iSCSI 2.0 with FAS2xxx or the scaling path of a small data center
Preservation of investments claimed by any company. It is important to have such a data center infrastructure concept that would allow for easy scaling, if necessary, while maximizing the utilization of existing equipment for new business needs. The transition from iSCSI to iSCSI 2.0 can be the basis for such a concept. iSCSI over DCB is often referred to as iSCSI 2.0 due to additional DCB extensions for Ethernet.

In continuation of the article " FC & Ethernet ".
DCB consists of
DCB- enabled switches often also support Shortest Path Bridging IEEE 802.1AQ and / or IETF TRILL allowing you to choose the shortest path for Ethernet traffic, which has a positive effect on iSCSI performance.
iSCSI managed to evolve by learning to work with Thin Provisioning (SCSI SBC-3) and Space Reclamation (T10 UNMAP), it has load balancing and path resiliency capabilities (using MPIO and / or MCS ).
It is important to note that all NetApp FAS storage devices support iSCSI protocol on all their Ethernet data ports. Starting with Data ONTAP 8.1.3, SCSI SBC-3 and UNMAP are supported , starting from DATA Ontap 8.2.1, FAS storage systems support DCB .
Thus, iSCSI can be an ideal candidate for the growth of a small data center if it provides:
')
To this end, I propose to consider the advantages and disadvantages of several designs while observing a single concept - connecting NetApp FAS storage systems via iSCSI . These designs should be relatively simple to convert a small data center into a large one.
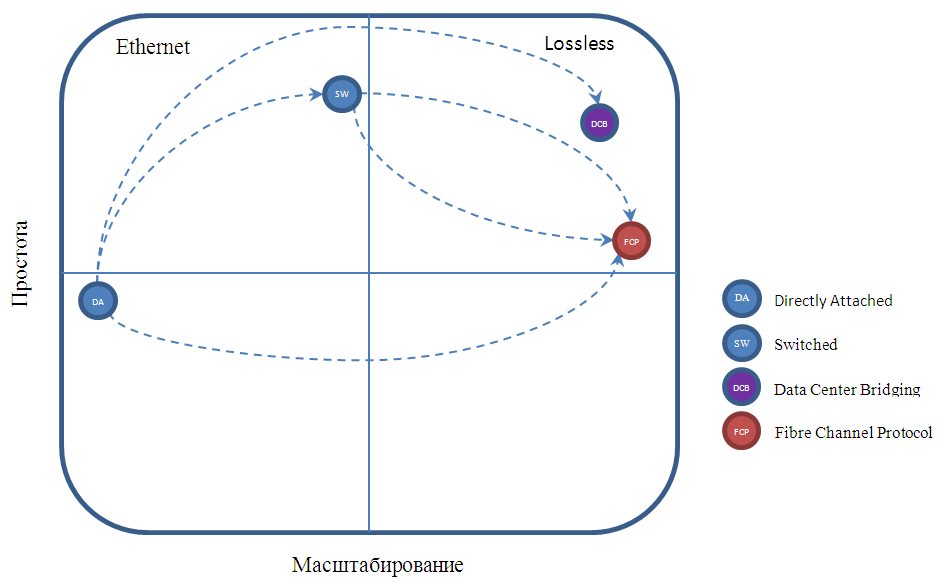
Schematic designation of the proposed paths of transition between configurations with the growth of the data center, a la Gartner square:
Since iSCSI lives on top of Ethernet, you need to configure Flow Control (do not confuse “normal” FlowControl with PFC IEEE 802.1Qbb for DCB Losless Ethernet) and configure Jumbo Frames on the network adapters of the hosts, on the storage and on the switches (if they exist). Using MPIO / MCS within a single link can increase its total throughput compared to using a single connection in a link. It is recommended to allocate a separate VLAN for iSCSI traffic if the switch is used for a mixed type of traffic.
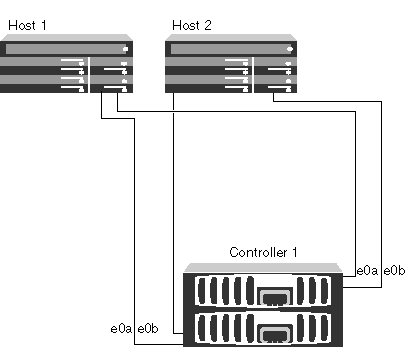
The design of such a “small data center” consists of one or two servers directly connected to the storage system, each with at least two links for fault tolerance: one to one storage controller and the other to the other. At this stage, it is logical to use the free Software iSCSI Initiator. In case of increase in hosts, you must either add ports to the storage or install switches. Depending on the storage model, there may be a different number of Ethernet ports. It is important to note that all Ethernet ports on NetApp FAS storages (no “dedicated” iSCSI ports) can be used for these types of traffic: iSCSI , NFS , CIFS ( SMB ), including at the same time.
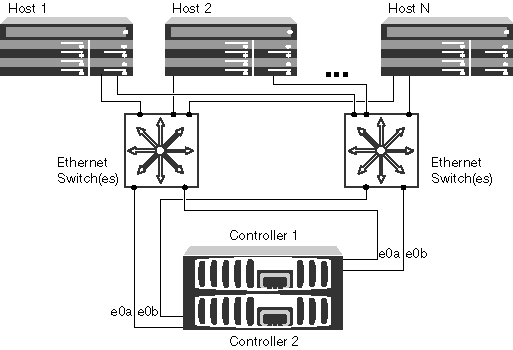
In such a scheme, you must have at least two links from each node, each link connected via different switches. This will provide full fault tolerance at the output of the controller, switch or path. At this stage, you can still use the Software iSCSI Initiator or a combination with a dedicated iSCSI HBA (which would load the load from the host CPU ).
Like Switched iSCSI , in the case of iSCSI 2.0 , switches are used, but they must support DCB . This design will also require network adapters that support DCB on both the host and the storage. Thus, DCB should be supported all the way through iSCSI traffic. DCB is also known as Lossless Ethernet , it provides guaranteed frame delivery, increasing reliability, performance, and responsiveness to FC level. It is important to note that DCB supports all converged Ethernet ports on NetApp FAS storages (no “dedicated” iSCSI or FCoE ports) and can be used for all types of traffic: iSCSI (2.0), FCoE , NFS , CIFS ( SMB ), including and at the same time. CNA (HBA) QLogic 8300 adapters for working with DCB are supported on the host, this adapter allows offloading the load from the host CPU providing a low response speed of the storage. Some additional features of switches can improve the already low response rate for iSCSI , for example CLEAR-Flow .

The advantages of iSCSI over DCB include:
Disadvantages of iSCSI over DCB:
There are several ways to grow NetApp FAS systems:
Thus, the iSCSI protocol with NetApp FAS storage can be the basis for starting growth from the “small data center” to the “large” one, gradually and simply updating the network design, observing a single concept of addressing and multipassing. When updating, the equipment that has already been purchased is utilized to the maximum. Each upgrade step increases the scalability of the data center infrastructure, its speed and reduces the response for applications, while at the same time fulfilling costs as needed. Thanks to the versatility of FAS storage systems , support of advanced data center development trends and the ability to mutually replace protocols (or use them all at the same time including the same ports), easy scalability, it is a good investment investment for both small and “large data centers”.
Learn more about network topology and zoning recommendations for NetApp in pictures .
It is very important to follow best practices when configuring the infrastructure and check the compatibility matrix for maximum performance and fault tolerance:
TR-3441 Windows Multipathing Options with Data ONTAP: Fiber Channel and iSCSI
WP-7071: "How Do I Get to Ethernet from Here?"
TR-3519: "The Road to 10-Gigabit Ethernet"
WP-7046: "Ethernet Storage"
TR-3441: "iSCSI Multipathing Possibilities on Windows with Data ONTAP"
TR-3163: "Data Protection for Network-Attached Storage over IP / Ethernet Networks"
WP-7052: “Converged Enhanced Ethernet — Good for iSCSI SANs”
TR-3519: "The Road to 10-Gigabit Ethernet"
iSCSI 10Gig Performance Tuning With Windows Server
iSCSI Configuration and Provisioning for Windows
TR-3802 Ethernet Storage Best Practices
TR-4182 Ethernet Storage Design Considerations and Best Practices
Best Practices for Network Configuration with NetApp Storage Systems
NetApp Verifying that DCB is configured correctly
NetApp SAN Design and SAN Fundamentals on Data ONTAP courses are available at the NetApp Academy.
Sources:
sniaesfblog.org/?p=210&cpage=1#comment-82839
blogs.cisco.com/datacenter/the-napkin-dialogues-lossless-iscsi
www.storage-switzerland.com/Articles/Entries/2012/1/17_iSCSI_2.0_-_Using_Data_Center_Bridging_To_Enhance_iSCSI.html
www.snia.org/sites/default/education/tutorials/2010/spring/networking/GaryGumanow-JasonBlosil_iSCSI_Lossless_Ethernet_DCB.pdf
www.slideshare.net/extreme-muk/i-scsi-extremeintelnetappclearflow
Comments on errors and suggestions for changes in the text please send to the LAN .

In continuation of the article " FC & Ethernet ".
DCB consists of
- PFC (802.1Qbb) - Enables lossless Ethernet frames (Lossless Ethernet)
- ETS (802.1Qaz) - Assigns bandwidth to frames, allows low priority traffic to use bandwidth if it is not locked.
- CN (802.1Qau) - Pauses the source
- DCBX - Defines the DCB domain
DCB- enabled switches often also support Shortest Path Bridging IEEE 802.1AQ and / or IETF TRILL allowing you to choose the shortest path for Ethernet traffic, which has a positive effect on iSCSI performance.
iSCSI managed to evolve by learning to work with Thin Provisioning (SCSI SBC-3) and Space Reclamation (T10 UNMAP), it has load balancing and path resiliency capabilities (using MPIO and / or MCS ).
It is important to note that all NetApp FAS storage devices support iSCSI protocol on all their Ethernet data ports. Starting with Data ONTAP 8.1.3, SCSI SBC-3 and UNMAP are supported , starting from DATA Ontap 8.2.1, FAS storage systems support DCB .
Thus, iSCSI can be an ideal candidate for the growth of a small data center if it provides:
- High performance (can be achieved with the help of no more tuning, as well as thanks to DCB ).
- Unified storage connectivity concept in the case of growth from “small” to “large data center”, to preserve investments.
- A relatively simple transition from the design of a “small data center” direct-attached or switched (with cheap switches) storage connections to the design of a “large data center”, for future growth.
')
To this end, I propose to consider the advantages and disadvantages of several designs while observing a single concept - connecting NetApp FAS storage systems via iSCSI . These designs should be relatively simple to convert a small data center into a large one.
Schematic designation of the proposed paths of transition between configurations with the growth of the data center, a la Gartner square:
iSCSI tuning
Since iSCSI lives on top of Ethernet, you need to configure Flow Control (do not confuse “normal” FlowControl with PFC IEEE 802.1Qbb for DCB Losless Ethernet) and configure Jumbo Frames on the network adapters of the hosts, on the storage and on the switches (if they exist). Using MPIO / MCS within a single link can increase its total throughput compared to using a single connection in a link. It is recommended to allocate a separate VLAN for iSCSI traffic if the switch is used for a mixed type of traffic.
Directly-attached iSCSI
The design of such a “small data center” consists of one or two servers directly connected to the storage system, each with at least two links for fault tolerance: one to one storage controller and the other to the other. At this stage, it is logical to use the free Software iSCSI Initiator. In case of increase in hosts, you must either add ports to the storage or install switches. Depending on the storage model, there may be a different number of Ethernet ports. It is important to note that all Ethernet ports on NetApp FAS storages (no “dedicated” iSCSI ports) can be used for these types of traffic: iSCSI , NFS , CIFS ( SMB ), including at the same time.
- The positive side is the relative cheapness (no need for specialized adapters for hosts, no need for switches) and simplicity.
- The negative side of this solution will be low scalability and additional load on the host CPU performing the Software iSCSI Initiator function.

| Attribute | Value |
|---|---|
| Fully redundant | Yes |
| Type of network | None, direct-attached |
| Different host operating systems | Yes, with multiple-host configurations |
| Multipathing required | Yes |
| Type of Storage configuration | HA pair |
Switched iSCSI
In such a scheme, you must have at least two links from each node, each link connected via different switches. This will provide full fault tolerance at the output of the controller, switch or path. At this stage, you can still use the Software iSCSI Initiator or a combination with a dedicated iSCSI HBA (which would load the load from the host CPU ).
- Upgrading from a Direct-Attached configuration is relatively simple and can be performed without disabling the service; you may need to add a couple of additional paths after connecting the switches. In case you need to install an iSCSI HBA adapter, stopping the host is inevitable.
- The positive side of this design can be attributed to the relatively high scalability, ease of configuration and low cost of the network.
- The negative side of this solution is the loss of frames in the network leading to an increase in response between the storage and the host. For smaller configurations, it will provide a more than acceptable response level.

| Attribute | Value |
|---|---|
| Fully redundant | Yes |
| Type of network | Multi-network |
| Different host operating systems | Yes, with multiple-host configurations |
| Multipathing required | Yes |
| Type of Storage configuration | HA pair |
iSCSI 2.0
Like Switched iSCSI , in the case of iSCSI 2.0 , switches are used, but they must support DCB . This design will also require network adapters that support DCB on both the host and the storage. Thus, DCB should be supported all the way through iSCSI traffic. DCB is also known as Lossless Ethernet , it provides guaranteed frame delivery, increasing reliability, performance, and responsiveness to FC level. It is important to note that DCB supports all converged Ethernet ports on NetApp FAS storages (no “dedicated” iSCSI or FCoE ports) and can be used for all types of traffic: iSCSI (2.0), FCoE , NFS , CIFS ( SMB ), including and at the same time. CNA (HBA) QLogic 8300 adapters for working with DCB are supported on the host, this adapter allows offloading the load from the host CPU providing a low response speed of the storage. Some additional features of switches can improve the already low response rate for iSCSI , for example CLEAR-Flow .
- Thus, to switch from Switched iSCSI to iSCSI 2.0, it is necessary to replace network cards and switches with DCB compatible ones, leaving the network topology and multipaging scheme as it were. DCB is configured on network cards and switches. Remaining after the replacement of the old "ordinary" switches can be used to connect clients to servers. Upgrading from a switched iSCSI configuration without a pause in service is possible provided that the iSCSI HBA adapter is already installed on the host. In case you need to install an iSCSI HBA adapter, stopping the host is inevitable.

The advantages of iSCSI over DCB include:
- Relative ease of switch configuration
- Low response from storage to application
- Ability to use QoS in mixed traffic environments
- Prevents frame loss and increases the viability of Ethernet frames
- Increased performance of IP protocols including iSCSI .
Disadvantages of iSCSI over DCB:
- The architecture provides for a small number of hops from the host to the repository; ideally, there should be one hop.
- The need to calculate the level of oversubscription and compliance with the Fan-In ratio in case of an increase in the number of hops.
| Attribute | Value |
|---|---|
| Fully redundant | Yes |
| Type of network | DCB , Dual fabric |
| Different host operating systems | Yes, with multiple-host configurations |
| Multipathing required | Yes |
| Type of Storage configuration | HA pair |
- Backup option : All converged NetApp FAS ports can be easily modified by simply replacing SFP + modules, instead of Ethernet switches with DCB for iSCSI , you can always buy FC switches or use the same Ethernet switches with DCB to connect via FCoE , and since NetApp FAS supports access to the same moon for all these protocols, switching between FC / FCoE / iSCSI protocols occurs without data loss or conversion. The negative side of FC and FCoE can be attributed to the relatively high complexity in configuring switches. Choosing between FC and FCoE pay attention to the article " FCoE: The Future of the Fiber Channel " and the article " Consolidation of LAN and SAN data center networks based on the DCB and FCoE protocols "
FAS scaling
There are several ways to grow NetApp FAS systems:
- Add shelves with disks (without stopping)
- Combine the system into a cluster with the same or older business (without stopping)
- Convert the FAS255x controller to the shelf, purchase new controllers, switch the converted and all other shelves to new controllers (idle time is not avoided)
- Cluster, migrate data online, bring the old system out of the cluster, convert FAS255x to the shelf and switch the old shelves to the new system (without stopping)
findings
Thus, the iSCSI protocol with NetApp FAS storage can be the basis for starting growth from the “small data center” to the “large” one, gradually and simply updating the network design, observing a single concept of addressing and multipassing. When updating, the equipment that has already been purchased is utilized to the maximum. Each upgrade step increases the scalability of the data center infrastructure, its speed and reduces the response for applications, while at the same time fulfilling costs as needed. Thanks to the versatility of FAS storage systems , support of advanced data center development trends and the ability to mutually replace protocols (or use them all at the same time including the same ports), easy scalability, it is a good investment investment for both small and “large data centers”.
Best practics
Learn more about network topology and zoning recommendations for NetApp in pictures .
It is very important to follow best practices when configuring the infrastructure and check the compatibility matrix for maximum performance and fault tolerance:
TR-3441 Windows Multipathing Options with Data ONTAP: Fiber Channel and iSCSI
WP-7071: "How Do I Get to Ethernet from Here?"
TR-3519: "The Road to 10-Gigabit Ethernet"
WP-7046: "Ethernet Storage"
TR-3441: "iSCSI Multipathing Possibilities on Windows with Data ONTAP"
TR-3163: "Data Protection for Network-Attached Storage over IP / Ethernet Networks"
WP-7052: “Converged Enhanced Ethernet — Good for iSCSI SANs”
TR-3519: "The Road to 10-Gigabit Ethernet"
iSCSI 10Gig Performance Tuning With Windows Server
iSCSI Configuration and Provisioning for Windows
TR-3802 Ethernet Storage Best Practices
TR-4182 Ethernet Storage Design Considerations and Best Practices
Best Practices for Network Configuration with NetApp Storage Systems
NetApp Verifying that DCB is configured correctly
NetApp SAN Design and SAN Fundamentals on Data ONTAP courses are available at the NetApp Academy.
Sources:
sniaesfblog.org/?p=210&cpage=1#comment-82839
blogs.cisco.com/datacenter/the-napkin-dialogues-lossless-iscsi
www.storage-switzerland.com/Articles/Entries/2012/1/17_iSCSI_2.0_-_Using_Data_Center_Bridging_To_Enhance_iSCSI.html
www.snia.org/sites/default/education/tutorials/2010/spring/networking/GaryGumanow-JasonBlosil_iSCSI_Lossless_Ethernet_DCB.pdf
www.slideshare.net/extreme-muk/i-scsi-extremeintelnetappclearflow
Comments on errors and suggestions for changes in the text please send to the LAN .
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/258881/
All Articles