Forensic VS Schroeder: Gaining Access to Deleted Files
 The basis of one of the tasks of the online stage NeoQUEST-2016 was the forsensica, namely, working with the means of restoring the previous state of Windows partitions. Professionals know and often use the capabilities of this technology during pentest or investigation of information security incidents.
The basis of one of the tasks of the online stage NeoQUEST-2016 was the forsensica, namely, working with the means of restoring the previous state of Windows partitions. Professionals know and often use the capabilities of this technology during pentest or investigation of information security incidents.Many well-known Volume Shadow Copy is a volume shadow copy service that first appeared in Windows Sever 2003. It allows you to take and restore snapshots of the file system (snapshots), including the system partition. Also, past snapshots of a partition can be mounted to a drive letter or folder, just like a regular partition. Thus, it is possible to gain access to the previous state of the system along with ALL files, including the files currently removed from this section. All these properties of Volume Shadow Copy can be used by information security experts in the following ways:
- Access and copy files used by the system or user applications (application password databases, Outlook mailboxes, Thunderbird, Active Directory database).
- Access and copy deleted files (including securely wiped with a shredder).
- Hiding the executable files and modules of the malicious backdoor (a snapshot of the file system in which they are present is taken, after which they are removed from the current partition while remaining in the shadow copy).
The use of the opportunity from the second point was based on the solution of the NeoQUEST task forignics. Read more - under the cut!
Initial data
In the task with the name “Missing file”, the participant was given a link to a torrent; when downloading, participants received 2 files — a hard disk dump (* .vhdx file) and a RAM dump (* .dmp file). When mounting the main file with a dump of the hard disk, the participant found a text file encrypted with the Encrypted File System (EFS). The contents of this file just can not read! The private keys of user certificates in Windows OS, including EFS, are protected with an account password. That is why when it is reset, a warning appears about access to EFS files.
Knowledge of one NTLM password hash, as well as SYSKEY, LSAKEY and NL $ KM keys to decrypt a user's private key is not enough. Thus, having one hard disk dump is not enough. You must also know the password of the user. At this stage, participants may not yet know why they need it, but they can restore it.
')
After a quick scan of the contents of the hard disk, the participants found an EFS-encrypted file, the contents of which was clearly the key.
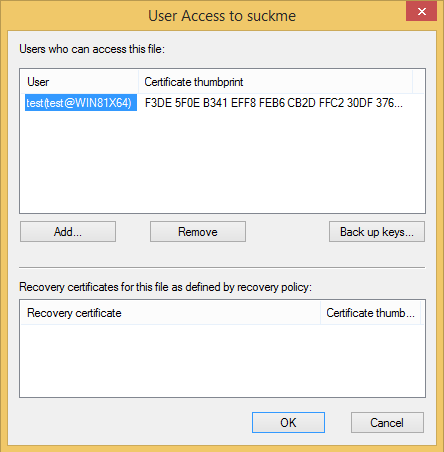
It was possible to read it only with the help of the certificate of the specified user, and for this you need to know his password.
Password retrieval
That is why the participants were given a dump of RAM. It is easy to guess that the password is extracted from it using the well-known utility mimikatz. You can do this, for example, using WinDBG and the corresponding extension mimilib.dll. Below is the process of getting a user password in steps.
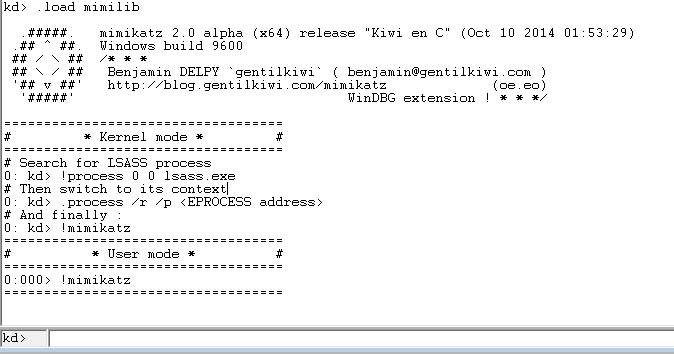
How to use the extension is displayed when it is loaded. It remains only to execute the sequence of these commands. As a result, we obtain:

After receiving the password, the easiest way to complete the task is to boot from the hard disk image in the virtual machine and log in with the corresponding user. However, the participants are most disappointed: the EFS certificate with which the file was encrypted is deleted.
After all the above steps, you need to restore the deleted certificate. The dump was made in such a way that it was impossible to recover the certificate using various recovery tools for deleted files. And here the service of shadow copies of the volume comes to the rescue.
Get out of the shadows
You can view existing shadow copies using the vssadmin utility, which is enabled by default on Windows 7 and higher.
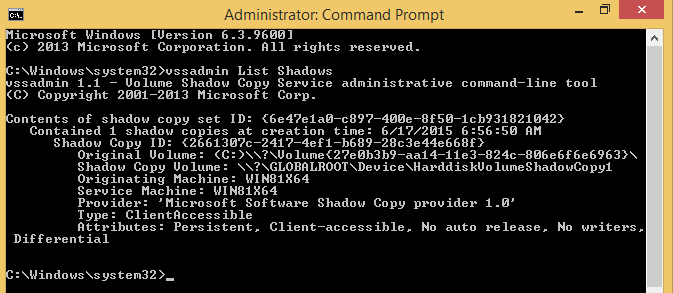
It can be seen that each shadow copy is characterized by a unique identifier in the form of a GUID. The shadow copies themselves are represented as objects of the “Generic Volume Shadow Copy” type.
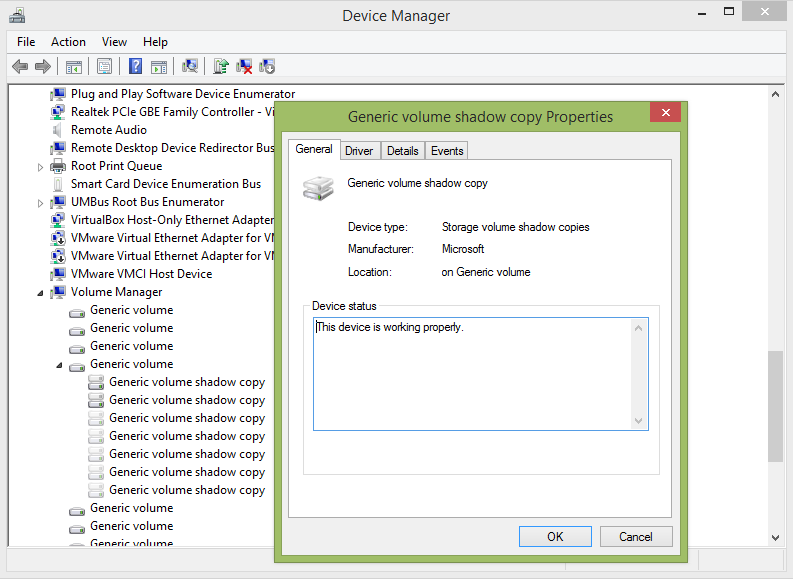
You can mount it as a volume in a new drive letter or create a link as a folder. It is also possible to access the contents of the shadow copy using the device name, which appears in the properties of the copy itself.
Now the participants had to restore the certificate's private key values for the user's store (in this case, access to the file is open).
This can be done by restoring the corresponding registry keys and the private key file in the% AppData% \ Microsoft \ Crypto \ RSA folder in which the user's private keys are stored. The necessary information can be obtained from the shadow copy (by mounting it or making a link to it).
Or you could go a simpler way - roll back the state of the partition to the shadow copy. After that, it was enough to log in to the system and export the certificate with the private key to a file.
In the current state of the system, it was necessary to import the certificate with the private key into the user's personal certificate store and open the file.
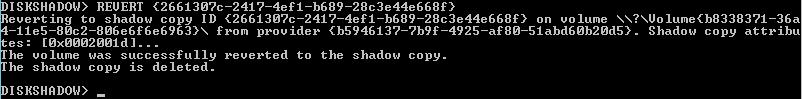
You can roll back using the diskshadow tool from the Windows Sever toolkit by connecting the disk to a virtual machine with this OS, or you can use the corresponding WMI objects for the volumes and their copies. Using diskshadow is an easier and faster way. To roll back a partition to a snapshot, you need to request a copy ID, and then restore it.
We get the shadow copy ID:

Restoring the shadow copy:
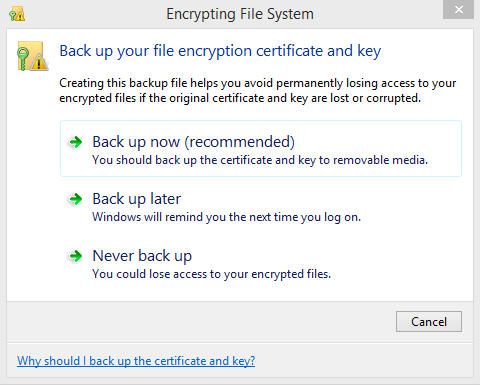
Boot from the resulting "past" state of the system. Certificate present. This can be understood by the fact that immediately there is an offer from Windows to backup the key. Export it to a file.
Load in the "current" state of the disk. We import the certificate on the “current” state of the system in the user's personal certificate storage. Now the file can be opened and read. The contents of the file is the key to the passage of the job!
Draw conclusions
From all of the above, the following conclusions can be drawn:
1. It is not necessary to save important data, which must then be deleted, on the system volume (the “C: \” drive). They may be in the shadow copy, but you may not know or remember.
2. If you accidentally deleted some important file from the system partition, you can try your luck and try to find it in the saved shadow copy.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/264597/
All Articles