XcodeGhost - malware apocalypto for iOS
Researchers at the famous American security company Palo Alto Networks reported on the detection of many malicious applications in the App Store. This app store is maintained by Apple and is known as the most reliable and secure application distribution center for iOS. The peculiarity of getting there malicious applications was that they were compiled by the illegitimate tool Xcode. Xcode itself is an iOS application development environment, which all developers use.

Compiled with fake Xcode applications are called XcodeGhost, and their number, according to the latest data, amounts to thousands, and more than a thousand still remain in the App Store at the moment. ESET antivirus products detect XcodeGhost malware as iOS / XcodeGhost (F-Secure: Backdoor: iPhoneOS / XCodeGhost.A , Sophos: iPh / XcdGhost-A , Symantec: OSX.Codgost ).
')
Fake Xcode affected Chinese developers, because they were the first to use this tool, deciding not to download it from Apple’s developer portal, but to resort to torrents and other unreliable “places” for this. The introduction of malicious code into a legitimate compiled application was carried out at the linkage stage, when the linker linked the object code of the application itself to the malicious object code, resulting in an application that looks completely legitimate to the developer, and in fact is already malicious. The received application was signed by a digital developer certificate and placed on the App Store as legitimate.
The malicious code XcodeGhost, i.e., the one that the linker implemented in a legitimate application, does not perform any destructive functions for the device, but simply collects statistics about the device and sends it to the C & C server of the attackers in an encrypted form. The malicious object file whose data was added to a legitimate application was called CoreServices, and it was located in one of the directories of the Xcode framework.
The following files have been added to the Xcode development framework, which has been compromised.
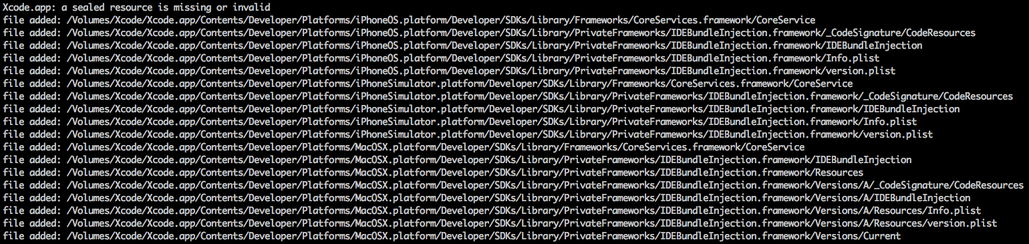
Fig. Files added to the Xcode environment are required to successfully build a program with malicious code (data from Palo Alto Networks).
XcodeGhost only specializes in collecting system information.
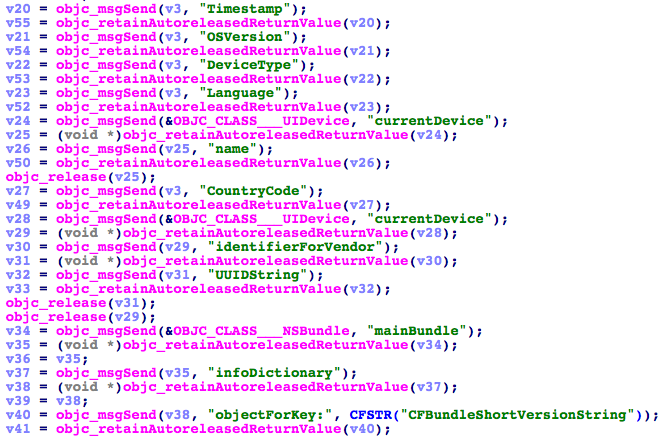
Fig. The system information collected by XcodeGhost (data from Palo Alto Networks).
Apple has already begun clearing the App Store of malicious applications, among which were popular instances of users.
XcodeGhost was the first mass malware or infection technology of one of the safest operating systems - Apple iOS. Prior to XcodeGhost, the number of malware for iOS was barely a dozen and they were all designed for devices with a jailbreak, not to mention that anyone could distribute them through the App Store. The high level of security of the latest versions of this mobile OS (DEP / ASLR, sandboxing, rootless, code signing, secure bootchain, binding to the App Store) made it almost completely impenetrable for various kinds of exploits and malware.

Compiled with fake Xcode applications are called XcodeGhost, and their number, according to the latest data, amounts to thousands, and more than a thousand still remain in the App Store at the moment. ESET antivirus products detect XcodeGhost malware as iOS / XcodeGhost (F-Secure: Backdoor: iPhoneOS / XCodeGhost.A , Sophos: iPh / XcdGhost-A , Symantec: OSX.Codgost ).
')
Fake Xcode affected Chinese developers, because they were the first to use this tool, deciding not to download it from Apple’s developer portal, but to resort to torrents and other unreliable “places” for this. The introduction of malicious code into a legitimate compiled application was carried out at the linkage stage, when the linker linked the object code of the application itself to the malicious object code, resulting in an application that looks completely legitimate to the developer, and in fact is already malicious. The received application was signed by a digital developer certificate and placed on the App Store as legitimate.
The malicious code XcodeGhost, i.e., the one that the linker implemented in a legitimate application, does not perform any destructive functions for the device, but simply collects statistics about the device and sends it to the C & C server of the attackers in an encrypted form. The malicious object file whose data was added to a legitimate application was called CoreServices, and it was located in one of the directories of the Xcode framework.
The following files have been added to the Xcode development framework, which has been compromised.

Fig. Files added to the Xcode environment are required to successfully build a program with malicious code (data from Palo Alto Networks).
XcodeGhost only specializes in collecting system information.

Fig. The system information collected by XcodeGhost (data from Palo Alto Networks).
- The time at which the data was received.
- The name of the application is XcodeGhost.
- Bundle ID of the XcodeGhost application.
- Type of device and its name.
- Current country and language.
- The current UUID.
- Network type
Apple has already begun clearing the App Store of malicious applications, among which were popular instances of users.
XcodeGhost was the first mass malware or infection technology of one of the safest operating systems - Apple iOS. Prior to XcodeGhost, the number of malware for iOS was barely a dozen and they were all designed for devices with a jailbreak, not to mention that anyone could distribute them through the App Store. The high level of security of the latest versions of this mobile OS (DEP / ASLR, sandboxing, rootless, code signing, secure bootchain, binding to the App Store) made it almost completely impenetrable for various kinds of exploits and malware.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/267443/
All Articles