The new generation of HP 3PAR StorServ sharpened to use flash memory
Our last post on HP 3PAR StorServ storage systems was released in the middle of last year , and this summer, HP completely updated this line of disk arrays, not only increasing their scalability and performance, but also greatly expanding the possibilities of using solid-state memory in them.


HP 3PAR StorServ Controller Hub
Recall that a feature of HP 3PAR StorServ, compared with traditional modular and monolithic arrays, is the use of a fully interconnected full mesh architecture, providing stable performance with a sharp increase in load, uniform loading of array controllers and high fault tolerance of the system. Thanks to full mesh, each logical volume of the array is served simultaneously by all its controllers. In the older HP 3PAR StorServ models, using full mesh, up to eight array controllers are combined into a single system, and up to four in the younger ones. Another feature of the HP 3PAR StorServ is the use of specialized Thin Express ASIC microchips in controllers, in which some of the storage management functions implemented in traditional arrays are performed by controllers, for example, RAID checksum calculations. ASIC independently processes data and metadata, reducing the response time of the array. The use of the Thin Express ASIC reduces the load on the CPUs of the controllers, thereby increasing the overall performance of the array and reducing delays in processing requests from applications for data access. Finally, the third feature of HP 3PAR StorServ is the implementation of Thin Express ASICs that improve the efficiency of data storage and the use of disk space in an array of different “thin” technologies, starting with the dynamic allocation of thin provisioning capacity, which was originally built into the 3PAR architecture.
')
The HP 3PAR StorServ update was done in two steps. First, on June 1, HP Discover in Las Vegas presented two high-end HP 3PAR StorServ models of the 20,000th series, and on August 26, the announcement of the four lower-end HP 3PAR StorServ 8000-series models was launched along with another model from the 20,000th series.
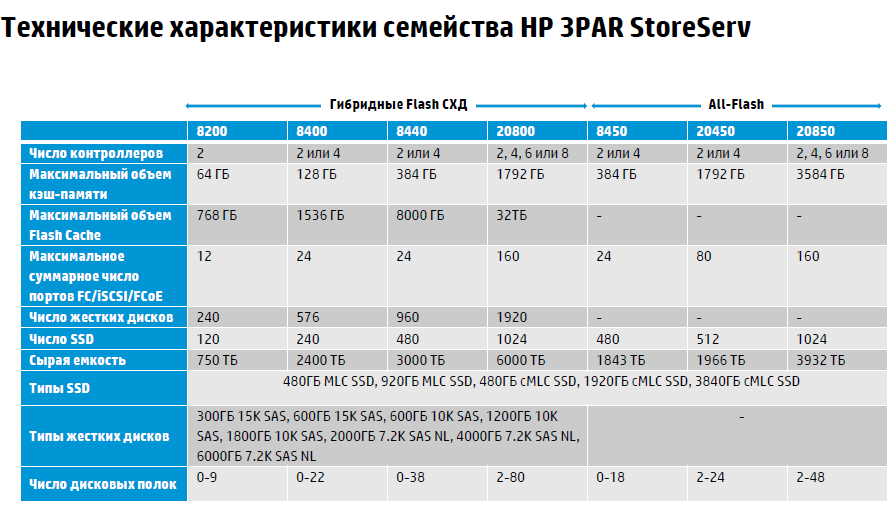
Compared with the previous generation HP 3PAR StorServ in the new arrays of solid-state drives from the option turned into the main type of drive. The three All-Flash models, which are focused on getting maximum performance, whose number ends with “50” (8450, 20450 and 20850), use only SSDs and do not support traditional hard drives. The remaining four models (8200, 8400, 8440 and 20800) are hybrid arrays, designed for a combination of solid-state and hard drives. Younger models 8200 and 8400 are designed for customers with a limited IT budget, and the more powerful HP 3PAR StorServ 8440 and 20800 are for those customers who need maximum capacity scalability.

HP 3Par StorServ 20000 Stand
If in the previous generation HP 3PAR StorServ the maximum capacity of the solid-state disk was 1.92 TB, the new models support SSD Commercial MLC (cMLC) with a capacity of 3.84 TB. The use of multi-terabyte cMLC increased the scalability of solid-state configurations and the density of solid-state memory (280 TB of usable capacity can be placed in a dual-disk disk shelf, and 5.5 GB of a useful capacity in one rack), and also reduced the cost of one gigabyte of flash memory capacity. Taking into account the various technologies used by HP 3PAR StorServ to use flash memory more efficiently (Adaptive Sparing, thin provisioning and deduplication) when using the new cMLC, the cost of storing 1 GB of data is lower than that of 10K RPM hard drives.
In addition to the increased capacity SSDs, the HP 3PAR StorServ 8000 and 20000 have significantly upgraded the hardware — the latest Intel Xeon Ivy Bridge processors are installed in the controllers, the cache memory is increased, the system bus is based on PCI Express Gen3, and 12 Gigabit SAS is used as an internal interconnect and the optical ports of the arrays support 16 gigabit Fiber Channel. Combined with the improved HP 3PAR StorServ software and the new, twice as powerful fifth generation HP 3PAR Gen5 Thin Express ASIC chips, this provided the HP 3PAR StorServ 20000 with a performance of 3.2 million IOPS with a response time of 0.2 - 0.8 milliseconds and bandwidth up to 75 GB / s, as well as the scalability of one system up to 15 Petabytes of usable capacity. Thus, the HP 3PAR StorServ multi-controller mesh-architecture allows to get the maximum performance benefit when switching to the use of solid-state memory. In addition, the built-in Storage Federation functions allow you to integrate up to four HP 3PAR StorServ arrays with a usable capacity of up to 60 PB without a special hardware “storage virtualizers”, and in the same federation can work as eight or twenty thousand meters and models previous generation.
HP engineers have added a number of new technologies to the functionality of the HP 3PAR OS 3.2.2 operating system, which improve the efficiency of disk space utilization and implement additional means of ensuring protection and continuous data availability.
Using the HP 3PAR Gen5 Thin Express chip, thin deduplication (thin deduplication) is implemented, which saves array capacity by preventing repeated recording of the same data. Thin deduplication works online and does not involve the central processors of the array controllers, so its use introduces minimal delay to the operation of writing data to the array. Unlike most vendors offering deduplication in their disk arrays, HP supports the option to disable thin deduplication in cases where the application needs to ensure the highest possible write speed or the use of deduplication does not make sense due to the low degree of repeatability.
The ASIC generates and assigns a hash signature to each incoming write request. HP 3PAR StoreServ uses the HP 3PAR Express Indexing indexing mechanism, which speeds up table searches and is able to quickly find previously made identical write requests. When a new write request arrives in the system, Express Indexing searches for metadata to compare the signature of this request with the signatures of previous write operations. If an identical query is found, the system marks the new query as a duplicate and instead of re-writing identical data to the array disks, a pointer is written to the metadata table to the data block already stored on the array. To prevent hash conflicts, ASIC performs a bit-by-bit comparison before marking a new write request as a duplicate.
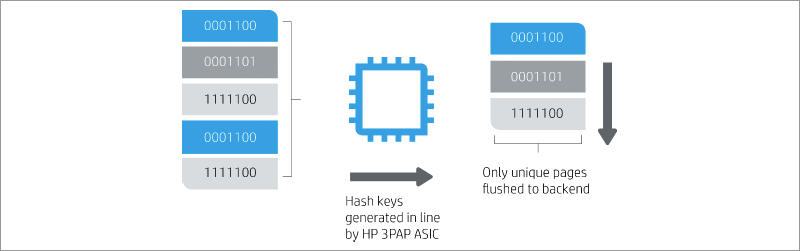
Online deduplication based on hash signatures generated by ASIC
To ensure data integrity during transmission within the array components, the new generation HP 3PAR StoreServ has implemented a hardware-level Persistent Checksum mechanism implemented inside the 3PAR Gen5 Thin Express ASIC, which works in accordance with the T10-PI data protection standard (Protection Information). Persistent Checksum is designed to protect data from “invisible damage” that may occur due to the failure of a separate component of the I / O stack when transferring data from / to the solid state drive from the server's HBA adapter through a SAN switch to the array HBAs. Persistent Checksum works completely transparently to the applications and operating systems of the hosts and is integrated with HBA adapters and server hardware drivers, which guarantees checking the integrity of data all the way from the server to the HP 3PAR StoreServ drives.
T10-PI is a SCSI standard that implements an additional level of data protection using an additional eight-byte Data Integrity Field (DIF) field for each disk sector. Usually, the data obtained as a result of a successful disk read is considered correct and is immediately transferred to the host who requested it. T10-PI implements the verification of the data read from the disk before it is transferred to the host. For write requests, the use of T10-PI ensures that the exact data that the host has sent for recording will be written to the SSD. If data corruption is detected, the HP 3PAR operating system will respond to the write request with an error message and the host will again issue a write request.
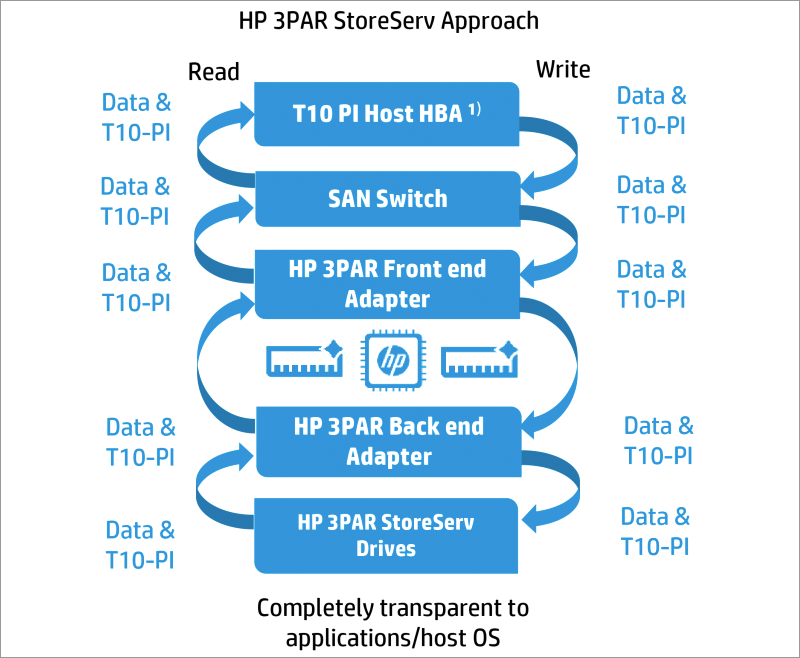
Persistent Checksum Data Integrity Checker
When using hard drives, when the response time to a request for data is measured in tens of milliseconds, the delay that synchronous replication brings to the remote array is acceptable from the SLA point of view. However, when switching to flash memory, when the response time is reduced to fractions of a millisecond, the delay due to synchronous replication will seriously “slow down” access to application data, therefore support for Asynchronous Streaming mode has been added to the HP 3PAR Remote Copy package, which allows a remote array is an almost exact (near exact) copy of data with a target recovery point (RPO) of no more than a few seconds. The use of asynchronous streaming replication ensures data availability in the event of a major crash in the main data center without reducing the performance of applications that use this data (in addition to this new mode, HP 3PAR Remote Copy supports synchronous and periodic asynchronous replication between the three data centers).
Of the other HP 3PAR 8000 and 20000 features, it is worth noting the implementation of bi-directional volume transfer between the four-file federation using Peer Motion and the ability to use this technology, which is implemented at the Thin Express ASIC level, to import data from the outdated Hitachi arrays (before that, Peer Motion supported import from EMC arrays only). Updated Priority Optimization software will allow you to set access time targets of up to 0.5 milliseconds to provide the necessary level of service for critical business applications.
In addition, the StoreOnce Recovery Manager Central for VMware (RMC-V) for 3PAR StoreServ virtual machine backup and recovery package, which creates consistent snapshots of virtual machines, and then automatically copies them directly from the HP 3PAR StoreServ to the HP StoreOnce Disk Library, support for VMware vSphere 6.0 with VMware Virtual Volumes (VVOLs), as well as the possibility of granular recovery of individual virtual machines and files. Using RMC-V reduces the cost of backup compared to traditional methods based on a dedicated backup management server and specialized software, and by switching from hierarchical to flat backup, it accelerates backup recording operations up to 5 times and restores up to 5 times. on them virtual machines.
According to reports from the Gartner analytical agency, last year, HP had the highest growth rates in sales of flash arrays among the major players in the storage market. The new generation of HP 3PAR StorServ, introduced this summer, incorporates new features that improve flash memory efficiency and lowers the cost of solid-state drives, strengthening HP's leading position in the rapidly growing flash array market.


HP 3PAR StorServ Controller Hub
Recall that a feature of HP 3PAR StorServ, compared with traditional modular and monolithic arrays, is the use of a fully interconnected full mesh architecture, providing stable performance with a sharp increase in load, uniform loading of array controllers and high fault tolerance of the system. Thanks to full mesh, each logical volume of the array is served simultaneously by all its controllers. In the older HP 3PAR StorServ models, using full mesh, up to eight array controllers are combined into a single system, and up to four in the younger ones. Another feature of the HP 3PAR StorServ is the use of specialized Thin Express ASIC microchips in controllers, in which some of the storage management functions implemented in traditional arrays are performed by controllers, for example, RAID checksum calculations. ASIC independently processes data and metadata, reducing the response time of the array. The use of the Thin Express ASIC reduces the load on the CPUs of the controllers, thereby increasing the overall performance of the array and reducing delays in processing requests from applications for data access. Finally, the third feature of HP 3PAR StorServ is the implementation of Thin Express ASICs that improve the efficiency of data storage and the use of disk space in an array of different “thin” technologies, starting with the dynamic allocation of thin provisioning capacity, which was originally built into the 3PAR architecture.
')
New model range
The HP 3PAR StorServ update was done in two steps. First, on June 1, HP Discover in Las Vegas presented two high-end HP 3PAR StorServ models of the 20,000th series, and on August 26, the announcement of the four lower-end HP 3PAR StorServ 8000-series models was launched along with another model from the 20,000th series.
Compared with the previous generation HP 3PAR StorServ in the new arrays of solid-state drives from the option turned into the main type of drive. The three All-Flash models, which are focused on getting maximum performance, whose number ends with “50” (8450, 20450 and 20850), use only SSDs and do not support traditional hard drives. The remaining four models (8200, 8400, 8440 and 20800) are hybrid arrays, designed for a combination of solid-state and hard drives. Younger models 8200 and 8400 are designed for customers with a limited IT budget, and the more powerful HP 3PAR StorServ 8440 and 20800 are for those customers who need maximum capacity scalability.

HP 3Par StorServ 20000 Stand
If in the previous generation HP 3PAR StorServ the maximum capacity of the solid-state disk was 1.92 TB, the new models support SSD Commercial MLC (cMLC) with a capacity of 3.84 TB. The use of multi-terabyte cMLC increased the scalability of solid-state configurations and the density of solid-state memory (280 TB of usable capacity can be placed in a dual-disk disk shelf, and 5.5 GB of a useful capacity in one rack), and also reduced the cost of one gigabyte of flash memory capacity. Taking into account the various technologies used by HP 3PAR StorServ to use flash memory more efficiently (Adaptive Sparing, thin provisioning and deduplication) when using the new cMLC, the cost of storing 1 GB of data is lower than that of 10K RPM hard drives.
In addition to the increased capacity SSDs, the HP 3PAR StorServ 8000 and 20000 have significantly upgraded the hardware — the latest Intel Xeon Ivy Bridge processors are installed in the controllers, the cache memory is increased, the system bus is based on PCI Express Gen3, and 12 Gigabit SAS is used as an internal interconnect and the optical ports of the arrays support 16 gigabit Fiber Channel. Combined with the improved HP 3PAR StorServ software and the new, twice as powerful fifth generation HP 3PAR Gen5 Thin Express ASIC chips, this provided the HP 3PAR StorServ 20000 with a performance of 3.2 million IOPS with a response time of 0.2 - 0.8 milliseconds and bandwidth up to 75 GB / s, as well as the scalability of one system up to 15 Petabytes of usable capacity. Thus, the HP 3PAR StorServ multi-controller mesh-architecture allows to get the maximum performance benefit when switching to the use of solid-state memory. In addition, the built-in Storage Federation functions allow you to integrate up to four HP 3PAR StorServ arrays with a usable capacity of up to 60 PB without a special hardware “storage virtualizers”, and in the same federation can work as eight or twenty thousand meters and models previous generation.

New HP 3PAR StorServ functionality
HP engineers have added a number of new technologies to the functionality of the HP 3PAR OS 3.2.2 operating system, which improve the efficiency of disk space utilization and implement additional means of ensuring protection and continuous data availability.
Thin deduplication
Using the HP 3PAR Gen5 Thin Express chip, thin deduplication (thin deduplication) is implemented, which saves array capacity by preventing repeated recording of the same data. Thin deduplication works online and does not involve the central processors of the array controllers, so its use introduces minimal delay to the operation of writing data to the array. Unlike most vendors offering deduplication in their disk arrays, HP supports the option to disable thin deduplication in cases where the application needs to ensure the highest possible write speed or the use of deduplication does not make sense due to the low degree of repeatability.
The ASIC generates and assigns a hash signature to each incoming write request. HP 3PAR StoreServ uses the HP 3PAR Express Indexing indexing mechanism, which speeds up table searches and is able to quickly find previously made identical write requests. When a new write request arrives in the system, Express Indexing searches for metadata to compare the signature of this request with the signatures of previous write operations. If an identical query is found, the system marks the new query as a duplicate and instead of re-writing identical data to the array disks, a pointer is written to the metadata table to the data block already stored on the array. To prevent hash conflicts, ASIC performs a bit-by-bit comparison before marking a new write request as a duplicate.

Online deduplication based on hash signatures generated by ASIC
Persistent Checksum
To ensure data integrity during transmission within the array components, the new generation HP 3PAR StoreServ has implemented a hardware-level Persistent Checksum mechanism implemented inside the 3PAR Gen5 Thin Express ASIC, which works in accordance with the T10-PI data protection standard (Protection Information). Persistent Checksum is designed to protect data from “invisible damage” that may occur due to the failure of a separate component of the I / O stack when transferring data from / to the solid state drive from the server's HBA adapter through a SAN switch to the array HBAs. Persistent Checksum works completely transparently to the applications and operating systems of the hosts and is integrated with HBA adapters and server hardware drivers, which guarantees checking the integrity of data all the way from the server to the HP 3PAR StoreServ drives.
T10-PI is a SCSI standard that implements an additional level of data protection using an additional eight-byte Data Integrity Field (DIF) field for each disk sector. Usually, the data obtained as a result of a successful disk read is considered correct and is immediately transferred to the host who requested it. T10-PI implements the verification of the data read from the disk before it is transferred to the host. For write requests, the use of T10-PI ensures that the exact data that the host has sent for recording will be written to the SSD. If data corruption is detected, the HP 3PAR operating system will respond to the write request with an error message and the host will again issue a write request.

Persistent Checksum Data Integrity Checker
Asynchronous stream replication
When using hard drives, when the response time to a request for data is measured in tens of milliseconds, the delay that synchronous replication brings to the remote array is acceptable from the SLA point of view. However, when switching to flash memory, when the response time is reduced to fractions of a millisecond, the delay due to synchronous replication will seriously “slow down” access to application data, therefore support for Asynchronous Streaming mode has been added to the HP 3PAR Remote Copy package, which allows a remote array is an almost exact (near exact) copy of data with a target recovery point (RPO) of no more than a few seconds. The use of asynchronous streaming replication ensures data availability in the event of a major crash in the main data center without reducing the performance of applications that use this data (in addition to this new mode, HP 3PAR Remote Copy supports synchronous and periodic asynchronous replication between the three data centers).
Of the other HP 3PAR 8000 and 20000 features, it is worth noting the implementation of bi-directional volume transfer between the four-file federation using Peer Motion and the ability to use this technology, which is implemented at the Thin Express ASIC level, to import data from the outdated Hitachi arrays (before that, Peer Motion supported import from EMC arrays only). Updated Priority Optimization software will allow you to set access time targets of up to 0.5 milliseconds to provide the necessary level of service for critical business applications.
In addition, the StoreOnce Recovery Manager Central for VMware (RMC-V) for 3PAR StoreServ virtual machine backup and recovery package, which creates consistent snapshots of virtual machines, and then automatically copies them directly from the HP 3PAR StoreServ to the HP StoreOnce Disk Library, support for VMware vSphere 6.0 with VMware Virtual Volumes (VVOLs), as well as the possibility of granular recovery of individual virtual machines and files. Using RMC-V reduces the cost of backup compared to traditional methods based on a dedicated backup management server and specialized software, and by switching from hierarchical to flat backup, it accelerates backup recording operations up to 5 times and restores up to 5 times. on them virtual machines.
findings
According to reports from the Gartner analytical agency, last year, HP had the highest growth rates in sales of flash arrays among the major players in the storage market. The new generation of HP 3PAR StorServ, introduced this summer, incorporates new features that improve flash memory efficiency and lowers the cost of solid-state drives, strengthening HP's leading position in the rapidly growing flash array market.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/268043/
All Articles