Simple phone interface from Nokia
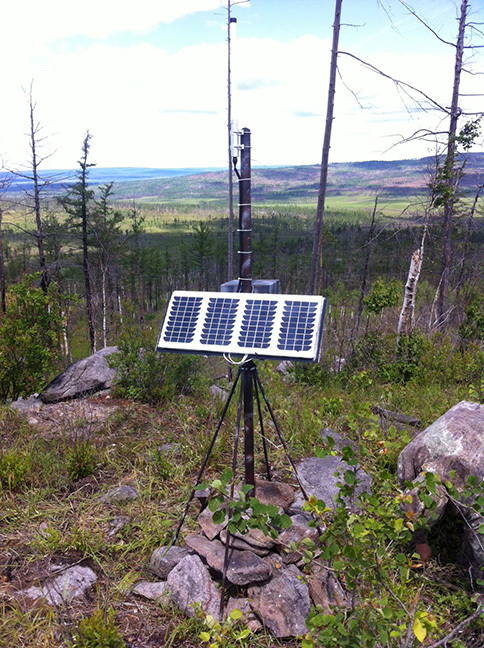

Our autonomous echo repeater is controlled by DTMF signals in a common communication channel. To do this, you need to use a radio station with a keyboard and be in the zone of sustainable radio coverage. Since these conditions are not always feasible, we decided to make access to the radio network through a telephone network. For this, a classic solution was used - installation of a telephone interface. But in its non-classical form.
A classic version of the telephone interface has long been a bunch of type CSI-800 + radio station + telephone line. We do not have a wired telephone line, which means that we also need a GSM gateway. If you do everything according to science, it will turn out reliably, beautifully, functionally, but expensive. We have chosen a different path.
')
From the interface were needed: receiving an incoming call, sending DTMF commands to the radio network and broadcasting a signal from the receiver to the telephone line. An old Nokia handled the incoming call. For the rest of the scheme was developed.
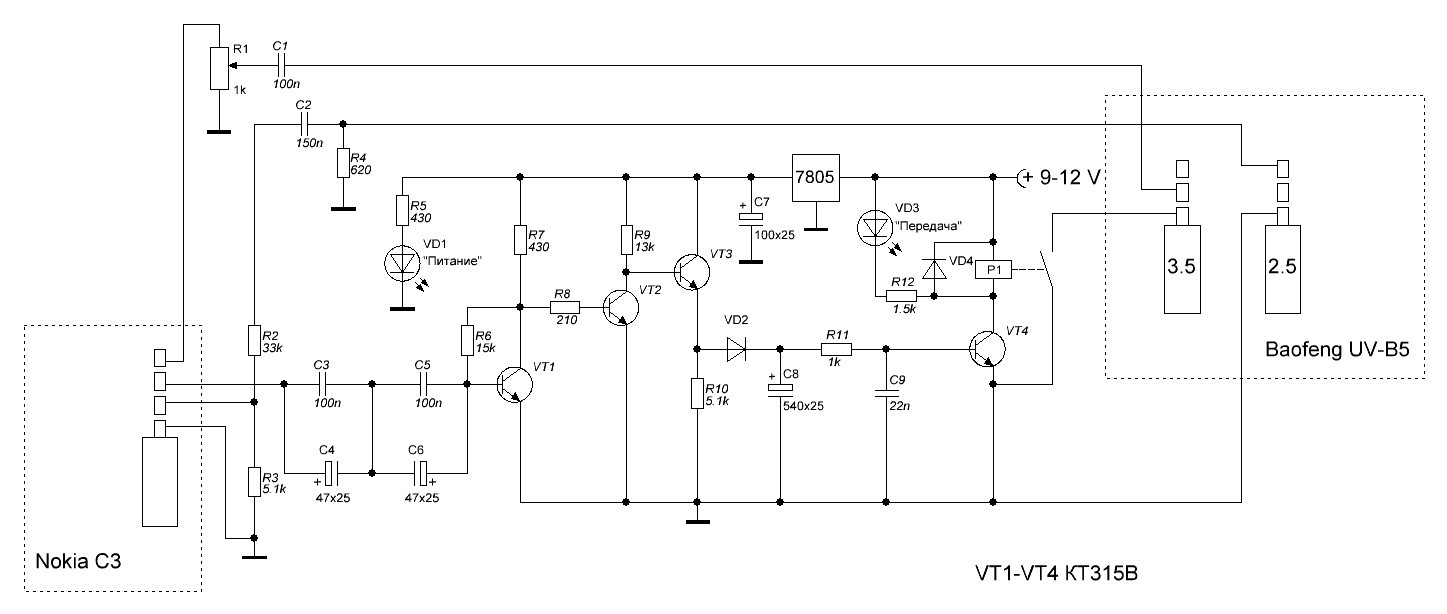
This is a regular VOX with a release delay. We did not make a fuss with the sound recording microcircuit, donating the phrase “beginning to eat”. For DTMF transmission this was not so categorical, in the sending of the request the first digit of the command is simply doubled. The signal from the receiver is not processed and goes immediately to the microphone input of the phone.
At first it was not clear which station the interface would work with and how it would be necessary to control the PTT mode, therefore an electromagnetic relay is present in the circuit (from a faulty car alarm). Surely it can be replaced with something non-contact, with an optocoupler, for example. There is also no galvanic isolation in the form of transformers, everything worked in our country without them.
Setting up the device starts with the inclusion of auto-call on the phone. In Nokia, auto raise does not work if the call volume is set to zero. So that the melody of the call did not go on the air, we recorded three seconds of silence on the recorder and then used this recording as a ringtone. Now the phone picks up the phone, but no sounds in the radio fly.
Then you need to adjust the transmission level. To do this, the phone is placed next to the receiver tuned to Vesti-FM, there is a lot of speaking, and then with the help of the resistor R1, the sound in the air reaches a loud, but without distortion. The volume on the phone at the same time should be set to maximum (we used the Nokia C3, but it is quiet for some reason).
After that, you need to set the volume on the radio. It is better to do this when receiving real signals from the radio network. We also achieve loud, but without distortion of the signal. In our case, it turned out the leftmost position of the volume control on the radio station Baofeng UV-B5.
The device and radio station are powered from a single source of 7.5 volts. The phone runs on its own battery. To charge it once a day, a regular charger is turned on after a timer for a couple of hours.
The printed circuit board was not developed, the circuit is assembled on a breadboard. On the wires going to the radio station, put on ferrite rings (closer to the board).
A serious disadvantage of this design is the lack of verification of the incoming call number. Nokia will respond to any subscriber. The simplest solution, offhand, is to use the White List service (MTS). There you can configure the reception of calls only from certain numbers.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/262851/
All Articles