New critical vulnerabilities in Android: What is the problem, and how to protect

Information security researchers have discovered a number of serious vulnerabilities in one of the components of the Android mobile OS kernel called Stagefright (a library for working with multimedia files, such as PDF). The first about the problems in the component Stagefright said a researcher from the company Zimperium Labs Joshua Drake ( Joshua J. Drake ). In addition, TrendMicro announced the discovery of a serious vulnerability in Android.
Stagefright
The researcher has published an exploit that demonstrates an attack using a malicious MMS message - in order to accomplish it, the attacker needs to know only the victim's phone number. At the same time, the user does not even need to carry out any actions with the message (open the file, click on the links, etc.), the malicious code is executed automatically.
')
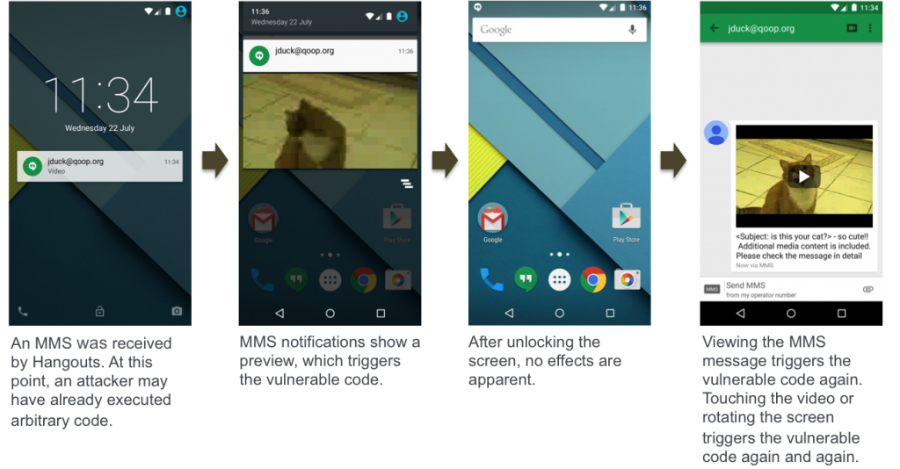
As reported in a post on the ZImperium blog, hackers can even delete the message itself before the user sees it (in this case, the smartphone will only show an incoming message alert).
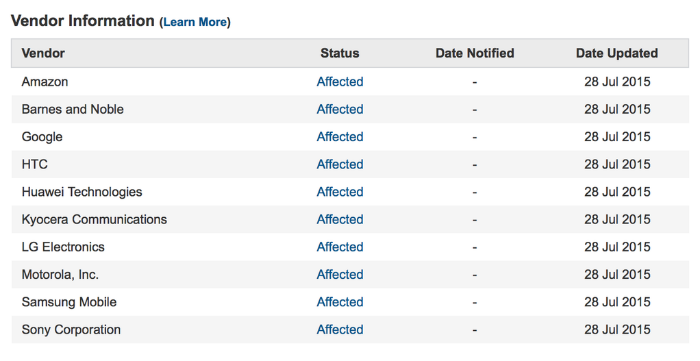
List of vulnerable devices
According to Drake, despite the presence in Android of a special security sandbox, which blocks for most applications the ability to access user data from other programs, it is possible to create exploits that access the audio and video streams of the smartphone, as well as to the internal storage.
Vulnerabilities are subject to phones running Android from version 2.2 to version 5.1 (according to media estimates, up to 950 million smartphones and tablets worldwide are vulnerable).
According to the publication Ars Technica, the vulnerability of Stagefright also affects the Firefox browser on all platforms except Linux (including Firefox OS). The editors contacted Joshua Drake, who confirmed that there were problems:
If you install Firefox 38, then you will no longer be able to attack you through Firefox. However, if you upload a malicious video through a browser with the tag
video width="300" height="150" , and will not play it, it will still download malicious Android code.It is noteworthy that Drake was the first to report security problems at Stagefright (he plans to tell more about his findings at the DEFCON conference on August 7), but not the only one who discovered them. According to Forbes, a 36-year-old Moscow researcher Yevgeny Legerov also discovered two zero-day vulnerabilities in this component. Google has released a series of patches for partners ( one , two , three ) that fixes vulnerabilities found by Legerov.
Joshua Drake gave information about the vulnerability to Google (along with possible patches), and the company paid him a reward of $ 1.337 (the alert was sent before the official launch of the bug bounty program for Android). If the information about the vulnerability had been transferred to the exploit vendors, the researcher could have counted on a sum of about $ 100,000 - Zerodium, in its Twitter, said it was ready to pay for such vulnerabilities as much:

So far, patches have been received only by Silent Circle Blackphone and devices with Cyanogen firmware, vulnerabilities discovered by Evgeny Legerov were also added to the VulnDisco exploit kit (available to government and commercial organizations using the Canvas penetration testing tool). Legerov told reporters that his team provides customers with exploits for internal testing, so their functionality is curtailed and does not allow for full-scale real attacks.
Zimperium specialists also recommend that Android users update the OS to the latest version (although they point to the fact that it is unknown when the patch will appear and whether it will be for older devices — it is recommended to install the Cyanogen firmware for them), disable the automatic downloading of MMS (for Hangouts and "default" application for SMS).
Attack to the media server
In addition to the Stagefright vulnerability, a serious security bug in Android (versions starting from 4.3 Jelly Bean up to 5.1.1 Lollipop, that is, more than half of all Android devices in the world), was announced by TrendMicro. The exploitation of this vulnerability is possible by installing a malicious application on the device (causing the operating system to crash) or by redirecting the user to the site prepared by the attackers.
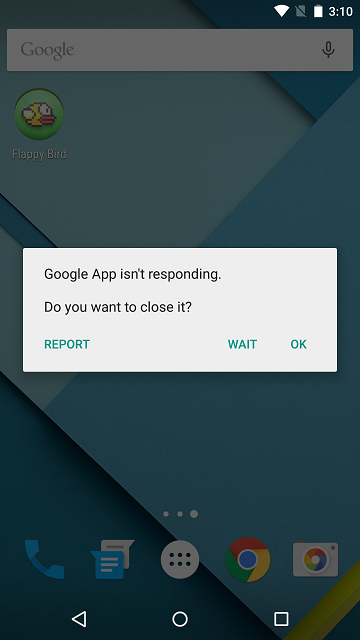
A vulnerability has been discovered in the media server service, which Android uses to index media files stored on the device. The service cannot correctly process malicious video (usually with a .mkv extension) using the Matroska container , which causes the entire operating system to crash. TrendMicro has posted the code for the
frameworks/av/media/libstagefright/matroska/MatroskaExtractor.cpp file on the blog showing 865 size_t offset = 1; 866 size_t len1 = 0; 867 while (offset < codecPrivateSize && codecPrivate[offset] == 0xff) {//codecPrivate is controlled by the mkv file 868 len1 += 0xff; 869 ++offset; 870 } 871 if (offset >= codecPrivateSize) { 872 return ERROR_MALFORMED; 873 } 874 len1 += codecPrivate[offset++]; 875 876 size_t len2 = 0; 877 while (offset < codecPrivateSize && codecPrivate[offset] == 0xff) { 878 len2 += 0xff; 879 ++offset; 880 } 881 if (offset >= codecPrivateSize) { 882 return ERROR_MALFORMED; 883 } 884 len2 += codecPrivate[offset++]; 885 886 if (codecPrivateSize < offset + len1 + len2) {//len1 or len2 maybe 0xffffffff, then integer overflow happened 887 return ERROR_MALFORMED; 888 } 889 890 if (codecPrivate[offset] != 0x01) { 891 return ERROR_MALFORMED; 892 } 893 meta->setData(kKeyVorbisInfo, 0, &codecPrivate[offset], len1);//crash in here TrendMicro employees created a special application that exploits this vulnerability. The video below shows an attack on a smartphone with it:
They managed to reproduce and attack using the URL. For this, a special website was created, the malicious video is embedded in the HTML code. While the site was loading, Chrome browser had the same effect:
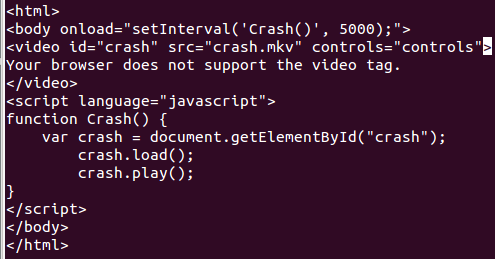
Researchers say that you can protect against this vulnerability with the help of special protective applications for mobile devices.
At conferences on information security, Positive Technologies researchers also demonstrated the results of a study on the security of 4G communications and SIM cards (they can also be hacked ).
During the Positive Hack Days forum held in May in Moscow, a competition was also held on hacking MiTM Mobile mobile communications - we published an analysis of its tasks in Habré (some event attendees received reports about hacking their devices). Here is a webinar entry on this topic.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/263903/
All Articles