Optimization of communication channels for mining in the north of Russia

When we went to the installation, next to get a tractor from the ravine
There are such harsh Russian men who extract various minerals, which are meanly grouped in hard to reach places. Often, just getting and pulling them out of the ground can be very, very expensive. Therefore, a developed infrastructure at the mining site is a rare phenomenon. So, in the Far East, in many places, fiber is still a science fiction section, and the wire is found in the wild only if you bring it in your hands.
Communication there is made via satellite. Accordingly, the requirements for the channel are growing, but expanding is very painful and expensive - the satellite resource is not the most scalable, and it will not be possible to drive gigabytes through it.
')
We solved the channel optimization problem by compressing traffic and prioritizing applications in the channels so that the most important thing always goes first. It turned out a whole network detective.
Introductory
There is a channel on the satellite, and to expand it is expensive. There are Riverbed solutions that allow you to compress traffic, optimize the exchange at the protocol level (so that no redundant data is transmitted), plus cache the compression dictionary itself. All this as a whole can give from 20% to 80% of the gain per lane, depending on what the data is and how it flies.
The task began with the fact that we were asked to calculate the possibility of prioritizing critical traffic so that it stands out from the entire exchange on the points. After that, it became clear that optimization was also very profitable, because one had to pay constantly for a raised satellite channel, and for iron only once.
Survey
The architecture of the exchange - a few "wheels with knitting" with hubs in large cities. For example, in Irkutsk, Magadan and Moscow. Optics or copper are suitable for hubs. At remote points at mining companies, a satellite communications station is used in 90% of cases, there are literally a pair of radio relay lines and at several points those who in one way or another dragged it past for the sake of the main line are sharing optics.
Put the diagnostic system that collects data.
There are many applications, but there are few users, the main exchange is technical. Here is an example of what can work at one of the enterprises somewhere far, far beyond the snow:
Recognized application | Interpretation of observed traffic |
Microsoft-DS Active Directory | File exchange by the operating system Windows (SMB Direct). |
Microsoft Terminal Server (RDP) | Remote Desktop |
Https | Outlook Web Access |
SMTP | Mail forwarding between Exchange servers |
MS SQL | Access to MS SQL server |
netview-aix-2 | Client connection 1C |
domain | Domain Name Service (DNS) |
webcache | Internet access through a proxy server |
For the most part, everyday traffic is file transfer, real time traffic, there is also production control, accounting and raw sensor data. Many applications that send information are "talkative", that is, they send many packages where it would be possible to do with one. Accordingly, such things are solved Riverbed quite simply.
Here, compare how applications work before and after optimization:

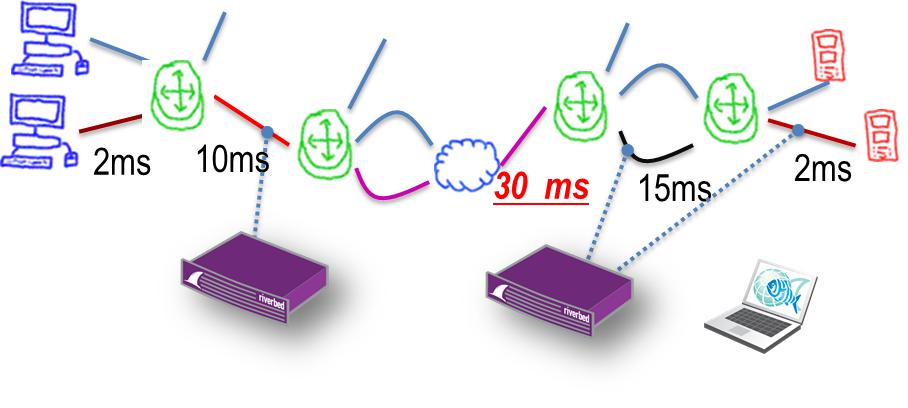
For example, the well-known "chatty" protocol CIFS, which is used to access files. A file of 20-40 MB in size on the local network will be downloaded in seconds. If the file is downloaded from a remote office via a WAN communication channel, as shown in the diagram above, the download time can be increased to 5 minutes or more.

To reduce download time to a remote office, you need to minimize the number of passes in both directions.
To prioritize the traffic, it was necessary to disassemble the packets — we had to raise the DPI analog and look at the 7th level, since it was obviously not enough to scatter the ports used — the same type of traffic could be either an important sensor or talkative exchange of something noncritical. Or, it was necessary to allocate Exchange sessions and give them a band at the stage of establishing a connection.
Before that, of course, we tried it just on routers, but there it’s a very difficult control, plus it’s all difficult to maintain the config. So that there is a complete understanding - in our case, there is no support team in the central office in Moscow. The principal was sitting at an equidistant distance from the mining points and the head organization. The place is so chosen because of time zones - there are chances to find a working day both there and there. There is also an intermediate team for operational tasks, but none of these people absolutely needed to create so many problems for manual settings. And without a guarantee of proper operation in the future.
Iron
Here we must interrupt and say that this whole story sounds smooth only on paper. Difficulties, of course, were - starting from such a banal thing as connecting traffic mirroring devices. Just imagine a mining company somewhere very, very far, where there is no road. Getting there by land can only be a few months a year. Accordingly, the iron after sending still somewhere at least 1 month gets to the point. How to get it - you need to connect it, and it will be connected by someone local from the customer support service.
All this was connected, fortunately, to a gap at the exit from the server through the bypass, so the work was quite simple. The only time was to give all the instructions BEFORE the engineer at the point pulled the cable, because the same telephony was tied to him.

Optimizer is the bottom
As a result, the following scheme was worked out:
- We received iron at our warehouse in Moscow
- They did diagnostics and pre-tuning, so that you can control the device right after the connection.
- Sent by branch
- Then they played “Avatar”, helping the specialists on the spot to make movements with the cable that were incomprehensible to them. Sometimes all this was observed through a video stream with a large lag. Nobody was funny.
- Later, a year later, the second part of the quest came - from some points the measuring equipment had to be removed and put on others.
Again, the romance of the North - one data center reached the place on a sled, well, at least not dogs. Datacenter on the sled, yes, yes.
Continuation
So, we saw what traffic goes and in what amounts. With what delays, what is business critical, what is not. What is important for the company is that it can be “slaughtered” - “slaughtered” if there was important traffic in the lane. They identified 4 classes of service for different types of information, coordinated them with telecom operators. Actually, we “painted” this traffic - and the telecom operator made shaping on the spot. There was another peculiarity in the fact that each facility had its own telecom operator: somewhere it was necessary to pay additionally for the service, somewhere it simply did not have the technical ability to shape correctly, had to fit in fewer service classes and come up with different hacks.
Rule network problems. Our mirror sensors have become an ideal debugging tool. Sensors were placed in all regions, had a copy of the traffic - it was possible to take a copy of the traffic from several points from the branch and from the center and compare. It turned out that we had the opportunity to fix each package here and there. As a result, we could assess what is happening with the operator of communication with each of them really. Here is an example:
An example of diagnostics at the customer:
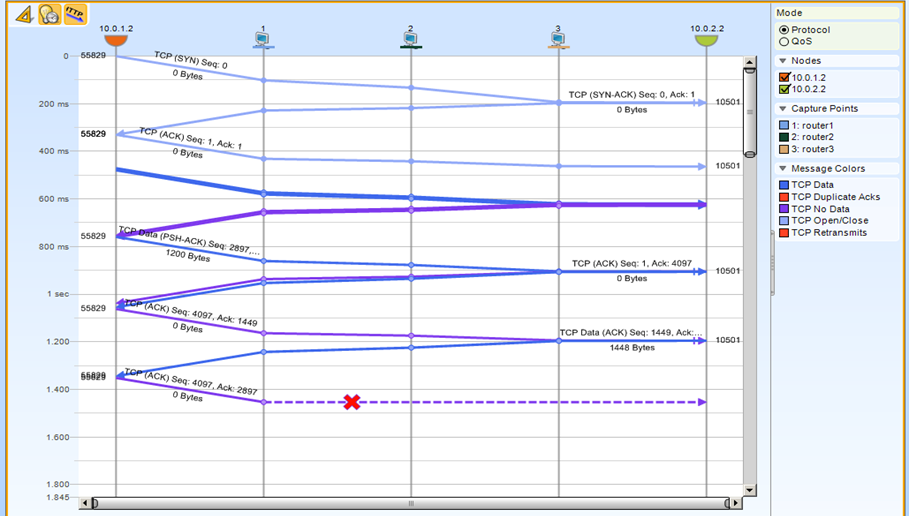
We see on which hop package was lost on the way from the server to the client
There was a case - the big boss came to the branch and said, they say, something you have here is one specific terminal falls off. "I come in the morning on the included car - and he fell off." The engineer on-site simply connected to the sensor and collected the last session packets to see why the connection ended. For half an hour in the packages it was found that the client itself breaks the connection on timeout. The reason is written in the package - and he scored her code on Google - and immediately saw the setting so as not to break.
What is iron?

Different optimizer models were installed ranging from the younger ones to the older ones, depending on the width of the communication channel and the number of users and information resources on the site. I wrote more about Riverbed solutions here and here in theory .
What is the total traffic savings?
Here is an example from one of the points:
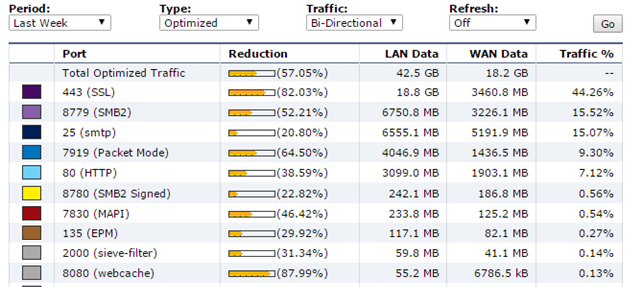
Total optimization here is 57.05 per week for optimized traffic on one of the large nodes.
Actually, this is the story. If you are interested in the details specifically on your project - I can roughly calculate by mail AVrublevsky@croc.ru. Well, ready to answer any questions here or in the mail.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/267883/
All Articles