Basic principles of virtualization on the fingers
In itself, the concept of virtualization has existed for 50-60 years. Back in the 60s of the last century, IBM dealt with this issue. However, at that time virtualization did not find sufficient use in existing technologies, since there were few computers and they were always used to the eye. After the appearance of personal computers in the 1980s, the situation did not change radically, since the idea was to run only one program on one device, and therefore the use of resources was very low. All this for a long time suited up to the onset of the energy crisis, when the price of electricity rose throughout the world. As a result, there was a question of saving resources.
In 1999, VMware first virtualized a computer based on Intel: several operating systems and, accordingly, several applications were running on the same machine. At the same time, the costs of electricity were distributed to several operating systems already on one set of hardware, which made it possible to rationalize the load.
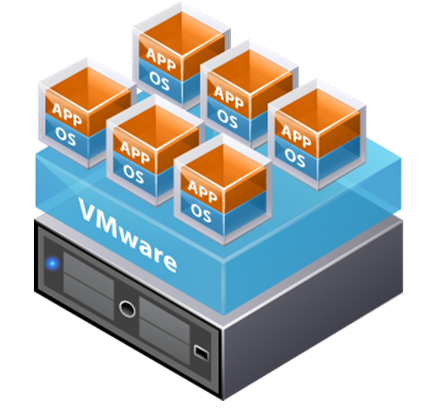
How does all this work? Between the server and the operating systems there is a thin layer of software for virtualization, or on the server an OS is installed on which the level of virtualization is imposed.
')
The task of virtualization is to mislead the OS so that it identifies it as its own hardware. Such tricks are necessary because of too many applications created for a specific OS. Thus, the virtual machine has a number of advantages, such as encapsulation , isolation of a separate application, its combination with the OS and other programs, and this creates a certain independence of the hardware. Consider these components separately.
Encapsulation is the collection of data or functions into a single component. A program is created that is disguised as a separate physical machine that performs all its functions. And the OS, instead of identifying a set of different devices, actually sees a set of different files.
Isolation means that all applications, working on the same device, work independently of each other, identifying themselves as different devices. As a result, if one OS freezes or crashes, it does not affect the operation of other OS and applications.
Combining means creating a separate cluster, where the OS and all the systems that work with it have all the functions of an individual computer. But, although the machine is virtual, and not real, it interacts with all the operating systems and applications that run on Intel x86 in any case.
The independence of the hardware means that the virtual machine can be transferred from real hardware on one system to another without any problems. For example, consider two servers: HP and Cisco. To transfer a running program to the OS and ensure HP to Cisco under normal conditions, it would be necessary to reinstall this program on the new OS. As a result, a lot of work on the installation and testing of the entire system. A virtual machine allows unimpeded transfer from one system to another. Moreover, most virtual machine systems allow you to transfer a specific virtual machine from one system to another in the working mode of servers. It also allows sharing of resources, disk space and processor power. So, for an application that requires a large amount of disk space, there is no need to add disks to the physical server - they can be reconfigured during operation. Thus, system administrators get much more room for creativity.

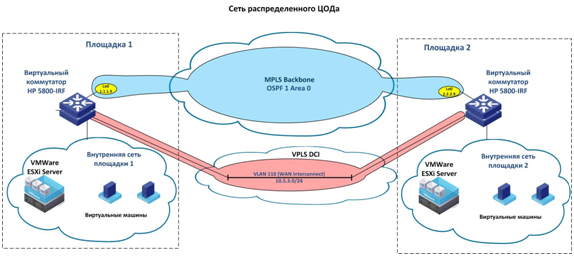
In modern conditions, when new data is installed in the data center, all the machines are virtualized. Networks, storage systems and the data centers themselves are becoming virtual. Today, if you want to have your own data center, you only need to decide on the configuration of the equipment, contact the hosting company, where a personal data center will be created. Naturally, physically all the declared equipment should be somewhere. The main data center (production) is the part visible by the user. But there is another data center (backup), which has a dual role: it functions as a backup copy of the real data center and as a site for developers. The main data center is designed for the user, and the place for developers is a backup data center where there is a ground for application testing. After testing, virtual machines are transferred from the backup data center to the primary, where they are directly used. In case of emergency situations in the main data center, virtual machines can also be dragged to the backup. Thus, the whole system becomes much more accessible.
What are the main reasons for the popularity of virtualization in our time? Firstly, this is a reduction in the cost of physical infrastructure, which means fewer servers, cabinets, and rooms. Secondly, lower operational costs such as electricity and cooling. Third, it increases the operational flexibility and performance of system administrators.
As a vivid example of physical economy, you can bring a model where 4 servers equipped with a VMware system replace 50 physical servers. At the same time, productivity increased from 5-10% to 80%, and instead of 10 cabinets only one is required. With regards to operating costs, energy consumption is reduced by 80%, while another 25% of energy is reduced by optimizing the load. Productivity of system administrators increases elementary by reducing the number of tasks performed and greater availability of equipment.
At the moment, half the servers around the world are virtual. It is virtualization that guides the entire IT industry, so all the latest software is already being prepared for the tasks of virtualization.
In 1999, VMware first virtualized a computer based on Intel: several operating systems and, accordingly, several applications were running on the same machine. At the same time, the costs of electricity were distributed to several operating systems already on one set of hardware, which made it possible to rationalize the load.
How does all this work? Between the server and the operating systems there is a thin layer of software for virtualization, or on the server an OS is installed on which the level of virtualization is imposed.

')
The task of virtualization is to mislead the OS so that it identifies it as its own hardware. Such tricks are necessary because of too many applications created for a specific OS. Thus, the virtual machine has a number of advantages, such as encapsulation , isolation of a separate application, its combination with the OS and other programs, and this creates a certain independence of the hardware. Consider these components separately.
Encapsulation is the collection of data or functions into a single component. A program is created that is disguised as a separate physical machine that performs all its functions. And the OS, instead of identifying a set of different devices, actually sees a set of different files.
Isolation means that all applications, working on the same device, work independently of each other, identifying themselves as different devices. As a result, if one OS freezes or crashes, it does not affect the operation of other OS and applications.
Combining means creating a separate cluster, where the OS and all the systems that work with it have all the functions of an individual computer. But, although the machine is virtual, and not real, it interacts with all the operating systems and applications that run on Intel x86 in any case.
The independence of the hardware means that the virtual machine can be transferred from real hardware on one system to another without any problems. For example, consider two servers: HP and Cisco. To transfer a running program to the OS and ensure HP to Cisco under normal conditions, it would be necessary to reinstall this program on the new OS. As a result, a lot of work on the installation and testing of the entire system. A virtual machine allows unimpeded transfer from one system to another. Moreover, most virtual machine systems allow you to transfer a specific virtual machine from one system to another in the working mode of servers. It also allows sharing of resources, disk space and processor power. So, for an application that requires a large amount of disk space, there is no need to add disks to the physical server - they can be reconfigured during operation. Thus, system administrators get much more room for creativity.

In modern conditions, when new data is installed in the data center, all the machines are virtualized. Networks, storage systems and the data centers themselves are becoming virtual. Today, if you want to have your own data center, you only need to decide on the configuration of the equipment, contact the hosting company, where a personal data center will be created. Naturally, physically all the declared equipment should be somewhere. The main data center (production) is the part visible by the user. But there is another data center (backup), which has a dual role: it functions as a backup copy of the real data center and as a site for developers. The main data center is designed for the user, and the place for developers is a backup data center where there is a ground for application testing. After testing, virtual machines are transferred from the backup data center to the primary, where they are directly used. In case of emergency situations in the main data center, virtual machines can also be dragged to the backup. Thus, the whole system becomes much more accessible.

What are the main reasons for the popularity of virtualization in our time? Firstly, this is a reduction in the cost of physical infrastructure, which means fewer servers, cabinets, and rooms. Secondly, lower operational costs such as electricity and cooling. Third, it increases the operational flexibility and performance of system administrators.
As a vivid example of physical economy, you can bring a model where 4 servers equipped with a VMware system replace 50 physical servers. At the same time, productivity increased from 5-10% to 80%, and instead of 10 cabinets only one is required. With regards to operating costs, energy consumption is reduced by 80%, while another 25% of energy is reduced by optimizing the load. Productivity of system administrators increases elementary by reducing the number of tasks performed and greater availability of equipment.
At the moment, half the servers around the world are virtual. It is virtualization that guides the entire IT industry, so all the latest software is already being prepared for the tasks of virtualization.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/265529/
All Articles