Reach: GPS accurate to centimeter
Modern satellite navigation technologies provide location determination with an accuracy of about 10-15 meters. In most cases, this is sufficient, however, in some cases more is needed: for example, an autonomous drone, moving rather quickly over the earth's surface, will feel uncomfortable in the cloud from the coordinates with meter errors.
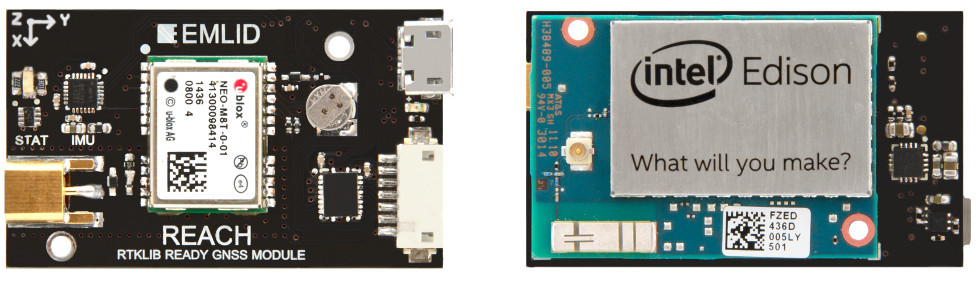
To clarify satellite data, differential systems and RTK (real-time kinematics) technologies are used, but until recently, such devices were expensive and cumbersome. Recent advances in digital technology in the face of the Intel Edison microcomputer helped solve this problem. So, meet: Reach - the first compact high-precision GPS receiver, very affordable, and, moreover, developed in Russia.
First, let's talk a little about differential technologies that allow Reach to achieve such high results. They are well known and widely implemented. Differential navigation systems (DNSS) improve the accuracy of the positioning and speed of mobile users by providing measurement data or corrective information from one or more base stations.
The coordinates of each base station are known with high accuracy, so that the station measurement data serves to calibrate the data of adjacent receivers. The receiver can calculate the theoretical distance and propagation time of the signal between itself and each satellite. When these theoretical values are compared with observational data, the differences are errors in the received signals. Corrective information (RTCM data) is derived from these differences.
')
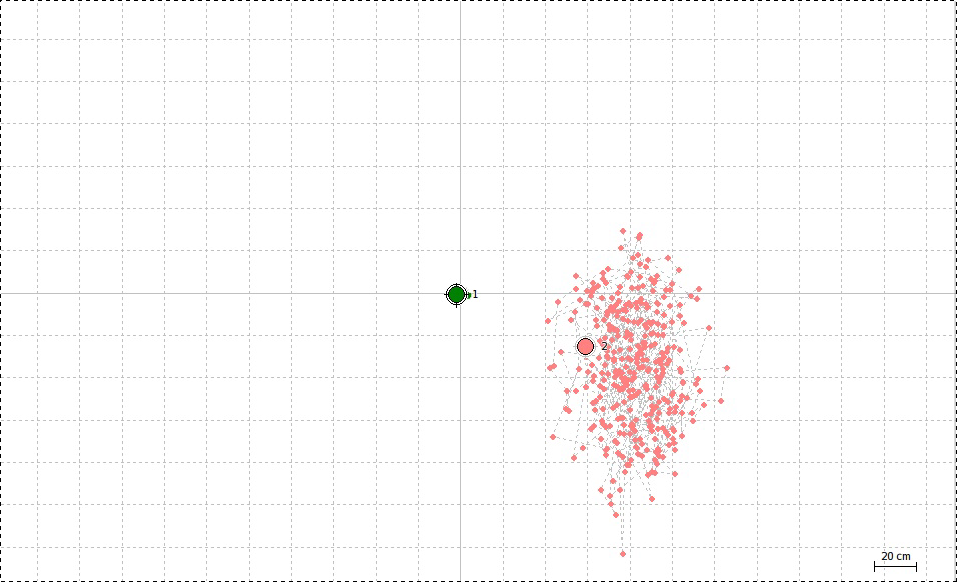
Accuracy of coordinates with Reach. Pay attention to the scale.
Corrective information can be obtained from a Reach device from two sources. Firstly, from the public network of base stations via the Internet via the NTRIP (Networked Transport of RTCM via Internet Protocol) protocol, implementing the idea described above with reference to the global computer network. Secondly, using the second Reach, which occupies a fixed position near the first one and is thus a base station in terms of a DSSS. The second option is preferable (the accuracy of the DSSS drops dramatically with increasing distance between the receiver and the BS) - it is not by chance that during the crowdfunding campaign on the Indiegogo website, the creators of Reach offer to buy a set of two devices with the first position.
The device specifications are shown in the table below. As you can see, it consists of 3 parts in hardware: Intel Edison computer, which runs Linux and RTK software RTKLIB; U-blox NEO-M8T GPS receiver and Tallysman TW4721 antenna. Please note that the receiver supports all existing satellite systems: GPS, GLONASS, Beidou and QZSS. All this set of software and hardware components provides an impressive accuracy in determining the coordinates: up to 2 cm!
| Satellite receiver | U-blox NEO-M8T - 72 channels, up to 18Hz, supports GPS / QZSS L1 C / A, GLONASS L10F, BeiDou B1, SBAS L1 C / A: WAAS, EGNOS, MSAS, Galileo-ready E1B / C |
| Computer platform | Intel Edison - dual-core 500MHz |
| Interfaces | I2C, UART, GPIO, TimeStamp, OTG USB, Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, GNSS |
| Antenna | Tallysman TW4721 Dual Feed GPS / BeiDou / Galileo / GLONASS |
| Dimensions | 26x36 mm |
| Weight | 13 g |
The creators of Reach, the company Emlid, successfully performed on indiegogo: in less than a month almost the requested amount was collected. Hence, the project will certainly be implemented. You still have time to pre-order and be among the first to get a brand new navigation device. Distribution of goods is scheduled for July.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/258779/
All Articles