Trojan Android app bypasses Google Bouncer checks
ESET analysts have discovered an interesting method of covert attacks on Android users, which contains an interesting feature. In the Google Play application store, we were able to detect several applications that were disguised as legitimate, but in fact contained another application with malicious functions. This embedded application was called systemdata or resourcea .

This second application is secretly reset to the device’s memory from the first, but asks the user for permission to install. It is presented as a tool for managing the settings of the “Manage Settings” device. After its installation, the application runs as a service in the background.
')
ESET anti-virus products detect applications that contain this additional application as Android / TrojanDropper.Mapin . According to our data, India has the largest number of infections of Android devices with this malware.
The malware is a backdoor, which gains control of the device and incorporates it into the botnet. The backdoor uses a special internal timer for deferred execution of its payload. Thus, authors can deceive various automatic systems for analyzing files that may rank a file as suspicious due to its behavior. In some cases, the backdoor can wait three days before activating the payload. Most likely, such a measure allows the authors to bypass the Google Bouncer file analysis tool verification mechanisms used by Google to verify applications downloaded to Play.
After activating the payload, the Trojan requests administrator rights in the system and starts interacting with its C & C server. Android / Mapin contains various functions, for example, displaying various notifications to the user, downloading, installing and launching other applications, as well as receiving personal user information on the device. At the same time, its main function is to display fullscreen advertising on an infected device.
Distribution vectors
Malicious apps were placed in the Google Play app store at the end of 2013 and in 2014. The names of the apps were different, including, “Hill climb racing the game”, “Plants vs zombies 2”, “Subway suffers”, “Traffic Racer” , Temple Run 2 Zombies, Super Hero Adventure by TopGame24h, TopGameHit and SHSH. Exact application download dates were November 24-30, 2013 and November 22, 2014. According to MIXRANK resource statistics , the Plants vs zombies 2 application was downloaded more than 10 thousand times before it was removed from the store. At the same time, the System Optimizer, Zombie Tsunami, tom cat talk, Super Hero adventure, Classic brick game applications, as well as the aforementioned Google Play applications with malicious capabilities, were downloaded to alternative stores. Android applications by the same authors. The same backdoor was found bundled with other applications that were uploaded to the store by the PRStudio developer (not to be confused with prStudio) in alternative app stores with links to Google Play. This developer has downloaded at least five other Trojan apps into alternative app stores: Candy crush or Jewel crush, Racing rivals, Super maria journey, Zombie highway killer, Plants vs Zombies. These applications are still available for download from these stores. The listed applications have been downloaded by users hundreds of times.
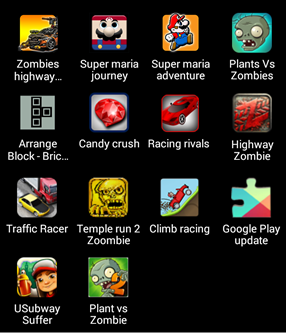
Fig. Malicious application icons.
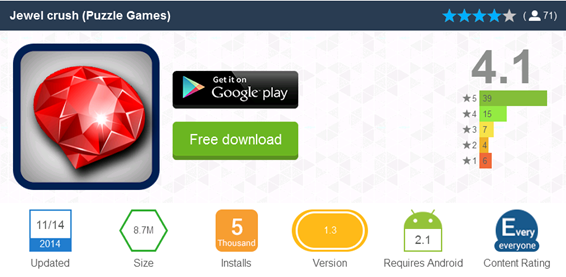
Fig. Malicious application that has received quite positive ratings.
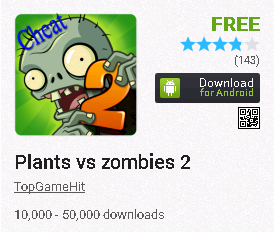
Fig. Another application that received positive ratings.
Analysis
There are various variants of the execution of a malicious program after a user has downloaded an illegitimate application. One of the options assumes that the victim will be asked to launch the file with the malicious program 24 after the first execution of the downloaded application. This method is less suspicious for the user, who believes that the launch request came from the OS. Another method involves the issuance of an instant request to the user. Both options are designed to trigger after a change in the network connection; for this, the malicious program registers a so-called. broadcast receiver in the manifest.

Fig. Registration t. broadcast receiver.
After changing the connection, the user will be prompted to install the “system application”. The malicious application itself, dropped onto the device, may be called “Google Play Update” or “Manage Settings”.
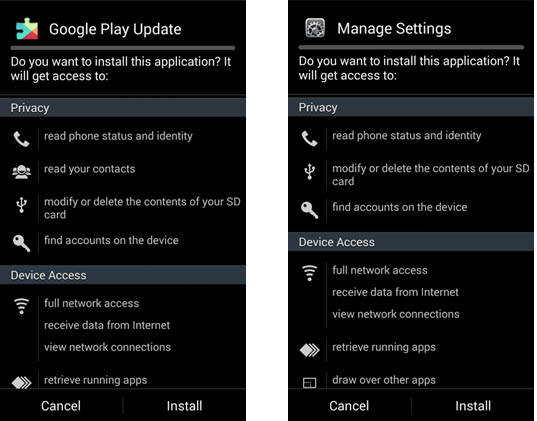
Fig. Malicious application disguised as a system.
In that case, if the user chooses to cancel the installation, then the malicious program will show a request every time when the network connection is changed. It can be assumed that a simple user will be sure of the seriousness of the displayed notification and at some point, most likely, will press the install button only to get rid of it. Once launched, the trojan is executed as a service with its registered broadcast receiver, awaiting a connection change.
When such a change occurs, the Trojan will attempt to register itself using the Google Cloud Messages (GCM) service to receive messages later. After that, Android / Mapin will try to register the infected device on the attacker's server, sending information such as your username, Google account, IMEI, registration ID (ID) and the name of your application package there.
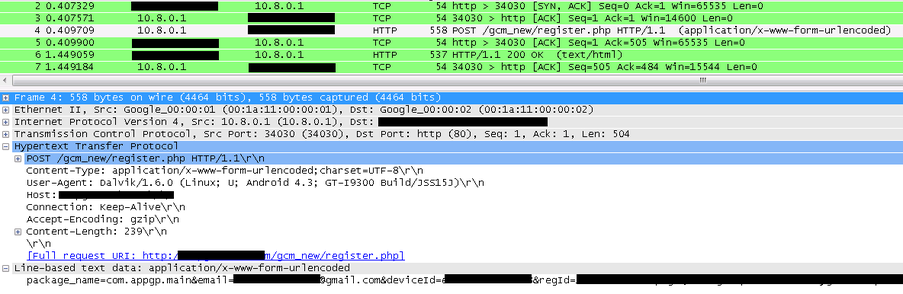
Fig. The process of registering a device on the attackers server.
In order to exclude the possibility of its removal from the system, the Trojan requires the user to activate the device administrator mode.
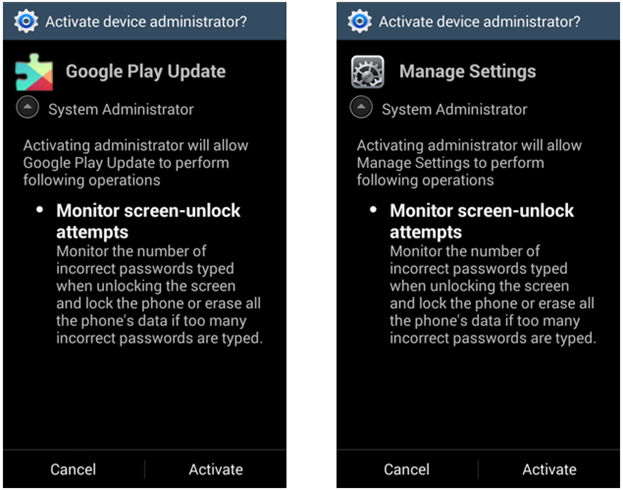
Fig. Suggestion to the user to activate the device administrator mode.
The trojan will report to the remote server about the successful activation of the device administrator mode. Once such an operation occurs, the malware will show the user advertisements in full screen mode ( interstitial ). Such advertising (interstitial ad) will be displayed to the user again every time you change the connection. Development of this type of advertising is possible using the legitimate AdMob SDK.
Fig. Full-screen advertising (interstitial ad).
Networking
A trojan interacts with its controlling server using the Google Cloud Messaging (GCM) service. This service is increasingly used by modern malware for its own purposes, through which attackers can instruct the bot to perform the actions they need.

Fig. Processed by the bot command.
Not all functions of a malicious program are fully implemented in its code, except for this, not all already implemented functions are used. It is possible that the threat itself is still at the level of development and will be improved in the future. As we have already mentioned, its main goal is to deliver aggressive full-screen advertising for displaying it to the user, disguised as a system application. A bot can also be used by attackers to install other malware on a compromised device.
In addition to displaying advertisements, the list of supporting functions performed by it is quite extensive: changing the publisher ID of the displayed advertisement, loading and launching other applications, displaying notifications to the user, disabling the device administrator mode, changing the address of the C & C server managing to the URLs of the application download. After each task received using GCM, the bot will inform the remote server using the HTTPS protocol.
Conclusion
The Trojan program was successfully uploaded to the Google Play store, because it contained a mechanism for delaying activation of malicious functions and, thus, did not arouse suspicion from the Bouncer tool. An interesting question is why Bouncer does not specialize in static analysis of executable files inside downloaded applications. For these reasons, the Trojan program was freely distributed to users through the official Google app store for Android. The malicious game Super Hero adventure was uploaded to the Play Store by the SHSH developer. It is possible that this developer has downloaded more applications in the Play Store. Ultimately, they were all removed from the store, but went unnoticed there for a year and a half. It is possible that such cases are the reason that in March 2015, Google announced that all applications and updates should be tested by a person.
The best practice for keeping your device safe is to use only the official app store to download them. In addition, it is necessary to pay attention to reviews and user comments to the applications hosted there. When installing the application, you should closely monitor the rights requested by the application. If you notice anything suspicious in the behavior of the application, you can send it as a sample to the anti-virus laboratory with appropriate comments about the reasons for sending.
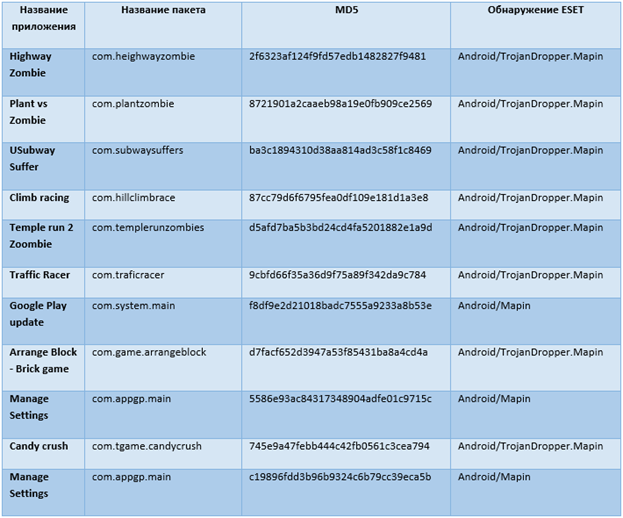
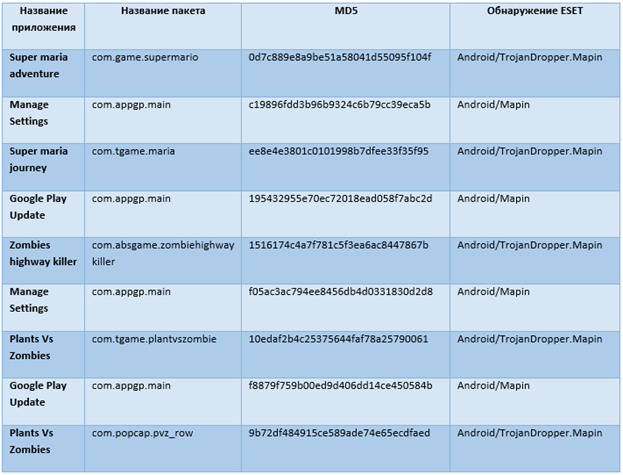
Below is information about malware samples we analyzed.

This second application is secretly reset to the device’s memory from the first, but asks the user for permission to install. It is presented as a tool for managing the settings of the “Manage Settings” device. After its installation, the application runs as a service in the background.
')
ESET anti-virus products detect applications that contain this additional application as Android / TrojanDropper.Mapin . According to our data, India has the largest number of infections of Android devices with this malware.
The malware is a backdoor, which gains control of the device and incorporates it into the botnet. The backdoor uses a special internal timer for deferred execution of its payload. Thus, authors can deceive various automatic systems for analyzing files that may rank a file as suspicious due to its behavior. In some cases, the backdoor can wait three days before activating the payload. Most likely, such a measure allows the authors to bypass the Google Bouncer file analysis tool verification mechanisms used by Google to verify applications downloaded to Play.
After activating the payload, the Trojan requests administrator rights in the system and starts interacting with its C & C server. Android / Mapin contains various functions, for example, displaying various notifications to the user, downloading, installing and launching other applications, as well as receiving personal user information on the device. At the same time, its main function is to display fullscreen advertising on an infected device.
Distribution vectors
Malicious apps were placed in the Google Play app store at the end of 2013 and in 2014. The names of the apps were different, including, “Hill climb racing the game”, “Plants vs zombies 2”, “Subway suffers”, “Traffic Racer” , Temple Run 2 Zombies, Super Hero Adventure by TopGame24h, TopGameHit and SHSH. Exact application download dates were November 24-30, 2013 and November 22, 2014. According to MIXRANK resource statistics , the Plants vs zombies 2 application was downloaded more than 10 thousand times before it was removed from the store. At the same time, the System Optimizer, Zombie Tsunami, tom cat talk, Super Hero adventure, Classic brick game applications, as well as the aforementioned Google Play applications with malicious capabilities, were downloaded to alternative stores. Android applications by the same authors. The same backdoor was found bundled with other applications that were uploaded to the store by the PRStudio developer (not to be confused with prStudio) in alternative app stores with links to Google Play. This developer has downloaded at least five other Trojan apps into alternative app stores: Candy crush or Jewel crush, Racing rivals, Super maria journey, Zombie highway killer, Plants vs Zombies. These applications are still available for download from these stores. The listed applications have been downloaded by users hundreds of times.

Fig. Malicious application icons.

Fig. Malicious application that has received quite positive ratings.

Fig. Another application that received positive ratings.
Analysis
There are various variants of the execution of a malicious program after a user has downloaded an illegitimate application. One of the options assumes that the victim will be asked to launch the file with the malicious program 24 after the first execution of the downloaded application. This method is less suspicious for the user, who believes that the launch request came from the OS. Another method involves the issuance of an instant request to the user. Both options are designed to trigger after a change in the network connection; for this, the malicious program registers a so-called. broadcast receiver in the manifest.

Fig. Registration t. broadcast receiver.
After changing the connection, the user will be prompted to install the “system application”. The malicious application itself, dropped onto the device, may be called “Google Play Update” or “Manage Settings”.

Fig. Malicious application disguised as a system.
In that case, if the user chooses to cancel the installation, then the malicious program will show a request every time when the network connection is changed. It can be assumed that a simple user will be sure of the seriousness of the displayed notification and at some point, most likely, will press the install button only to get rid of it. Once launched, the trojan is executed as a service with its registered broadcast receiver, awaiting a connection change.
When such a change occurs, the Trojan will attempt to register itself using the Google Cloud Messages (GCM) service to receive messages later. After that, Android / Mapin will try to register the infected device on the attacker's server, sending information such as your username, Google account, IMEI, registration ID (ID) and the name of your application package there.

Fig. The process of registering a device on the attackers server.
In order to exclude the possibility of its removal from the system, the Trojan requires the user to activate the device administrator mode.

Fig. Suggestion to the user to activate the device administrator mode.
The trojan will report to the remote server about the successful activation of the device administrator mode. Once such an operation occurs, the malware will show the user advertisements in full screen mode ( interstitial ). Such advertising (interstitial ad) will be displayed to the user again every time you change the connection. Development of this type of advertising is possible using the legitimate AdMob SDK.

Fig. Full-screen advertising (interstitial ad).
Networking
A trojan interacts with its controlling server using the Google Cloud Messaging (GCM) service. This service is increasingly used by modern malware for its own purposes, through which attackers can instruct the bot to perform the actions they need.

Fig. Processed by the bot command.
Not all functions of a malicious program are fully implemented in its code, except for this, not all already implemented functions are used. It is possible that the threat itself is still at the level of development and will be improved in the future. As we have already mentioned, its main goal is to deliver aggressive full-screen advertising for displaying it to the user, disguised as a system application. A bot can also be used by attackers to install other malware on a compromised device.
In addition to displaying advertisements, the list of supporting functions performed by it is quite extensive: changing the publisher ID of the displayed advertisement, loading and launching other applications, displaying notifications to the user, disabling the device administrator mode, changing the address of the C & C server managing to the URLs of the application download. After each task received using GCM, the bot will inform the remote server using the HTTPS protocol.
Conclusion
The Trojan program was successfully uploaded to the Google Play store, because it contained a mechanism for delaying activation of malicious functions and, thus, did not arouse suspicion from the Bouncer tool. An interesting question is why Bouncer does not specialize in static analysis of executable files inside downloaded applications. For these reasons, the Trojan program was freely distributed to users through the official Google app store for Android. The malicious game Super Hero adventure was uploaded to the Play Store by the SHSH developer. It is possible that this developer has downloaded more applications in the Play Store. Ultimately, they were all removed from the store, but went unnoticed there for a year and a half. It is possible that such cases are the reason that in March 2015, Google announced that all applications and updates should be tested by a person.
The best practice for keeping your device safe is to use only the official app store to download them. In addition, it is necessary to pay attention to reviews and user comments to the applications hosted there. When installing the application, you should closely monitor the rights requested by the application. If you notice anything suspicious in the behavior of the application, you can send it as a sample to the anti-virus laboratory with appropriate comments about the reasons for sending.
Below is information about malware samples we analyzed.


Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/267577/
All Articles