Two opposite directions VIDEO ANALYTICS: "hard" and "flexible", who is stronger?
The problem - reducing redundant video information - is extremely relevant for today's video surveillance, the amount of data that is not able to digest people. Only everyone decides it differently: some by searching for important points, others by filtering minor ones. What is more effective?

In previous articles, as soon as I touched on this topic, I immediately got into a discussion with apologists for video analytics. Even the founders of classical video analytics - former Intel programmers - have fixed their positions on this issue, for which many thanks! On this portal there are many who are considered to be luminaries in this area - it’s a sin not to use this. I think to start with them. In this article, I will only outline the differences - and I hope for a professional discussion. And then we'll see how events will develop.
Unfortunately, I can’t afford to give links to the sites of “analysts” so that they don’t ban me before the discussion, so I’ll try to describe the basic concepts in my own words, well, and a little using Wikipedia. After studying a huge number of domestic and foreign companies, I can identify two specific areas of video analysis used in video surveillance to reduce information:
')
1. Hard video analytics is a classic that is based on the good old Intel Open CV library, but which Intel no longer develops. In most of its base - the object detector. This algorithm localizes in a stream of video frames changing closed areas on certain grounds. We have already reviewed it on the example of the company " Sinesis ". These “objects” are trying to analyze the video surveillance program in order to calculate useful goals in them: people, cars ... When they are detected, the main idea is an analysis of actions, movements and, ultimately, the resulting behavioral pattern suitable for interpretation in a social and criminal sense.

2. Flexible video analytics is a younger area of knowledge that appeared, apparently, in the Russian countries. Wikipedia calls it video semantics and interprets it like this: “Video semantics is a brief logical presentation of video information by decomposing it into semantic units (video pieces), each of which has its own complete meaning, which differs from the previous and subsequent video segments. This is a special direction of video analytics - the so-called flexible video analytics, which does not have rigid parameters and precise formalization. ”
In general, on the move after rereading, the first option suits me better. Still, it is necessary to clearly and immediately say who is preparing the terrorist attack. In addition, this is what our “comrades” demand, for billions of procuring systems of intelligent video surveillance to safe cities and subways across the country. It only scares that the results are often negative. But let's leave politics to politicians.
So, what is the opposite of these two approaches? If you listen to the text - that's it. The first are looking for crime in the video stream or the actions of people (cars) that pose a threat. The second - deny this possibility, appealing to the theory of building the world. Sorry if I expressed my incorrect attitude to the descriptions, which usually begin with the fact that hard video analytics is impossible in principle. Strangely enough, I also started my articles on video analytics with this - but I was based only on specific examples of specific manufacturers. It does not mean that I will end up with the fact that flexible video analytics is something better. Felting - so blame everything, a lot of wood!
Well, here, I have already outweighed my attitude towards being tough, saying that it suits me better - I need to correct the scales, I will say something about the other: I like the word “flexible” more, it is more beautiful!
So, the first ones formalize the behavior of objects (I don’t know if they can do it), others cannot (well, or don’t want to). The first shout to the guard - look, fight! The second - pay attention, something happened! Again, the first are drawn in the best light - more understandable. Although, but the second sounds somehow more honest.
"Hard" are looking for important, "flexible" remove unnecessary. After this phrase, I suddenly felt that there was no difference between them. However, they themselves consider themselves to be class technological enemies.
We have already said that tough video analytics is based on the classification of objects: man, car, cat ... But how is she looking for crime? The overwhelming number of companies offer virtual line intersection algorithms, a crowd of people, various options for moving targets. Those. most often you need to clearly know the “boundaries of the permitted” - specific places on the object, the intersection of which is a crime or a reason to check. We will talk about all this later, now only about comparing the methods of the approach. But in all cases in the "hard" it is assumed that the ways and means of unauthorized actions are defined.
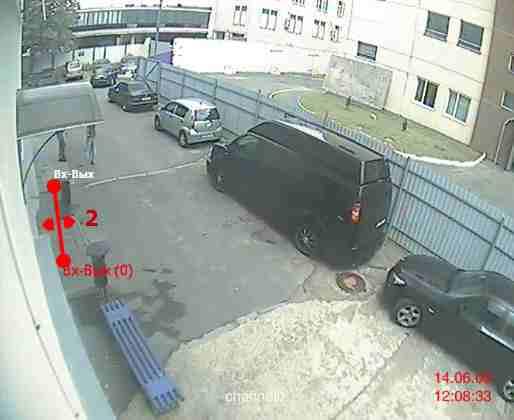

Proponents of agile video analytics ridicule the question itself with phrases like “Do you know exactly how you will be killed?”. In the "flexible" do not bind to anything, do not expect anything, give their security completely into the hands of the computer. And this phrase is concerned! And how does flexible video analytics generally protect human peace? According to Wikipedia, “video semantics tracks the characteristics of video content as a result of analyzing statistical changes,” i.e. The basis is STATISTICS. Take, say, 1000 frames, it is checked whether there is anything new or unusual in any of them, or their character of changes completely falls under the previous 1000, or even the previous 100,000 frames. Suppose all people always walked straight along this road, and someone suddenly crossed the lawn. Or just jumped where no one jumped. He ran sharply ...

In the middle of the road I crouched, lay down, pulled the trunk out of my pocket ... - any non-standard. Here I am confused only by the phrase of one of the company “got the trunk out of a pocket or handkerchief”, i.e. There is no threat formalization. But let's not press anyone yet.
By the way, in “tough” all the moments of determining the class of a target and its actions require quite difficult, in my opinion, settings, and any camera failure (from wind, vibration, etc.) or rearrangement of large objects on the ground entail failure functioning. And in the “flexible” there are no settings at all, as some manufacturers claim, which, judging by the logic of its work, may correspond to the truth.
Hard video analytics, as we have already considered, is very sensitive to interference, especially street. About flexible Wikipedia says: "The absence of hard-coded parameters and accurate formalization protects against interference, as they are included in the overall analysis and are subtracted from themselves as a result of the difference in statistical changes." Well, yes, if the spider sat on the camera, then this spider will be on all frames - theoretically there shouldn't be any changes in the statistics. If not crawl another spider.
Something I will throw from the previous discussion about low-contrast purposes. It means that the villain is crawling in the camouflage and merges with the terrain, but it is necessary to calculate it. In order to classify a human figure, an object detector needs greater sensitivity and greater contrast, otherwise it will take a lot of scattered small targets, some areas of the camouflage will still merge completely - well, since we are talking about a serious low contrast. Thus, a tough video analytics in this matter is probably inferior to a flexible one - for which the classification of the goal is not important in principle. But how much is this significant? While I threw this topic only for discussion, there is no conclusion here.
Another discussion topic is a solvable transaction. For example, the definition of a cluster of people falls under both the rigid and flexible video analytics. Both of them - according to the statements - cope with this issue. Only by different methods. So which one is more effective?

The number of questions here is still a lot, I will try not to torment the length of the article, the rest will be discussed later. (If not banned.)

In previous articles, as soon as I touched on this topic, I immediately got into a discussion with apologists for video analytics. Even the founders of classical video analytics - former Intel programmers - have fixed their positions on this issue, for which many thanks! On this portal there are many who are considered to be luminaries in this area - it’s a sin not to use this. I think to start with them. In this article, I will only outline the differences - and I hope for a professional discussion. And then we'll see how events will develop.
Unfortunately, I can’t afford to give links to the sites of “analysts” so that they don’t ban me before the discussion, so I’ll try to describe the basic concepts in my own words, well, and a little using Wikipedia. After studying a huge number of domestic and foreign companies, I can identify two specific areas of video analysis used in video surveillance to reduce information:
')
1. Hard video analytics is a classic that is based on the good old Intel Open CV library, but which Intel no longer develops. In most of its base - the object detector. This algorithm localizes in a stream of video frames changing closed areas on certain grounds. We have already reviewed it on the example of the company " Sinesis ". These “objects” are trying to analyze the video surveillance program in order to calculate useful goals in them: people, cars ... When they are detected, the main idea is an analysis of actions, movements and, ultimately, the resulting behavioral pattern suitable for interpretation in a social and criminal sense.

2. Flexible video analytics is a younger area of knowledge that appeared, apparently, in the Russian countries. Wikipedia calls it video semantics and interprets it like this: “Video semantics is a brief logical presentation of video information by decomposing it into semantic units (video pieces), each of which has its own complete meaning, which differs from the previous and subsequent video segments. This is a special direction of video analytics - the so-called flexible video analytics, which does not have rigid parameters and precise formalization. ”
In general, on the move after rereading, the first option suits me better. Still, it is necessary to clearly and immediately say who is preparing the terrorist attack. In addition, this is what our “comrades” demand, for billions of procuring systems of intelligent video surveillance to safe cities and subways across the country. It only scares that the results are often negative. But let's leave politics to politicians.
So, what is the opposite of these two approaches? If you listen to the text - that's it. The first are looking for crime in the video stream or the actions of people (cars) that pose a threat. The second - deny this possibility, appealing to the theory of building the world. Sorry if I expressed my incorrect attitude to the descriptions, which usually begin with the fact that hard video analytics is impossible in principle. Strangely enough, I also started my articles on video analytics with this - but I was based only on specific examples of specific manufacturers. It does not mean that I will end up with the fact that flexible video analytics is something better. Felting - so blame everything, a lot of wood!
Well, here, I have already outweighed my attitude towards being tough, saying that it suits me better - I need to correct the scales, I will say something about the other: I like the word “flexible” more, it is more beautiful!
So, the first ones formalize the behavior of objects (I don’t know if they can do it), others cannot (well, or don’t want to). The first shout to the guard - look, fight! The second - pay attention, something happened! Again, the first are drawn in the best light - more understandable. Although, but the second sounds somehow more honest.
"Hard" are looking for important, "flexible" remove unnecessary. After this phrase, I suddenly felt that there was no difference between them. However, they themselves consider themselves to be class technological enemies.
We have already said that tough video analytics is based on the classification of objects: man, car, cat ... But how is she looking for crime? The overwhelming number of companies offer virtual line intersection algorithms, a crowd of people, various options for moving targets. Those. most often you need to clearly know the “boundaries of the permitted” - specific places on the object, the intersection of which is a crime or a reason to check. We will talk about all this later, now only about comparing the methods of the approach. But in all cases in the "hard" it is assumed that the ways and means of unauthorized actions are defined.

Proponents of agile video analytics ridicule the question itself with phrases like “Do you know exactly how you will be killed?”. In the "flexible" do not bind to anything, do not expect anything, give their security completely into the hands of the computer. And this phrase is concerned! And how does flexible video analytics generally protect human peace? According to Wikipedia, “video semantics tracks the characteristics of video content as a result of analyzing statistical changes,” i.e. The basis is STATISTICS. Take, say, 1000 frames, it is checked whether there is anything new or unusual in any of them, or their character of changes completely falls under the previous 1000, or even the previous 100,000 frames. Suppose all people always walked straight along this road, and someone suddenly crossed the lawn. Or just jumped where no one jumped. He ran sharply ...

In the middle of the road I crouched, lay down, pulled the trunk out of my pocket ... - any non-standard. Here I am confused only by the phrase of one of the company “got the trunk out of a pocket or handkerchief”, i.e. There is no threat formalization. But let's not press anyone yet.

By the way, in “tough” all the moments of determining the class of a target and its actions require quite difficult, in my opinion, settings, and any camera failure (from wind, vibration, etc.) or rearrangement of large objects on the ground entail failure functioning. And in the “flexible” there are no settings at all, as some manufacturers claim, which, judging by the logic of its work, may correspond to the truth.
Hard video analytics, as we have already considered, is very sensitive to interference, especially street. About flexible Wikipedia says: "The absence of hard-coded parameters and accurate formalization protects against interference, as they are included in the overall analysis and are subtracted from themselves as a result of the difference in statistical changes." Well, yes, if the spider sat on the camera, then this spider will be on all frames - theoretically there shouldn't be any changes in the statistics. If not crawl another spider.
Something I will throw from the previous discussion about low-contrast purposes. It means that the villain is crawling in the camouflage and merges with the terrain, but it is necessary to calculate it. In order to classify a human figure, an object detector needs greater sensitivity and greater contrast, otherwise it will take a lot of scattered small targets, some areas of the camouflage will still merge completely - well, since we are talking about a serious low contrast. Thus, a tough video analytics in this matter is probably inferior to a flexible one - for which the classification of the goal is not important in principle. But how much is this significant? While I threw this topic only for discussion, there is no conclusion here.
Another discussion topic is a solvable transaction. For example, the definition of a cluster of people falls under both the rigid and flexible video analytics. Both of them - according to the statements - cope with this issue. Only by different methods. So which one is more effective?

The number of questions here is still a lot, I will try not to torment the length of the article, the rest will be discussed later. (If not banned.)
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/258451/
All Articles