Corporate networks can be hacked using Windows Update
Windows updates in recent days become dangerous for users. A few days ago, those wishing to upgrade their operating system to Windows 10 became victims of the encryption virus. Another story took place at the Black Hat 2015 conference, where researchers from the UK showed how to deliver malware to corporate Windows PCs via a local WSUS update server.
Using WSUS, system administrators coordinate software updates on servers and workstations. By default, Microsoft uses the non-secure HTTP protocol for WSUS, and to enable HTTPS, the administrator must perform a number of manipulations. But they are carried out far from always. Taking advantage of the lack of SSL encryption, the specialists of Context Information Security, a British company, were able to download and install fake updates on the target system. Such updates can be used by attackers to download any malicious program and gain access with administrative rights.
')
The researchers carried out a MITM attack using ARP spoofing (a variant with WPAD injection is also possible), intercepting and changing SOAP requests between clients and the WSUS server, as well as modifying the metadata in the updates.
Today, any Windows-based computer that downloads updates from a WSUS server other than HTTPS is vulnerable to such attacks, according to British experts, and recommend that companies check their current security policies for WSUS.
To determine the presence of SSL encryption in WSUS, you need to look at the following registry keys:
WUServer is the URL of the update server. If this address (for example,
If it is 0, then the WUServer parameter will be ignored. If it is 1, SSL in WSUS will work. Other Windows Update registry keys can be found here .
Administrators can check the WSUS Group Policy settings at the following address:
The procedure for enabling SSL in WSUS is described on the Microsoft website.
To prevent the download of fake updates, experts advise Microsoft to use a separate certificate for Windows Update. As the authors of this study write, now any file signed by Microsoft can be mistaken for an update. In addition, British experts recommend to sign and update metadata, as they contain basic information about updates, including handler tags. Signed with a Microsoft certificate, the tags will avoid the need to create a trusted channel between the client and the WSUS server.
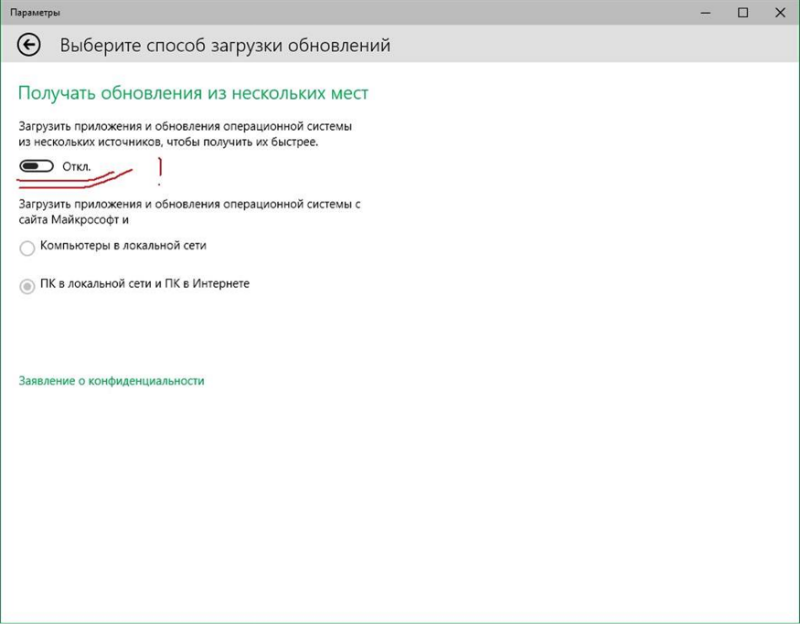
In recent days, concerns about the originality of Windows updates have added a new p2p system in Windows 10 called WUDO (Windows Update Delivery Optimization). It allows you to download Windows updates from computers of other users. You can disable peering downloads for security purposes (or to save traffic) from the section “Select the method of downloading updates” (Windows Update-> Advanced Options-> Select the method for downloading updates):
Details of the study "Compromising the Windows Enterprise via Windows Update" can be found here .

Using WSUS, system administrators coordinate software updates on servers and workstations. By default, Microsoft uses the non-secure HTTP protocol for WSUS, and to enable HTTPS, the administrator must perform a number of manipulations. But they are carried out far from always. Taking advantage of the lack of SSL encryption, the specialists of Context Information Security, a British company, were able to download and install fake updates on the target system. Such updates can be used by attackers to download any malicious program and gain access with administrative rights.
')
The researchers carried out a MITM attack using ARP spoofing (a variant with WPAD injection is also possible), intercepting and changing SOAP requests between clients and the WSUS server, as well as modifying the metadata in the updates.
Today, any Windows-based computer that downloads updates from a WSUS server other than HTTPS is vulnerable to such attacks, according to British experts, and recommend that companies check their current security policies for WSUS.
To determine the presence of SSL encryption in WSUS, you need to look at the following registry keys:
HKLM\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\WindowsUpdate
WUServer is the URL of the update server. If this address (for example,
HTTP: / /wsus-server.local: 8530 ) does not start with HTTPS, then the computer is vulnerable to attack.HKLM\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\WindowsUpdate\AU
If it is 0, then the WUServer parameter will be ignored. If it is 1, SSL in WSUS will work. Other Windows Update registry keys can be found here .
Administrators can check the WSUS Group Policy settings at the following address:
Windows Components > Windows Update > Specify intranet Microsoft update
The procedure for enabling SSL in WSUS is described on the Microsoft website.
To prevent the download of fake updates, experts advise Microsoft to use a separate certificate for Windows Update. As the authors of this study write, now any file signed by Microsoft can be mistaken for an update. In addition, British experts recommend to sign and update metadata, as they contain basic information about updates, including handler tags. Signed with a Microsoft certificate, the tags will avoid the need to create a trusted channel between the client and the WSUS server.
In recent days, concerns about the originality of Windows updates have added a new p2p system in Windows 10 called WUDO (Windows Update Delivery Optimization). It allows you to download Windows updates from computers of other users. You can disable peering downloads for security purposes (or to save traffic) from the section “Select the method of downloading updates” (Windows Update-> Advanced Options-> Select the method for downloading updates):

Details of the study "Compromising the Windows Enterprise via Windows Update" can be found here .
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/264479/
All Articles