AccountLogic 2.0: brought to mind, but not to the end
The history of the creation of this "product" can be traced to the posts on Habré (the latest, dedicated to the release of version 1.0, is here ).
In version 2.0, functions have been added that allow talking about some, albeit not final, approach to the ceiling of methodological possibilities.
To date, “Accounting Logic” (the new Russianized name “Accounting Logic”) allows - at least, it should allow according to the specification - quite a lot.
')
Brazen advertisement that does not cancel the obvious fact that the code is amateur with the ensuing grave consequences. At the same time, the method incorporated in the program is professional: it was created on the basis of a theoretical basis, which took a decade to develop.
There is no point in listing the features available in version 1.0, so I’ll start by describing new features, in order of increasing importance.
I.
Service functions: archiving, passwording, localization (English - machine translation, adjusted to the extent of my meager interpretations).

Everything is standard, does not represent the slightest methodological interest.
Ii.
The data in the database are divided into two parts: actual (main) and planned (additional, taken into account in parallel with the main ones for comparison with them). Typical opportunity, not inclined to diversity.
The reporting folders provide for both separate and joint presentation of actual and planning data.
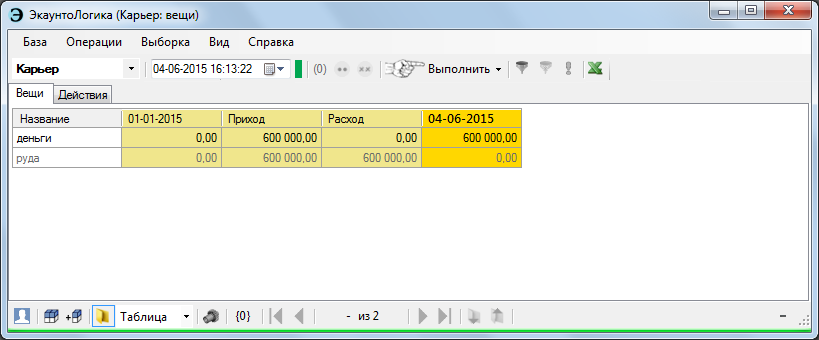
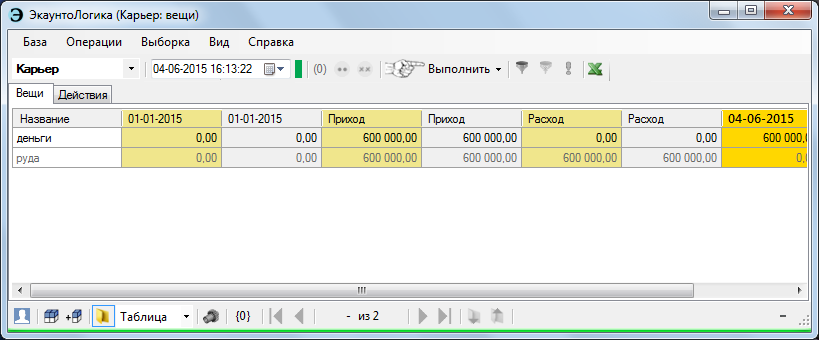
Theoretically, it was not difficult to realize a multitude of planned (parallel to each other) information flows, but why?
Iii.
File binding is a simplest function to execute, however, due to the unusual software architecture, it is not without interest. As is customary, drag and drop files into the workspace.
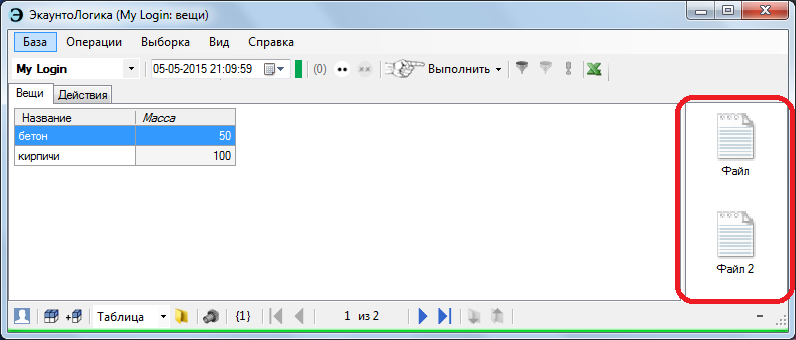
You can correlate a file with one of the following elements:
Since the terminology is different from the usual accounting, should be clarified. There is a thing with some properties, let's say: [name] = “apple”, [grade] = “Antonovka”. Accordingly, its receipt is reflected by the action - the account, an analogue of the accounting entry. So, you can correlate a file with an apple as a whole (thing), either with a record of its arrival (action), or with a property (name, grade, etc.) according to which the reporting folder is formed - in fact, with the value in single cell.
Useful service, no more.
Iv.
I pass directly to accounting innovations, namely to editing things.
When reviewing version 1.0, they scolded me - not in the eyebrow, but in the eye. The claim was: “There are several things in the room. Suppose I moved all the things to the balcony, thereby changing the property of these things. It was [location] = "room", it became [location] = "balcony". And what, I have to change the property of each thing one by one? Is it really impossible right away? ”
Now you can. Select the necessary things and change the property to the desired.
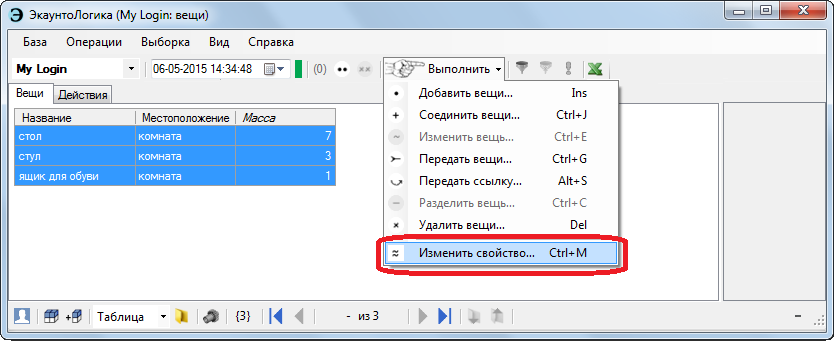
Another specific possibility is the automatic separation of things (in the first version it was implemented for one particular case, now everywhere).
The ideology of the program is as close to reality as possible; therefore, it is allowed to work with things in a natural sequence. If you have 100 rubles, and you transfer 10 of them to the counterparty, it is impossible to simply transfer them, because for the time being 10 rubles. make up part of 100 rubles. Following the accountancy postulates, you first have to divide the total amount by 90 rubles. and 10 rubles., then received a solid object can be transferred to the destination. Instead of a clear one transfer, two operations arise: seemingly unnecessary separation and transfer. This, despite an impeccable theoretical substantiation, is unnerving, therefore the function of automatic separation of things into parts is written.
In the action window, on the “Things by consumption” label, which was previously inaccessible, we indicate which quantitative part of the thing undergoes a change.
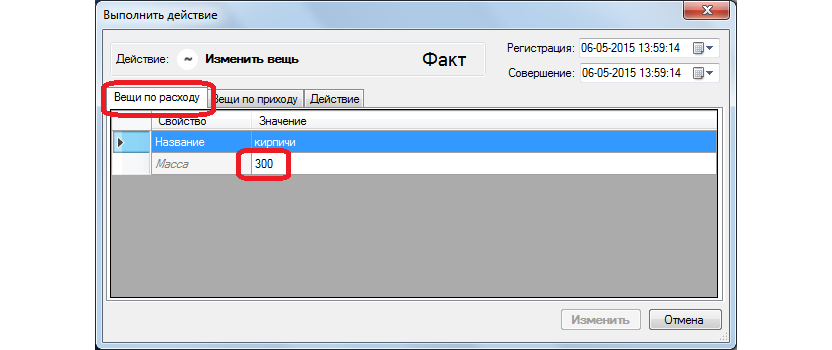
"Accounting Logic" itself will separate the specified part from the whole object and record this action as the precursor of the main one.
The result will be the recording of two actions, in fact, performed jointly. Nervous about the "unnecessary" operation is not necessary.
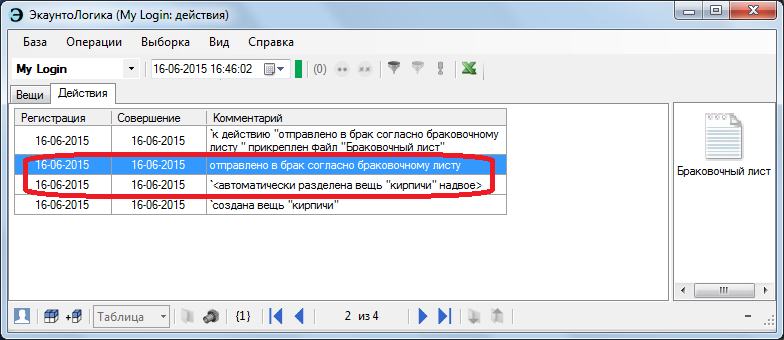
I will make a reservation that this function is applicable only to elementary, also to compound homogeneous things (formed on the basis of chemical association — a bunch of things that are indistinguishable from each other in composition). Composite heterogeneous things (formed on the basis of a mechanical union, which can thus consist of different parts from each other) - simply speaking, the mechanisms - will have to first be disassembled, then performed with the pulled-out part of the action.
Automatic separation of composite inhomogeneous things into parts requires a noticeable complication of the interface, the need for which is not seen at the moment.
V.
Further, the time accuracy of the program is increased.
Legislation requires accounting to the nearest days. However, there is no fundamental difference in which time units to keep records, so the user is given the opportunity to choose.
In Accounting Logic 2.0, accounting indicators (balances and turnover, and income and expenses derived from them) can be calculated to the nearest second.
As far as I understand, per-second accuracy is not difficult for execution, therefore a task worthy of attention. For me, it is remarkable because it allows you to visually demonstrate innovations in the accounting of obligations - future things, in accordance with the account management approach.
In the comments to the previous post, readers complained that they did not understand the novelty of accounological methods in relation to the accounting of obligations, although the obligations - and if you look more broadly, the attitude of things to the time scale - is exactly what I myself regard as unconditional achievements and discoveries. It was difficult to explain in words, it took a day to show in the program: only after a day it was possible to see how the thing from the future turns into a real one. Now, thanks to a second count, the effect appears instantly.
Let's make a simple experiment.
If folders are open, turn them off to watch only the current ones - those present at the moment - things.

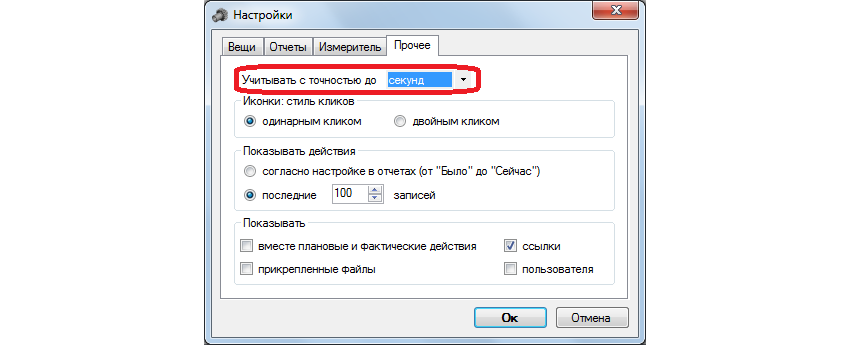
Go to the "Settings" and set the account up to seconds.
Open the add window, specify the name of the item and - most importantly - set the time for performing the operation 20 seconds longer than the current moment (the moment of registration). Do not forget to specify the probability of less than 100%.
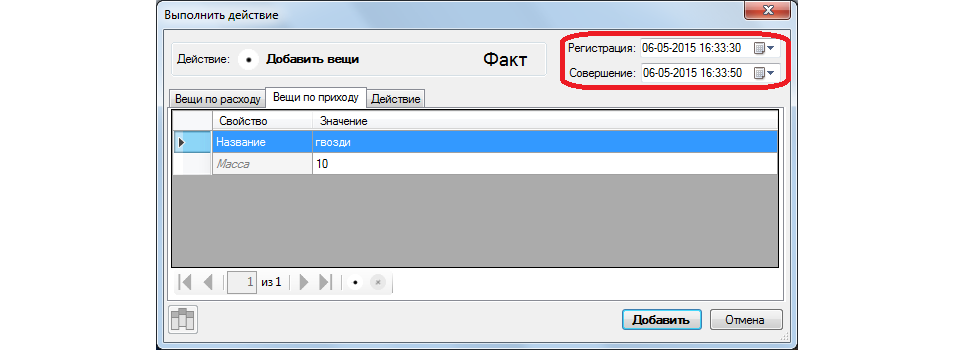
Add a thing. In the working window (for clarity, set the mode of icons), it is not yet visible: correct, because the thing will arrive in a few seconds.

After 20 seconds, update the timer. If everything is done without errors, the added item will appear in the working window.
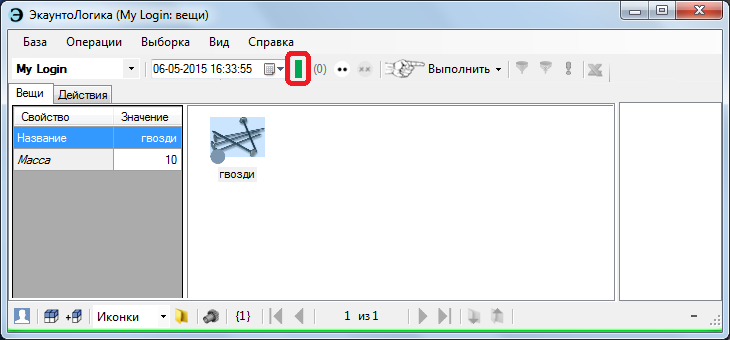
If you include folders, and do this before the item arrives, that is, until the appointed moment, the thing will appear in them as a future one — an obligation (provided that the registration time for the action is shorter than the time it was committed. Otherwise, the obligation will not happen: the thing will arrive at a given moment and that's it.
According to e-bookological views, a commitment is a future thing registered earlier. If you know for sure: in an hour, the thing that you will register upon receipt will go to the warehouse - this is a future thing, you can complete the recording in advance, in the future. But if you are registering the future receipt of a thing NOW - this is already an obligation).
Nevermind. Is it worth it to go into the subtleties of a theory that the general public is not in demand and is unlikely to ever be? Moreover, to demonstrate the per second accuracy can be more simple way.
The way is this. Set per second accuracy in the settings, then add the item. Now set the time before the operation on the timer (reduce the minute) - the thing will disappear, because it was added later. Return the original time - the item will appear.
Vi.
As an addition to the natural accounting of obligations, the option “Auto actions” was added (it seems that in the accounting software this is called automatic postings).
If a thing with known properties arrives, changes or drops out periodically, the corresponding actions can be performed automatically. When you start the program, the time of the last visit is checked: if necessary, the operations specified in the settings are performed.

Nothing is remarkable either from a practical or theoretical point of view.
When this article was ready for publication, he realized that he did not provide for automatic actions for planned records, and also a plurality of changes in properties for actions. It happens. If the next version appears, this omission will be corrected.
VII.
Accounting of exchange differences is attached.
Suppose a thing worth 100 rubles. Received March 1 (course of 50 rubles. For 1 dollar), and retired on March 30 (course of 75 rubles for 1 dollar). Then the cost of receipt of things is $ 2, and the cost of disposal of 1.33 dollars. The difference between them is called the exchange rate.
We will set the necessary parameters, for which we will have to connect the previously prepared Access database. Otherwise, exchange differences do not calculate. How to calculate them, if you can keep records at the same time in rubles, dollars, euros or any other meters - there is no base currency, are they all basic? But if you take the base with currency rates, then the meter set in the settings automatically becomes the main currency, the currency is considered additional, the time-based ratio of which is specified in the base.
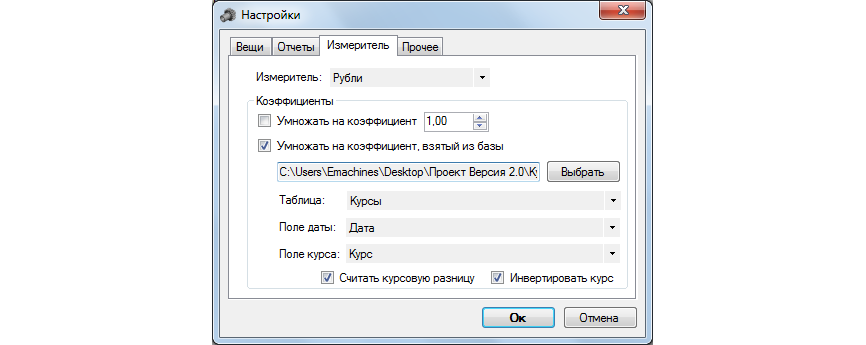
As a result, an additional column will appear in the report folders.

The method does not formally comply with the accounting rules, at least in that the exchange difference does not join anywhere (in the sense of any accounting object), it is simply calculated, it can be calculated in any currency for any period that is in accounting, due to archaic his methods are not representable.
I do not know how modern accounting software (with which, to my shame, I am not very familiar), but formally representable methods for calculating exchange differences are poorly projected onto classical accounting rules.
Suppose accounting is in rubles. In accordance with the accounting rules, there is no exchange difference. But in the real economy, there are dollars, they are turning - therefore, the difference can be calculated, because the cost of buying and selling, actually held in rubles, can always be converted into dollars. In this case, the cost of buying and selling will not match, there will be a difference - the exchange rate, and what else!
To calculate with a single currency accounting of a similar exchange rate difference from the accounting point of view, it is necessary to connect the reference book of courses and set the options “Read exchange difference” and “Invert rate”.
For example, a thing worth 100 rubles was received, the exchange rate for this moment was 50 rubles. for a dollar. After a while, the thing (worth the same 100 rubles, certainly) dropped out, the dollar exchange rate was already 55 rubles. So, the exchange rate difference between these dates (that is, at the date of disposal) was ... Consider yourself: a thing worth $ 2 arrived, the same thing cost about $ 1.82 dropped out. The exchange difference in this case will amount to 18 cents in the direction of reducing the dollar value for the period. "Accounting Logic" is able to fix this fact (unless, of course, I did not mess up with algorithms, which are very cumbersome because of the many settings).
Viii.
A very practical feature is the connection of reference books.
The user has the right to set things and actions for any number of text properties (fields), but in some sequence of fields the values can be repeated - for example, when specifying the properties of identical groups of things. Reference books are traditionally used to select related values.
After some hesitation, I chose the option to connect third-party databases. It is assumed that the user maintains reference books using Access tools, and they are imported into the “Accounting Logic” as a finished product, using the appropriate dialog box.
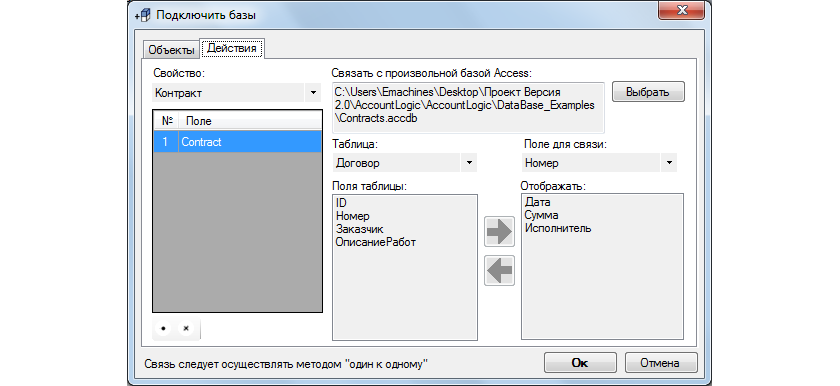
According to the fields from reference books it is allowed to build the reporting hierarchy, in general, to do everything, except for changing the reference books themselves.
On this list of new features is complete. Some functions, interesting and practically written, were thrown out for the reason that I realized with horror: to use them at this stage of historical development is impossible, too inconvenient. Therefore, we can say: “Accounting Logic” 2.0 has rested against the ceiling of methodological possibilities.
The main thing that remains unrealized is the network functionality, which cannot be built at the moment ... However, let's see: the grandmother said it in two.
By the way, about the network functionality. In the comments to one of the previous posts I was asked how the compatibility of properties will be realized when transferring things between users of different nationalities. Japanese names properties in Japanese, Russian - in Russian, it is clear that when transferring things from a Japanese user to a Russian or vice versa, properties will be perceived as different, thus lost. Then I did not know, having grunted in reply about the translation from one language to another, now I can answer. In the "Accounting Logic" properties are identified by the first name: in the future, properties can be renamed, but the identifier - the very first name - is preserved. Thus, in order to achieve linguistic compatibility, it is sufficient, when setting a property, to assign it an agreed name in the language adopted as international (in English), after which the properties can be called in any national language, identification will not suffer.
The program comes with a small conditional - I emphasize, conditional - an example. It can be used to trace the movement of things from the Career, in which ore is mined, through the processing plant, where metal is smelted from the ore, and the Metal Stamping Factory, to the final point of sale - the Store. It is shown how to take into account things in the context of contracts and calculate the financial result.
What is the complexity of the implementation of these - generally speaking, standard accounting - functions in “Accounting Logic”? The fact that the program is universal - the accounting designer - therefore, no mandatory fields responsible for contracts and financial results are provided for in it. The user must independently organize accounting by entering the fields he needs (in the language of accountology, properties of things or actions).
Let us assume that the action performed with the things may relate to a contract or not relate to any of them. The most common sales contracts, they are considered in the example.
For fixing the financial result (profit or loss), the seller overestimates the thing at the selling price, for example: the thing cost so much (cost price), began to cost so much (sale price). The difference between these values represents profit or loss. To separate the financial result from other turnovers, we create a new property (as we call it, of course, it doesn’t matter: Cost, Income Expenses or otherwise, in the example we intentionally use different names) and specify the value as ... we set and specify: financial results.
Now the thing is valued at the sale price, you can transfer it to the buyer or accept a prepayment from the buyer, the main thing is to remember to indicate in the corresponding property a value reflecting calculations with the counterparty. Specify: calculations.
With the correct setting, we get the status of payments, as well as the financial result in the context of any contract.
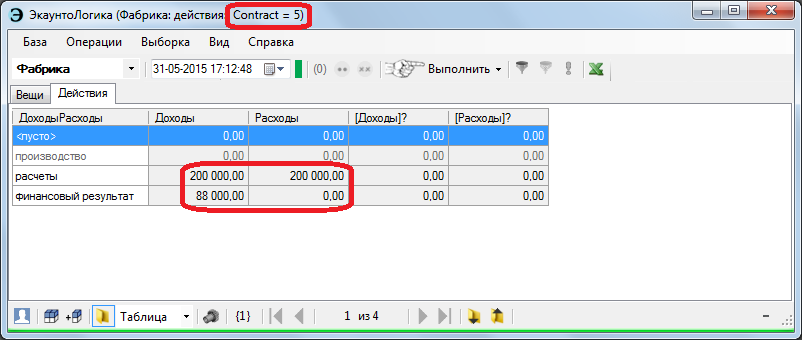
The condition under contract No. 5 is shown here: the profit amounted to 88 thousand rubles, the mutual settlements for the fixed moment by zero (turnover 200 thousand rubles). And even if they were not based on zeros, the above figures allow us, by means of simple comparison, to calculate profits using any method (this includes such well-known accounting troubles as the cash and accrual methods).
Accounting is realized with the help of universal functions: you can take into account incomes with expenses in the context of contracts, or vice versa, contracts in terms of income / expenses, enter additional properties - the sequence of properties (which in the context of which to reflect in reporting folders) does not matter. This is the pleasant side of universalism, the unpleasant side is the need to customize the program, which is possible only if you perfectly understand its capabilities and architecture.
However, the user should not only add new data to the accounting base, but also clean the base of things that were disposed of (like: we ate herring at dinner yesterday; I took the nightstand to the garbage can; oh, my wife, it turns out, bought a new blouse for myself; and etc.).
The ultimate goal of the maximum project is to integrate “Accounting Logic” into payment systems: so that manufacturers and sellers automatically send information about products purchased by users directly into their personal accounting bases. Then the advantages of the accounological methods will manifest themselves, become obvious to everyone.
Download Accounting Logic 2.0 here . System requirements have not changed: 32-bit Microsoft Office is required. For 64-bit Windows, you must install the Microsoft Access Database Engine 2010 (32-bit). Working with 64-bit Windows and Microsoft Office, as far as I understand, is impossible: what to do with this scourge, I won’t attach my mind.
The example is located in the DataBase_Examples folder. To connect it, you need to restore the backup (“From archive” command). In the specified folder there are also two Access test bases: contracts and exchange rates. The first of them can be connected in the form of a reference book, the second - as a base, necessary when calculating exchange differences.
My programming experience is a little over 1 year old, figure out what it means. (For the slow-witted, I explain: I searched for a lot of errors of the first buggy version, but this does not mean that I managed not to fit the new ones). At the same time, my experience as a methodologist is a quarter of a century: in other words, I am responsible not so much for the program code as for the accounting methodology implemented in it.
I convinced myself thoroughly of the advantages of the accounological method that it is not important whether it is possible to convince the majority. Who wants to hear.
In version 2.0, functions have been added that allow talking about some, albeit not final, approach to the ceiling of methodological possibilities.
To date, “Accounting Logic” (the new Russianized name “Accounting Logic”) allows - at least, it should allow according to the specification - quite a lot.
')
Accounting Logic Features
√ Create and edit accounting objects in accordance with their real nature.
√ Track not only their past, but also future changes (commitments) up to a second.
√ Evaluate accounting objects by an arbitrary number of meters.
√ Integrate ready-made directories into objects and actions.
√ Consistently transfer objects between user databases.
√ Automatically perform repetitive actions.
√ Track material connections between objects.
√ Bind files to individual objects, actions or folders.
√ Maintain planned, parallel to the main database.
√ Create hierarchical reports (reporting folders), including taking into account exchange differences and in comparison with planning data.
√ View data in tabular mode and in icon mode.
√ Track not only their past, but also future changes (commitments) up to a second.
√ Evaluate accounting objects by an arbitrary number of meters.
√ Integrate ready-made directories into objects and actions.
√ Consistently transfer objects between user databases.
√ Automatically perform repetitive actions.
√ Track material connections between objects.
√ Bind files to individual objects, actions or folders.
√ Maintain planned, parallel to the main database.
√ Create hierarchical reports (reporting folders), including taking into account exchange differences and in comparison with planning data.
√ View data in tabular mode and in icon mode.
Brazen advertisement that does not cancel the obvious fact that the code is amateur with the ensuing grave consequences. At the same time, the method incorporated in the program is professional: it was created on the basis of a theoretical basis, which took a decade to develop.
There is no point in listing the features available in version 1.0, so I’ll start by describing new features, in order of increasing importance.
I.
Service functions: archiving, passwording, localization (English - machine translation, adjusted to the extent of my meager interpretations).

Everything is standard, does not represent the slightest methodological interest.
Ii.
The data in the database are divided into two parts: actual (main) and planned (additional, taken into account in parallel with the main ones for comparison with them). Typical opportunity, not inclined to diversity.
The reporting folders provide for both separate and joint presentation of actual and planning data.


Theoretically, it was not difficult to realize a multitude of planned (parallel to each other) information flows, but why?
Iii.
File binding is a simplest function to execute, however, due to the unusual software architecture, it is not without interest. As is customary, drag and drop files into the workspace.

You can correlate a file with one of the following elements:
- thing (as pictured),
- action,
- a folder.
Since the terminology is different from the usual accounting, should be clarified. There is a thing with some properties, let's say: [name] = “apple”, [grade] = “Antonovka”. Accordingly, its receipt is reflected by the action - the account, an analogue of the accounting entry. So, you can correlate a file with an apple as a whole (thing), either with a record of its arrival (action), or with a property (name, grade, etc.) according to which the reporting folder is formed - in fact, with the value in single cell.
Useful service, no more.
Iv.
I pass directly to accounting innovations, namely to editing things.
When reviewing version 1.0, they scolded me - not in the eyebrow, but in the eye. The claim was: “There are several things in the room. Suppose I moved all the things to the balcony, thereby changing the property of these things. It was [location] = "room", it became [location] = "balcony". And what, I have to change the property of each thing one by one? Is it really impossible right away? ”
Now you can. Select the necessary things and change the property to the desired.

Another specific possibility is the automatic separation of things (in the first version it was implemented for one particular case, now everywhere).
The ideology of the program is as close to reality as possible; therefore, it is allowed to work with things in a natural sequence. If you have 100 rubles, and you transfer 10 of them to the counterparty, it is impossible to simply transfer them, because for the time being 10 rubles. make up part of 100 rubles. Following the accountancy postulates, you first have to divide the total amount by 90 rubles. and 10 rubles., then received a solid object can be transferred to the destination. Instead of a clear one transfer, two operations arise: seemingly unnecessary separation and transfer. This, despite an impeccable theoretical substantiation, is unnerving, therefore the function of automatic separation of things into parts is written.
In the action window, on the “Things by consumption” label, which was previously inaccessible, we indicate which quantitative part of the thing undergoes a change.

"Accounting Logic" itself will separate the specified part from the whole object and record this action as the precursor of the main one.
The result will be the recording of two actions, in fact, performed jointly. Nervous about the "unnecessary" operation is not necessary.

I will make a reservation that this function is applicable only to elementary, also to compound homogeneous things (formed on the basis of chemical association — a bunch of things that are indistinguishable from each other in composition). Composite heterogeneous things (formed on the basis of a mechanical union, which can thus consist of different parts from each other) - simply speaking, the mechanisms - will have to first be disassembled, then performed with the pulled-out part of the action.
Automatic separation of composite inhomogeneous things into parts requires a noticeable complication of the interface, the need for which is not seen at the moment.
V.
Further, the time accuracy of the program is increased.
Legislation requires accounting to the nearest days. However, there is no fundamental difference in which time units to keep records, so the user is given the opportunity to choose.
In Accounting Logic 2.0, accounting indicators (balances and turnover, and income and expenses derived from them) can be calculated to the nearest second.

As far as I understand, per-second accuracy is not difficult for execution, therefore a task worthy of attention. For me, it is remarkable because it allows you to visually demonstrate innovations in the accounting of obligations - future things, in accordance with the account management approach.
In the comments to the previous post, readers complained that they did not understand the novelty of accounological methods in relation to the accounting of obligations, although the obligations - and if you look more broadly, the attitude of things to the time scale - is exactly what I myself regard as unconditional achievements and discoveries. It was difficult to explain in words, it took a day to show in the program: only after a day it was possible to see how the thing from the future turns into a real one. Now, thanks to a second count, the effect appears instantly.
Let's make a simple experiment.
If folders are open, turn them off to watch only the current ones - those present at the moment - things.

Go to the "Settings" and set the account up to seconds.
Open the add window, specify the name of the item and - most importantly - set the time for performing the operation 20 seconds longer than the current moment (the moment of registration). Do not forget to specify the probability of less than 100%.

Add a thing. In the working window (for clarity, set the mode of icons), it is not yet visible: correct, because the thing will arrive in a few seconds.

After 20 seconds, update the timer. If everything is done without errors, the added item will appear in the working window.

If you include folders, and do this before the item arrives, that is, until the appointed moment, the thing will appear in them as a future one — an obligation (provided that the registration time for the action is shorter than the time it was committed. Otherwise, the obligation will not happen: the thing will arrive at a given moment and that's it.
According to e-bookological views, a commitment is a future thing registered earlier. If you know for sure: in an hour, the thing that you will register upon receipt will go to the warehouse - this is a future thing, you can complete the recording in advance, in the future. But if you are registering the future receipt of a thing NOW - this is already an obligation).
Nevermind. Is it worth it to go into the subtleties of a theory that the general public is not in demand and is unlikely to ever be? Moreover, to demonstrate the per second accuracy can be more simple way.
The way is this. Set per second accuracy in the settings, then add the item. Now set the time before the operation on the timer (reduce the minute) - the thing will disappear, because it was added later. Return the original time - the item will appear.
Vi.
As an addition to the natural accounting of obligations, the option “Auto actions” was added (it seems that in the accounting software this is called automatic postings).
If a thing with known properties arrives, changes or drops out periodically, the corresponding actions can be performed automatically. When you start the program, the time of the last visit is checked: if necessary, the operations specified in the settings are performed.

Nothing is remarkable either from a practical or theoretical point of view.
When this article was ready for publication, he realized that he did not provide for automatic actions for planned records, and also a plurality of changes in properties for actions. It happens. If the next version appears, this omission will be corrected.
VII.
Accounting of exchange differences is attached.
Suppose a thing worth 100 rubles. Received March 1 (course of 50 rubles. For 1 dollar), and retired on March 30 (course of 75 rubles for 1 dollar). Then the cost of receipt of things is $ 2, and the cost of disposal of 1.33 dollars. The difference between them is called the exchange rate.
We will set the necessary parameters, for which we will have to connect the previously prepared Access database. Otherwise, exchange differences do not calculate. How to calculate them, if you can keep records at the same time in rubles, dollars, euros or any other meters - there is no base currency, are they all basic? But if you take the base with currency rates, then the meter set in the settings automatically becomes the main currency, the currency is considered additional, the time-based ratio of which is specified in the base.

As a result, an additional column will appear in the report folders.

The method does not formally comply with the accounting rules, at least in that the exchange difference does not join anywhere (in the sense of any accounting object), it is simply calculated, it can be calculated in any currency for any period that is in accounting, due to archaic his methods are not representable.
I do not know how modern accounting software (with which, to my shame, I am not very familiar), but formally representable methods for calculating exchange differences are poorly projected onto classical accounting rules.
Suppose accounting is in rubles. In accordance with the accounting rules, there is no exchange difference. But in the real economy, there are dollars, they are turning - therefore, the difference can be calculated, because the cost of buying and selling, actually held in rubles, can always be converted into dollars. In this case, the cost of buying and selling will not match, there will be a difference - the exchange rate, and what else!
To calculate with a single currency accounting of a similar exchange rate difference from the accounting point of view, it is necessary to connect the reference book of courses and set the options “Read exchange difference” and “Invert rate”.
For example, a thing worth 100 rubles was received, the exchange rate for this moment was 50 rubles. for a dollar. After a while, the thing (worth the same 100 rubles, certainly) dropped out, the dollar exchange rate was already 55 rubles. So, the exchange rate difference between these dates (that is, at the date of disposal) was ... Consider yourself: a thing worth $ 2 arrived, the same thing cost about $ 1.82 dropped out. The exchange difference in this case will amount to 18 cents in the direction of reducing the dollar value for the period. "Accounting Logic" is able to fix this fact (unless, of course, I did not mess up with algorithms, which are very cumbersome because of the many settings).
Viii.
A very practical feature is the connection of reference books.
The user has the right to set things and actions for any number of text properties (fields), but in some sequence of fields the values can be repeated - for example, when specifying the properties of identical groups of things. Reference books are traditionally used to select related values.
After some hesitation, I chose the option to connect third-party databases. It is assumed that the user maintains reference books using Access tools, and they are imported into the “Accounting Logic” as a finished product, using the appropriate dialog box.

According to the fields from reference books it is allowed to build the reporting hierarchy, in general, to do everything, except for changing the reference books themselves.
On this list of new features is complete. Some functions, interesting and practically written, were thrown out for the reason that I realized with horror: to use them at this stage of historical development is impossible, too inconvenient. Therefore, we can say: “Accounting Logic” 2.0 has rested against the ceiling of methodological possibilities.
The main thing that remains unrealized is the network functionality, which cannot be built at the moment ... However, let's see: the grandmother said it in two.
By the way, about the network functionality. In the comments to one of the previous posts I was asked how the compatibility of properties will be realized when transferring things between users of different nationalities. Japanese names properties in Japanese, Russian - in Russian, it is clear that when transferring things from a Japanese user to a Russian or vice versa, properties will be perceived as different, thus lost. Then I did not know, having grunted in reply about the translation from one language to another, now I can answer. In the "Accounting Logic" properties are identified by the first name: in the future, properties can be renamed, but the identifier - the very first name - is preserved. Thus, in order to achieve linguistic compatibility, it is sufficient, when setting a property, to assign it an agreed name in the language adopted as international (in English), after which the properties can be called in any national language, identification will not suffer.
The program comes with a small conditional - I emphasize, conditional - an example. It can be used to trace the movement of things from the Career, in which ore is mined, through the processing plant, where metal is smelted from the ore, and the Metal Stamping Factory, to the final point of sale - the Store. It is shown how to take into account things in the context of contracts and calculate the financial result.
What is the complexity of the implementation of these - generally speaking, standard accounting - functions in “Accounting Logic”? The fact that the program is universal - the accounting designer - therefore, no mandatory fields responsible for contracts and financial results are provided for in it. The user must independently organize accounting by entering the fields he needs (in the language of accountology, properties of things or actions).
Let us assume that the action performed with the things may relate to a contract or not relate to any of them. The most common sales contracts, they are considered in the example.
For fixing the financial result (profit or loss), the seller overestimates the thing at the selling price, for example: the thing cost so much (cost price), began to cost so much (sale price). The difference between these values represents profit or loss. To separate the financial result from other turnovers, we create a new property (as we call it, of course, it doesn’t matter: Cost, Income Expenses or otherwise, in the example we intentionally use different names) and specify the value as ... we set and specify: financial results.
Now the thing is valued at the sale price, you can transfer it to the buyer or accept a prepayment from the buyer, the main thing is to remember to indicate in the corresponding property a value reflecting calculations with the counterparty. Specify: calculations.
With the correct setting, we get the status of payments, as well as the financial result in the context of any contract.

The condition under contract No. 5 is shown here: the profit amounted to 88 thousand rubles, the mutual settlements for the fixed moment by zero (turnover 200 thousand rubles). And even if they were not based on zeros, the above figures allow us, by means of simple comparison, to calculate profits using any method (this includes such well-known accounting troubles as the cash and accrual methods).
Accounting is realized with the help of universal functions: you can take into account incomes with expenses in the context of contracts, or vice versa, contracts in terms of income / expenses, enter additional properties - the sequence of properties (which in the context of which to reflect in reporting folders) does not matter. This is the pleasant side of universalism, the unpleasant side is the need to customize the program, which is possible only if you perfectly understand its capabilities and architecture.
However, the user should not only add new data to the accounting base, but also clean the base of things that were disposed of (like: we ate herring at dinner yesterday; I took the nightstand to the garbage can; oh, my wife, it turns out, bought a new blouse for myself; and etc.).
The ultimate goal of the maximum project is to integrate “Accounting Logic” into payment systems: so that manufacturers and sellers automatically send information about products purchased by users directly into their personal accounting bases. Then the advantages of the accounological methods will manifest themselves, become obvious to everyone.
Download Accounting Logic 2.0 here . System requirements have not changed: 32-bit Microsoft Office is required. For 64-bit Windows, you must install the Microsoft Access Database Engine 2010 (32-bit). Working with 64-bit Windows and Microsoft Office, as far as I understand, is impossible: what to do with this scourge, I won’t attach my mind.
The example is located in the DataBase_Examples folder. To connect it, you need to restore the backup (“From archive” command). In the specified folder there are also two Access test bases: contracts and exchange rates. The first of them can be connected in the form of a reference book, the second - as a base, necessary when calculating exchange differences.
My programming experience is a little over 1 year old, figure out what it means. (For the slow-witted, I explain: I searched for a lot of errors of the first buggy version, but this does not mean that I managed not to fit the new ones). At the same time, my experience as a methodologist is a quarter of a century: in other words, I am responsible not so much for the program code as for the accounting methodology implemented in it.
I convinced myself thoroughly of the advantages of the accounological method that it is not important whether it is possible to convince the majority. Who wants to hear.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/261873/
All Articles