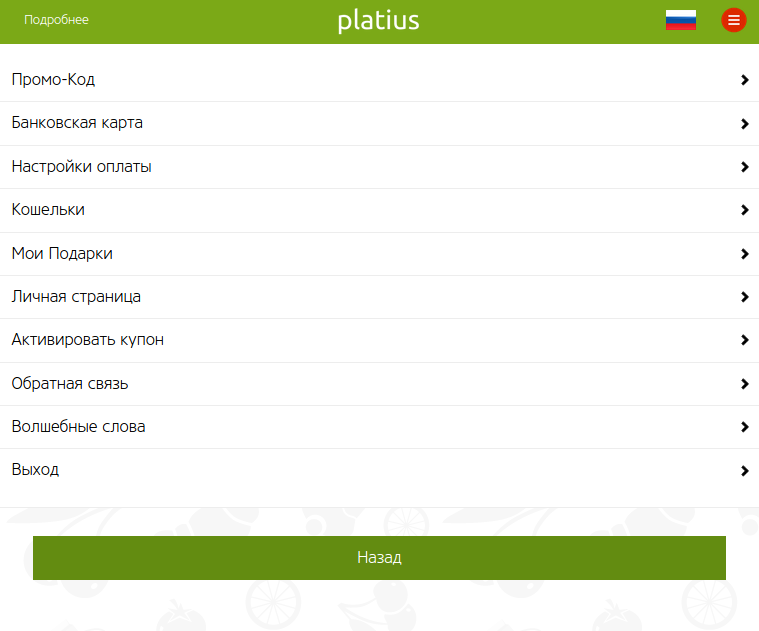
This all can be accessed
The first time I went to the interview with the knowledge of serious holes in the security of applications - an interesting experience, I tell you. Waves of adrenaline alternate with periods of calm. In an interview after ritual dances with tests and puzzles (which were inherited from iiko), I talked about the vulnerabilities found. However, apparently, this is not considered something critical, and no one hurries to plug holes. What grieves.
After almost two weeks nothing has been repaired. As it turned out, they do not have a bagbauti, and in general everything is sad. It is not clear why they forget about the things that bear, in my opinion, enormous reputational problems and possible financial losses for clients.
The question of finding phone numbers with an office in the platus remains open, but I am sure that there are direct or indirect ways to get this data. For example, by profiles like the Platius group on VKontakte . Also open is the question of logging in to a mobile application without first sending an SMS to the number of the attacker. The task is likely to be reduced in the substitution of the local storage of the application. So researchers have where to turn.
It turned out that the “provision” of free access to the accounts of its users.

After 5 minutes, Google found out:
')
- their software for paying bills using a smartphone and for various loyalty programs;
- everyone started doing this in iiko , where I was once in an interview;
- Sberbank bought them at the beginning of the year;
- They have 3.5 million users.
Played with the promotional code, did not find anything interesting. I decided to see how the authorization and registration takes place. After entering the phone number are asked to enter the captcha. Behind his back was the experience of automatically passing some captchas. In this case, you could not even look at the insides of the implementation of a captcha, and even heavy OCR algorithms are not needed. The numbers on the image are always:
- at one place
- one color
- there are always 4

Typical captcha
That is, we have enough of checking a pair of control points for the passage of a captcha. Here is the first weak point. But as it turned out, you can not even pass the captcha.
After checking the captcha, an SMS with a password to enter the account comes to the specified number. But apparently a bunch of captcha-session is not marked passed, and we can send new passwords to any phone number in unlimited quantities. Thereby, it is possible to arrange an attack on the sending module.
Signature "If the SMS did not come, ask for the password again. This can be done in 10 minutes ”is just a fiction, there is no time limit for requesting a new password, as well as the functionality for requesting it.
Go to the cherry on the cake: the password for authorization in the office. The password is 4 decimal digits. I tried to drive a couple of invalid - I received an invitation to try again. I tried: the limit on the number of attempts and does not smell like my own and the lifetime of such a password. Quickly dashed script for "hacking" your account:
seq --equal-width 0 9999 | parallel 2> /dev/null -j 0 --halt 2 -q bash -c " header=\$(curl 'https://platius.ru/ru-RU/Login/PasswordStep' --data 'Login=%2B7xxxxxxxxxx&Password={}' -kis | tac | tac | head -n 1); if [[ \$header == *\"302\"* ]]; then echo {}; exit 1; fi" The experiment showed that my three-day password was still valid for login. As you can guess, the password is not marked used after successful authorization, which gives an attacker the ability to log into any account without even disturbing the owner of the SMS.
Access to the account allows you to access various personal data and it is possible to pay, which passes through a bank card attached to the account. I did not dare to test this part, because it is terrible to bind my hard-earned money to such unreliable things.

This all can be accessed
The first time I went to the interview with the knowledge of serious holes in the security of applications - an interesting experience, I tell you. Waves of adrenaline alternate with periods of calm. In an interview after ritual dances with tests and puzzles (which were inherited from iiko), I talked about the vulnerabilities found. However, apparently, this is not considered something critical, and no one hurries to plug holes. What grieves.
Epilogue
After almost two weeks nothing has been repaired. As it turned out, they do not have a bagbauti, and in general everything is sad. It is not clear why they forget about the things that bear, in my opinion, enormous reputational problems and possible financial losses for clients.
The question of finding phone numbers with an office in the platus remains open, but I am sure that there are direct or indirect ways to get this data. For example, by profiles like the Platius group on VKontakte . Also open is the question of logging in to a mobile application without first sending an SMS to the number of the attacker. The task is likely to be reduced in the substitution of the local storage of the application. So researchers have where to turn.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/268305/
All Articles