HP Helion OpenStack Network Infrastructure
We continue our series of articles on HP Helion OpenStack with a story about how cloud networking is built in HP's OpenStack implementation. The HP Helion OpenStack cloud networking mechanisms should provide two functions — communication between the cloud and the outside world and the ability to create internal networks for different cloud inhabitants. With the help of technologies of software-defined networks, it is required to implement for users (tenant) clouds, which have the necessary rights, to create, modify and delete networks on the fly.

Before proceeding to the description of the network infrastructure of HP Helion OpenStack, you need to say a few words about the Neutron service, which in OpenStack is responsible for implementing network functions.
In OpenStack, the following abstractions are used to describe network resources:
')
- Network. Isolated L2 segment, similar to VLAN in physical networks;
- Subnet. Block of IP addresses and their corresponding configurations;
- Port. Point of connection of one device (for example, NIC or virtual server) to a virtual network, as well as the MAC and IP address of this port.
Of these three components, a virtual multilevel network is built, serving the various inhabitants of the cloud (multitenant).
The distributed virtual router Distributed Virtual Router (DVR), which appeared on Neutron in last year’s Juno OpenStack release, improves cloud scalability by shifting some of the network traffic processing functions to compute nodes. HP Helion OpenStack DVR support has been implemented since the very first release 1.0.
In previous (before Juno) releases of OpenStack, traffic from instances to external networks passed through several Neutron cloud nodes (including instances with a floating IP address) and as the number of instances increased, the cloud computing nodes also there was no direct connection to external networks.

Routing to the external network without DVR
When using DVR, traffic from instances with a floating IP address to the external network is processed by the compute nodes, so data is transmitted directly from the compute node to the external network through the NIC of the server that performs the function of the compute node, and not through the network nodes.
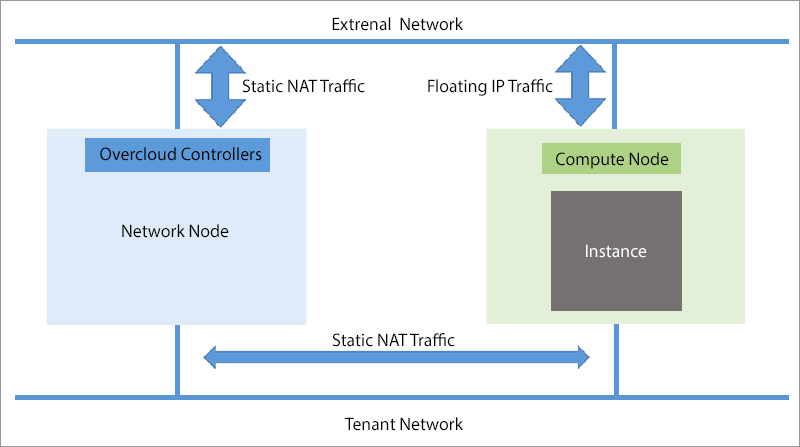
Routing to the external network when using DVR
By default, the HP Helion OpenStack with the KVM hypervisor has DVR support enabled, although it can be disabled if necessary, but for the VMware ESXi hypervisor, DVR support is not yet implemented.
HP in addition to the standard Neurton functionality in its implementation OpenStack added L2 gateway functions. In HP Helion OpenStack, the L2 gateway connects the cloud between virtual VXLANs and existing VLANs using an HP FlexFabric 5930 physical switch.
Other enhancements to the HP Helion OpenStack networking features, which are implemented in addition to the standard OpenStack Neutron, support for the VMware ESX hypervisor (in addition to KVM) and the ability to scale Neutron to 1000 nodes instead of 50 in the standard distribution.
For the HP Helion OpenStack cloud to work, the necessary network infrastructure connecting all components of its infrastructure, including “seed” virtual machines, lower and upper cloud controllers, which we described in a previous post, Cinder block data stores based on VSA or 3PAR disk array, computing Swift object data warehouse nodes and nodes.
The HP Helion OpenStack cloud with the KVM hypervisor uses three mandatory networks and four optional networks (see Illustration 3). Let's start with the mandatory networks:
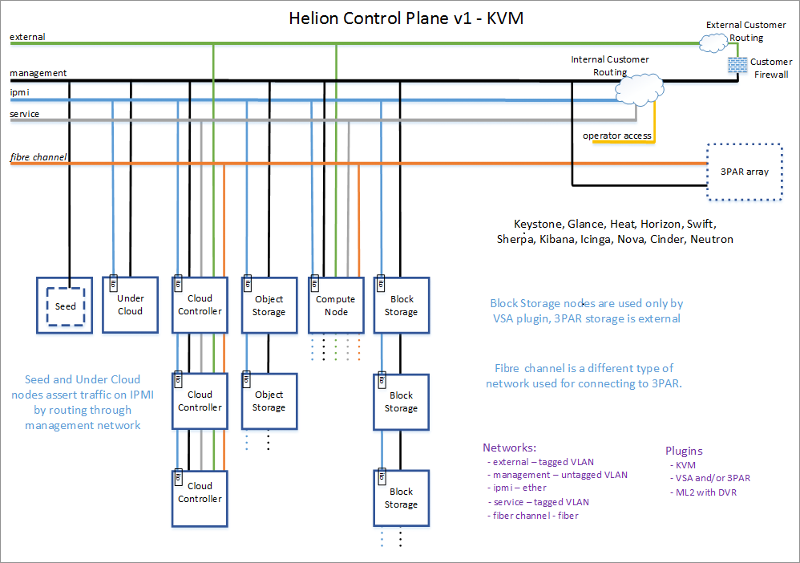
HP Helion OpenStack Cloud Network Infrastructure Using KVM Hypervisor and 3Par Disk Array
Optional networks:
To implement the listed virtual networks, the HP Helion OpenStack physical network infrastructure must use a network fabric consisting of two separate physical links for IPMI and an operating system / hypervisor, and network switches that support basic VLAN, L2, and L3 functions. In addition, each server should have two network ports (one IPMI port, the second Ethernet for the operating system / hypervisor).
Based on the Neutron service, the HP Helion OpenStack cloud network infrastructure provides data exchange within the cloud and with external networks, management of virtual machines and physical servers. The use of a distributed virtual router DVR improves its scalability, and the L2 gateway implements the connection of virtual VXLAN cloud networks to existing VLANs.
Thank you for your attention, we are ready to answer your questions in the comments.

Neutron Network Service
Before proceeding to the description of the network infrastructure of HP Helion OpenStack, you need to say a few words about the Neutron service, which in OpenStack is responsible for implementing network functions.
In OpenStack, the following abstractions are used to describe network resources:
')
- Network. Isolated L2 segment, similar to VLAN in physical networks;
- Subnet. Block of IP addresses and their corresponding configurations;
- Port. Point of connection of one device (for example, NIC or virtual server) to a virtual network, as well as the MAC and IP address of this port.
Of these three components, a virtual multilevel network is built, serving the various inhabitants of the cloud (multitenant).
Distributed Virtual DVR Router
The distributed virtual router Distributed Virtual Router (DVR), which appeared on Neutron in last year’s Juno OpenStack release, improves cloud scalability by shifting some of the network traffic processing functions to compute nodes. HP Helion OpenStack DVR support has been implemented since the very first release 1.0.
In previous (before Juno) releases of OpenStack, traffic from instances to external networks passed through several Neutron cloud nodes (including instances with a floating IP address) and as the number of instances increased, the cloud computing nodes also there was no direct connection to external networks.

Routing to the external network without DVR
When using DVR, traffic from instances with a floating IP address to the external network is processed by the compute nodes, so data is transmitted directly from the compute node to the external network through the NIC of the server that performs the function of the compute node, and not through the network nodes.

Routing to the external network when using DVR
By default, the HP Helion OpenStack with the KVM hypervisor has DVR support enabled, although it can be disabled if necessary, but for the VMware ESXi hypervisor, DVR support is not yet implemented.
HP in addition to the standard Neurton functionality in its implementation OpenStack added L2 gateway functions. In HP Helion OpenStack, the L2 gateway connects the cloud between virtual VXLANs and existing VLANs using an HP FlexFabric 5930 physical switch.
Other enhancements to the HP Helion OpenStack networking features, which are implemented in addition to the standard OpenStack Neutron, support for the VMware ESX hypervisor (in addition to KVM) and the ability to scale Neutron to 1000 nodes instead of 50 in the standard distribution.
HP Helion OpenStack Virtual and Physical Networks
For the HP Helion OpenStack cloud to work, the necessary network infrastructure connecting all components of its infrastructure, including “seed” virtual machines, lower and upper cloud controllers, which we described in a previous post, Cinder block data stores based on VSA or 3PAR disk array, computing Swift object data warehouse nodes and nodes.
The HP Helion OpenStack cloud with the KVM hypervisor uses three mandatory networks and four optional networks (see Illustration 3). Let's start with the mandatory networks:
- An external network (external) connects cloud instances to external public networks, for example, a private cloud with a corporate intranet or public to the Internet. This network is allocated a specific range of IP addresses (Floating IPs), which can be assigned to instances to organize their communications with the corresponding intranet or the Internet;
- Management network (management) for transfer of the main commands of cloud management of HP Helion OpenStack. Upper and lower cloud controllers, seed VM, compute nodes, Swift object storage nodes and, as an option, Cinder block storage nodes based on 3PAR array or VSA cluster are connected to this network. In addition to control commands, this network also includes traffic from Swift and Cinder data warehouses. During the installation of HP Helion OpenStack, the servers are loaded using the PXE protocol via the control network. Since this is the most important network in the cloud, it is recommended to use 10 Gigabit Ethernet or faster Ethernet for it.
- The IPMI network is designed to remotely manage cloud servers using the IPMI protocol. In addition, it uses the Ironic bare metal deployment service to monitor the status of servers.

HP Helion OpenStack Cloud Network Infrastructure Using KVM Hypervisor and 3Par Disk Array
Optional networks:
- service network. This network is only needed to deploy the HP Helion Development Platform (HDP) package and provides connectivity between the PaaS management components and the lower cloud. It is recommended to implement it even if in the future it is planned to use HDP, since the service network cannot be built for an existing cloud;
- Operator Access Network. This network will be needed if for some reason (for example, due to security constraints) system administrators and operators do not have access directly to the management network.
- Fiber Channel network, which is needed when using 3Par disk array in the cloud. This is a SAN storage network that provides data transfer between cloud servers and 3Par. Fiber Channel switches are required to build this network.
- An ESX network is needed if the VMware ESX hypervisor is running in the cloud. This network transmits traffic from virtual machines running on ESX hosts and the vCenter proxy.
- ESX tenant networks for VLANs serving networks of cloud dwellers (using the ESX hypervisor).
To implement the listed virtual networks, the HP Helion OpenStack physical network infrastructure must use a network fabric consisting of two separate physical links for IPMI and an operating system / hypervisor, and network switches that support basic VLAN, L2, and L3 functions. In addition, each server should have two network ports (one IPMI port, the second Ethernet for the operating system / hypervisor).
findings
Based on the Neutron service, the HP Helion OpenStack cloud network infrastructure provides data exchange within the cloud and with external networks, management of virtual machines and physical servers. The use of a distributed virtual router DVR improves its scalability, and the L2 gateway implements the connection of virtual VXLAN cloud networks to existing VLANs.
Thank you for your attention, we are ready to answer your questions in the comments.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/261729/
All Articles