Another serious Android vulnerability found

At the end of July, researchers from TrendMicro discovered a serious vulnerability in the Android media server (information about this appeared almost simultaneously with data on the Stagefright vulnerability ). A little later, IBM specialists found another security bug affecting 55% of Android users.
On August 17, a description of another serious media server vulnerability appeared in the TrendMicro blog , which could lead to remote code execution. Using this security bug, an attacker can remotely attack a smartphone using a special multimedia message.
')
Vulnerability CVE-2015-3842 affects almost all versions of Android, starting with version 2.3 of Gingerbeard to Android 5.1 Lollipop - this means that hundreds of millions of devices running a mobile OS are potentially vulnerable. Google has already released a patch and published the details in the Android Open Source Project (AOSP) community. There is currently no information about successful attacks using this vulnerability.
How it works
The vulnerability is contained in the mediaserver component, known as AudioEffect. To carry out the attack, attackers need to convince the victim to install a malicious application - it does not require special permissions, which does not arouse suspicion among users.

Later, the application sends an incorrect buffer size of some files to the media server component, which causes heap overflow.
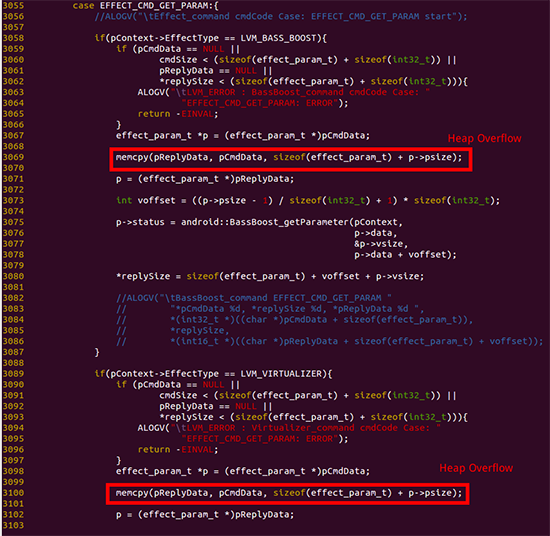
The researchers were able to create a proof-of-concept attack demonstration using the Nexus 6 device with Android 5.1.1 LMY47Z. An application was created that causes the mediaserver component to crash, overflowing the ReplyData buffer in the heap.
The picture below shows the sending of a malicious code to a media server:
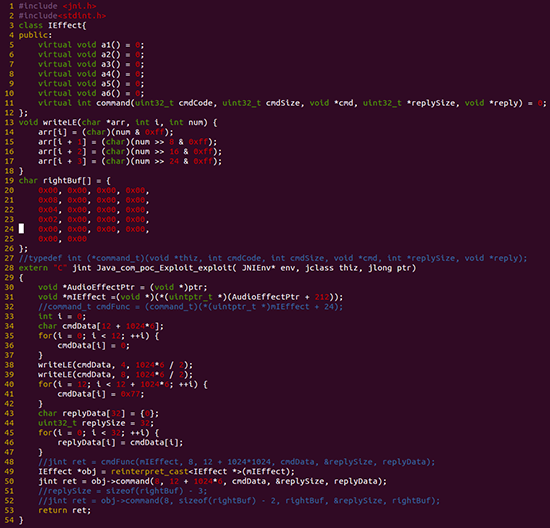
Possible attack scenarios
An attack using a detected vulnerability can be completely controlled - this means that a malicious application can decide when to launch an attack and when to complete it. The attacker will be able to run his code with the same rights that the mediaserver component already has. Since this component is used in many processes related to media processing (for example, taking a photo or recording a video), the victim can be seriously damaged.
In their material, the researchers note the fact that it will be difficult for users who are victims of an attack to notice it. During the demonstration, the attack began by launching the application. However, in real life, malicious applications are not so easy to detect, which can lead to the disclosure of important data over many days and even months.
Researchers claim that you can protect against this vulnerability by installing special anti-virus applications for mobile devices.
At conferences on information security, Positive Technologies researchers also demonstrated the results of a study on the security of 4G communications and SIM cards (they can also be hacked ).
During the Positive Hack Days forum held in May in Moscow, a competition was also held on hacking MiTM Mobile mobile communications - we published an analysis of its tasks in Habré (some event attendees received reports about hacking their devices). Here is a webinar entry on this topic.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/265161/
All Articles