The study "The global state of information security 2015" (GSISS 2015). Part 1
The PwC study is very voluminous, so it is published in parts.
Today, information security is an integral part of business risk. Now this question concerns not only information technologies and security specialists, top management and boards of directors are now involved in IS issues. Consumers are also concerned and willing to stay informed about possible incidents and security threats.

Security incident media reports (a security incident is defined as an unwanted incident that threatens several aspects of information security) have become commonplace as weather forecasts, and over the past 12 months, virtually every industry sector around the world has been exposed to some type of cyber threat. With the increase in the number of incidents, governments are becoming increasingly active in assisting organizations in the fight against cyber crime. For example, the FBI announced that 3,000 companies, including banks, retailers, and military contractors, were victims of cyber attacks in 2013. Subsequently, the US Department of Justice charged five Chinese military hackers with conducting economic cyber espionage against American companies in the nuclear energy, metal and solar energy sectors. This was the first time that the United States accused government officials of economic espionage through external cyber attacks in accordance with section 1831 of the Economic Spying Act. This trend is likely to continue, as predicted by Shaun Joyce (head of consulting at PwC and former deputy director of the FBI). “I think we will see how the Department of Justice and the FBI will continue to implement an aggressive strategy against entities that cause significant economic damage to the US economy,” says Joyce.
The attacks on large companies in the retail sector reached an incredible scale last year, which resulted in the theft of hundreds of millions of customer payment card records. This led to a significant increase in the number of court proceedings and the urgent introduction of a new standard of payment cards in the United States. In the UK, an insider in the company stole information on wages and bank account numbers of 100,000 supermarket chain employees, after which this information was published online. South Korea has also reported theft of consumer data on a massive scale, 105 million payment card accounts have been attacked. In Werden, Germany, city officials have announced the theft of 18 million email addresses, passwords, and other information.
')

Following Snowden's revelations, attacks on retailers have given even greater publicity to information security issues. Loud exposures in surveillance pushed international corporations and even governments to revise the list of suppliers of goods and services, excluding from there companies that may be associated with government bodies. In particular, Symantec reported detecting espionage for the governments of the main EU countries. Based on selected targets and extremely nontrivial malware programs, Symantec concluded that the group was coordinating the attacks with the support of one of the states. Geopolitical conflicts, especially between Russia and Ukraine, result in counter-attacks against government sites and the spread of malicious programs on embassy devices.
Other important infrastructure providers are also under attack. A group of hackers successfully penetrated the US public utility through the Internet and compromised the control system, although the invasion was stopped before any damage was done. The criminals, behind whose backs are third states, use sophisticated malware to infiltrate the industrial control systems of hundreds of power companies in the US and Europe.
The leaders among the victims of cyber attacks are financial sector companies. Attacks on stock exchanges have become commonplace. A study of 46 stock exchanges around the world, conducted by the International Organization of Securities Commissions (IOSCO) and the World Federation of Exchanges, showed that more than half (53%) of the sites were subjected to cyber attacks. The banking sector is also not lagging, during one of the attacks, cyber criminals robbed the ATMs of two Middle Eastern banks around the world in the amount of $ 45 million.
We are also seeing an increase in attacks on the so-called “Internet of Things” segment - the growing ecosystem of devices connected to the network and designed to make life easier for us, such as baby monitors, home thermostats, new TVs, etc. These Internet-connected devices are extremely vulnerable to attack, because even elementary security systems are not embedded in them, which is confirmed by a recent study by HP Fortify on Demand. HP has investigated the 10 most popular connected devices and confirms that 70% of them contain serious vulnerabilities.
IOActive has published a study that demonstrates in detail how hackers can control electronic control units of specific cars and offer mechanisms for detecting attacks. It is reported that cars that contain dozens of electronic devices that are connected to each other, and in some cases connect to the outside world through wireless communication, can be hacked with the subsequent control of brakes, steering and even the engine.

Regulators
Some of the world's most respected and popular news organizations, including The New York Times, The Financial Times, CNN, Reuters, were compromised last year. Many of the most famous attacks were carried out by hackers associated with the authorities of the Middle East region. This list is far from complete, it is impossible to know the exact number of companies that have been attacked or compromised, and there are several explanations for this. First, some companies still do not know that they were attacked, and secondly, companies are afraid to publicly report incidents in order to avoid reputational or material losses, lawsuits and other inspections. Speaking of inspections, regulators around the world are starting to tighten the rules and requirements for companies in the field of information security.
As a confirmation of the above, we can give an example of the plans of the US Securities and Exchange Commission to conduct tests on information security in more than 50 broker-dealers and investment consulting companies. In Asia, the Singapore Personal Data Protection Act sets new standards for the collection, use and disclosure of personal data. Organizations that fail to comply with new requirements will face a fine of up to 1 million SGD or $ 788'995.

In the new manual from the US Securities and Exchange Commission there are several new and unique requirements, such as insurance against cyber attacks and the ability to make a complete inventory of all incidents and violations. Management also requires enterprises to implement risk assessment mechanisms, as well as more effectively assess the risks and due diligence of vendors.
The leaders of transnational organizations, pending the adoption of European standards for data protection (European Union Data Protection Protection), the final version of which is expected in 2015. Market participants expect stricter requirements for companies that process personal data, in particular, conducting risk assessments and audits of information security systems, and more than double the increase in fines for compromised companies (from 2% to 5% of the company's annual turnover). The new EU requirements for notifications in the event of security incidents will make it possible to assess the situation with cyber attacks in Europe more accurately. According to John Woods (one of the leading employees of the cyber security practice department at the law firm Baker & McKenzie): “In the US, state laws on notifications in cases of security incidents revealed a lot of attacks and compromises, which led to more serious attention and information security. It will be interesting to see if the European norms have the same result. ”
We are also seeing new government efforts to help organizations improve their information security on a voluntary basis. In the United States in 2013, a special presidential order to raise the level of information security created the standard of the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). Version 1.0 of the standard is voluntarily implemented by individual companies to evaluate and improve information security, and also creates a common platform for discussion, cooperation and tactics to respond to cyber threats. Private sector efforts to promote security are presented by launching Google’s initiative Project Zero, which aims to promote security by identifying and blocking unknown threats before hackers can take advantage of them. Google says that Project Zero engineers will work to increase the security of widely used software, as well as study the motivations and techniques of the attackers and conduct research in the field of effective monitoring and eliminating the effects of compromises.
The market for information security services is growing.
As a result of the increase in the number of incidents (by 48% in 2014 compared to 2013) and the tightening of regulatory requirements, companies and government agencies are forced to raise the level of information security in order to protect their data. This in turn gives impetus to the growth of the number of solutions and technologies in the field of information security.

Research firm Gartner predicts that global IT security costs will grow by 7.9% to $ 71'100'000'000 in 2014, and by 8.2% to $ 76'900'000'000 in 2015. The growth of security incidents and their media coverage helped open the flow of venture capital investment to companies that provide information security services. During the first six months of 2014, venture capital funds invested $ 894'000'000 in the United States in startups of the information security segment. The amount is almost similar to investments in all startups in 2013. This exceeds all investments in the information security sector over the past 10 years. At the same time, the capitalization of some security firms reached new highs last year.
For example, the network security provider FireEye, after being valued at $ 304 million during an IPO in 2013, currently has a market capitalization of about $ 4.6 billion. Palo Alto Networks (specializing in corporate information security) raised $ 260 million in 2012 for an IPO , and now has a market capitalization of about $ 6.2 billion.

At the height of the boom of everlasting capitalism, the valuation of some companies in the information security segment was five to ten of their annual revenues. At the moment, there is a correction in the market, everyone understands that the segment has become a “bubble”, and in order to avoid a collapse, investors are gradually reducing the rate of investment in information security. This led to the fact that some companies have lost up to half the previous estimates. We believe that the software and services market in the field of information security will continue to grow because top management and boards of directors understand that cyber attacks will never cease, and regulators will only be tightened.
The venture capital market in the field of information security is also growing in Europe:
- London-based company 5Capital raised a fund focused on information security in the amount of $ 125 million and announced investments in BalaBit 22 in the amount of $ 8 million;
- Index Ventures fund opened its doors to information security companies from Europe, Israel and the USA, allocating $ 550 million to this segment. The Fund was also active this year in the field of mergers and acquisitions in the information security segment;
- FireEye acquired Mandiant for about $ 1 billion;
- Cisco Systems acquired Sourcefire for $ 2.7 billion
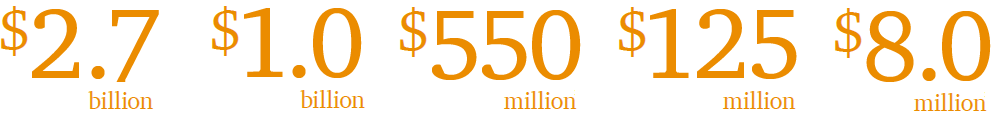
Additionally: this study is separately for the financial services segment is here .
TO BE CONTINUED…
Today, information security is an integral part of business risk. Now this question concerns not only information technologies and security specialists, top management and boards of directors are now involved in IS issues. Consumers are also concerned and willing to stay informed about possible incidents and security threats.

Security incident media reports (a security incident is defined as an unwanted incident that threatens several aspects of information security) have become commonplace as weather forecasts, and over the past 12 months, virtually every industry sector around the world has been exposed to some type of cyber threat. With the increase in the number of incidents, governments are becoming increasingly active in assisting organizations in the fight against cyber crime. For example, the FBI announced that 3,000 companies, including banks, retailers, and military contractors, were victims of cyber attacks in 2013. Subsequently, the US Department of Justice charged five Chinese military hackers with conducting economic cyber espionage against American companies in the nuclear energy, metal and solar energy sectors. This was the first time that the United States accused government officials of economic espionage through external cyber attacks in accordance with section 1831 of the Economic Spying Act. This trend is likely to continue, as predicted by Shaun Joyce (head of consulting at PwC and former deputy director of the FBI). “I think we will see how the Department of Justice and the FBI will continue to implement an aggressive strategy against entities that cause significant economic damage to the US economy,” says Joyce.
The attacks on large companies in the retail sector reached an incredible scale last year, which resulted in the theft of hundreds of millions of customer payment card records. This led to a significant increase in the number of court proceedings and the urgent introduction of a new standard of payment cards in the United States. In the UK, an insider in the company stole information on wages and bank account numbers of 100,000 supermarket chain employees, after which this information was published online. South Korea has also reported theft of consumer data on a massive scale, 105 million payment card accounts have been attacked. In Werden, Germany, city officials have announced the theft of 18 million email addresses, passwords, and other information.
')

Following Snowden's revelations, attacks on retailers have given even greater publicity to information security issues. Loud exposures in surveillance pushed international corporations and even governments to revise the list of suppliers of goods and services, excluding from there companies that may be associated with government bodies. In particular, Symantec reported detecting espionage for the governments of the main EU countries. Based on selected targets and extremely nontrivial malware programs, Symantec concluded that the group was coordinating the attacks with the support of one of the states. Geopolitical conflicts, especially between Russia and Ukraine, result in counter-attacks against government sites and the spread of malicious programs on embassy devices.
Other important infrastructure providers are also under attack. A group of hackers successfully penetrated the US public utility through the Internet and compromised the control system, although the invasion was stopped before any damage was done. The criminals, behind whose backs are third states, use sophisticated malware to infiltrate the industrial control systems of hundreds of power companies in the US and Europe.
The leaders among the victims of cyber attacks are financial sector companies. Attacks on stock exchanges have become commonplace. A study of 46 stock exchanges around the world, conducted by the International Organization of Securities Commissions (IOSCO) and the World Federation of Exchanges, showed that more than half (53%) of the sites were subjected to cyber attacks. The banking sector is also not lagging, during one of the attacks, cyber criminals robbed the ATMs of two Middle Eastern banks around the world in the amount of $ 45 million.
We are also seeing an increase in attacks on the so-called “Internet of Things” segment - the growing ecosystem of devices connected to the network and designed to make life easier for us, such as baby monitors, home thermostats, new TVs, etc. These Internet-connected devices are extremely vulnerable to attack, because even elementary security systems are not embedded in them, which is confirmed by a recent study by HP Fortify on Demand. HP has investigated the 10 most popular connected devices and confirms that 70% of them contain serious vulnerabilities.
IOActive has published a study that demonstrates in detail how hackers can control electronic control units of specific cars and offer mechanisms for detecting attacks. It is reported that cars that contain dozens of electronic devices that are connected to each other, and in some cases connect to the outside world through wireless communication, can be hacked with the subsequent control of brakes, steering and even the engine.

Regulators
Some of the world's most respected and popular news organizations, including The New York Times, The Financial Times, CNN, Reuters, were compromised last year. Many of the most famous attacks were carried out by hackers associated with the authorities of the Middle East region. This list is far from complete, it is impossible to know the exact number of companies that have been attacked or compromised, and there are several explanations for this. First, some companies still do not know that they were attacked, and secondly, companies are afraid to publicly report incidents in order to avoid reputational or material losses, lawsuits and other inspections. Speaking of inspections, regulators around the world are starting to tighten the rules and requirements for companies in the field of information security.
As a confirmation of the above, we can give an example of the plans of the US Securities and Exchange Commission to conduct tests on information security in more than 50 broker-dealers and investment consulting companies. In Asia, the Singapore Personal Data Protection Act sets new standards for the collection, use and disclosure of personal data. Organizations that fail to comply with new requirements will face a fine of up to 1 million SGD or $ 788'995.

In the new manual from the US Securities and Exchange Commission there are several new and unique requirements, such as insurance against cyber attacks and the ability to make a complete inventory of all incidents and violations. Management also requires enterprises to implement risk assessment mechanisms, as well as more effectively assess the risks and due diligence of vendors.
The leaders of transnational organizations, pending the adoption of European standards for data protection (European Union Data Protection Protection), the final version of which is expected in 2015. Market participants expect stricter requirements for companies that process personal data, in particular, conducting risk assessments and audits of information security systems, and more than double the increase in fines for compromised companies (from 2% to 5% of the company's annual turnover). The new EU requirements for notifications in the event of security incidents will make it possible to assess the situation with cyber attacks in Europe more accurately. According to John Woods (one of the leading employees of the cyber security practice department at the law firm Baker & McKenzie): “In the US, state laws on notifications in cases of security incidents revealed a lot of attacks and compromises, which led to more serious attention and information security. It will be interesting to see if the European norms have the same result. ”
We are also seeing new government efforts to help organizations improve their information security on a voluntary basis. In the United States in 2013, a special presidential order to raise the level of information security created the standard of the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). Version 1.0 of the standard is voluntarily implemented by individual companies to evaluate and improve information security, and also creates a common platform for discussion, cooperation and tactics to respond to cyber threats. Private sector efforts to promote security are presented by launching Google’s initiative Project Zero, which aims to promote security by identifying and blocking unknown threats before hackers can take advantage of them. Google says that Project Zero engineers will work to increase the security of widely used software, as well as study the motivations and techniques of the attackers and conduct research in the field of effective monitoring and eliminating the effects of compromises.
The market for information security services is growing.
As a result of the increase in the number of incidents (by 48% in 2014 compared to 2013) and the tightening of regulatory requirements, companies and government agencies are forced to raise the level of information security in order to protect their data. This in turn gives impetus to the growth of the number of solutions and technologies in the field of information security.

Research firm Gartner predicts that global IT security costs will grow by 7.9% to $ 71'100'000'000 in 2014, and by 8.2% to $ 76'900'000'000 in 2015. The growth of security incidents and their media coverage helped open the flow of venture capital investment to companies that provide information security services. During the first six months of 2014, venture capital funds invested $ 894'000'000 in the United States in startups of the information security segment. The amount is almost similar to investments in all startups in 2013. This exceeds all investments in the information security sector over the past 10 years. At the same time, the capitalization of some security firms reached new highs last year.
For example, the network security provider FireEye, after being valued at $ 304 million during an IPO in 2013, currently has a market capitalization of about $ 4.6 billion. Palo Alto Networks (specializing in corporate information security) raised $ 260 million in 2012 for an IPO , and now has a market capitalization of about $ 6.2 billion.

At the height of the boom of everlasting capitalism, the valuation of some companies in the information security segment was five to ten of their annual revenues. At the moment, there is a correction in the market, everyone understands that the segment has become a “bubble”, and in order to avoid a collapse, investors are gradually reducing the rate of investment in information security. This led to the fact that some companies have lost up to half the previous estimates. We believe that the software and services market in the field of information security will continue to grow because top management and boards of directors understand that cyber attacks will never cease, and regulators will only be tightened.
The venture capital market in the field of information security is also growing in Europe:
- London-based company 5Capital raised a fund focused on information security in the amount of $ 125 million and announced investments in BalaBit 22 in the amount of $ 8 million;
- Index Ventures fund opened its doors to information security companies from Europe, Israel and the USA, allocating $ 550 million to this segment. The Fund was also active this year in the field of mergers and acquisitions in the information security segment;
- FireEye acquired Mandiant for about $ 1 billion;
- Cisco Systems acquired Sourcefire for $ 2.7 billion
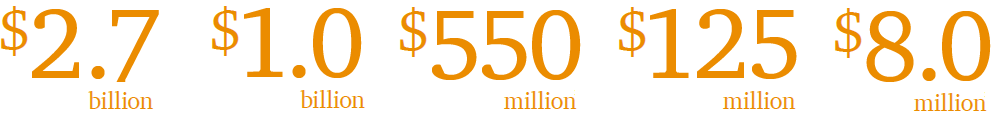
Additionally: this study is separately for the financial services segment is here .
TO BE CONTINUED…
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/264385/
All Articles