Fundamentals of successful implementation of push notifications for mobile applications
Our Techmas developers are often confronted with push notifications. Despite the simplicity and popularity of the technology, its implementation has a number of features, which will be discussed in this article.
Push messages can be a great marketing tool if they are correctly implemented. Any mobile application or game should not only perform its direct functions, but also (to a greater extent) interact with users so that the latter return with pleasure to the application and buy additions to it. By the way, according to statistics from the Kahuna service, well-designed push notifications increased the rate of user returns to applications by more than 2 times. Analyzed periods: 30, 60, 90 days. But before talking about a competent implementation, let's see how push notifications work.
')
Push notifications are a way to distribute content (system messages) when notifications are sent from the server to the client at the initiative of the server based on certain parameters. Unlike the reverse client-server ( Pull ) scheme, push-technology is beneficial in that it gives the user targeted information that may be useful to him, but he may not yet know about this benefit.
Initially, Push Notification technology was not related to mobile applications, but to the PointCast network, which was responsible for sending stock market news. The same system has long been used by US courts to send process data to subscribers. Later, Microsoft and Netscape included the technology in their browsers, but due to the low user connection speed, it was then supplanted by the RSS pull technology. And only then the term became widely known after the introduction of technology by Google in the Android OS ( Google Cloud Messaging , GCM) and Apple in iOS 3 ( Apple Push Notification Service , APNS). For example, the last consider the elementary scheme of the Push-notifications.

It is important to know! In order for the notification to be displayed on the device screen, the application itself does not have to be started — it is the OS that acts as an intermediary to realize this advantage. By the way, this approach allows you to save and charge the battery of the smartphone (phone), and traffic.
There are nuances in the push notifications for different mobile platforms (Android, iOS, Windows Phone). Suppose, if an application has been removed by a user, then all services report on which devices should no longer be sent notifications. This process is carried out through a message to the server tokens of these devices. However, if GCM sends IDs immediately, then APNS has a special feedback server (feedback server) from which the list of such tokens is retrieved once a day. For routine work with these differences, intermediate services are needed.
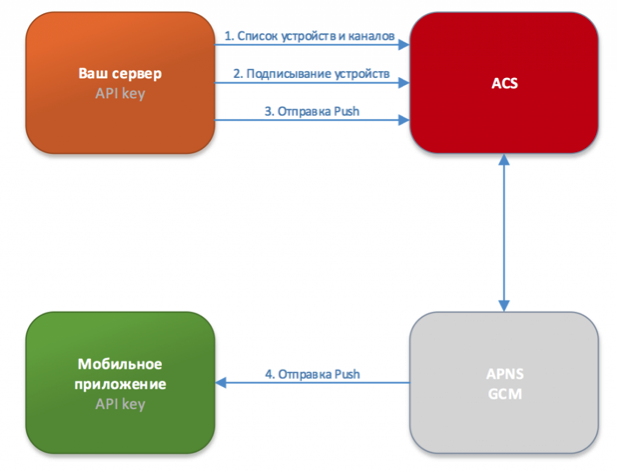
In the case of developing a mobile application using any cross-platform solution (for example, Appcelerator ), such an intermediate service is usually integrated into it. For example, in the same Appcelerator, this is Appcelerator Cloud Services (ACS), which is an additional service of notification channels. Such a channel (channel) combines several devices, being a kind of identifier, consisting of numbers and letters. ACS allows you to send pushes and device tokens. So, this intermediate service takes on the function of updating information about devices and interacts with APNS and GCM.
The scheme of this interaction is as follows:
Subscription form. Modern user does not like obsession. For this reason, it is better not to show the notification subscription dialog box when the application is started, because the user does not yet know whether he will be interested in your mailings. It is good if the subscription form for pushing, for example, new prices for goods appears only when the user activates a subscription to lots or directions interesting to him. Or agrees to receive push notifications in the application settings.
Notification form. Immediately give interesting information, better in the title. Identical fluffs like "New sales in our store" do not work: give specifics. It is also a good idea to use Deep Linking (specify in the message external links to a specific page of the site).
Flexible customization. The more detailed the setting of what the user wants to receive a message about within your product, the better. Personalized mailings always have a greater response. Allow the user to set up notifications in a way that is interesting and convenient for him, with maximum details.
User interest. Tell the user what he wants to hear, not what you want to tell him. For this you need to collect information about what is interesting to the user. A simple push about a new restaurant from a city guide does not compare with a push about a new restaurant in the area where a user lives with information about morning discounts - he often has breakfast in a cafe. Analytics and analytics again.
Statistics. It needs to be collected to understand: when is it more efficient to send messages; what types of notifications are more effective; how much those who receive your pushes go to the application more often than those who are not signed; how many users opened the application for one push or another; other types of user behavior analysis.
Testing. Use different subscription forms, notification texts, distribution time and general push strategy. Stay tuned for online feedback - this will give you a wealth of information on how to improve the newsletter.
The sound of notifications. Customize your own, unique. That the user knew that the new message came from your application. Do not make it annoying - make it comfortable.
Push woosh . It gives convenient and understandable reports, is compatible with many platforms, perfectly segments the audience into different groups of signs.
Urban Airship . Targets and analyzes the audience, allows you to select different user retention strategies and create advanced format notifications.
Appsfire`s Appbooster . Free service with standard features.
Parse Push . Allows you to collect unique data for analytics, easily integrated into any application.
In conclusion, we note that push notifications, of course, are a simple and effective way to return and retain the user in particular, and a powerful marketing tool in general. But this is from the user's point of view. From the developer’s side, there are some difficulties. The implementation of notifications is highly dependent on external input: changes in the OS or in the intermediate software leads to the need to finalize the application. So, in Appcelerator, a new tool, Arrow Push, has come to replace ACS - and this is just one example. Moreover, push delivery is not guaranteed in principle, and this raises the question of the reliability of Push Notification technology. However, any technology has its pros and cons, and that outweighs in this case - an open question.

Push messages can be a great marketing tool if they are correctly implemented. Any mobile application or game should not only perform its direct functions, but also (to a greater extent) interact with users so that the latter return with pleasure to the application and buy additions to it. By the way, according to statistics from the Kahuna service, well-designed push notifications increased the rate of user returns to applications by more than 2 times. Analyzed periods: 30, 60, 90 days. But before talking about a competent implementation, let's see how push notifications work.
')
Push Notification Technology Overview
Push notifications are a way to distribute content (system messages) when notifications are sent from the server to the client at the initiative of the server based on certain parameters. Unlike the reverse client-server ( Pull ) scheme, push-technology is beneficial in that it gives the user targeted information that may be useful to him, but he may not yet know about this benefit.
Initially, Push Notification technology was not related to mobile applications, but to the PointCast network, which was responsible for sending stock market news. The same system has long been used by US courts to send process data to subscribers. Later, Microsoft and Netscape included the technology in their browsers, but due to the low user connection speed, it was then supplanted by the RSS pull technology. And only then the term became widely known after the introduction of technology by Google in the Android OS ( Google Cloud Messaging , GCM) and Apple in iOS 3 ( Apple Push Notification Service , APNS). For example, the last consider the elementary scheme of the Push-notifications.
Push Notification operation diagram using the example of an APNS service

It is important to know! In order for the notification to be displayed on the device screen, the application itself does not have to be started — it is the OS that acts as an intermediary to realize this advantage. By the way, this approach allows you to save and charge the battery of the smartphone (phone), and traffic.
- To receive Push messages, the OS must register the mobile application;
- OS requests a device identifier (token) from APNS;
- The application receives the token from the APNS server;
- The application sends the token back to the server so that the server will use it to send Push notifications;
- When an event defined by the developer occurs, the server, using tokens, sends Push messages through APNS;
- APNS sends notifications to the application.
Why do we need intermediate services
There are nuances in the push notifications for different mobile platforms (Android, iOS, Windows Phone). Suppose, if an application has been removed by a user, then all services report on which devices should no longer be sent notifications. This process is carried out through a message to the server tokens of these devices. However, if GCM sends IDs immediately, then APNS has a special feedback server (feedback server) from which the list of such tokens is retrieved once a day. For routine work with these differences, intermediate services are needed.
In the case of developing a mobile application using any cross-platform solution (for example, Appcelerator ), such an intermediate service is usually integrated into it. For example, in the same Appcelerator, this is Appcelerator Cloud Services (ACS), which is an additional service of notification channels. Such a channel (channel) combines several devices, being a kind of identifier, consisting of numbers and letters. ACS allows you to send pushes and device tokens. So, this intermediate service takes on the function of updating information about devices and interacts with APNS and GCM.
The scheme of this interaction is as follows:

- When developing a mobile application, a key is introduced into it that is issued by ACS;
- Any notification is a JSON dictionary consisting of a token device, some service information and a payload. The payload is the data itself that is sent to the phone.
- Server using the key:
- gets a list of channels and devices subscribed to the channels;
- signs (and unsubscribes) devices on a specific channel;
- sends push notifications to all devices or only on certain tokens or device channels.
- Devices, depending on their operating system, receive push messages from GCM or APNS.
Subscription form. Modern user does not like obsession. For this reason, it is better not to show the notification subscription dialog box when the application is started, because the user does not yet know whether he will be interested in your mailings. It is good if the subscription form for pushing, for example, new prices for goods appears only when the user activates a subscription to lots or directions interesting to him. Or agrees to receive push notifications in the application settings.
Notification form. Immediately give interesting information, better in the title. Identical fluffs like "New sales in our store" do not work: give specifics. It is also a good idea to use Deep Linking (specify in the message external links to a specific page of the site).
Flexible customization. The more detailed the setting of what the user wants to receive a message about within your product, the better. Personalized mailings always have a greater response. Allow the user to set up notifications in a way that is interesting and convenient for him, with maximum details.
User interest. Tell the user what he wants to hear, not what you want to tell him. For this you need to collect information about what is interesting to the user. A simple push about a new restaurant from a city guide does not compare with a push about a new restaurant in the area where a user lives with information about morning discounts - he often has breakfast in a cafe. Analytics and analytics again.
Statistics. It needs to be collected to understand: when is it more efficient to send messages; what types of notifications are more effective; how much those who receive your pushes go to the application more often than those who are not signed; how many users opened the application for one push or another; other types of user behavior analysis.
Testing. Use different subscription forms, notification texts, distribution time and general push strategy. Stay tuned for online feedback - this will give you a wealth of information on how to improve the newsletter.
The sound of notifications. Customize your own, unique. That the user knew that the new message came from your application. Do not make it annoying - make it comfortable.
Push automation services
Push woosh . It gives convenient and understandable reports, is compatible with many platforms, perfectly segments the audience into different groups of signs.
Urban Airship . Targets and analyzes the audience, allows you to select different user retention strategies and create advanced format notifications.
Appsfire`s Appbooster . Free service with standard features.
Parse Push . Allows you to collect unique data for analytics, easily integrated into any application.
In conclusion, we note that push notifications, of course, are a simple and effective way to return and retain the user in particular, and a powerful marketing tool in general. But this is from the user's point of view. From the developer’s side, there are some difficulties. The implementation of notifications is highly dependent on external input: changes in the OS or in the intermediate software leads to the need to finalize the application. So, in Appcelerator, a new tool, Arrow Push, has come to replace ACS - and this is just one example. Moreover, push delivery is not guaranteed in principle, and this raises the question of the reliability of Push Notification technology. However, any technology has its pros and cons, and that outweighs in this case - an open question.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/262411/
All Articles