How DIY robots will change education by 2035
In the past , we post reviewed the history of designers. Now let's take a look at the future. On Monday, a round table on robotics in the Russian education system was held at Robotstation . It was about all the ideas and plans for the Russian education system up to 2035, representatives of technical universities gathered and told about their plans for the future, do not consider it offtopic, we will talk about DIY sets and it is DIY robotics.
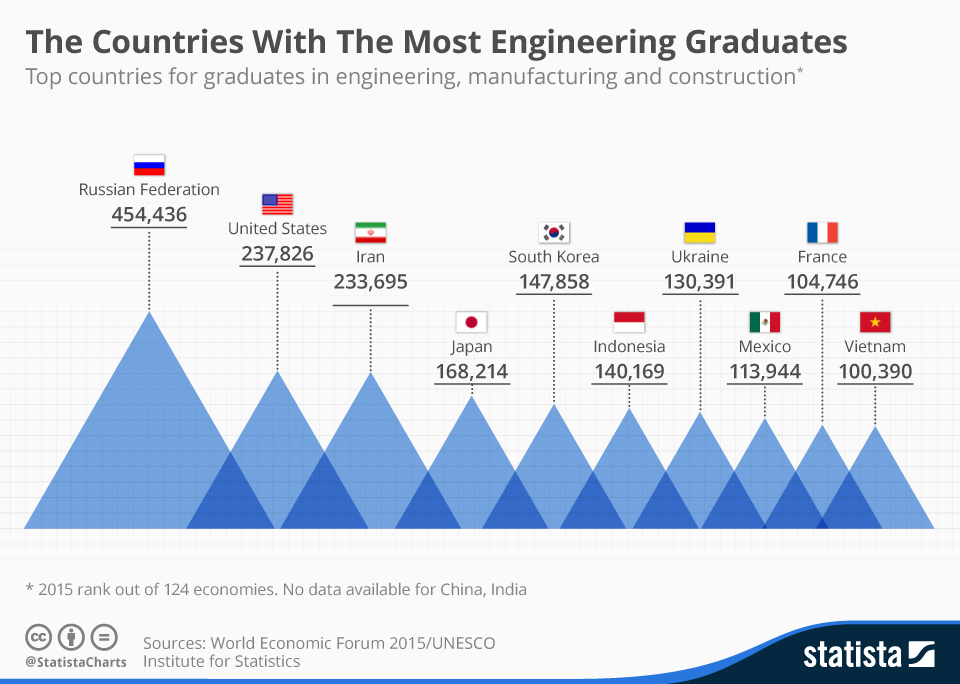
Russia produces engineers more than anyone. At the same time, there are 18 million schoolchildren in Russia, 12 million of them go to circles and sections, and only 9,000 people are engaged in modeling (air, car, hydro, and robo). Only nine thousand! This is clearly not enough; moreover, such electives are not integrated into the educational process, but often contradict it. The result is something like this:
')

What is the Ministry of Education going to do? Something like this:
Surprisingly, the plans include a prominent place for DIY robotics. By 2020, ASI plans to build four large children's technology parks dedicated to robotics (as before, the palaces of the pioneers) and generally make this area a major one. This is a pilot who is expected to work from the fall somewhere, from September, as soon as the voting in the State Duma takes place. 4 regions: Khanty-Mansiysk region, Kaliningrad, Moscow region and Ulyanovsk. Depending on the results of this large-scale experiment, determine the format of our entire education system after 2015.
Olga Kayrova gave a small educational program:
All this is just perpendicular and often hostile to the classical school system. Why this happens is easy to answer, but it will have to make a history review. The system of secondary education is one of the oldest social systems. It was created by the Jesuits and has not undergone any changes since the publication of the School Charter of the Society of Christ, and this, for a moment, is 1599!
The Jesuits created everything to the last detail - they invented classes, 45-minute lessons, textbooks, notebooks, grades, essays, presentations, tests, seminars and lectures and brought out the “schooling” technology itself: endless repetition of abstract logical techniques and strict adherence to the rules. The teacher, like the students, was deprived of any kind of independence in work, his every step was regulated by the school statute. The goal of such a school is not so much to educate a person as to accustom him to monotonous mental work and to make a unified element of the system by suppressing the creative beginning.

Nothing like?
This system has hardly undergone any changes, except that in 1905 the Venetian teacher Roberto Nevelis invented giving additional tasks to the house instead of whipping the careless students. Why was the Jesuit system so good that it has been working for five (!) Hundreds of years without any special changes? And works well, efficiently.
The meaning of the school is not in school, but in school. Knowledge and techniques of thinking are not so important. It is important to kill the hormonal explosion during puberty and to teach the brain to work in an enhanced mode. To prevent the torturer teachers from becoming confused, it is advisable to tie the school to a single discipline. In the gymnasiums of the 19th century, they were obsessed with dead languages, in the schools of the mid-20th century - at mathematics. The more abstract and meaningless the better - it's like a drill in the army. For example, in Swiss panzergrinadera a rookie runs around the stadium with a log on his shoulder, right up to the moment he stops asking himself why he does it. This is the idea of the school brought to the limit.
But this is the floor of the picture, because the schools were not by themselves. They prepared unified cadres for Jesuit universities (which is considered all European universities are). As a result, everything was standardized and everyone understood each other very well, of these students and teachers it is already possible to build "production chains" in the university. A Jesuit university is ... a medieval computer. A library is a hard disk, a processor sits in the directorate, and an audience is an output system. The essence of this "computer" is simple copying of information, in the form of rewriting by hand into a notebook, and the rewriting of lectures of which is often not even in printed form. For each manuscript, the university falls into the pocket of money, literally from the air - it is not surprising that the system has been working for so many years.
It is not difficult to see that all this machinery is designed for a society with a fatal lack of information, that is, a hypo-information society. And it is absolutely not designed for a modern hyperinformation society.
Historically, the university and school were institutions where a certain amount of knowledge was transferred to a person. People worked under the supervision of specialists who facilitated the process of assimilation and processing of information. However, in modern society, these functions have ceased to be significant. Who needs university libraries or archives, if 99% of the information can be obtained via the Internet, and a hundred times more efficiently. Students also do not need housing and benefits. Why live inside a huge retro computer when a real computer fits into a pocket for a long time?

So represented the formation of the future in 1900.
Therefore, the seminar was devoted to the question of how to integrate robotic education into this system without profaning it.
Andrei Ponomarev , expert of the Center for Development of Youth Entrepreneurship of the University of Mechanical Engineering:
Yes, now a diploma of higher education requires even sellers in the store, but this does not mean the value of the diploma, but rather the opposite. In today's hyperinformation society, the problem of gaining knowledge is not a problem - everything is available in two clicks. But students do not know what kind of knowledge they need.
Andrei Ponomarev , expert of the Center for Development of Youth Entrepreneurship of the University of Mechanical Engineering:
The 21st century puts the situation on its head - the Internet gives access to all the knowledge of mankind, so children often know more than their school teacher and cannot wait to put their knowledge into practice. This is the purpose that robotic education serves - these are electives that are built in contrast to the classical lessons with grades. What is its purpose? It turns out to put the question in the student's head in such a way that he himself asked the question “Why” - in this way the initiative passes from the teacher to the student.

1933
Nargiz Isaeva , expert:
This approach is intended to change the basic element of learning. Instead of copying and imitation classes are built on creative tasks. Let the student use the Internet, looking for material, it is processed. We have no grades, diplomas and homework, instead of competing with other students for grades everything is presented in a game form.
Diana Strelets , Bation robotics center:
In addition, there is another important difference - if a classic diploma is issued to a student, then a diploma must be obtained. That is, you can not just sit out a course of lectures, you need to collect or do something. It seems a trifle, but it turns the whole educational process.
Konstantin Yermishin , graduate student and teacher of robotics at Moscow State Technical University. Bauman, Department of Robotics RK-10:

1958
It is this object-orientation that conflicts with the ideas of online education. But if you look closely, the contradiction may be helpful.
Mustafin Sergey , robotics teacher:
, . , . , «- » , , — . — , , . — .

1970, .
DIY . , , . DIY , . , : 1 + 2 + 1 . , , , , .
, . . , — 1957 DARPA, NASA NDEA. , - , . National Defense Education Act 1958 — -- , . , .
, — , , — .
It sounds great, but will it work? In a sense, the Rostantstation is a demonstration model of this system and shows the effectiveness of the idea.

2015, education how it turned out really.
Igor Nikitin , the founder of the Robostation:
. , , — .


Russia produces engineers more than anyone. At the same time, there are 18 million schoolchildren in Russia, 12 million of them go to circles and sections, and only 9,000 people are engaged in modeling (air, car, hydro, and robo). Only nine thousand! This is clearly not enough; moreover, such electives are not integrated into the educational process, but often contradict it. The result is something like this:
')

What is the Ministry of Education going to do? Something like this:

Surprisingly, the plans include a prominent place for DIY robotics. By 2020, ASI plans to build four large children's technology parks dedicated to robotics (as before, the palaces of the pioneers) and generally make this area a major one. This is a pilot who is expected to work from the fall somewhere, from September, as soon as the voting in the State Duma takes place. 4 regions: Khanty-Mansiysk region, Kaliningrad, Moscow region and Ulyanovsk. Depending on the results of this large-scale experiment, determine the format of our entire education system after 2015.
Olga Kayrova gave a small educational program:
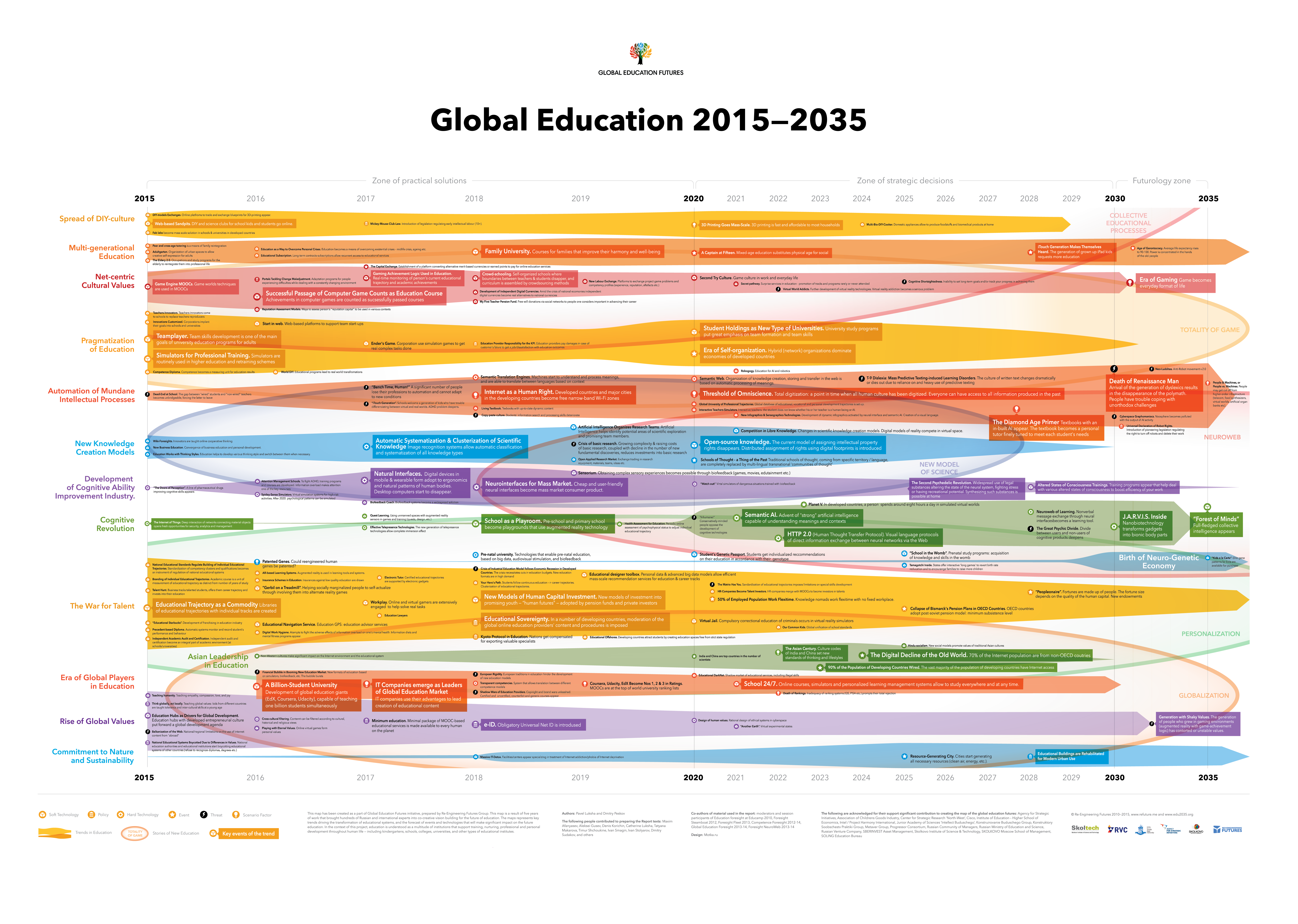
The first trend and the most important trend is the spread of “do you it your self” culture. Now 3D printing technology has emerged and, accordingly, everything that was previously produced centrally will now gradually go away, now everything can be done in the garage.
The second is intergenerational, that is, different generations can study together and a format such as family universities will emerge. And, accordingly, education at work, it already exists, but it will be further aggravated. Then, due to the fact that the Internet is spreading here, then the IT culture, it leaves its mark on the values that are now emerging in our society. And from IT comes a lot of new technology formats. For example, online courses, they are already. On the edu2035 website, you can look directly at the technologies inside each trend.
The third is the pragmatization of education. That is, teachers who broadcast and share knowledge will leave, and education will be sharpened for the specific goals of the individual. And in this regard, there will be simulators there that allow you to achieve specific goals. If you want a group work, say, a skill education, it will be spread out and you can make up your own educational profile, an individual one. There will be automation of basic intellectual processes, now you can google everything on the Internet. This is the automation of the search component, let's say, in humans. It will be aggravated with the development of artificial intelligence and to the extent that the external environment begins to prompt the person how to act in different situations.
Fourth, new knowledge creation models. Now wiki format and crowdsourcing are spreading, now anyone can create knowledge. And big-date technologies will allow them to be collected, analyzed and researched. In general, new research will accumulate from open sources. There is an industry of development of human cognitive abilities. That is, if it used to be nootropics, which were used to improve memory, now this is achieved by hardware. And there will be techniques for working with the brain. And such simulators for the development of cognitive abilities. And in principle, in the absolute, it will go into the era of the neuronette, when the Internet ends and people begin to communicate from brain to brain. Accordingly, a cognitive revolution arises on this trend.
The next trend is the fight for talents. This is about individual educational trajectories, about the fact that a person will build his life on the basis of his abilities. Here, here's who watched the Gattaka film, all the genetic experiments and building up, let's say, pre-established makings in children, will get there. And it turns out that genetics will initially form the prerequisites, and neurotechnology will train the child in the right direction, depending on its purpose. Or the goals of his parents. Over time, if now we rather have such a variety of educational formats only arising, and then, around 2017, some order will come out and those who offer the most successful solutions will come out and global players will appear in online education.
From here, we form approximately such an educational landscape in 3 horizons. In the short horizon, 3-5 years, there will be many educational formats online, there will be a change, that is, assessments will leave and a system of recognition of achievements and competence passports will appear, models of investing in talents will appear. In the longer horizon, we will have global online universities that will be taught by billions to people. Mentoring networks will appear, solutions for learning without classical universities will appear, gamification will penetrate everywhere. And things like neural interfaces and biometrics will allow you to collect objective feedback about your learning process. And in a very long horizon, everything will be built on the game, and artificial intelligence will prompt the person a decision on his life trajectory. In the end, new types of pedagogy will emerge that are still difficult to predict.
And in the short horizon, teachers will leave who carry simply knowledge, standard tests will go away and will be replaced by intellectual-educational trajectories. Accordingly, the assessment will leave for the semester. In the long will go diplomas, performance journals, author's textbooks. In very long, in principle, classical types of schools and universities will go away (by 2035).
All this is just perpendicular and often hostile to the classical school system. Why this happens is easy to answer, but it will have to make a history review. The system of secondary education is one of the oldest social systems. It was created by the Jesuits and has not undergone any changes since the publication of the School Charter of the Society of Christ, and this, for a moment, is 1599!
The Jesuits created everything to the last detail - they invented classes, 45-minute lessons, textbooks, notebooks, grades, essays, presentations, tests, seminars and lectures and brought out the “schooling” technology itself: endless repetition of abstract logical techniques and strict adherence to the rules. The teacher, like the students, was deprived of any kind of independence in work, his every step was regulated by the school statute. The goal of such a school is not so much to educate a person as to accustom him to monotonous mental work and to make a unified element of the system by suppressing the creative beginning.

Nothing like?
This system has hardly undergone any changes, except that in 1905 the Venetian teacher Roberto Nevelis invented giving additional tasks to the house instead of whipping the careless students. Why was the Jesuit system so good that it has been working for five (!) Hundreds of years without any special changes? And works well, efficiently.
The meaning of the school is not in school, but in school. Knowledge and techniques of thinking are not so important. It is important to kill the hormonal explosion during puberty and to teach the brain to work in an enhanced mode. To prevent the torturer teachers from becoming confused, it is advisable to tie the school to a single discipline. In the gymnasiums of the 19th century, they were obsessed with dead languages, in the schools of the mid-20th century - at mathematics. The more abstract and meaningless the better - it's like a drill in the army. For example, in Swiss panzergrinadera a rookie runs around the stadium with a log on his shoulder, right up to the moment he stops asking himself why he does it. This is the idea of the school brought to the limit.
But this is the floor of the picture, because the schools were not by themselves. They prepared unified cadres for Jesuit universities (which is considered all European universities are). As a result, everything was standardized and everyone understood each other very well, of these students and teachers it is already possible to build "production chains" in the university. A Jesuit university is ... a medieval computer. A library is a hard disk, a processor sits in the directorate, and an audience is an output system. The essence of this "computer" is simple copying of information, in the form of rewriting by hand into a notebook, and the rewriting of lectures of which is often not even in printed form. For each manuscript, the university falls into the pocket of money, literally from the air - it is not surprising that the system has been working for so many years.
It is not difficult to see that all this machinery is designed for a society with a fatal lack of information, that is, a hypo-information society. And it is absolutely not designed for a modern hyperinformation society.
Historically, the university and school were institutions where a certain amount of knowledge was transferred to a person. People worked under the supervision of specialists who facilitated the process of assimilation and processing of information. However, in modern society, these functions have ceased to be significant. Who needs university libraries or archives, if 99% of the information can be obtained via the Internet, and a hundred times more efficiently. Students also do not need housing and benefits. Why live inside a huge retro computer when a real computer fits into a pocket for a long time?

So represented the formation of the future in 1900.
Therefore, the seminar was devoted to the question of how to integrate robotic education into this system without profaning it.
Andrei Ponomarev , expert of the Center for Development of Youth Entrepreneurship of the University of Mechanical Engineering:
Having plunged into the practice-oriented education in the fall, we found such an interesting thing. It was meant that the students, united in groups of 3-5 people, would begin working with projects with glands. And it turned out that they have nowhere in the technical university to settle in to work with the glands. All laboratories somewhere under the departments, somehow covered, somehow closed. And the last 1.5-2 years, students began to annoy closed audiences, laboratories. That is, when they can not come, sit down and make some noise in the reading room. They even had a project "Anti-Library", which was successfully replaced by coworking for them. But, nevertheless, they still cannot knock, make noise, hum, drill. This turned out to be not a ready technical education.
This year we are fully immersed, and we now have the opportunity to free up a whole platform for this practice-oriented education, they will still work with glands. It was there (in the diagram above) that it was beautifully written that he would leave, but I would say so rudely the teacher. The teacher will not leave, and will not leave soon. And we will see how ours, it’s written there for 20 years, just today's students will have their children, they will bring them to you and say: “Work out, I don’t want him to work through the Internet”. Because a child at the age of 5-10 cannot choose a course on the Internet himself. This will have to do parents. Parents have limited time, either you earn money, or you orient your child somewhere on the Internet.
But when I was offered to buy a robot designer for a child, approximately from 25 thousand rubles, then in collaboration with neighboring dads, we decided that the garage and the old penny for 20 thousand rubles would fill all their technical knowledge, assemble and disassemble. And it will be cheaper than robotic under the supervision of an adult, under the supervision of control. That thing that they are even more interesting than a robot. Because they do not represent how the crank mechanism works.
This work with glands, in the mud tempts them more than to go somewhere for 1.5-2 hours to work in a circle. Or another example. When you come, they give you, well, we have our own children, if dad comes with one child they slip him, another 3-5, and they take apart the VCR. Assorted it under the comments of the instructor who runs, serves several tables. Children do not know what a VCR is, they don’t know how a computer works, a laptop is a mystery to them, and up to 15 years is just fantastic.
What am I getting at? Here's a colleague correctly said that we are now striving to unite several universities, students of different universities into teams. We hardly do it inside the university, almost pounding these teams with kicks. Designers understand that this team needs a designer, where the girls make a self-propelled suitcase, the robot technician understands that they need robotics, but at the same time we combine them there almost with kicks. The result, whoever we forcibly drove and forced this business to form, the result, oddly enough, is most striking in their assessments and they remain to work with the teams with some changes. The rating will not go anywhere, the rating will still remain. It will be 5 points or 100 points, as we now have to somehow differentiate it according to a 100-point system. They do not care for each point, they come and say: "I have 75 points, but he, he worked with me in the team, he has 77 points." These 2 points against 100, these 2% mean nothing. In this way, by chance, somewhere an extra check was put to him, somewhere he went to an extra event, but they fight for it.
But the worst is not even that. It was there when it was written that diplomas would be gone. Do an experiment, go to any employer and tell me that you are without a diploma. And he just won't understand you. That just will not understand. You come to the clinic - they demand a card from you. We come to the employer to arrange for the practice of students, he says: “Fine, everything, fine. Let's put him into practice, and in a year he will come to me, and I will send him ... this is an engineer, to courses, in order to complete my studies in controlling CNC machines. We bought a lot of machines. ” We say to him: “This is the technical school. They are doing it there, preparing it for your machine. ”-“ No, I don't need a technical school. I need a higher education. ”
Today, stores are recruiting sellers with higher education, not lower. And we are trying here to give them some ... They know perfectly well, people who want to be sellers, they know perfectly well what is required of them. Crust. Crust. And that's all, nothing else is needed. There are these ...
Yes, now a diploma of higher education requires even sellers in the store, but this does not mean the value of the diploma, but rather the opposite. In today's hyperinformation society, the problem of gaining knowledge is not a problem - everything is available in two clicks. But students do not know what kind of knowledge they need.
Andrei Ponomarev , expert of the Center for Development of Youth Entrepreneurship of the University of Mechanical Engineering:
When we offer children a 3D printer at their full disposal and asked what they want to print, do you know what they all answered? Anything! Only after lengthy questioning of them can you pull the phone case. But then we say a simple thing: why print a case for $ 10 that will hide the case of the phone, on the design of which millions were spent? Only then the child begins to think and we already tell him what and how can be printed, after that they can already think of something. This is a very big progress in just 45 minute classes - here, thinking more abstractly and systematizing and solving creative problems is more abstract.
The 21st century puts the situation on its head - the Internet gives access to all the knowledge of mankind, so children often know more than their school teacher and cannot wait to put their knowledge into practice. This is the purpose that robotic education serves - these are electives that are built in contrast to the classical lessons with grades. What is its purpose? It turns out to put the question in the student's head in such a way that he himself asked the question “Why” - in this way the initiative passes from the teacher to the student.

1933
Nargiz Isaeva , expert:
In my opinion, the most important thing is to answer the question "Why?". It is necessary to answer this question and teachers, and that children understand why they need it? Why do they come to the laboratory of robotics, why is it necessary? It is great that you said that the role of the teacher, it still changes in this system. This is no longer a person who stands behind the department and invests some knowledge that no one understands why these children need them. And children can never take advantage of it. Knowledge in abundance, knowledge is worthless, knowledge can be obtained not only from the teacher. They are teeming with the Internet, and the farther, the more. And only when the child answers the question why he needs it, only then, and if there is an adult who orients him and says: “You know, you’ve conceived such an interesting thing, let me show you where you can find the knowledge where you are you can get the knowledge with which you embody your idea. " That's exactly the way the role of the teacher changes.
This approach is intended to change the basic element of learning. Instead of copying and imitation classes are built on creative tasks. Let the student use the Internet, looking for material, it is processed. We have no grades, diplomas and homework, instead of competing with other students for grades everything is presented in a game form.
Diana Strelets , Bation robotics center:
Olga said in her report that in the near future we will disappear performance journals, and the classical education system will be replaced by some other. We, too, are moving away from the usual journal about academic performance and from the classical assessment system. We have each child has his own profile online, and during the school year he gains a rating like in the game. He passes tests in the classroom, he participates in the educational process, performs some tasks. And for successful passing of tests, for participation in the educational process, he gets a certain number of points. He goes through some levels, get some titles, some funny titles, which, in general, inspire, motivate. Get some points. Then these points can be changed to some kind of material buns, he can take some devices to his home. Well, in general, it still motivates the child, in addition to the end in itself, that he comes to study robotics. Well, this aspect of the competition is added, the aspect of the game.
In addition, there is another important difference - if a classic diploma is issued to a student, then a diploma must be obtained. That is, you can not just sit out a course of lectures, you need to collect or do something. It seems a trifle, but it turns the whole educational process.
Konstantin Yermishin , graduate student and teacher of robotics at Moscow State Technical University. Bauman, Department of Robotics RK-10:
I would like to share our experience, the experience of MSTU. Bauman on work with students, well, probably, from 8 to 11 grade. We have a partner organization “Children's Land”, this is a physical and mathematical forum in Yakutia, where for probably the last 3 years we have weekly and 2-week visiting workshops for specially developed for 2 years. the program. In short, this is an educational process, as close as possible to what a university teacher is doing with an applicant when he enrolls at MGTU. Bauman, on the program "Step into the Future." The program “Step into the Future” is a competition of technical projects. Already today, technical olympiads were mentioned by a colleague from MAMI, which are gradually equal in status to olympiads in physics and mathematics, and which later give additional points to the Unified State Exam or some bonuses for admission to the university. The “Step into the Future” program is about the same. Those. This is a technical project competition, this is a project. The project is as close as possible to the graduation project of a university graduate, but is carried out by students on a primitive basis. Those. These are all the design stages from the formulation of the definition of a problem and the formulation of a problem, the development of a draft design right up to the implementation of a prototype, but on an accessible element base. They are designers, arduino electronics, anything printed on a 3D printer, etc. In principle, I have already been involved in this for 2 years, my colleagues have been involved in this matter for a couple of years before. We are implementing such a program with students, including which of them later come to us at the Faculty of Robotics.

1958
It is this object-orientation that conflicts with the ideas of online education. But if you look closely, the contradiction may be helpful.
Mustafin Sergey , robotics teacher:
I would like to say a couple of arguments against online education in robotics. In general, in principle, all engineering specialties, they are somehow handicraft, i.e. the result of an engineer’s activity is the introduction of his developments in any industrial process, technological, production, etc. And the main component in the process of introducing any results of engineering activity is the start-up process, which requires certain experience, competence from specialists, work with physical equipment, with iron equipment. Those. it is impossible at the stage of any remote design, remote design to take into account all the nuances associated with the development of a project, and of the subsequent nuances of its implementation and operation. There is such an old Soviet saying, that electrical engineering is the science of contacts, i.e. it is impossible to study electronics, the design process of all disciplines related to remote instrumentation. The lecture material can be remotely taught, some courses can be remotely. But without the physical participation of a student, a schoolchild in the design process, in the process of soldering, setting up, putting this device and equipment into operation, it is impossible to achieve any results.
On the other hand, we all know that in the world of robotics there are quite a lot of expensive professional equipment. And often it is not available to individual developers, students, even often, departments in universities. So, including, at our robotics department, a number of projects require equipment for successful implementation, when, say, one laser scanning range finder costs about half a million rubles. And for the development of an autonomous robot it is necessary. In this regard, we have established a process for remote work of students with a robot model; this is both a virtual robot model and a semi-natural robot model, when there is a physical robot in the training laboratory, it is one, it is accessible to all students, it is equipped with the necessary amount of equipment, The robot has remote access for students. They, accordingly, having tested their algorithms, having handed over to the teacher for a virtual model of the robot, subsequently have access remotely, if they need it, to a physical object, or already in reality in the laboratory to work it out on a real robot.
, . , . , «- » , , — . — , , . — .

1970, .
DIY . , , . DIY , . , : 1 + 2 + 1 . , , , , .
, . . , — 1957 DARPA, NASA NDEA. , - , . National Defense Education Act 1958 — -- , . , .
, — , , — .
It sounds great, but will it work? In a sense, the Rostantstation is a demonstration model of this system and shows the effectiveness of the idea.

2015, education how it turned out really.
Igor Nikitin , the founder of the Robostation:
, . , - . , - . , , , , , , . , , , - , , , , , « ». 4 , , , . , . , . ! ? !
, , , , , . , . , . , — . , , .
. , , — .

Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/260855/
All Articles