Secrets of testing Ethernet channels
Good afternoon dear friends. For several years she worked as a sysadmin in a certain number of corporate and home providers of St. Petersburg and to this day I often encounter the fact that when buying equipment operators look more at the price and description of functions than at real indicators, suppliers usually do not write anything about them, as a result which, instead of a single switch, has to be installed again and again, and the quality of the connection may not be better. About the existence of the concept of SLA (Service Level Agreement), too, not all operators are aware of, for this reason, I collected reliable information on testing networks and equipment, and is ready to provide it to your attention.

')
Ethernet need to be tested!
Are there precise definitions and recipes of how to conduct bandwidth tests and the quality of the communication provided? I found a few articles, of which only one became clear, today in Russia the networks are tested using methods designed for other purposes, and this cannot help but surprise, because communication services in large cities of our country are quite developed, there is a high-speed channel in literally every apartment, and some operators already provide gigabit channels to home customers, but not everyone knows about the methods of testing the quality of telematic services provided.
What specifically and why you need to test?
Consider how often a cat is bought in a bag today:
These are a tiny handful of examples of what customers and telecom operators are currently risking.
Software utilities for testing the "Internet"
Full channel testing cannot be echo requests, ping and mtr will never tell what channel bandwidth is. Iperf and other software utilities will not be able to tell about this, because when using the network at the same time and testing software utilities, the amount of user data currently in the channel is not known, as well as a number of inaccuracies due to the presence of packet headers depending on From the frame size, the headers remain standard length, and the body with the data increases or decreases, the software utilities determine the channel capacity without taking into account the size of the headers The size of the packages brings a certain confusion to such testing.
You will not be able to assess the quality of the rented vlan, looking at the download schedule of the channel or downloading large files from the Internet. Why speedtest.net is not proof of the speed of the channel provided probably should not be clarified? After all, it is immediately clear that it is unknown which channels and through which networks they go to the speedtest servers, as well as it’s not known how much the channel is loaded during the test, and many other test parameters, and if there are so many unknowns in the test, then its results cannot be accurate at all. The result of speedtest is rather a certain delta from certain indicators, and not real numbers.
The quality of communication services provided is a combination of many parameters, and using the right tools you can quickly and efficiently obtain accurate data about the service provided. It is important not only to obtain accurate data, but also to have confidence that the data can be used to prove one’s case, for example, in court.
Ethernet techniques and analyzers
To date, there are two main methods of testing bandwidth: the old - RFC-2544 and a little younger: Y.1564 . The ITU-T Y.1564 technique is more relevant today, it has descriptions for testing modern, high-speed communication channels with modern concepts of SLA (Service Layer Agreement).
Since the quality of the ethernet channel is a combination of many factors, therefore, proper testing should cover all these aggregates to the maximum. When testing, it is necessary to take into account many aspects and it would be useful to have advanced features, such as BER Test , packet jitter, support for MPLS, QoS, load testing of application layer protocols (http, ftp, etc ...).
To test channels from 1G to 10G and higher, it is quite difficult to do load tests using non-specialized iron, often processors are not able to generate a sufficient amount of traffic, unlike specialized testers-analyzers. Such devices can be put in a rack, cabinet, even in a box in the attic and run the tests remotely, and you can do automatic measurements at different time intervals. Any portable analyzer devices will not deteriorate in the harsh conditions of sewage, as they pass through severe tests for strength.
Delivery acceptance of communication channels.
For delivery or acceptance of built lines and highways, to work at high standards, it is best to have a tester-analyzer in the standard arsenal, although on the Internet you can find companies specializing in field testing. For some reason, it is considered that buying a tester-analyzer is very expensive.
Learn more about the RFC-2544 testing methodology and how it works.
RFC-2544 recommends measuring different frame sizes: for Ethernet traffic, frames with sizes 64, 128, 256, 512, 1024, 1280, 1518 octets, for each frame size a separate start of serial testing is necessary. If necessary, you can conduct testing for the Jumbo frame (frames of 4096 or 9000 octets). Different frame sizes are needed to simulate different types of traffic.
Initially, the technique was developed directly for testing network devices, for example, when developing switches, but the set of functions was adapted to measure the quality of channels. The methodology was approved in 1999 by ISOC .

The technique offers a set of 6 tests, I will describe in more detail how the tests are conducted, for clarity of perception:
Determining the bandwidth of the device under test (Throughput)
Test description: a small amount of packets, specially formed by the tester, is sent, at a certain speed, to the input port of the device, to the output port, the quantity is counted, if more than received is transmitted - the speed decreases and the test starts again.
Determination of frame delay time (Latency)
Test description: after determining the throughput (Throughput), for each frame size, at the corresponding maximum speed, a stream of packets is sent to a specific address. The stream must have a minimum duration of 120 seconds. A label is inserted into 1 packet after 60 seconds. The label format is determined by the hardware manufacturer. On the transmitting side, the time by which the packet with the tag was completely sent is recorded. At the receiving side, a label is determined and the time of full reception of a packet with a label is recorded. Delay (latency) - is the difference between the time of sending and the time of receipt. This test, according to the method, must be repeated at least 20 times. Based on the results of 20 measurements, the average delay is calculated. The test should be carried out by sending the entire test stream to one address and sending each frame to a new address.
Frame Loss Determination
Test description: A certain number of frames are sent to the input port of the device at a certain speed and the number of packets received from the output port of the device is counted. The frame loss rate is calculated as follows:
((number of frames transmitted - number of frames received) * 100) / number of frames transmitted
The first dispatch occurs at the maximum possible speed, then the dispatch rate decreases with a maximum step of 10%; according to the method, reducing% step will give the most accurate results. The speed reduction should be continued until the last two shipments will be without errors, namely, we will know the maximum data transfer rate at which the frame loss rate becomes equal to 0.
Testing the ability to handle back-to-back frames (Back-to-back frames)
Test description: the test is reduced to sending a certain number of frames with a minimum interframe delay to the input port of the device under test and counting frames from the output port of the device. If the number of frames sent and received is equal, then the volume of frames sent is increased and the test is repeated, if the received packets are smaller than the number of frames sent, the frames are reduced and the test is repeated. As a result, we should get the maximum number of packets sent and received without loss for each packet size, this will be the value of the back-to-back test. According to the method, the duration of sending frames to the device port should not be less than two seconds, and the minimum number should be at least 50 times. The final figure is the average result of 50 tests.
Recovery after overload (System recovery), applicable only for testing devices
Test description: a stream of frames is sent to the device input for at least 60 seconds at a speed of 110% relative to the measured throughput test. If the throughput test showed perfect results, then the maximum speed of this connection is chosen. At the time of the overload, the flow rate is halved, and the difference between the time taken to reduce the flow rate and the time when the last frame was lost is detected.
Recovery time of the device under test after a restart (Reset), applicable only for testing devices
Test description: a continuous stream of frames is sent to the device input at a speed determined by a throughput test with a minimum frame size. The device is reset. Recovery time after a reset is the difference between the time the last packet was received before the reset and the time it took the first packet after a reset. Both hardware and software device reset types are tested.
What has changed with the fresh Y.1564 methodology?
New recommendations were reviewed and approved by ITU in 2011. RFC 2544 adds packet jitter (jitter) to the already stated recommendations, namely the ability to calculate the time difference when receiving a series of consecutive data packets belonging to the same stream, in an ideal world it should not exist, but there can be a sequence in problem networks broken, which may affect the speed of data processing. RFC2544 allows you to check only at the maximum speed of the channel, which will not be packet loss, and it is usually higher than the speed of CIR (Committed Information Rate - guaranteed bandwidth) . Y.1564 was created specifically for SLA , assessment of the speed and quality of the provided channel according to key performance indicators (KPI) and allows you to check the provided channel in accordance with the contract.
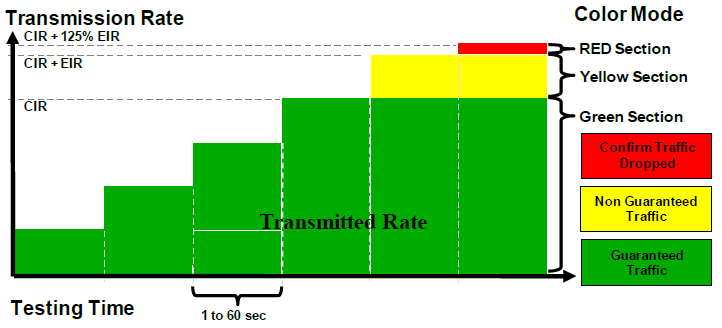
Y.1564 allows you to check the guaranteed bandwidth, the maximum allowable, as well as give the load over the band, for example to check the settings of the shaper.
There are several other differences between the methodologies, RFC2544 does not verify the correctness of the service setup (KPI matching is specified, and the speed limit is higher than the EIR (Excess Information Rate is the maximum non-guaranteed bandwidth), in order to avoid network overload). In the original version of RFC2544, jitter is not measured. According to RFC2544, each test is launched as a separate stream, which does not allow measuring the quality of the services provided in the aggregate and increases the testing time, another disadvantage of RFC2544 is that there is no profiling ability to check different types of traffic in one channel, for example, if QoS is used in the network , Y.1564 takes into account shortcomings and slightly expanded functionality.
Can you test only new channels or are you already working too?
You need to test and new channels, and the more old. You can learn in advance about the emerging issues, without bringing customers to call for support. Up-to-date testers-analyzers can be used for checking in a working network, checking channels with a speed of 10/100 / 1000Mbit, and 10/40 / 100G. There is one BUT, it is very important to understand what and how you are doing, it is important that you do not inadvertently put a test channel.
Test Modes - In / Out of service.
Today, network testing is committed to complete systematization and continuous monitoring of channels, earlier versions of the RFC2544 methodology were created for testing channels / equipment in OutOfService mode, and were used mainly for equipment testing, but today all manufacturers of test devices are switching to newer testing standards that allow continuous monitoring of the network in InService mode. Such testing allows you to check the speed of the bandwidth without disconnecting customers, which is important for telecom service providers.
Epilogue
Comrades, as one friend says, let's fight together with the “co-hackers” and start testing what we build and what we exploit.
Used Books:
RFC 2544 methodology: https: //www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc2544.txt
Method Y.1564: www.itu.int/rec/T-REC-Y.1564-201103-I/en
André article on the difference in methods: www.mrv.com/blog/why-rcf2544-not-sufficient-anymore
* Opinion of the company may not coincide with the opinion of the author ;-)

')
Ethernet need to be tested!
Are there precise definitions and recipes of how to conduct bandwidth tests and the quality of the communication provided? I found a few articles, of which only one became clear, today in Russia the networks are tested using methods designed for other purposes, and this cannot help but surprise, because communication services in large cities of our country are quite developed, there is a high-speed channel in literally every apartment, and some operators already provide gigabit channels to home customers, but not everyone knows about the methods of testing the quality of telematic services provided.
What specifically and why you need to test?
Consider how often a cat is bought in a bag today:
- Your leased or leased communication channels;
- Delivery-acceptance of communication channels, built by you or for you;
- Communication services provided, especially in the presence of a penalty in the contract;
- The equipment you want to buy, but they want to sell it to you, and tell you that it is super-cool and inexpensive.
These are a tiny handful of examples of what customers and telecom operators are currently risking.
Software utilities for testing the "Internet"
Full channel testing cannot be echo requests, ping and mtr will never tell what channel bandwidth is. Iperf and other software utilities will not be able to tell about this, because when using the network at the same time and testing software utilities, the amount of user data currently in the channel is not known, as well as a number of inaccuracies due to the presence of packet headers depending on From the frame size, the headers remain standard length, and the body with the data increases or decreases, the software utilities determine the channel capacity without taking into account the size of the headers The size of the packages brings a certain confusion to such testing.
You will not be able to assess the quality of the rented vlan, looking at the download schedule of the channel or downloading large files from the Internet. Why speedtest.net is not proof of the speed of the channel provided probably should not be clarified? After all, it is immediately clear that it is unknown which channels and through which networks they go to the speedtest servers, as well as it’s not known how much the channel is loaded during the test, and many other test parameters, and if there are so many unknowns in the test, then its results cannot be accurate at all. The result of speedtest is rather a certain delta from certain indicators, and not real numbers.
The quality of communication services provided is a combination of many parameters, and using the right tools you can quickly and efficiently obtain accurate data about the service provided. It is important not only to obtain accurate data, but also to have confidence that the data can be used to prove one’s case, for example, in court.
Ethernet techniques and analyzers
To date, there are two main methods of testing bandwidth: the old - RFC-2544 and a little younger: Y.1564 . The ITU-T Y.1564 technique is more relevant today, it has descriptions for testing modern, high-speed communication channels with modern concepts of SLA (Service Layer Agreement).
Since the quality of the ethernet channel is a combination of many factors, therefore, proper testing should cover all these aggregates to the maximum. When testing, it is necessary to take into account many aspects and it would be useful to have advanced features, such as BER Test , packet jitter, support for MPLS, QoS, load testing of application layer protocols (http, ftp, etc ...).
To test channels from 1G to 10G and higher, it is quite difficult to do load tests using non-specialized iron, often processors are not able to generate a sufficient amount of traffic, unlike specialized testers-analyzers. Such devices can be put in a rack, cabinet, even in a box in the attic and run the tests remotely, and you can do automatic measurements at different time intervals. Any portable analyzer devices will not deteriorate in the harsh conditions of sewage, as they pass through severe tests for strength.
Delivery acceptance of communication channels.
For delivery or acceptance of built lines and highways, to work at high standards, it is best to have a tester-analyzer in the standard arsenal, although on the Internet you can find companies specializing in field testing. For some reason, it is considered that buying a tester-analyzer is very expensive.
Learn more about the RFC-2544 testing methodology and how it works.
RFC-2544 recommends measuring different frame sizes: for Ethernet traffic, frames with sizes 64, 128, 256, 512, 1024, 1280, 1518 octets, for each frame size a separate start of serial testing is necessary. If necessary, you can conduct testing for the Jumbo frame (frames of 4096 or 9000 octets). Different frame sizes are needed to simulate different types of traffic.
Initially, the technique was developed directly for testing network devices, for example, when developing switches, but the set of functions was adapted to measure the quality of channels. The methodology was approved in 1999 by ISOC .

The technique offers a set of 6 tests, I will describe in more detail how the tests are conducted, for clarity of perception:
Determining the bandwidth of the device under test (Throughput)
Test description: a small amount of packets, specially formed by the tester, is sent, at a certain speed, to the input port of the device, to the output port, the quantity is counted, if more than received is transmitted - the speed decreases and the test starts again.
Determination of frame delay time (Latency)
Test description: after determining the throughput (Throughput), for each frame size, at the corresponding maximum speed, a stream of packets is sent to a specific address. The stream must have a minimum duration of 120 seconds. A label is inserted into 1 packet after 60 seconds. The label format is determined by the hardware manufacturer. On the transmitting side, the time by which the packet with the tag was completely sent is recorded. At the receiving side, a label is determined and the time of full reception of a packet with a label is recorded. Delay (latency) - is the difference between the time of sending and the time of receipt. This test, according to the method, must be repeated at least 20 times. Based on the results of 20 measurements, the average delay is calculated. The test should be carried out by sending the entire test stream to one address and sending each frame to a new address.
Frame Loss Determination
Test description: A certain number of frames are sent to the input port of the device at a certain speed and the number of packets received from the output port of the device is counted. The frame loss rate is calculated as follows:
((number of frames transmitted - number of frames received) * 100) / number of frames transmitted
The first dispatch occurs at the maximum possible speed, then the dispatch rate decreases with a maximum step of 10%; according to the method, reducing% step will give the most accurate results. The speed reduction should be continued until the last two shipments will be without errors, namely, we will know the maximum data transfer rate at which the frame loss rate becomes equal to 0.
Testing the ability to handle back-to-back frames (Back-to-back frames)
Test description: the test is reduced to sending a certain number of frames with a minimum interframe delay to the input port of the device under test and counting frames from the output port of the device. If the number of frames sent and received is equal, then the volume of frames sent is increased and the test is repeated, if the received packets are smaller than the number of frames sent, the frames are reduced and the test is repeated. As a result, we should get the maximum number of packets sent and received without loss for each packet size, this will be the value of the back-to-back test. According to the method, the duration of sending frames to the device port should not be less than two seconds, and the minimum number should be at least 50 times. The final figure is the average result of 50 tests.
Recovery after overload (System recovery), applicable only for testing devices
Test description: a stream of frames is sent to the device input for at least 60 seconds at a speed of 110% relative to the measured throughput test. If the throughput test showed perfect results, then the maximum speed of this connection is chosen. At the time of the overload, the flow rate is halved, and the difference between the time taken to reduce the flow rate and the time when the last frame was lost is detected.
Recovery time of the device under test after a restart (Reset), applicable only for testing devices
Test description: a continuous stream of frames is sent to the device input at a speed determined by a throughput test with a minimum frame size. The device is reset. Recovery time after a reset is the difference between the time the last packet was received before the reset and the time it took the first packet after a reset. Both hardware and software device reset types are tested.
What has changed with the fresh Y.1564 methodology?
New recommendations were reviewed and approved by ITU in 2011. RFC 2544 adds packet jitter (jitter) to the already stated recommendations, namely the ability to calculate the time difference when receiving a series of consecutive data packets belonging to the same stream, in an ideal world it should not exist, but there can be a sequence in problem networks broken, which may affect the speed of data processing. RFC2544 allows you to check only at the maximum speed of the channel, which will not be packet loss, and it is usually higher than the speed of CIR (Committed Information Rate - guaranteed bandwidth) . Y.1564 was created specifically for SLA , assessment of the speed and quality of the provided channel according to key performance indicators (KPI) and allows you to check the provided channel in accordance with the contract.

Y.1564 allows you to check the guaranteed bandwidth, the maximum allowable, as well as give the load over the band, for example to check the settings of the shaper.
There are several other differences between the methodologies, RFC2544 does not verify the correctness of the service setup (KPI matching is specified, and the speed limit is higher than the EIR (Excess Information Rate is the maximum non-guaranteed bandwidth), in order to avoid network overload). In the original version of RFC2544, jitter is not measured. According to RFC2544, each test is launched as a separate stream, which does not allow measuring the quality of the services provided in the aggregate and increases the testing time, another disadvantage of RFC2544 is that there is no profiling ability to check different types of traffic in one channel, for example, if QoS is used in the network , Y.1564 takes into account shortcomings and slightly expanded functionality.
Can you test only new channels or are you already working too?
You need to test and new channels, and the more old. You can learn in advance about the emerging issues, without bringing customers to call for support. Up-to-date testers-analyzers can be used for checking in a working network, checking channels with a speed of 10/100 / 1000Mbit, and 10/40 / 100G. There is one BUT, it is very important to understand what and how you are doing, it is important that you do not inadvertently put a test channel.
Test Modes - In / Out of service.
Today, network testing is committed to complete systematization and continuous monitoring of channels, earlier versions of the RFC2544 methodology were created for testing channels / equipment in OutOfService mode, and were used mainly for equipment testing, but today all manufacturers of test devices are switching to newer testing standards that allow continuous monitoring of the network in InService mode. Such testing allows you to check the speed of the bandwidth without disconnecting customers, which is important for telecom service providers.
Epilogue
Comrades, as one friend says, let's fight together with the “co-hackers” and start testing what we build and what we exploit.
Used Books:
RFC 2544 methodology: https: //www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc2544.txt
Method Y.1564: www.itu.int/rec/T-REC-Y.1564-201103-I/en
André article on the difference in methods: www.mrv.com/blog/why-rcf2544-not-sufficient-anymore
* Opinion of the company may not coincide with the opinion of the author ;-)
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/264295/
All Articles