5 data visualization experiments
This spring, we in the laboratory experimented with a variety of data: the characteristics of tanks in the World of Tanks game, statistics of correct and incorrect answers on the SDA simulator, temperature records in Russian cities, disruptions in the work of fixed-route taxis in Nizhny Novgorod, history of changes in prices for air tickets. The experiments resulted in 5 visual interactive visualizations:
I will tell you how we create visualizations and which principles we adhere to: in general, and by the example of each visualization. All examples include links to interactive prototypes, where you can independently “touch” the data and draw your own conclusions.
')
We begin work on visualization with the selection of a “brick” , the minimum indivisible unit of information, then we build a visual macromap of the bricks and enhance the result with interactivity.
A brick is an atom of data; in order to select it, it is necessary to examine data under a microscope. A trivial example of a brick is a thousand dead in an impressive visualization of the losses of World War II (author: Neil Halloran). After selecting a brick, we choose a visual way of visualizing its properties in such a way that the bricks differ from each other (comparability) and visually “folded” with each other (additivity) . In the above visualization, a brick is indicated by a little man with a gun or without, nationality is coded by color. The German soldier is easily distinguished from the Soviet civilian:

And adding the figures we get the total losses - in a particular battle, or a particular country, or all countries during the war:

High-quality visualization reflects the data structure. We group, sort and stack the bricks taking into account the data features, we highlight important measurements. Due to the comparability and additivity of bricks, at the macro level, patterns and anomalies inherent in the data as a whole appear.
The secret of powerful visualization is interactivity. Tips on hover and pop-up blocks enrich the visualization with additional information. Filters, sliders, drop-down lists control the selection and allow you to compare different slices. Sections are built from the original bricks and have the same accuracy and completeness as the macromap as a whole.
Let us turn to our experiments.
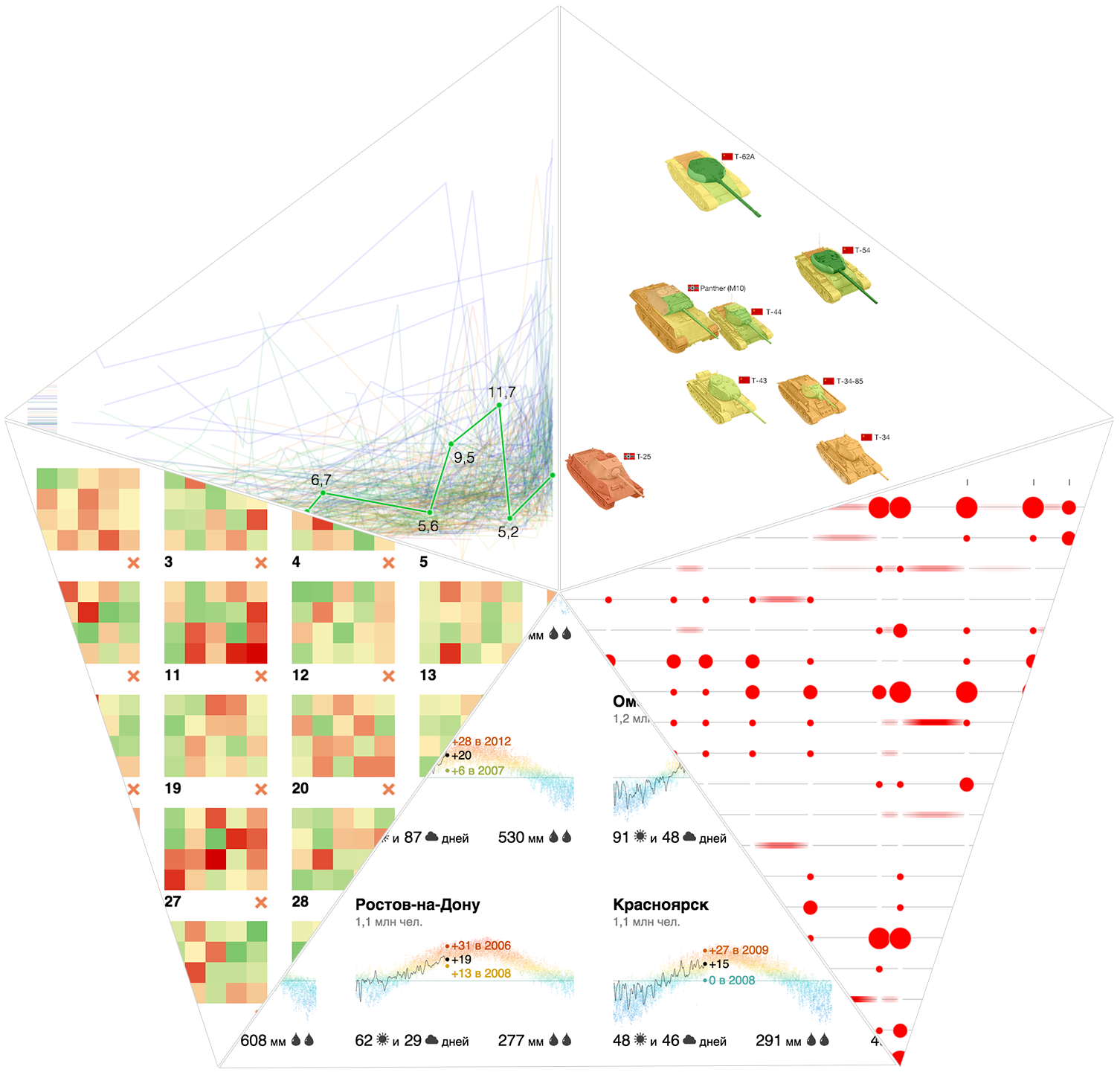
Objective: to compare the characteristics of tanks in the game World of Tanks. Data source: tanks-vs.com
We chose a tank as a brick, the most obvious and natural way of visualization is the tank image (see the example with cars ). The main characteristics of tanks are mobility, “attack” and “defense”. We will show the strength of different sections of the armor in color, so both the level of protection of the tank as a whole and weak points are immediately visible. Speed and attack manifest on a two-dimensional graph:
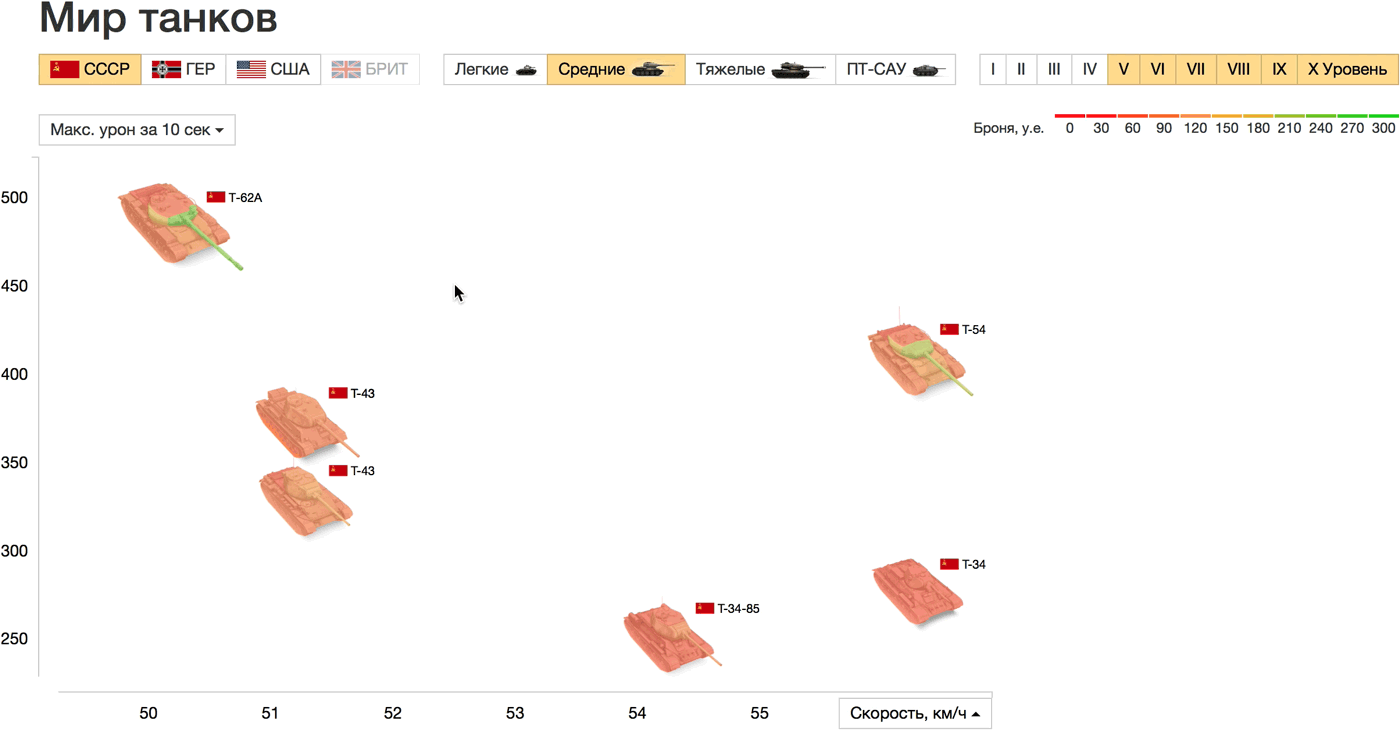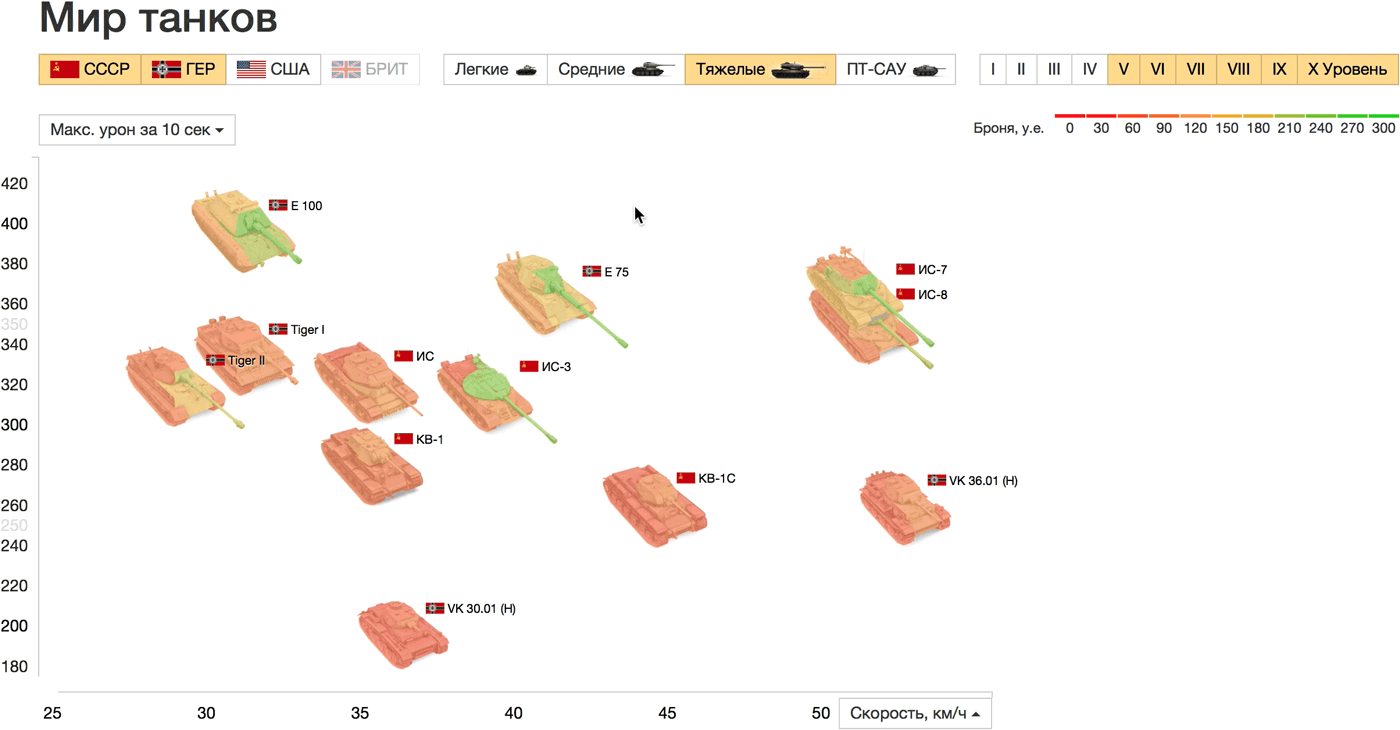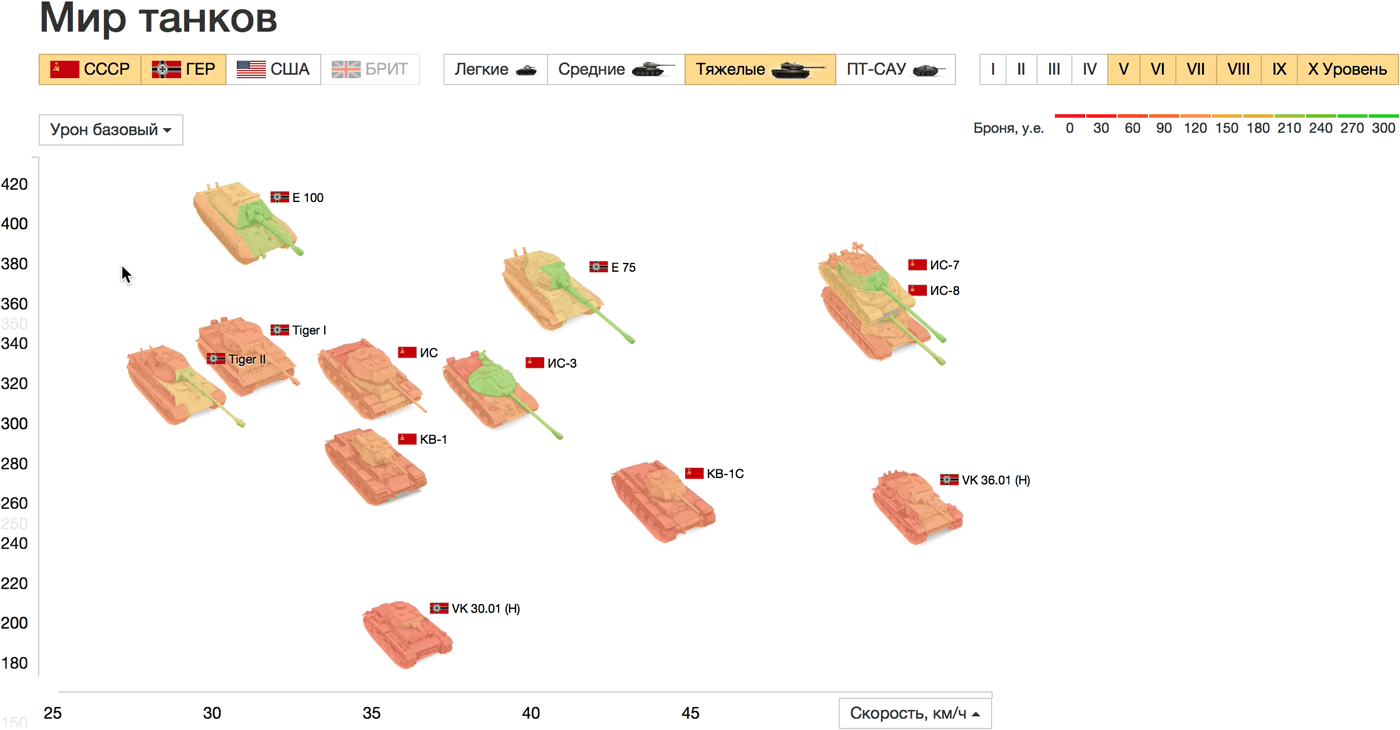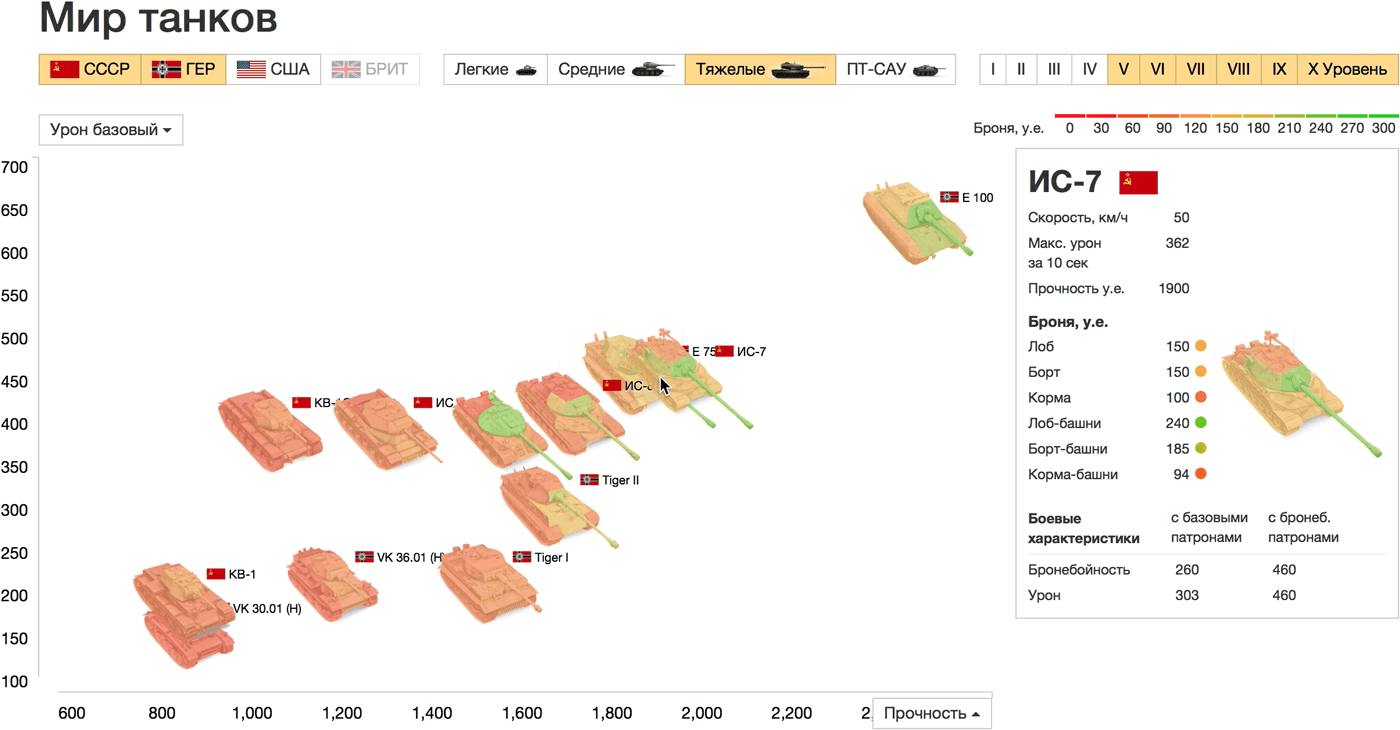
The speed is plotted horizontally, and the maximum damage for 10 seconds, which was selected as an attack parameter, vertically. Points on the graph are tanks on the battlefield, you can compare their appearance, size and key characteristics. Another direct analogy: the farther from the origin of coordinates the tank is located horizontally, the faster it will go (further) in life. Countries, types and levels of tanks are configured in the filters above the graph, on the axes, you can choose any other parameters. When hovering on the tanks all characteristics are shown in a list.
Compare, for example, heavy tanks of the USSR and Germany above level 5. The fastest tanks are the IS-7, IS-8 (USSR) and VK 36.01 (Germany), the latter is losing heavily in maximum damage. E 100, though slow, but the champion in damage and strength. On the graph of strength and base damage there is an almost linear relationship between the parameters. Only the German Tiger I (more durable than the shock) and the Soviet HF (more shock than the durable) differ in the ratio of these parameters from the rest of the sample tanks.
For the strength of the armor, we used a "traffic light" gradient: strong and reliable - green, weak and dangerous - red. For some readers, such a choice of colors caused a dissonance: for them, green indicates easily pierced armor, and red - complex. This question does not seem fundamental to me and can be solved in any way if there is an unequivocal legend.
Objective: to benefit from the statistics simulator tickets for traffic rules. Data provided by the Atren simulator: pdd.atrena.org
The data is hidden answer to the question of how much you need to train in order to successfully pass the exam. This is their main interest and benefit. The brick in this case is an attempt, the answer by a specific user to a specific question N times and the result (“correct” or “error”). To assess the complexity of a particular issue, we calculate the percentage of errors depending on the number of attempts.
The results will be encoded with a “traffic light” gradient and will be shown on the grid of questions grouped by ticket. When you hover over a question, we show the content and answer options, highlighting the correct one . We calculate the average number of errors per person in the ticket and add a passing indicator: two or less errors - the exam passed, more than two - not passed.
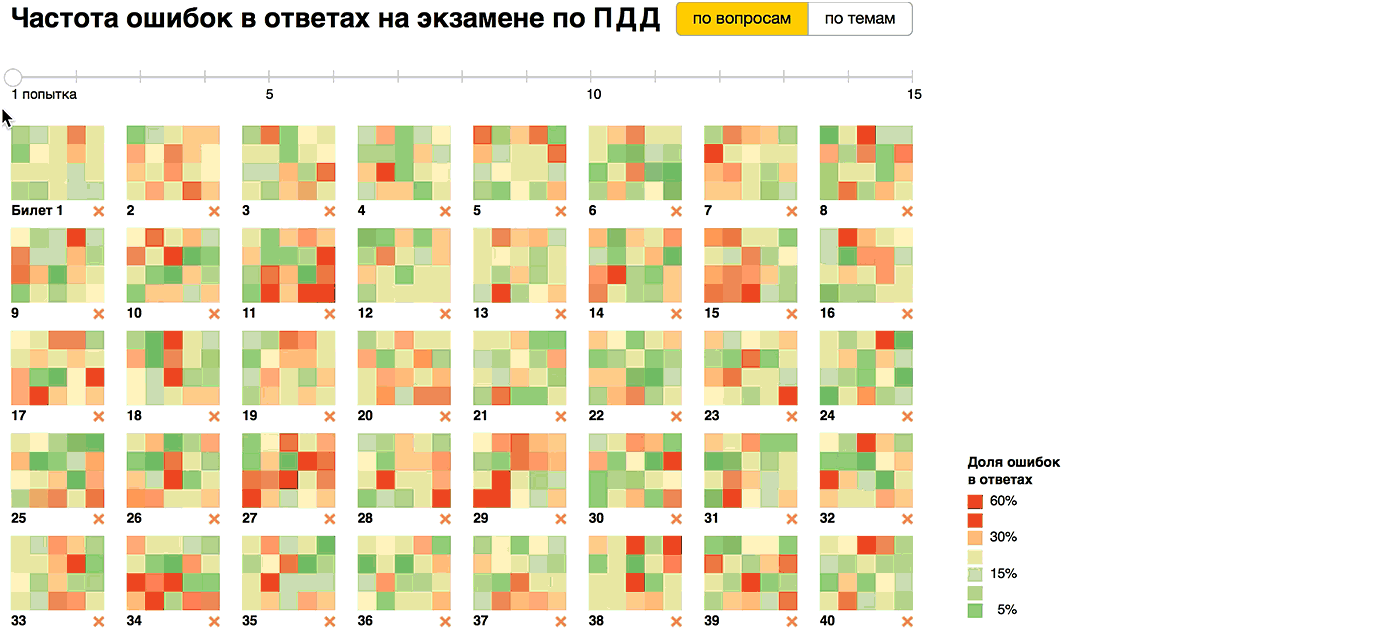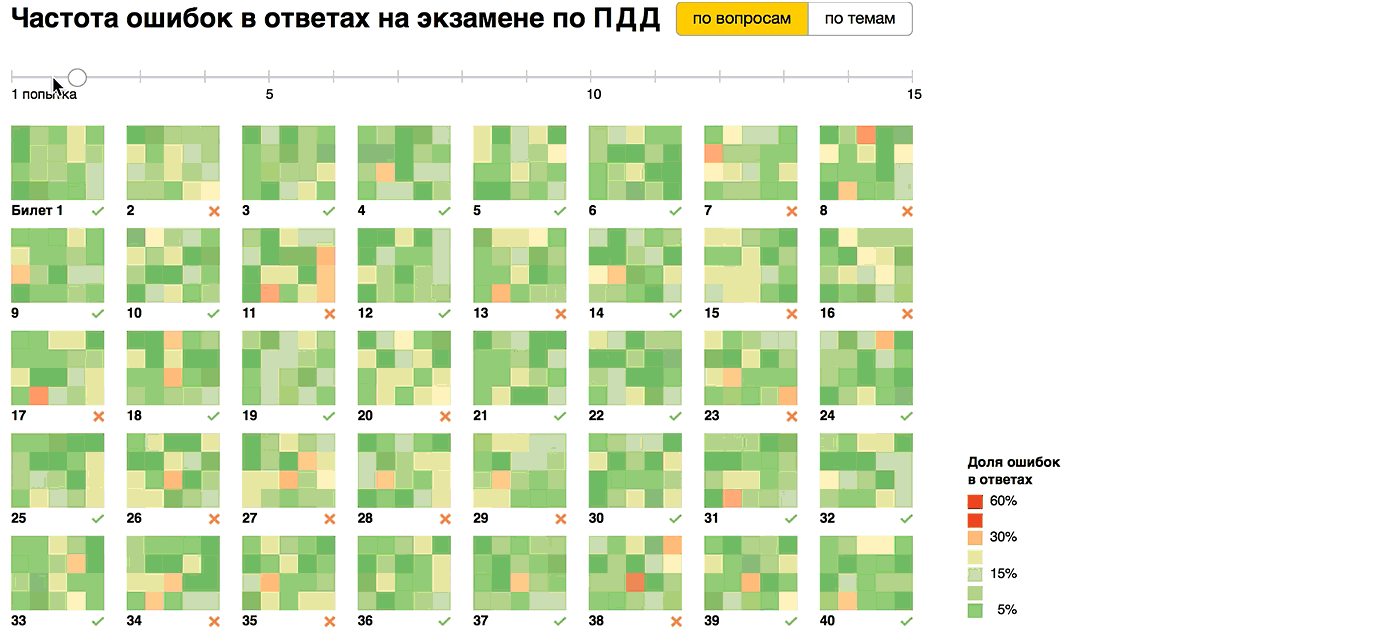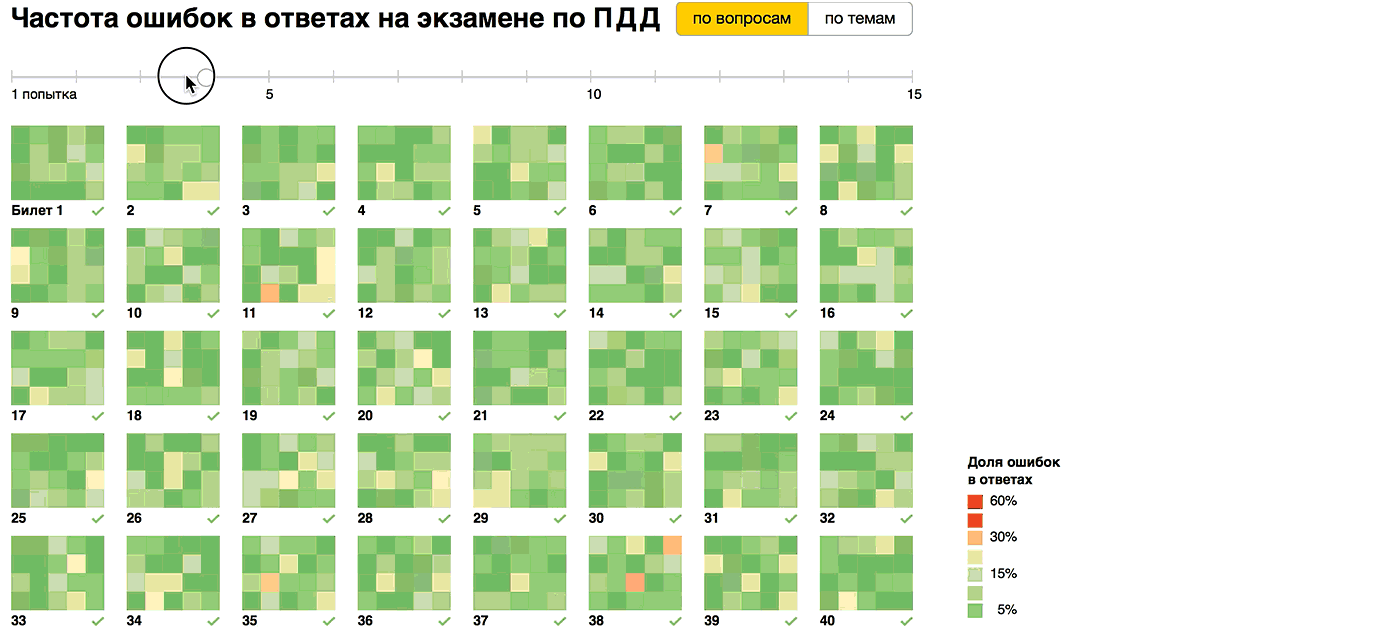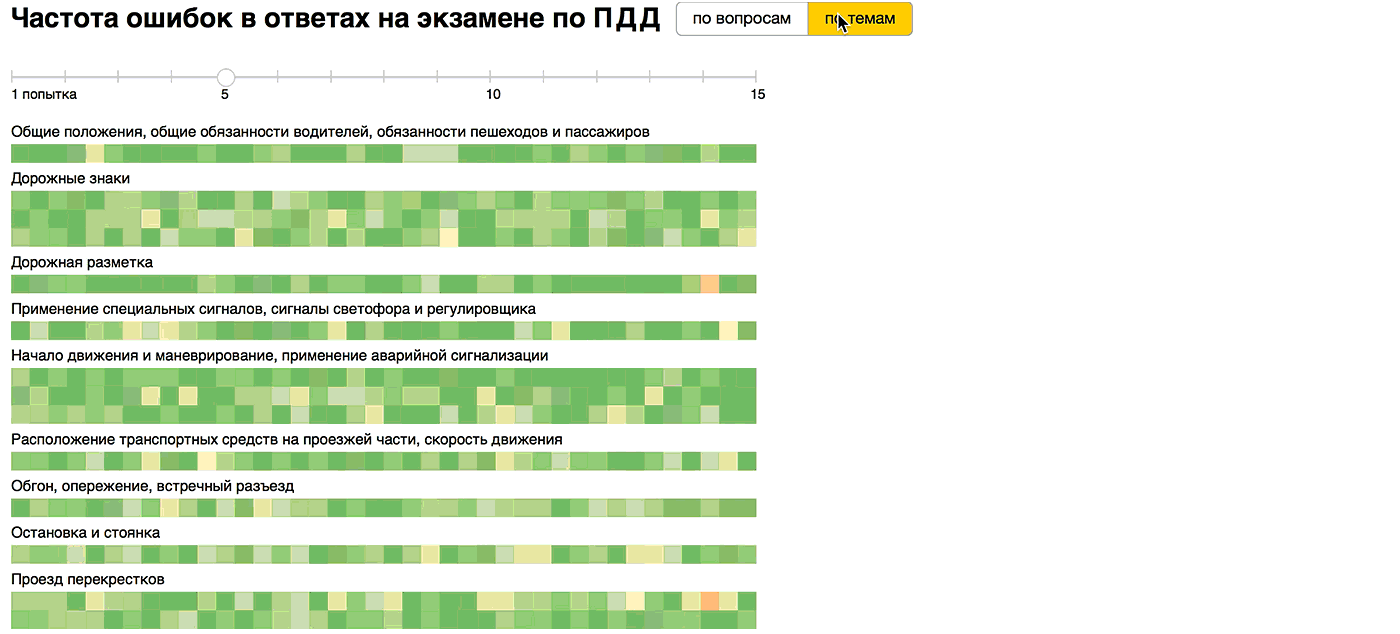
We see that without preparation, it is almost impossible to pass the exam, on average, each ticket has been made from 3 to 5 errors. But after the first training round, the situation is greatly improving: 23 tickets out of 40 are dealt with on the second attempt. On the third attempt, only the most difficult ones did not succumb: the 11th, 27th and 38th tickets, and it is clear which issues are causing the greatest difficulties. In the 11th and 27th tickets, there are several issues in which mistakes are made. And in the 38th, the 13th question causes problems for a third of the students, which is why the average number of errors per person remains above two. Starting from the fourth attempt, all the tickets were handed over on average , but the 13th question of the 38th ticket causes difficulties for a third of the students until the fifteenth attempt!
"Double tick" notes tickets, the average number of errors in which falls below one, that is, that are dealt with high probability. By the fifteenth attempt, there are 11 out of 40 of them. In general, the picture between the fifth and fifteenth attempts varies slightly. The most noticeable effect from the first training lap, and passing tickets more than 5 times is almost meaningless.
We also added grouping by topic. It can be seen that complex and simple questions are distributed over topics more or less evenly.
Task: to show daily temperature records so that it would be interesting to study them. Data source: rp5.ru
We showed the annual temperature chart with a dotted graph with a “thermal” gradient, focused on today's temperature and records, supplemented with a climate report (number of sunny and cloudy days, annual precipitation) and the population of the city - this is our brick. The emphasis on today's temperature and records adds relevance: “Now in Moscow + 22 ° C, and in 2014 that day was + 10 ° C - th!”.
From the bricks, we collected a macromap for the million-plus cities of Russia and added Sevastopol and Sochi for contrast:
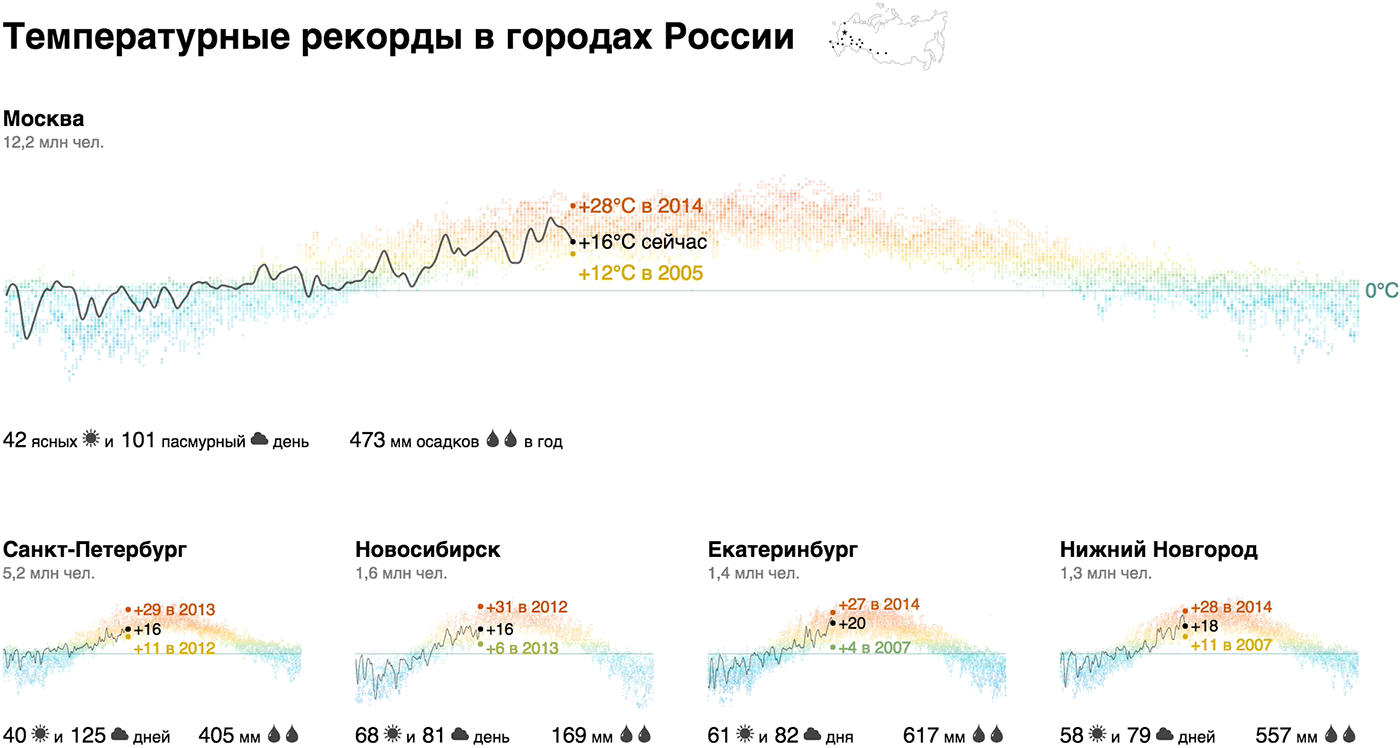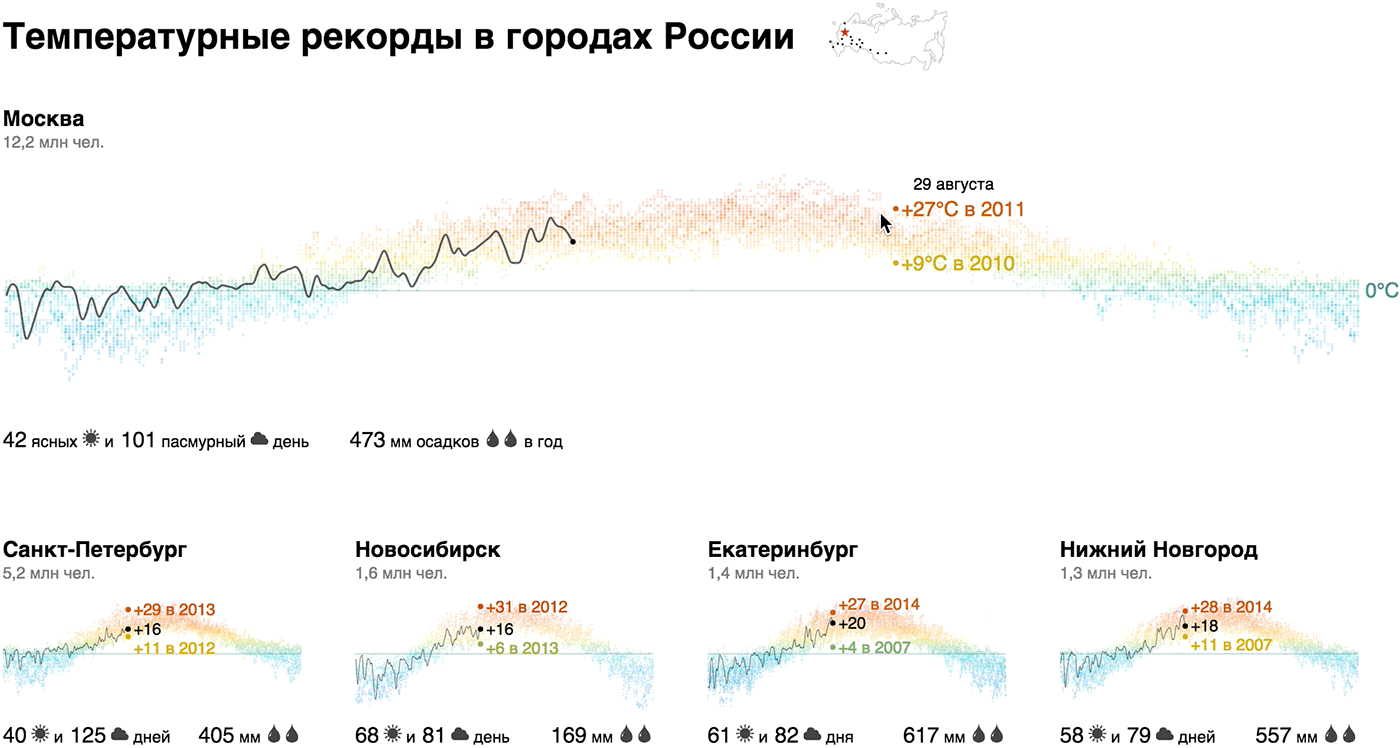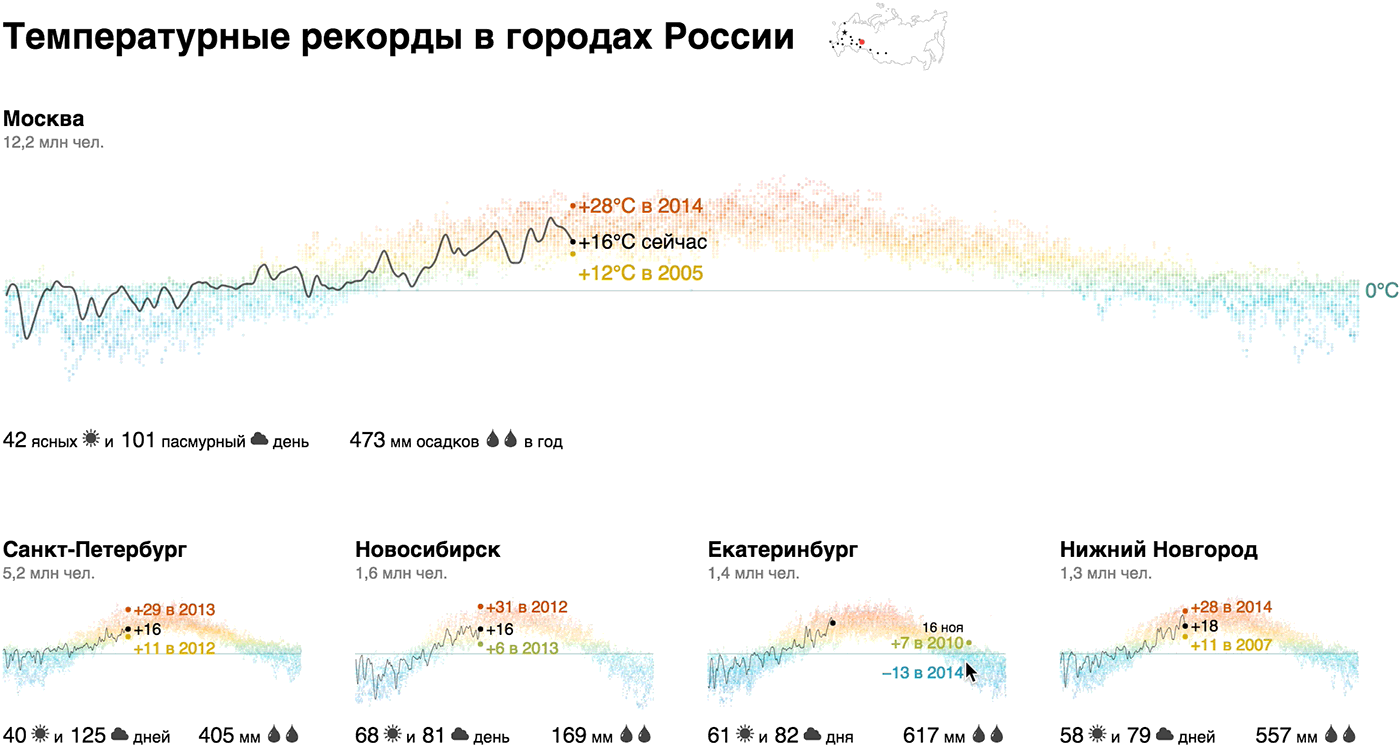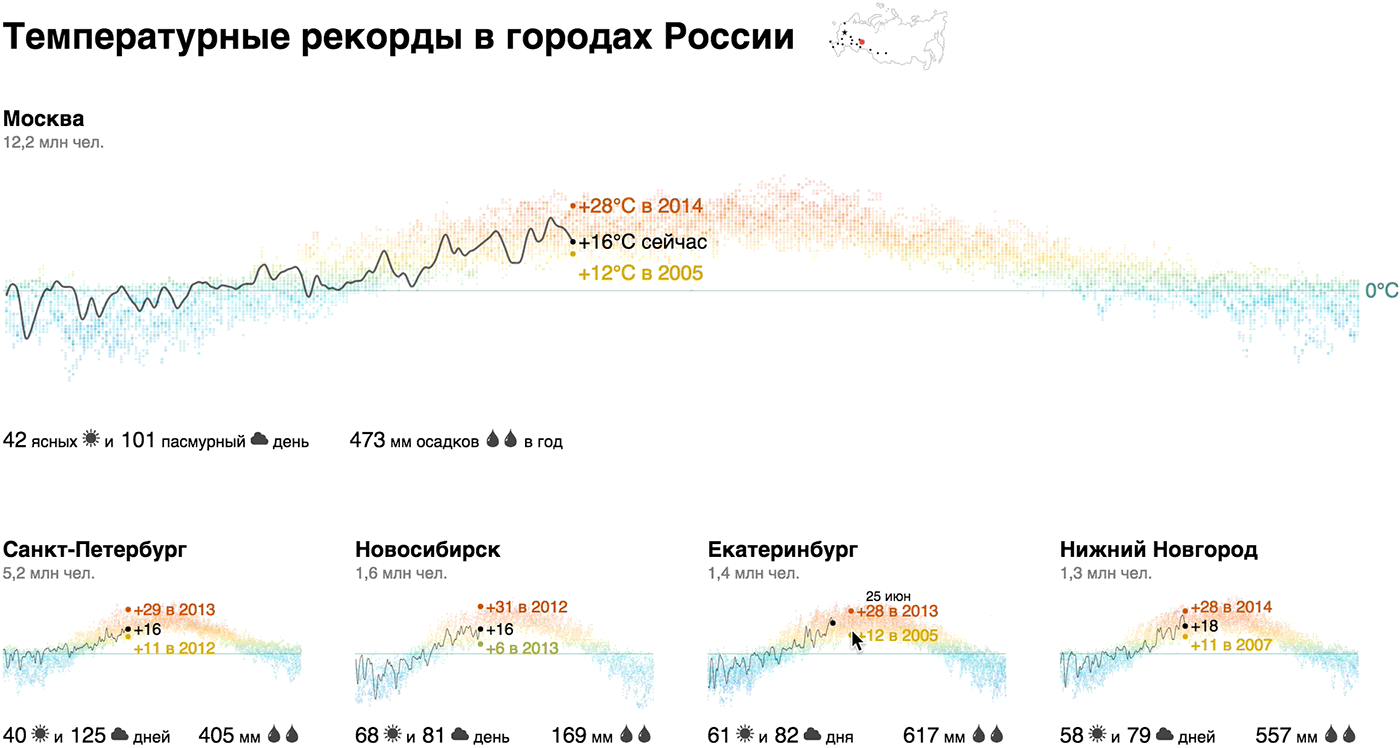
It turns out that the temperature profile of Novosibirsk is not so significantly different from Moscow. In winter, the temperature regularly rises above zero in Rostov, Volgograd and Voronezh, in Sevastopol the variation is from +20 to -20, and only Sochi does not fall below zero in principle. Record for sunny days - Sevastopol, Sochi, and, unexpectedly, Omsk, anti-record players - Peter, Moscow, Voronezh and Chelyabinsk. There is more rainfall in Moscow than in Petersburg, in Omsk two times more than in Novosibirsk, in Voronezh three times more than in Volgograd.
For those who, like me, poorly imagines the relative location of cities, we "secured" over the visualization of the micromap, on which cities are highlighted when hovering on the corresponding brick.
Task: to visualize violations of route taxis (deviations from the schedule and speeding). Data provided by Baseride: baseride.com
How to visually show deviations and exceeding the bus for one flight? Arrange the stops horizontally, maintaining the proportionality of the distances between them. Deviations from the schedule when visiting a particular stop will be shown in a circle whose area is proportional to being late / ahead in minutes. Paint overspeed areas with red: the higher the excess, the redder the area. Flights without violations or with minor violations look neutral, the more violations, the redder the flight. To make the picture clearer, we will revive it with a temporary slider:

Specific delays and exceedances can be shown on hover:

Such flights are easy to compare with each other. For example, you can take one look at all the morning flights, placing them under each other (on the left is the start time). The same picture of the day can be rolled into one line with the total lateness at the stops and the total (translucent) violations in the areas:
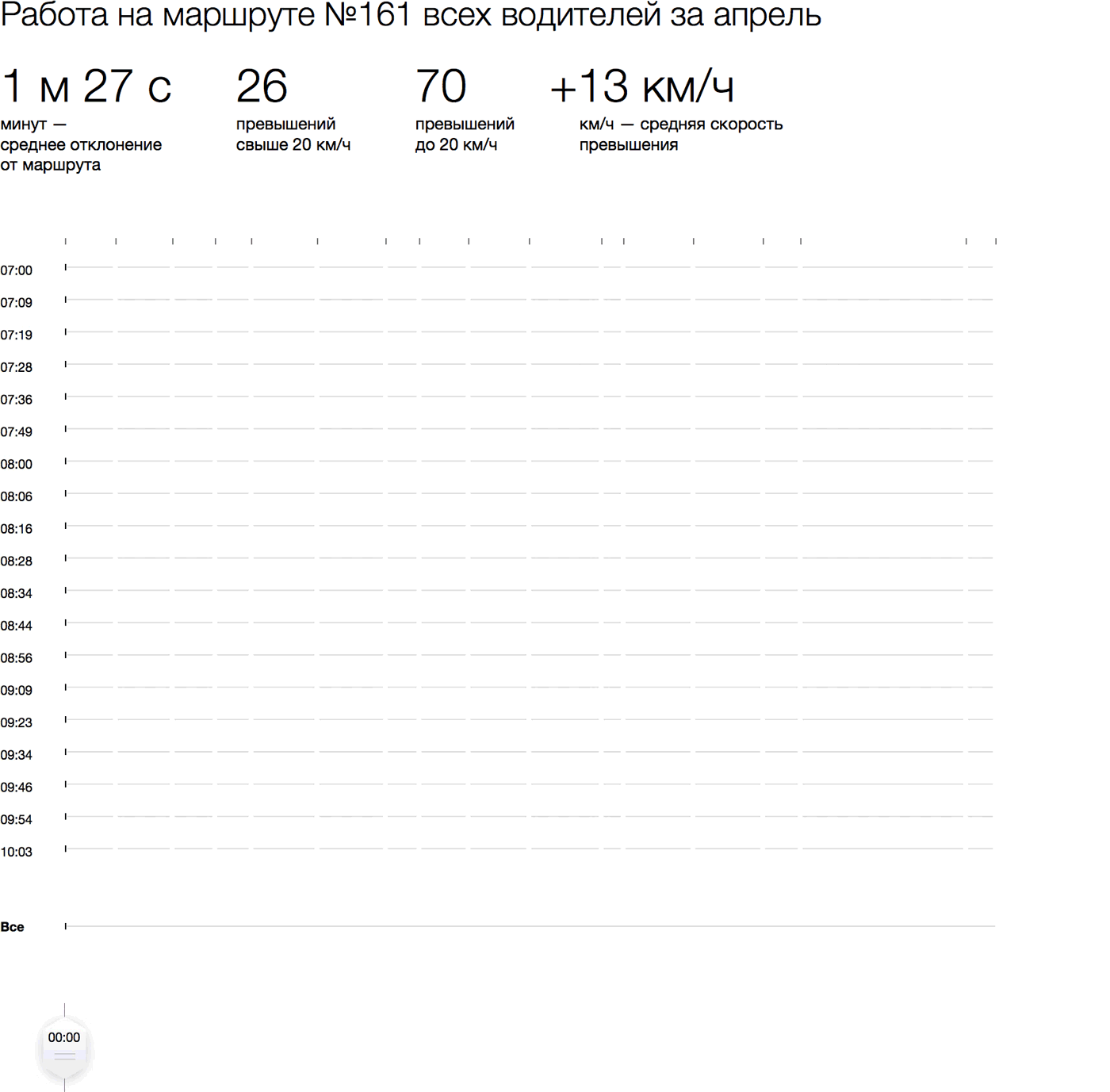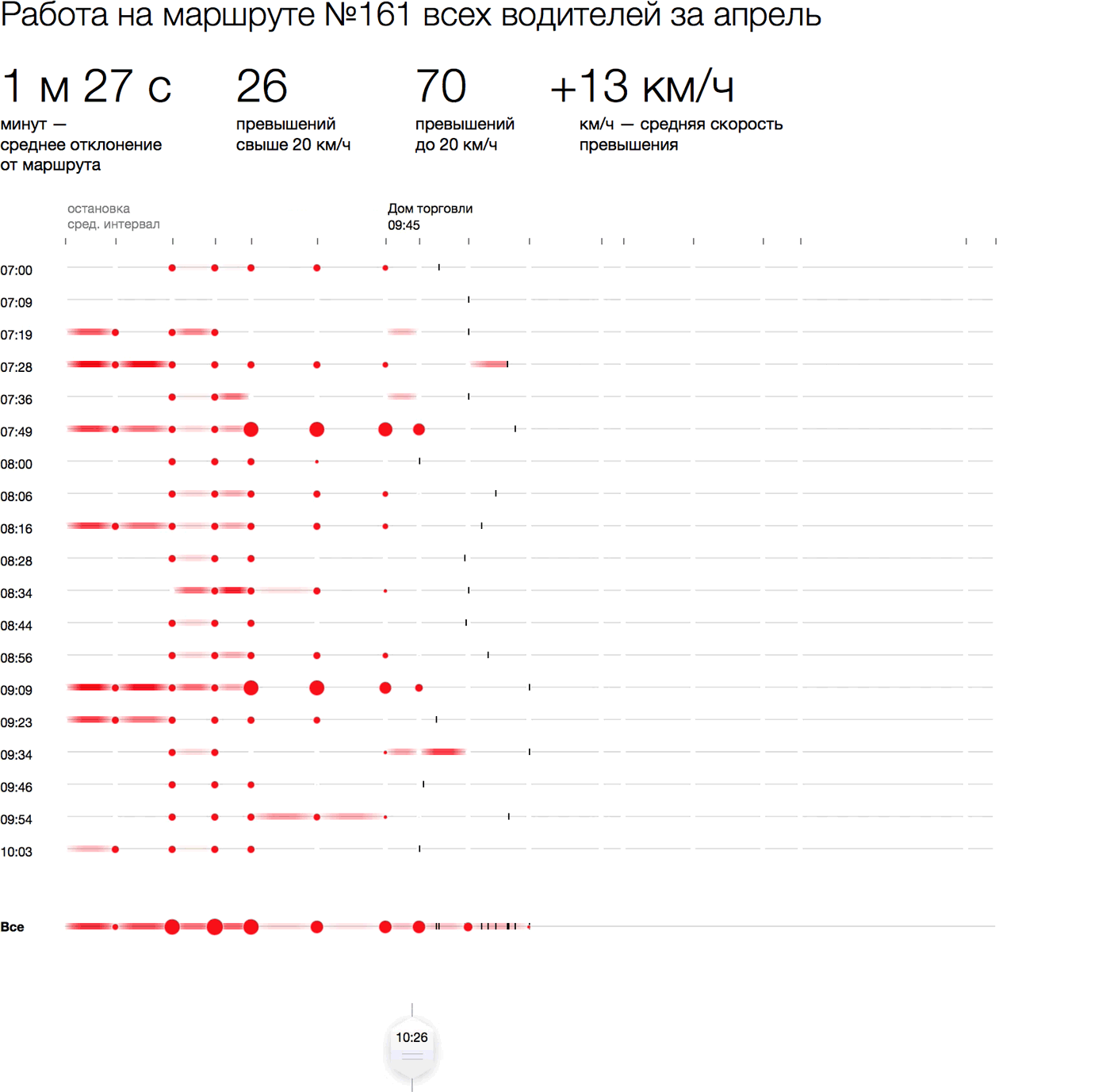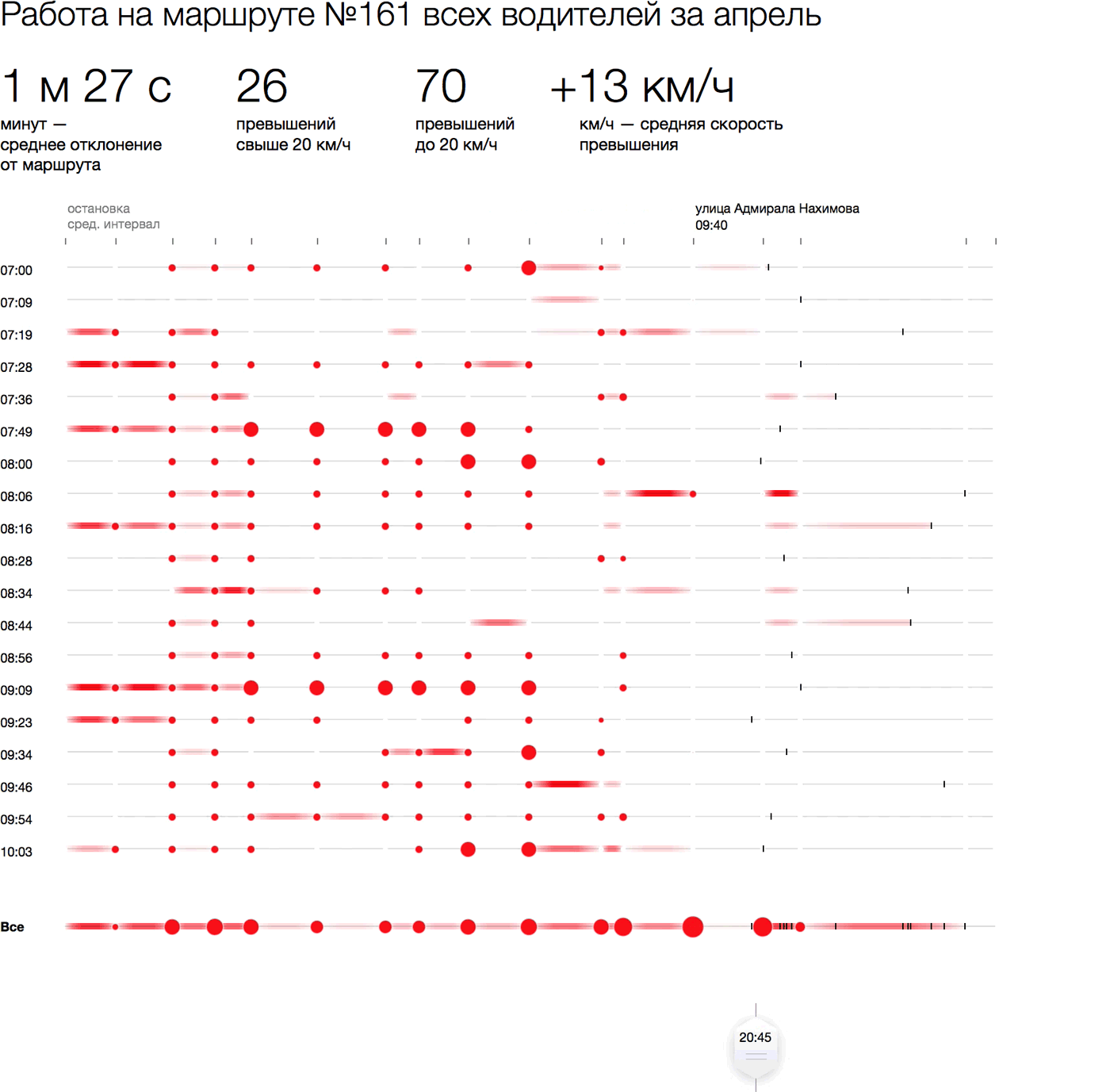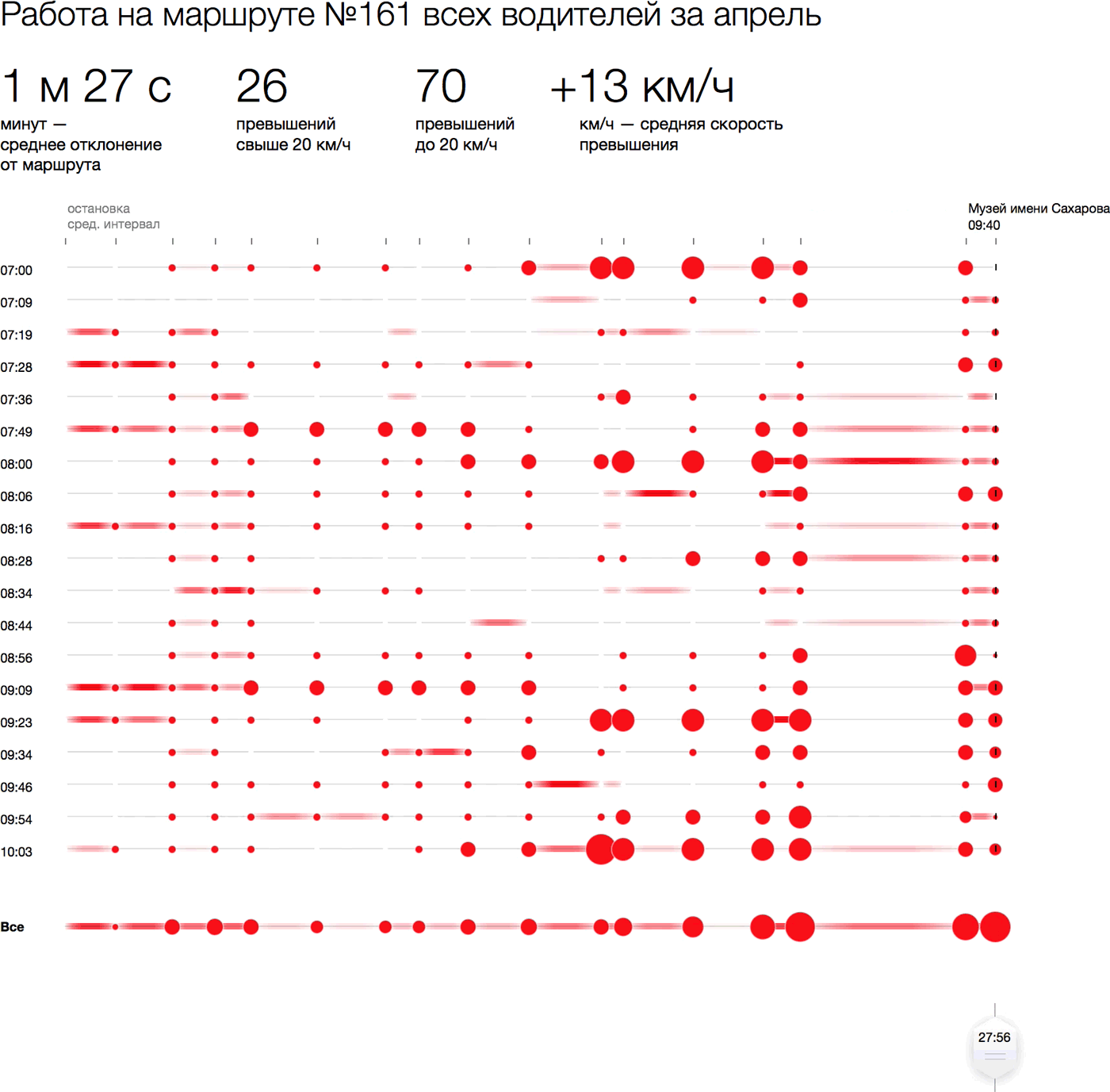
We see that the last four stops suffer more than others from schedule violations, and the speed is most often exceeded at the beginning and on a long leg at the end of the route. Thanks to the interactivity, you can see how minibuses that started at different times of the day are distributed along the route: who and where lags behind and, conversely, is ahead of the total mass.
The advantage of this approach is that you can visually show any cut by flights: for a certain date or time of the day, for a specific driver, for certain violations, and also to compare these sections with each other. So you can show all city routes with statistics for any time period on one screen. At the same time, the overall picture and each specific flight in a form convenient for further research will be visible.
Task: to show changes in prices for air tickets depending on the date of departure and the date of purchase. Data Tutu.ru: tutu.ru
The price schedule for a ticket on a specific departure date depending on the date of purchase is our brick in this case. This trend is interesting to study and compare for different dates and seasons of departure, carriers, directions. To distinguish between graphics using a color gradient for different dates of departure. On the vertical axis of the risk shows the distribution of prices.
When hovering over the time slider and on the chart, we highlight the trend with a specific departure date. The slider controls the selection: you can see summer, autumn, New Year, spring trends, May holidays, etc.

In general, the hypothesis is confirmed that the closer the departure, the more expensive the tickets: on the right side of the schedule of expensive purchases, the network is denser. But there are quite a few exceptions to this rule — descending graphs with early expensive purchases.
We will carefully study the most detailed and homogeneous data on the flight Moscow → Simferopol (only Aeroflot):

Last summer, tickets were bought both in advance and on the eve of departure, an average of 5 thousand rubles with random deviations of up to 7-10 thousand. In the fall, the density of the “tail” on the left decreased, purchases were made closer to the departure date, while the average price was early a little less late. In winter, no one bought the tickets earlier than six weeks before departure, but the purchase prices in recent days have jumped significantly - up to 10-15 thousand. In spring, pronounced steps (fixed tariffs) are visible: blue March steps to the price reduction at the direction of the president, green April - after.
High-quality visualization shows patterns and anomalies in the data, allows you to see them with the naked eye. It is a tool for studying data without cumbersome software and complex mathematics. We are sure that visualization is useful in a variety of tasks, and our experiments confirm this. To take part in the experiment, send interesting data to data@datalaboratory.ru with a note in the “Question-answer” rubric .

I will tell you how we create visualizations and which principles we adhere to: in general, and by the example of each visualization. All examples include links to interactive prototypes, where you can independently “touch” the data and draw your own conclusions.
')
General principles
We begin work on visualization with the selection of a “brick” , the minimum indivisible unit of information, then we build a visual macromap of the bricks and enhance the result with interactivity.
A brick is an atom of data; in order to select it, it is necessary to examine data under a microscope. A trivial example of a brick is a thousand dead in an impressive visualization of the losses of World War II (author: Neil Halloran). After selecting a brick, we choose a visual way of visualizing its properties in such a way that the bricks differ from each other (comparability) and visually “folded” with each other (additivity) . In the above visualization, a brick is indicated by a little man with a gun or without, nationality is coded by color. The German soldier is easily distinguished from the Soviet civilian:

And adding the figures we get the total losses - in a particular battle, or a particular country, or all countries during the war:

High-quality visualization reflects the data structure. We group, sort and stack the bricks taking into account the data features, we highlight important measurements. Due to the comparability and additivity of bricks, at the macro level, patterns and anomalies inherent in the data as a whole appear.
The secret of powerful visualization is interactivity. Tips on hover and pop-up blocks enrich the visualization with additional information. Filters, sliders, drop-down lists control the selection and allow you to compare different slices. Sections are built from the original bricks and have the same accuracy and completeness as the macromap as a whole.
Let us turn to our experiments.
Tanks
Objective: to compare the characteristics of tanks in the game World of Tanks. Data source: tanks-vs.com
We chose a tank as a brick, the most obvious and natural way of visualization is the tank image (see the example with cars ). The main characteristics of tanks are mobility, “attack” and “defense”. We will show the strength of different sections of the armor in color, so both the level of protection of the tank as a whole and weak points are immediately visible. Speed and attack manifest on a two-dimensional graph:

Living prototype: http://tanks.datalaboratory.ru/
The speed is plotted horizontally, and the maximum damage for 10 seconds, which was selected as an attack parameter, vertically. Points on the graph are tanks on the battlefield, you can compare their appearance, size and key characteristics. Another direct analogy: the farther from the origin of coordinates the tank is located horizontally, the faster it will go (further) in life. Countries, types and levels of tanks are configured in the filters above the graph, on the axes, you can choose any other parameters. When hovering on the tanks all characteristics are shown in a list.
Compare, for example, heavy tanks of the USSR and Germany above level 5. The fastest tanks are the IS-7, IS-8 (USSR) and VK 36.01 (Germany), the latter is losing heavily in maximum damage. E 100, though slow, but the champion in damage and strength. On the graph of strength and base damage there is an almost linear relationship between the parameters. Only the German Tiger I (more durable than the shock) and the Soviet HF (more shock than the durable) differ in the ratio of these parameters from the rest of the sample tanks.
For the strength of the armor, we used a "traffic light" gradient: strong and reliable - green, weak and dangerous - red. For some readers, such a choice of colors caused a dissonance: for them, green indicates easily pierced armor, and red - complex. This question does not seem fundamental to me and can be solved in any way if there is an unequivocal legend.
Traffic regulations
Objective: to benefit from the statistics simulator tickets for traffic rules. Data provided by the Atren simulator: pdd.atrena.org
The data is hidden answer to the question of how much you need to train in order to successfully pass the exam. This is their main interest and benefit. The brick in this case is an attempt, the answer by a specific user to a specific question N times and the result (“correct” or “error”). To assess the complexity of a particular issue, we calculate the percentage of errors depending on the number of attempts.
The results will be encoded with a “traffic light” gradient and will be shown on the grid of questions grouped by ticket. When you hover over a question, we show the content and answer options, highlighting the correct one . We calculate the average number of errors per person in the ticket and add a passing indicator: two or less errors - the exam passed, more than two - not passed.

Living prototype: pdd.datalaboratory.ru
We see that without preparation, it is almost impossible to pass the exam, on average, each ticket has been made from 3 to 5 errors. But after the first training round, the situation is greatly improving: 23 tickets out of 40 are dealt with on the second attempt. On the third attempt, only the most difficult ones did not succumb: the 11th, 27th and 38th tickets, and it is clear which issues are causing the greatest difficulties. In the 11th and 27th tickets, there are several issues in which mistakes are made. And in the 38th, the 13th question causes problems for a third of the students, which is why the average number of errors per person remains above two. Starting from the fourth attempt, all the tickets were handed over on average , but the 13th question of the 38th ticket causes difficulties for a third of the students until the fifteenth attempt!
"Double tick" notes tickets, the average number of errors in which falls below one, that is, that are dealt with high probability. By the fifteenth attempt, there are 11 out of 40 of them. In general, the picture between the fifth and fifteenth attempts varies slightly. The most noticeable effect from the first training lap, and passing tickets more than 5 times is almost meaningless.
We also added grouping by topic. It can be seen that complex and simple questions are distributed over topics more or less evenly.
Weather
Task: to show daily temperature records so that it would be interesting to study them. Data source: rp5.ru
We showed the annual temperature chart with a dotted graph with a “thermal” gradient, focused on today's temperature and records, supplemented with a climate report (number of sunny and cloudy days, annual precipitation) and the population of the city - this is our brick. The emphasis on today's temperature and records adds relevance: “Now in Moscow + 22 ° C, and in 2014 that day was + 10 ° C - th!”.
From the bricks, we collected a macromap for the million-plus cities of Russia and added Sevastopol and Sochi for contrast:

Living prototype: weather-records.datalaboratory.ru
It turns out that the temperature profile of Novosibirsk is not so significantly different from Moscow. In winter, the temperature regularly rises above zero in Rostov, Volgograd and Voronezh, in Sevastopol the variation is from +20 to -20, and only Sochi does not fall below zero in principle. Record for sunny days - Sevastopol, Sochi, and, unexpectedly, Omsk, anti-record players - Peter, Moscow, Voronezh and Chelyabinsk. There is more rainfall in Moscow than in Petersburg, in Omsk two times more than in Novosibirsk, in Voronezh three times more than in Volgograd.
For those who, like me, poorly imagines the relative location of cities, we "secured" over the visualization of the micromap, on which cities are highlighted when hovering on the corresponding brick.
Minibuses
Task: to visualize violations of route taxis (deviations from the schedule and speeding). Data provided by Baseride: baseride.com
How to visually show deviations and exceeding the bus for one flight? Arrange the stops horizontally, maintaining the proportionality of the distances between them. Deviations from the schedule when visiting a particular stop will be shown in a circle whose area is proportional to being late / ahead in minutes. Paint overspeed areas with red: the higher the excess, the redder the area. Flights without violations or with minor violations look neutral, the more violations, the redder the flight. To make the picture clearer, we will revive it with a temporary slider:

Specific delays and exceedances can be shown on hover:

Such flights are easy to compare with each other. For example, you can take one look at all the morning flights, placing them under each other (on the left is the start time). The same picture of the day can be rolled into one line with the total lateness at the stops and the total (translucent) violations in the areas:

Living prototype: minibus.datalaboratory.ru
We see that the last four stops suffer more than others from schedule violations, and the speed is most often exceeded at the beginning and on a long leg at the end of the route. Thanks to the interactivity, you can see how minibuses that started at different times of the day are distributed along the route: who and where lags behind and, conversely, is ahead of the total mass.
The advantage of this approach is that you can visually show any cut by flights: for a certain date or time of the day, for a specific driver, for certain violations, and also to compare these sections with each other. So you can show all city routes with statistics for any time period on one screen. At the same time, the overall picture and each specific flight in a form convenient for further research will be visible.
Air ticket prices
Task: to show changes in prices for air tickets depending on the date of departure and the date of purchase. Data Tutu.ru: tutu.ru
The price schedule for a ticket on a specific departure date depending on the date of purchase is our brick in this case. This trend is interesting to study and compare for different dates and seasons of departure, carriers, directions. To distinguish between graphics using a color gradient for different dates of departure. On the vertical axis of the risk shows the distribution of prices.
When hovering over the time slider and on the chart, we highlight the trend with a specific departure date. The slider controls the selection: you can see summer, autumn, New Year, spring trends, May holidays, etc.

Living prototype: ticket-prices.datalaboratory.ru
In general, the hypothesis is confirmed that the closer the departure, the more expensive the tickets: on the right side of the schedule of expensive purchases, the network is denser. But there are quite a few exceptions to this rule — descending graphs with early expensive purchases.
We will carefully study the most detailed and homogeneous data on the flight Moscow → Simferopol (only Aeroflot):

Last summer, tickets were bought both in advance and on the eve of departure, an average of 5 thousand rubles with random deviations of up to 7-10 thousand. In the fall, the density of the “tail” on the left decreased, purchases were made closer to the departure date, while the average price was early a little less late. In winter, no one bought the tickets earlier than six weeks before departure, but the purchase prices in recent days have jumped significantly - up to 10-15 thousand. In spring, pronounced steps (fixed tariffs) are visible: blue March steps to the price reduction at the direction of the president, green April - after.
High-quality visualization shows patterns and anomalies in the data, allows you to see them with the naked eye. It is a tool for studying data without cumbersome software and complex mathematics. We are sure that visualization is useful in a variety of tasks, and our experiments confirm this. To take part in the experiment, send interesting data to data@datalaboratory.ru with a note in the “Question-answer” rubric .
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/260161/
All Articles