Java programmer cheat sheet 3. Java collections (standard, guava, apache, trove, gs-collections, and others)
Today I would like to talk about collections in Java. This topic is found in almost any technical interview by a Java developer, but not all developers have mastered all the collections of even the standard library, not to mention all the libraries with alternative implementations of the collections, such as guava, apache, trove and a number of others. Let's see what collections can be found in the Java world and what methods of working with them exist.
This article is useful for both beginners (to get a general understanding of what a collection is and how to work with them), as well as for more experienced programmers who may find something useful in it or simply structure their knowledge. Actually, the main thing is that you have at least a basic knowledge of collections in any programming language, since the article will not have an explanation of what a collection is in principle.
')
Naturally, almost everyone knows the main collections in the JDK, but still remember them, if you are sure that you already know everything about standard collections, you can safely skip everything in the spoilers until the next section.
1) JDK Collection Interfaces
2) A table with a very brief description of all collections
3) Obsolete collections in the JDK
4) Collections that implement the List interface
5) Collections that implement the Set interface (set)
6) Collections that implement the Map interface (associative array)
7) Collections based on Queue / Deque interfaces
8) Other collections
9) Methods of working with collections
10) How are different types of JDK collections inside arranged?
11)
1) Wrapper implementations – . .
2) Adapter implementations –
3) Convenience implementations – «-» .
4) — ( ) .
4)
5) Ordering
6) Runtime exceptions
7)
8)
, : guava, apache, trove gs-collections. ? Guava Apache Commons Collections Java , Trove — , . GS-collections — github'e (>1300 ), «» guava. .
, , (: , - ).
( ) :
1) Guava — ,
, «» -
, Collections , .
.
2) Apache Commons Collections — «» guava,
, Java, wrapper'
. map'
.
3) Trove — ,
( ),
.
4) GS-collections — ,
-.
.
Here I will try to briefly consider what new interesting types of collections can be found in different libraries:
Official information: documentation , source codes , javadoc .
How to connect to the project:
Google has developed a number of interesting additions to existing collections, which are very, very useful if you can
use the guava library in your project. It can be said that these collections have long become the de facto standard
for most Java projects, so for any experienced developer it’s important to know them, even if for some reason
reasons can not use them in their projects, often at interviews you can hear questions on guava
collections.
Let's look at them in more detail. First, consider the interfaces of the main collections and the class groups in guava.
Note : if the table does not fit entirely, try zooming out the page or open it in another browser.
Official information : documentation , source codes , user documentation , javadoc .
How to connect to the project:
Note : if the table does not fit entirely, try zooming out the page or open it in another browser.
Unlike other libraries of alternative collections, Trove does not offer any new unique types.
collections, but it offers optimization of existing:
First, as you know, primitive Java types cannot be added to standard collections, only their wrappers, which dramatically
increases memory usage and somewhat degrades collection performance. Trove offers a collection of collections
whose keys and values may contain primitive types.
Secondly, standard collections are often not implemented in the most optimal way to consume memory, for example, each HashMap element is stored in a separate object, and HashSet is a HashMap that stores fake objects instead of keys. Trove offers its own implementation of such collections based on arrays and open addressing, which can significantly reduce the required memory and in some cases improve performance.
Update: In the comments to the article, it was suggested that Trove is poorly used in new projects, as it is inferior in all respects to fastutil or GS (number of bugs, full interface coverage, performance, support activity, etc.). Unfortunately, I don’t have the opportunity to conduct a full-fledged analysis / comparison of Trove with fastutil and GS, so I can’t check this opinion, just consider it when choosing a library of alternative collections.
Official information: documentation , source codes , javadoc .
How to connect to the project:
The main feature of this library is that it is illogical and ugly that the methods for processing collections (sorting, searching) are not added to the collection classes themselves, but are used by Collections.sort, etc. methods, so GS-collections offered the idea of “rich” collections (rich collections), which store all the methods of processing, searching, sorting, that is, instead of Collections.sort (list), it is simply called list.sort. Therefore, the library offers its analogues of standard collections and, in addition, a number of new collections.
Official information : documentation , source codes , user documentation , javadoc .
How to connect to the project:
Let's take a very brief look at this library for working with collections of primitive types.
More information can be found: documentation , source codes , javadoc
In addition to Trove and Fastutil, there are several other well-known libraries that implement collections of primitive types and faster analogs of standard collections:
1) HPPC - High Performance Primitive Collections for Java, also provides primitive collections similar to those from the JDK,
2) Koloboke (another name HFTC) - as can be understood from the name of this library of primitive types developed by a Russian programmer (Roman Leventov) in the framework of the OpenHFT project. The library also serves to implement high-performance primitive collections.
If you are interested in comparing the performance of different libraries, I advise you to look at this article , but you need to take into account that only the HashMap collections were tested and under certain conditions. In addition, they measured only the speed of work, not taking into account the memory occupied (for example, HashMap jdk can take much more memory than analogs from trove), and sometimes the memory can be even more important than performance.
Update: In the comments to the article, it was suggested that Trove is poorly used in new projects, as it is inferior in all respects to fastutil or GS (number of bugs, full interface coverage, performance, support activity, etc.). Unfortunately, I don’t have the opportunity to conduct a full-fledged analysis / comparison of Trove with fastutil and GS, so I can’t check this opinion, just consider it when choosing a library of alternative collections.
4.1 Implementing a multiset (MultiSet / Bag) in guava, Apache Commons Collections and GS libraries
So, a multiset is a set that preserves not only the fact that there are elements in the set, but also the number
occurrences in it. In the JDK, it can be emulated by the Map construct.
<T, Integer>, but, naturally, specialized collections allow using significantly less code. Compare
Which implementations of this collection are offered by different libraries:
Note : if the table does not fit entirely, try zooming out the page or open it in another browser.
There is a task : a line of the text “Hello World! Hello All! Hi World! ”, You need to disassemble it into separate
words where the separator is just a space, save to some collection and output the number of entries for each
words, the total number of words in the text and the number of unique words.
Let's see how to do this with
1. Different Multiset options from Guava:
2. Bag Apache Commons Collections:
3. Bag GS Collections:
4. , JDK multiSet HashMap
, Multimap map, .
.
, — ,
— , JDK
JDK .
: , .
, Apache Commons Collections ,
. guava ,
map' . GS Collections
multimap Bag (HashBagMultimap), . multiset multimap.
: «Hello World! Hello All! Hi World!»,
,
, Hello ..
1. Multimap Guava:
2. MultiValueMap Apache Commons Collections:
3. Multimap GS Collections:
4. , JDK multiMap HashMap
BiMap , HashBiMap guava GS Collections
BidiMap Apache Commons Collections. HashBiMap, guava Enum
, EnumHashBiMap EnumBiMap, Apache Commons Collections
, .
: ,
- , .
1. BiMap Guava:
2. C BidiMap Apache Commons Collections:
3. C HashBiMap GS Collections:
4. , JDK
, JDK. , , ( ), , .
Guava gs-collections new, jdk.
5.1.1) (List)
5.1.2) (set)
5.1.3) Map
, : collection — Collection, iterable — Iterable, list — List, orderedIterable mutableList GS (orderedIterable — , mutableList — )
:
:
( Java, ):
1) () — , ,
— — ,
— — , ,
— — ,
, ,
— —
,
2) (Stack) — , «LIFO» (« — »). AT
, /.
3) (Queue) — , «FIFO» (« — »). AT
/.
4) (Double-ended queue) — ,
.
5) (. priority queue) — ,
. ,
— (heap) — , ,
6) (), (Associative array, Dictionary) — ,
«— »
— - (hashtable) — , ,
— - (Multimap multihash) — -,
,
— - - (bi-map) — -,
, ,
— - (hashtable) — -, ,
— - (hashtable) — -, ,
7) — ,
,
— — , ,
,
— — , , ,
— — , , ,
8) — 1 0,
9) —
,
10) — , ,
11) — ,
Java :
: , .
, , , . , ( ) , - .
github' .
, :
1. java.util.concurrent.* tutorial
2. Trove library: using primitive collections for performance
3. Java performance tuning tips
4. Large HashMap overview
5. Memory consumption of popular Java data types
6. , , , javadoc
PPS I also advise you to look at my opensource project [useful-java-links] (https://github.com/Vedenin/useful-java-links/tree/master/link-rus) - perhaps the most comprehensive collection of useful Java libraries, frameworks and Russian-language instructional videos. There is also a similar [English version] (https://github.com/Vedenin/useful-java-links/) of this project and start the opensource subproject [Hello world] (https://github.com/Vedenin/useful-java -links / tree / master / helloworlds) for preparing a collection of simple examples for different Java libraries in one maven project (I will be grateful for any help).

This article is useful for both beginners (to get a general understanding of what a collection is and how to work with them), as well as for more experienced programmers who may find something useful in it or simply structure their knowledge. Actually, the main thing is that you have at least a basic knowledge of collections in any programming language, since the article will not have an explanation of what a collection is in principle.
')
General table of contents 'cheat sheets'
1. JPA and Hibernate in questions and answers
2. Three hundred fifty most popular non-mobile Java opensource projects on github
3. Collections in Java (standard, guava, apache, trove, gs-collections, and others
4. Java Stream API
5. Two hundred and fifty Russian-language teaching videos of lectures and reports on Java.
6. List of useful links for Java programmer
7 Typical tasks
7.1 Optimum way to convert an InputStream to a string
7.2 The most productive way to bypass the Map, count the number of occurrences of the substring
8. Libraries for working with Json (Gson, Fastjson, LoganSquare, Jackson, JsonPath and others)
2. Three hundred fifty most popular non-mobile Java opensource projects on github
3. Collections in Java (standard, guava, apache, trove, gs-collections, and others
4. Java Stream API
5. Two hundred and fifty Russian-language teaching videos of lectures and reports on Java.
6. List of useful links for Java programmer
7 Typical tasks
7.1 Optimum way to convert an InputStream to a string
7.2 The most productive way to bypass the Map, count the number of occurrences of the substring
8. Libraries for working with Json (Gson, Fastjson, LoganSquare, Jackson, JsonPath and others)
I. Standard Java Collection Library
Naturally, almost everyone knows the main collections in the JDK, but still remember them, if you are sure that you already know everything about standard collections, you can safely skip everything in the spoilers until the next section.
Beginner's Note on Collections
Sometimes it is quite difficult for beginners (especially if they came from other programming languages) to understand that only references / pointers are stored in the Java collection and nothing more. It seems to them that when calling add or put objects are actually stored somewhere inside the collection, this is true only for arrays, when they work with primitive types, but not for collections that store only links. Therefore, very often the beginners begin to answer something like “It depends on the type of objects that they store in” to interview questions like “Is it possible to call the exact size of the ArrayList collection”? This is absolutely not true, since collections never store objects themselves, but only links to them. For example, you can add the same object to the List a million times (more precisely, create a million references to one object).
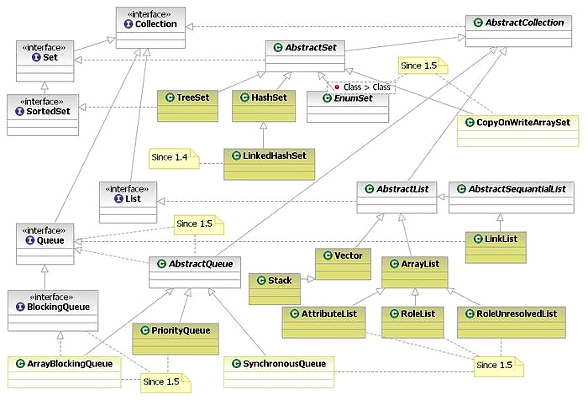
1) JDK Collection Interfaces
JDK Collection Interfaces
Collection interfaces
Interfaces from the java.util.concurrent package
If you are interested in more detailed information about interfaces and collections from java.util.concurrent I advise
read here this article .
| Title | Description |
|---|---|
| Iterable | An interface means that the collection has an iterator and can be circumvented with for (Type value: collection). There are almost all collections (except Map) |
| Collection | The main interface for most collections (except Map) |
| List | The list is an ordered collection, also known as a sequence. (sequence). Duplicate elements in most implementations are allowed. Allows access by item index Extends the Collection interface. |
| Set | Interface that implements work with sets (similar to mathematical sets), duplicating Items are prohibited. It may or may not be orderly. Extends the Collection interface. |
| Queue | A queue is a collection designed to store objects before processing, in contrast to the usual operations on collections, a queue provides additional methods for adding, retrieving, and viewing. Fast access on an index of an element, as a rule, does not contain. Extends the Collection interface |
| Deque | Two-way queue, supports adding and removing items from both ends. Expands Queue interface. |
| Map | Works with matching key - value. Each key corresponds to only one value. AT unlike other collections does not extend any interfaces (including Collection and Iterable) |
| SortedSet | Automatically sorted set, or in natural order (for details, see Comparable interface), or using the Comparator. Extends the Set Interface |
| SortedMap | This is a map whose keys are automatically sorted, either in natural order, or using comparator Extends the Map interface. |
| NavigableSet | This is SortedSet, to which additionally added methods for finding the closest value to the specified search value. NavigableSet can be accessed and accessed or in order. descending values or in ascending order. |
| NavigableMap | This is SortedMap, to which additionally added methods for finding the closest value to the specified search value. Available for access and bypass either in descending order of values or in ascending order. |
Interfaces from the java.util.concurrent package
| Title | Description |
|---|---|
| BlockingQueue | A multi-threaded Queue implementation containing the ability to set the queue size, condition locks, various methods that handle overflows differently when adding or missing data when received (throw an exception, block the stream continuously or temporarily, return false, etc.) |
| TransferQueue | This multi-threaded queue can block the insertion stream until the receiving thread pulls the element out of the queue, so that it can be used to implement synchronous and asynchronous message passing between threads. |
| Blockingdeque | Similar to BlockingQueue, but for a two-way queue |
| Concurrentmap | Interface, extends the Map interface. Adds a number of new atomic methods: putIfAbsent, remove, replace, which make it easier and more secure to make multi-threaded programming. |
| ConcurrentNavigableMap | Extends the NavigableMap interface for the multi-threaded version. |
If you are interested in more detailed information about interfaces and collections from java.util.concurrent I advise
read here this article .
2) A table with a very brief description of all collections
A table with a very brief description of all the collections.
* - in fact, although BitSet is called Set'om, the Set interface does not inherit.
| Type of | Single threaded | Multithreaded |
|---|---|---|
| Lists |
|
|
Queues / Deques |
|
|
| Maps |
|
|
| Sets |
|
|
* - in fact, although BitSet is called Set'om, the Set interface does not inherit.
3) Obsolete collections in the JDK
Legacy Java Collections
Universal collections of general purpose, which are considered obsolete (legacy)
Specialized collections built on legacy collections
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Hashtable | Originally conceived as a synchronized analogue of HashMap, when it was not yet possible get the collection version using Collecions.synchronizedMap. At the moment, as a rule use ConcurrentHashMap. HashTable is slower and less thread-safe than synchronous HashMap, since it provides synchronism at the level of individual operations, and not entirely at the level collections. |
| Vector | Previously used as a synchronous version of ArrayList, but outdated for the same reasons as HashTable. |
| Stack | It used to be used as a queue, but since it is built on the basis of Vector, also considered obsolete. |
Specialized collections built on legacy collections
| Name | Based on | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Properties | Hashtable | As a data structure built on Hashtable, Properties is a rather outdated construction, it is much better to use a Map containing strings. Read more why Properties not recommended use can be found in this discussion . |
| UIDefaults | Hashtable | The collection that stores the default settings for the Swing component. |
4) Collections that implement the List interface
Collections that implement the List interface
Universal general purpose collections that implement the List:
Collections from the java.util.concurrent package
Highly specialized collections based on the List.
* - the size is given in bytes for 32 bit systems and Compressed Oops, where N is the capacity of the list
| Title | Based on | Description | The size* |
|---|---|---|---|
| ArrayList | List | Implementing a List Interface Based on a Dynamically Variable Array. In most cases, the best possible implementation of the List interface is memory consumption and performance. In extremely rare cases where frequent insertions are required in the beginning or middle of the list with very small by the number of moves through the list, LinkedList will win in performance (but I advise you to use TreeList from apache in these cases). If you are interested in the details of ArrayList I advise you to look at this article . | 4 * N |
| Linkedlist | List | Implementing a List of an interface based on a two-way linked list, i.e. when each item indicates the previous and next item. As a rule, it requires more memory and is worse in performance than an ArrayList, it makes sense to use only in rare cases when it is often necessary to insert / delete in the middle of the list with minimal movements in the list (but I advise you to use TreeList from apache in these cases). It also implements Deque interface. When working through the Queue interface, LinkedList acts as a FIFO queue. If you are interested in the details LinkedList I advise you to look at this article . | 24 * N |
Collections from the java.util.concurrent package
| Title | Based on | Description |
|---|---|---|
| CopyOnWriteArrayList | List | The implementation of the List interface, similar to ArrayList, but each time the list is modified, is created new copy of the entire collection. This requires very large resources with every change in the collection, However, this type of collection does not require synchronization, even if the collection is changed during iteration time. |
Highly specialized collections based on the List.
| Title | Based on | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Rolelist | ArrayList | Collection to store a list of roles (Roles). Highly specialized collection based on ArrayList with several additional methods |
| RoleUnresolvedList | ArrayList | Collection to store a list of unresolved roles (Unresolved Roles). Highly specialized ArrayList based collection with several additional methods |
| Attributelist | ArrayList | Collection for storing MBean attributes. A highly specialized collection based on ArrayList with several additional methods |
* - the size is given in bytes for 32 bit systems and Compressed Oops, where N is the capacity of the list
5) Collections that implement the Set interface (set)
Collections that implement the Set interface (set)
* - the size is given in bytes for 32 bit systems and Compressed Oops, where C is the capacity of the list, S is the size of the list
Highly specialized Set-based collections
Collections from the java.util.concurrent package
| Title | Based on | Description | The size* |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hashset | Set | Implementing a Set interface using hash tables. In most cases, the best possible implementation of the Set interface. | 32 * S + 4 * C |
| LinkedHashSet | Hashset | The implementation of a Set interface based on hash tables and a linked list. Ordered by adding a set that works almost as fast as HashSet. In general, it is almost the same as HashSet, only the order of iteration over the set is determined by the order of adding an element in set for the first time. | 40 * S + 4 * C |
| Treeset | NavigableSet | Implement the NavigableSet interface using a red-black tree. Sorted using Comparator or natural order, that is, traversal / iteration over the set will occur depending on the sorting rule. Based on TreeMap, just like HashSet is based on HashMap | 40 * S |
| Enumset | Set | A high-performance implementation of a Set vector based on a bit vector. All elements of an EnumSet object must belong to a single enum type. | S / 8 |
* - the size is given in bytes for 32 bit systems and Compressed Oops, where C is the capacity of the list, S is the size of the list
Highly specialized Set-based collections
| Title | Based on | Description |
|---|---|---|
| JobStateReasons | Hashset | A collection for storing information about print jobs (print job's attribute set). A highly specialized HashSet-based collection with several additional methods. |
Collections from the java.util.concurrent package
| Title | Based on | Description |
|---|---|---|
| CopyOnWriteArraySet | Set | Similarly, CopyOnWriteArrayList with each change creates a copy of the entire set, therefore recommended for very rare collection changes and thread-safe requirements |
| ConcurrentSkipListSet | Set | It is a multi-threaded analogue of the TreeSet |
6) Collections that implement the Map interface (associative array)
Collections that implement the Map interface
Universal general purpose collections that implement Map:
* - the size is given in bytes for 32 bit systems and Compressed Oops, where C is the capacity of the list, S is the size of the list
Collections from the java.util.concurrent package
| Title | Based on | Description | The size* |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hashmap | Map | Implementation of the Map interface using hash tables (works as a non-synchronous Hashtable, with support for keys and null values). In most cases, the best in performance and Memory Map implementation interface. If you are interested in the details of the HashMap device, I advise you to look at this article . | 32 * S + 4 * C |
| LinkedHashMap | Hashmap | The implementation of the Map interface, based on the hash table and the linked list, that is, the keys in the Map stored and managed in the order of addition. This collection works almost as fast as HashMap. It can also be useful for creating caches (see removeEldestEntry (Map.Entry)). If you are interested in the details of the device LinkedHashMap I advise you to look at this article . | 40 * S + 4 * C |
| Treemap | NavigableMap | Implementing NavigableMap with a red-and-black tree, that is, while traversing the collection, keys will be sorted in order, also NavigableMap allows you to search for the closest value to the key. | 40 * S |
| Weakhashmap | Map | Same as HashMap, but all keys are weak links (weak references), that is, garbage collected can remove objects keys and objects values if there are no other references to these objects. WeakHashMap is one of the easiest ways to take full advantage of weak links. | 32 * S + 4 * C |
| Enummap | Map | High-performance implementation of the Map interface based on a simple array. All keys in Only one enum can belong to this collection. | 4 * C |
| IdentityHashMap | Map | Identity-based Map, like HashMap, is based on a hash table, but unlike HashMap it never compares objects to equals, only on whether they are really the same and the same object in memory. This is, firstly, greatly accelerates the work of the collection, secondly, it is useful for protection against “spoof attacks” when equals objects are consciously generated by another object. Third, this collection has many uses for traversing graphs (such as deep copying or serialization), when you need to avoid processing a single object several times. | 8 * C |
* - the size is given in bytes for 32 bit systems and Compressed Oops, where C is the capacity of the list, S is the size of the list
Collections from the java.util.concurrent package
| Title | Based on | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Concurrenthashmap | Concurrentmap | Multi-threaded analogue of HashMap. All data is divided into separate segments and blocked only. individual segments when changing, which significantly speeds up work in a multi-threaded mode. Iterators never throw a ConcurrentModificationException for this type of collection. |
| ConcurrentSkipListMap | ConcurrentNavigableMap | It is a multithreaded analogue of TreeMap |
7) Collections based on Queue / Deque interfaces
Queue / Deque based collections
* - the size is given in bytes for 32 bit systems and Compressed Oops, where C is the capacity of the list, S is the size of the list
Multi-threaded Queue and Deque, which are defined in java.util.concurrent, require a separate article, so here I will not give them if you are interested in information about them I advise you to read this article
| Title | Based on | Description | The size* |
|---|---|---|---|
| ArrayDeque | Deque | Effective implementation of the Deque interface, based on a dynamic array, similar ArrayList | 6 * N |
| Linkedlist | Deque | The implementation of the List and Deque interface based on a two-way linked list, that is, when each item points to the previous and next item. When working through the Queue interface, LinkedList acts as a FIFO queue. | 40 * N |
| PriorityQueue | Queue | Unlimited priority queue based on heap (heap). Items sorted in natural order or using the comparator. Cannot contain null elements. |
* - the size is given in bytes for 32 bit systems and Compressed Oops, where C is the capacity of the list, S is the size of the list
Multi-threaded Queue and Deque, which are defined in java.util.concurrent, require a separate article, so here I will not give them if you are interested in information about them I advise you to read this article
8) Other collections
Other collections
| Title | Description | The size* |
|---|---|---|
| Bit set | Despite the name, BitSet does not implement the Set interface. BitSet is used for compact recording of an array of bits. | N / 8 |
9) Methods of working with collections
Methods of working with collections
Algorithms- The Collections class contains many useful statistical methods.
To work with any collection:
To work with lists:
In Java 8, there was also such a way of working with collections as stream Api, but we will look at examples of its use further in section 5.
To work with any collection:
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| frequency (Collection, Object) | Returns the number of occurrences of this item in the specified collection. |
| disjoint (Collection, Collection) | Returns true if there are no common items in the two collections. |
| addAll (Collection <? super T>, T ...) | Adds all elements from the specified array (or listed in parameters) to the specified collection. |
| min (Collection) | Return the minimum item from the collection |
| max (Collection) | Returning the maximum item from the collection |
To work with lists:
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| sort (List) | Sorting using the sorting algorithm by the compound (merge sort algorithm), whose performance in most cases is close to the performance of quick sorting (high quality quicksort), is guaranteed by O (n * log n) performance (unlike quicksort), and stability (unlike quicksort). Stable sorting is one that does not change the order of the same elements when sorting. |
| binarySearch (List, Object) | Search for an item in the list (list) using the binary search algorithm. |
| reverse (List) | Change the order of all elements of the list (list) |
| shuffle (list) | Shuffle all items in the list in random order |
| fill (List, Object) | Rewriting each item in the list with any value |
| copy (List dest, List src) | Copying one list to another |
| rotate (List list, int distance) | Moves all items in the list for a specified distance. |
| replaceAll (List list, Object oldVal, Object newVal) | Replaces all occurrences of one value with another. |
| indexOfSubList (List source, List target) | Returns the index of the first occurrence of the target list in the source list. |
| lastIndexOfSubList (List source, List target) | Returns the index of the last occurrence of the target list in the source list. |
| swap (List, int, int) | Swaps the items in the specified positions |
In Java 8, there was also such a way of working with collections as stream Api, but we will look at examples of its use further in section 5.
10) How are different types of JDK collections inside arranged?
How different types of JDK collections are arranged inside
11)
1) Wrapper implementations – . .
- Collections.unmodifiableInterface – , UnsupportedOperationException
- Collections.synchronizedInterface – , -, , .
- Collections.checkedInterface –
( ), type-safe view ,
ClassCastException .
generic' JDK ,
, .
2) Adapter implementations –
- newSetFromMap(Map) – Set Map .
- asLifoQueue(Deque) - view Deque Last In First Out (LIFO).
3) Convenience implementations – «-» .
- Arrays.asList – (list)
- emptySet, emptyList emptyMap – empty set, list, or
map - singleton, singletonList singletonMap – set, list map, ( -)
- nCopies – , n
4) — ( ) .
- AbstractCollection – Collection , , ( «bag» multiset).
- AbstractSet — Set .
- AbstractList – List , (random access), .
- AbstractSequentialList – List , , (sequential access), linked list.
- AbstractQueue — Queue .
- AbstractMap — Map .
4)
- Iterators – Enumeration , .
- Iterator – Enumeration , .
- ListIterator – Iterator lists, Iterator , , , , .
5) Ordering
- Comparable — , . sorted set map.
- Comparator — Represents an order relation, which can be used to sort a list or maintin order in a sorted set or map. Can override a type's natural ordering or order objects of a type that does not implement the Comparable interface.
6) Runtime exceptions
- UnsupportedOperationException – , .
- ConcurrentModificationException – iterators list iterators, ( ) , views , .
7)
- RandomAccess — -, ( ) . .
8)
- Arrays – , , , , . .
II.
, : guava, apache, trove gs-collections. ? Guava Apache Commons Collections Java , Trove — , . GS-collections — github'e (>1300 ), «» guava. .
, , (: , - ).
2.1
( ) :
1) Guava — ,
, «» -
, Collections , .
.
2) Apache Commons Collections — «» guava,
, Java, wrapper'
. map'
.
3) Trove — ,
( ),
.
4) GS-collections — ,
-.
.
Iii.
Here I will try to briefly consider what new interesting types of collections can be found in different libraries:
3.1 Alternative Guava Collections
Official information: documentation , source codes , javadoc .
How to connect to the project:
Maven, gradle
Maven
Gradle
<dependency> <groupId>com.google.guava</groupId> <artifactId>guava</artifactId> <version>18.0</version> </dependency> Gradle
dependencies { compile 'com.google.guava:guava:18.0' } Google has developed a number of interesting additions to existing collections, which are very, very useful if you can
use the guava library in your project. It can be said that these collections have long become the de facto standard
for most Java projects, so for any experienced developer it’s important to know them, even if for some reason
reasons can not use them in their projects, often at interviews you can hear questions on guava
collections.
Let's look at them in more detail. First, consider the interfaces of the main collections and the class groups in guava.
Note : if the table does not fit entirely, try zooming out the page or open it in another browser.
| Title | Description | Implementation examples | Examples of using |
|---|---|---|---|
| Immmtabletable Immmutablelist ImmutableSet … etc. | Although in the standard Java collection framework it is possible to make the collection immutable by calling Collections.unmodifiableCollection (unmodifiableList or unmodifiableMap), but this approach is not the most optimal because a separate type for immutable collections allows you to be sure that the collection is really immutable, instead of runtime errors, when you try to change the collection, there will be errors during the compilation of the project, besides, in the standard Java collection framework, immutable collections still spend resources on synchronization support for multi-threaded reading, etc. operations, while the ImmutableCollection guava "knows" that they are immutable and optimized with considering this. | JDK: ImmutableCollection , Immmutablelist , ImmutableSet , ImmutableSortedSet , ImmutableMap , Immmutablesortedmap Guava: ImmutableMultiset , ImmutableSortedMultiset , ImmutableMultimap , ImmutableListMultimap , ImmutableSetMultimap , ImmutableBiMap , ImmutableClassToInstanceMap , Immmutabletable | - if the public method returns a collection that other classes are guaranteed not to change, - if it is known that the values of the collection should never change again |
| Multiset | The collection is similar to Set, but allows you to additionally count the number of additions of the element. Highly useful for those tasks when you need not only to know if a given element is in a given set, but also count their number (the simplest example is counting the number of references to certain words in any text). That is, this collection is a more convenient version of the collection Map <T, Integer>, with methods specifically designed for such collections, allows very much reduce the amount of excess code in such cases. | HashMultiset TreeMultiset , LinkedHashMultiset Concurrenthashmultiset , ImmmutableMultiset SortedMultiset | - count the number of occurrences of words in the text - count the number of letters in the text - counting the count of any objects |
| Multimap | Practically any experienced Java developer faced the need to use structures like Map <K, List <V >> or Map <K, Set <V >>, and you had to write a lot of extra code, to simplify the work of the guava library, Multimap was entered, There are collections that allow you to simply work with cases when one key and many values for this key. Unlike constructions like Map <K, Set <V >>, Multimap provides a number of convenient functions for shortening code and simplifying algorithms. | ArrayListMultimap , HashMultimap , LinkedListMultimap , LinkedHashMultimap , TreeMultimap , ImmutableListMultimap , ImmutableSetMultimap | - implementation of one-to-many relationships, such as: teacher - students department - employees chief - subordinates |
| Bimap | Quite often there are situations when you want to create a Map'u working in both directions, that is, when a key and a value can be swapped (for example, a Russian-English dictionary, when in one case it is required to receive in the Russian word - English, in another vice versa in English-Russian). Usually this it is solved by creating two Map, where in one will be key1-key2, in the other key2-key1). BiMap allows solve this problem with just one collection. In addition, it eliminates problems and errors. synchronization when using two collections. | HashBiMap ImmutableBiMap , EnumBiMap , EnumHashBiMap | - dictionary for translation from one language to another and vice versa - any data conversion in both directions, |
| Table | This collection is used to replace collections of the type Map <FirstName, Map <LastName, Person >>, which are inconvenient to use. | HashBasedTable TreeBasedTable , Immmutabletable ArrayTable | - table, for example, as in Excel - any complex data structures with a large number of columns, |
| ClassToInstanceMap | Sometimes you need to store in Map'e not a key-value, but a type-value of this type, for this purpose this collection. That is, it is technically more convenient and safer analog Map <Class <? extends B>, B> | MutableClassToInstanceMap , ImmutableClassToInstanceMap . | |
| Rangeset | Collection to store different open and closed segments of numerical values, while the segments can unite with each other. | ImmmutableRangeSet , TreeRangeSet | Geometric cuts Time slices |
| Rangemap | A collection that is similar to a RangeSet, but the segments are never merged with each other. | ImmutableRangeMap , TreeRangeMap | Geometric cuts Time slices |
| Loadingcache | A collection similar to ConcurrentMap, but you can also specify the time each is stored element. A very convenient collection for organizing caches, counting the number of incorrect passwords for some period of time, etc. tasks | ForwardingLoadingCache , ForwardingLoadingCache.SimpleForwardingLoadingCache | caches storage erroneous password entry attempts etc. |
3.2 New types of collections from Apache Commons Collections
Official information : documentation , source codes , user documentation , javadoc .
How to connect to the project:
Maven, Gradle, Ivy
Maven
Gradle
Ivy
<dependency> <groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId> <artifactId>commons-collections4</artifactId> <version>4.0</version> </dependency> Gradle
'org.apache.commons:commons-collections4:4.0' Ivy
<dependency org="org.apache.commons" name="commons-collections4" rev="4.0"/> Note : if the table does not fit entirely, try zooming out the page or open it in another browser.
| Title | Description | Implementation examples | Examples of using |
|---|---|---|---|
| Unmodifiable | Interface similar to Immutable guava classes | UnmodifiableBag , UnmodifiableBidiMap , UnmodifiableCollection , UnmodifiableList , UnmodifiableMap etc. | in all cases when you need to create an unmodified collection |
| IterableMap | Analogue of the Map interface, but allowing to iterate over the Map directly without creating an entry set. Used by in almost all implementations of Map in this library. | Hashedmap LinkedMap ListOrderedMap and a number of others | Same as usual maps. |
| Orderedmap | Allows you to create maps that are ordered by adding, but not using sorting | LinkedMap ListOrderedMap | In cases when the List is used separately and the Map separately |
| Bididmap | Analogue of BiMap from Guava, that is, the ability to get a value by key, and a key by value | TreeBidiMap DualHashBidiMap , DualLinkedHashBidiMap , DualTreeBidiMap etc. | Any one-to-one conversions that need to be done both ways. |
| Bags | Analogue Multiset from Guava, that is, the ability to save the number of elements of each type | CollectionBag , HashBag SynchronizedBag , Treebag other | counting the count of any objects |
| BoundedCollection Boundedmap | Allows you to create dynamic collections, limited to some size from above | CircularFifoQueue , FixedSizeList , FixedSizeMap , LRUMap | in the case when you know for sure that there cannot be more than a certain number in the collection items |
| Multimap | Analogue Multimap from Guava, that is, the ability to save multiple items for one key | MultiValueMap | for collections with connections one key - many values |
| Trie | Collection for creating and storing ordered trees | PatriciaTrie | making trees |
| Treelist | Replacing ArrayList and LinkedList if you want to insert an element into the middle of the list, since this list stores data in a tree form, which allows on the one hand to relatively quickly obtain data on the index, on the other hand to quickly insert data into the middle of the list. | Treelist | replacing LinkedList with frequent additions / accents in the middle of the list |
3.3 Trove collections
Unlike other libraries of alternative collections, Trove does not offer any new unique types.
collections, but it offers optimization of existing:
First, as you know, primitive Java types cannot be added to standard collections, only their wrappers, which dramatically
increases memory usage and somewhat degrades collection performance. Trove offers a collection of collections
whose keys and values may contain primitive types.
Secondly, standard collections are often not implemented in the most optimal way to consume memory, for example, each HashMap element is stored in a separate object, and HashSet is a HashMap that stores fake objects instead of keys. Trove offers its own implementation of such collections based on arrays and open addressing, which can significantly reduce the required memory and in some cases improve performance.
Update: In the comments to the article, it was suggested that Trove is poorly used in new projects, as it is inferior in all respects to fastutil or GS (number of bugs, full interface coverage, performance, support activity, etc.). Unfortunately, I don’t have the opportunity to conduct a full-fledged analysis / comparison of Trove with fastutil and GS, so I can’t check this opinion, just consider it when choosing a library of alternative collections.
Official information: documentation , source codes , javadoc .
How to connect to the project:
Maven, Gradle, Ivy
Maven
Gradle
Ivy
<dependency> <groupId>net.sf.trove4j</groupId> <artifactId>trove4j</artifactId> <version>3.0.3</version> </dependency> Gradle
'net.sf.trove4j:trove4j:3.0.3' Ivy
<dependency org="net.sf.trove4j" name="trove4j" rev="3.0.3"/> | Title | JDK Analog | Description |
|---|---|---|
| THashMap | Hashmap | The implementation of the Map interface, which uses a hash table with the " open addressing " algorithm to resolve collisions (unlike HashMap where the chaining method is used). This allows you not to store and create objects of the Node class, while greatly saving memory and, in some cases, improving performance. |
| THashSet | Hashset | An implementation of a Set interface that uses a hash table with an " open addressing " algorithm to resolve collisions |
| TLinkedHashSet | LinkedHashSet | Analogue to LinkedHashSet, but using hash tables with the " open addressing " algorithm |
| Tlinkedlist | Linkedlist | A more productive analogue of the linked list, but imposing a number of restrictions on the data. |
| TByteArrayList , TIntArrayList , etc. | ArrayList | An analogue of ArrayList, which directly stores primitive numeric values, which drastically reduces memory costs and speeds up processing. There are collections for all seven primitive numeric types, the naming pattern T [Type] ArrayList |
| TCharLinkedList , TFloatLinkedList , etc. | Linkedlist | Analog LinkedList for storing seven primitive numeric types, naming pattern T [Type] LinkedList |
| TByteArrayStack , TLongArrayStack | ArrayDequery | Implementing a stack to store primitive numeric types, naming pattern T [Type] LinkedList |
| TIntQueue , TCharQueue | ArrayDequery | Queue implementation for storing primitive numeric types, naming pattern T [Type] Queue |
| TShortHashSet , TDoubleHashSet | Hashset | Implementing a Set interface for storing primitive types, with an open addressing algorithm, naming pattern T [Type] HashSet |
| TLongLongHashMap , TFloatObjectHashMap , TShortObjectHashMap , etc. | Hashmap | Map implementation of an interface for storing primitive types, with an open addressing algorithm, naming pattern T [Type] [Type] HashMap, where the type can be Object |
3.4 GS-collections collections
The main feature of this library is that it is illogical and ugly that the methods for processing collections (sorting, searching) are not added to the collection classes themselves, but are used by Collections.sort, etc. methods, so GS-collections offered the idea of “rich” collections (rich collections), which store all the methods of processing, searching, sorting, that is, instead of Collections.sort (list), it is simply called list.sort. Therefore, the library offers its analogues of standard collections and, in addition, a number of new collections.
Official information : documentation , source codes , user documentation , javadoc .
How to connect to the project:
Maven, Gradle, Ivy
Maven
Ivy
<dependency> <groupId>com.goldmansachs</groupId> <artifactId>gs-collections-api</artifactId> <version>6.2.0</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.goldmansachs</groupId> <artifactId>gs-collections</artifactId> <version>6.2.0</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.goldmansachs</groupId> <artifactId>gs-collections-testutils</artifactId> <version>6.2.0</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.goldmansachs</groupId> <artifactId>gs-collections-forkjoin</artifactId> <version>6.2.0</version> </dependency> Gradle compile 'com.goldmansachs:gs-collections-api:6.2.0' compile 'com.goldmansachs:gs-collections:6.2.0' testCompile 'com.goldmansachs:gs-collections-testutils:6.2.0' compile 'com.goldmansachs:gs-collections-forkjoin:6.2.0' Ivy
<dependency org="com.goldmansachs" name="gs-collections-api" rev="6.2.0" /> <dependency org="com.goldmansachs" name="gs-collections" rev="6.2.0" /> <dependency org="com.goldmansachs" name="gs-collections-testutils" rev="6.2.0" /> <dependency org="com.goldmansachs" name="gs-collections-forkjoin" rev="6.2.0"/> | Title | JDK Analog | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Fastlist | ArrayList | Analog ArrayList with the ability to use functions like sort, select, etc. right at the collection object |
| Unifiedset | Hashset | Analog HashSet. See FastList |
| TreeSortedSet | Treeset | Analogue TreeSet. See FastList |
| Unifiedmap | Hashmap | Analog HashMap. See FastList |
| TreeSortedMap | Treemap | Analogue TreeMap. See FastList |
| Hashbimap | - | BiMap implementation, see Guava |
| Hashbag | - | Multiset implementation, see Guava |
| Treebag | - | Implementing a sorted BiMap, see Guava |
| ArrayStack | ArrayDeque | Implement a stack with a "last-in, first-out" order, similar to the Stack JDK class |
| FastListMultimap | - | Multimap implementation, see Guava |
| IntArrayList , Floatashset ArrayStack HashBag ByteIntHashMap | - | Collections of primitive different types, the principle of naming is the same as that of a trove, but besides analogs of JDK, there are also analogs of collections Stack, Bag |
3.5 Fastutil Collections
Let's take a very brief look at this library for working with collections of primitive types.
More information can be found: documentation , source codes , javadoc
| Title | Description |
|---|---|
| Byte2DoubleOpenHashMap, IntArrayList, IntArrayPriorityQueue etc. | Collections of various primitive types, naming principle [Type] ArrayList, [Type] ArrayPriorityQueue, etc. for lists or sets, and [Key Type] 2 [Type Values] OpenHashMap, etc. for Map. |
| Intbiglist, DoubleOpenHashBigSet, etc. | Collections of various primitive types are very large, these collections allow the use of long elements instead of int. Inside, data is usually stored as an array of arrays. It is not recommended to use such collections where the usual ones are enough, since productivity losses can reach approximately 30%, however such collections allow working with a really large amount of data. |
3.6 Other collection libraries and a little about the performance of primitive collections
In addition to Trove and Fastutil, there are several other well-known libraries that implement collections of primitive types and faster analogs of standard collections:
1) HPPC - High Performance Primitive Collections for Java, also provides primitive collections similar to those from the JDK,
2) Koloboke (another name HFTC) - as can be understood from the name of this library of primitive types developed by a Russian programmer (Roman Leventov) in the framework of the OpenHFT project. The library also serves to implement high-performance primitive collections.
If you are interested in comparing the performance of different libraries, I advise you to look at this article , but you need to take into account that only the HashMap collections were tested and under certain conditions. In addition, they measured only the speed of work, not taking into account the memory occupied (for example, HashMap jdk can take much more memory than analogs from trove), and sometimes the memory can be even more important than performance.
Update: In the comments to the article, it was suggested that Trove is poorly used in new projects, as it is inferior in all respects to fastutil or GS (number of bugs, full interface coverage, performance, support activity, etc.). Unfortunately, I don’t have the opportunity to conduct a full-fledged analysis / comparison of Trove with fastutil and GS, so I can’t check this opinion, just consider it when choosing a library of alternative collections.
Iv. Comparison of the implementation of the most popular alternative collections in different libraries
4.1 Implementing a multiset (MultiSet / Bag) in guava, Apache Commons Collections and GS libraries
Collections
So, a multiset is a set that preserves not only the fact that there are elements in the set, but also the number
occurrences in it. In the JDK, it can be emulated by the Map construct.
<T, Integer>, but, naturally, specialized collections allow using significantly less code. Compare
Which implementations of this collection are offered by different libraries:
Note : if the table does not fit entirely, try zooming out the page or open it in another browser.
| Collection type | Guava | Apache Commons Collections | GS Collections | JDK |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Collection order not defined | Hashmultiset | Hashbag | Hashbag | HashMap <String, Integer> |
| Sorted in preset or natural order | TreeMultiset | Treebag | Treebag | TreeMap <String, Integer> |
| In order of addition | LinkedHashMultiset | - | - | LinkedHashMap <String, Integere> |
| Multithreaded | Concurrenthashmultiset | SynchronizedBag | SynchronizedBag | Collections.synchronizedMap (HashMap <String, Integer>) |
| Multithreaded and sorted | - | SynchronizedSortedBag | SynchronizedSortedBag | Collections.synchronizedSortedMap (TreeMap <String, Integer>) |
| Not changeable | ImmmutableMultiset | UnmodifiableBag | UnmodifiableBag | Collections.unmodifiableMap (HashMap <String, Integer>) |
| Unmodifiable and sorted | ImmutableSortedMultiset | UnmodifiableSortedBag | UnmodifiableSortedBag | Collections.unmodifiableSortedMap (TreeMap <String, Integer>) |
Examples of using multiset (MultiSet / Bag) to count words in text
There is a task : a line of the text “Hello World! Hello All! Hi World! ”, You need to disassemble it into separate
words where the separator is just a space, save to some collection and output the number of entries for each
words, the total number of words in the text and the number of unique words.
Let's see how to do this with
1. Different Multiset options from Guava:
Use guava HashMultiset to count words
Note that the output order in System.out.println (multiset) and in
System.out.println (multiset.elementSet ()) is arbitrary, that is, not defined.
System.out.println (multiset.elementSet ()) is arbitrary, that is, not defined.
// String INPUT_TEXT = "Hello World! Hello All! Hi World!"; // Multiset Multiset<String> multiset = HashMultiset.create(Arrays.asList(INPUT_TEXT.split(" "))); // - System.out.println(multiset); // [Hi, Hello x 2, World! x 2, All!] - // System.out.println(multiset.elementSet()); // [Hi, Hello, World!, All!] - // System.out.println("Hello = " + multiset.count("Hello")); // 2 System.out.println("World = " + multiset.count("World!")); // 2 System.out.println("All = " + multiset.count("All!")); // 1 System.out.println("Hi = " + multiset.count("Hi")); // 1 System.out.println("Empty = " + multiset.count("Empty")); // 0 // System.out.println(multiset.size()); // 6 // System.out.println(multiset.elementSet().size()); // 4 Use guava's TreeMultiset to count words
Note that the output order in System.out.println (multiset) and in
System.out.println (multiset.elementSet ()) is natural, that is, the words are sorted alphabetically.
System.out.println (multiset.elementSet ()) is natural, that is, the words are sorted alphabetically.
// String INPUT_TEXT = "Hello World! Hello All! Hi World!"; // Multiset Multiset<String> multiset = TreeMultiset.create(Arrays.asList(INPUT_TEXT.split(" "))); // - System.out.println(multiset); // [All!, Hello x 2, Hi, World! x 2]- // System.out.println(multiset.elementSet()); // [All!, Hello, Hi, World!]- // System.out.println("Hello = " + multiset.count("Hello")); // 2 System.out.println("World = " + multiset.count("World!")); // 2 System.out.println("All = " + multiset.count("All!")); // 1 System.out.println("Hi = " + multiset.count("Hi")); // 1 System.out.println("Empty = " + multiset.count("Empty")); // 0 // System.out.println(multiset.size()); // 6 // System.out.println(multiset.elementSet().size()); // 4 LinkedHashMultisetTest guava
, System.out.println(multiset)
System.out.println(multiset.elementSet()) —
System.out.println(multiset.elementSet()) —
// String INPUT_TEXT = "Hello World! Hello All! Hi World!"; // Multiset Multiset<String> multiset = LinkedHashMultiset.create(Arrays.asList(INPUT_TEXT.split(" "))); // - System.out.println(multiset); // [Hello x 2, World! x 2, All!, Hi]- // System.out.println(multiset.elementSet()); // [Hello, World!, All!, Hi] - // System.out.println("Hello = " + multiset.count("Hello")); // 2 System.out.println("World = " + multiset.count("World!")); // 2 System.out.println("All = " + multiset.count("All!")); // 1 System.out.println("Hi = " + multiset.count("Hi")); // 1 System.out.println("Empty = " + multiset.count("Empty")); // 0 // System.out.println(multiset.size()); // 6 // System.out.println(multiset.elementSet().size()); // 4 ConcurrentHashMultiset guava
, System.out.println(multiset)
System.out.println(multiset.elementSet()) — , ,
HashMultiset
System.out.println(multiset.elementSet()) — , ,
HashMultiset
// String INPUT_TEXT = "Hello World! Hello All! Hi World!"; // Multiset Multiset<String> multiset = ConcurrentHashMultiset.create(Arrays.asList(INPUT_TEXT.split(" "))); // - System.out.println(multiset); // [Hi, Hello x 2, World! x 2, All!] - // System.out.println(multiset.elementSet()); // [Hi, Hello, World!, All!] - // System.out.println("Hello = " + multiset.count("Hello")); // 2 System.out.println("World = " + multiset.count("World!")); // 2 System.out.println("All = " + multiset.count("All!")); // 1 System.out.println("Hi = " + multiset.count("Hi")); // 1 System.out.println("Empty = " + multiset.count("Empty")); // 0 // System.out.println(multiset.size()); // 6 // System.out.println(multiset.elementSet().size()); // 4 2. Bag Apache Commons Collections:
HashBag Apache Commons Collections
, System.out.println(multiset)
System.out.println(multiset.elementSet()) — , .
System.out.println(multiset.elementSet()) — , .
// String INPUT_TEXT = "Hello World! Hello All! Hi World!"; // Multiset Bag bag = new HashBag(Arrays.asList(INPUT_TEXT.split(" "))); // - System.out.println(bag); // [1:Hi,2:Hello,2:World!,1:All!] - // System.out.println(bag.uniqueSet()); // [Hi, Hello, World!, All!] - // System.out.println("Hello = " + bag.getCount("Hello")); // 2 System.out.println("World = " + bag.getCount("World!")); // 2 System.out.println("All = " + bag.getCount("All!")); // 1 System.out.println("Hi = " + bag.getCount("Hi")); // 1 System.out.println("Empty = " + bag.getCount("Empty")); // 0 // System.out.println(bag.size()); // 6 // System.out.println(bag.uniqueSet().size()); // 4 TreeBag Apache Commons Collections
, System.out.println(multiset)
System.out.println(multiset.elementSet()) — , .
System.out.println(multiset.elementSet()) — , .
// String INPUT_TEXT = "Hello World! Hello All! Hi World!"; // Multiset Bag bag = new TreeBag(Arrays.asList(INPUT_TEXT.split(" "))); // - System.out.println(bag); // [1:All!,2:Hello,1:Hi,2:World!]- // System.out.println(bag.uniqueSet()); // [All!, Hello, Hi, World!]- // System.out.println("Hello = " + bag.getCount("Hello")); // 2 System.out.println("World = " + bag.getCount("World!")); // 2 System.out.println("All = " + bag.getCount("All!")); // 1 System.out.println("Hi = " + bag.getCount("Hi")); // 1 System.out.println("Empty = " + bag.getCount("Empty")); // 0 // System.out.println(bag.size()); // 6 // System.out.println(bag.uniqueSet().size()); // 4 SynchronizedBag Apache Commons Collections
, System.out.println(multiset)
System.out.println(multiset.elementSet()) — , ,
HashBag
System.out.println(multiset.elementSet()) — , ,
HashBag
// String INPUT_TEXT = "Hello World! Hello All! Hi World!"; // Multiset Bag bag = SynchronizedBag.synchronizedBag(new HashBag(Arrays.asList(INPUT_TEXT.split(" ")))); // - System.out.println(bag); // [1:Hi,2:Hello,2:World!,1:All!] - // System.out.println(bag.uniqueSet()); // [Hi, Hello, World!, All!] - // System.out.println("Hello = " + bag.getCount("Hello")); // 2 System.out.println("World = " + bag.getCount("World!")); // 2 System.out.println("All = " + bag.getCount("All!")); // 1 System.out.println("Hi = " + bag.getCount("Hi")); // 1 System.out.println("Empty = " + bag.getCount("Empty")); // 0 // System.out.println(bag.size()); // 6 // System.out.println(bag.uniqueSet().size()); // 4 SynchronizedSortedBag Apache Commons Collections
, System.out.println(multiset)
System.out.println(multiset.elementSet()) — , ,
SortedBag
System.out.println(multiset.elementSet()) — , ,
SortedBag
// String INPUT_TEXT = "Hello World! Hello All! Hi World!"; // Multiset Bag bag = SynchronizedSortedBag.synchronizedBag(new TreeBag(Arrays.asList(INPUT_TEXT.split(" ")))); // - System.out.println(bag); // [1:All!,2:Hello,1:Hi,2:World!]- // System.out.println(bag.uniqueSet()); // [All!, Hello, Hi, World!]- // System.out.println("Hello = " + bag.getCount("Hello")); // 2 System.out.println("World = " + bag.getCount("World!")); // 2 System.out.println("All = " + bag.getCount("All!")); // 1 System.out.println("Hi = " + bag.getCount("Hi")); // 1 System.out.println("Empty = " + bag.getCount("Empty")); // 0 // System.out.println(bag.size()); // 6 // System.out.println(bag.uniqueSet().size()); // 4 3. Bag GS Collections:
MutableBag GS Collections
, System.out.println(bag) System.out.println(bag.toSet()) —
// String INPUT_TEXT = "Hello World! Hello All! Hi World!"; // Multiset MutableBag<String> bag = HashBag.newBag(Arrays.asList(INPUT_TEXT.split(" "))); // - System.out.println(bag); // [Hi, World!, World!, Hello, Hello, All!]- // System.out.println(bag.toSet()); // [Hi, Hello, World!, All!] - // System.out.println("Hello = " + bag.occurrencesOf("Hello")); // 2 System.out.println("World = " + bag.occurrencesOf("World!")); // 2 System.out.println("All = " + bag.occurrencesOf("All!")); // 1 System.out.println("Hi = " + bag.occurrencesOf("Hi")); // 1 System.out.println("Empty = " + bag.occurrencesOf("Empty")); // 0 // System.out.println(bag.size()); // 6 // System.out.println(bag.toSet().size()); // 4 MutableSortedBag GS Collections
, System.out.println(bag) System.out.println(bag.toSortedSet()) — , ..
// String INPUT_TEXT = "Hello World! Hello All! Hi World!"; // Multiset MutableSortedBag<String> bag = TreeBag.newBag(Arrays.asList(INPUT_TEXT.split(" "))); // - System.out.println(bag); // [All!, Hello, Hello, Hi, World!, World!]- // System.out.println(bag.toSortedSet()); // [All!, Hello, Hi, World!]- // System.out.println("Hello = " + bag.occurrencesOf("Hello")); // 2 System.out.println("World = " + bag.occurrencesOf("World!")); // 2 System.out.println("All = " + bag.occurrencesOf("All!")); // 1 System.out.println("Hi = " + bag.occurrencesOf("Hi")); // 1 System.out.println("Empty = " + bag.occurrencesOf("Empty")); // 0 // System.out.println(bag.size()); // 6 // System.out.println(bag.toSet().size()); // 4 4. , JDK multiSet HashMap
multiSet HashMap
, , , multiSet
Bag.
Bag.
// String INPUT_TEXT = "Hello World! Hello All! Hi World!"; List<String> listResult = Arrays.asList(INPUT_TEXT.split(" ")); // Multiset c HashMap Map<String, Integer> fakeMultiset = new HashMap<String,Integer>(listResult.size()); for(String word: listResult) { Integer cnt = fakeMultiset.get(word); fakeMultiset.put(word, cnt == null ? 1 : cnt + 1); } // - System.out.println(fakeMultiset); // {World!=2, Hi=1, Hello=2, All!=1}- // System.out.println(fakeMultiset.keySet()); // [World!, Hi, Hello, All!] - // System.out.println("Hello = " + fakeMultiset.get("Hello")); // 2 System.out.println("World = " + fakeMultiset.get("World!")); // 2 System.out.println("All = " + fakeMultiset.get("All!")); // 1 System.out.println("Hi = " + fakeMultiset.get("Hi")); // 1 System.out.println("Empty = " + fakeMultiset.get("Empty")); // null // Integer cnt = 0; for (Integer wordCount : fakeMultiset.values()){ cnt += wordCount; } System.out.println(cnt); // 6 // System.out.println(fakeMultiset.size()); // 4 4.2 Multimap guava, Apache Commons Collections GS Collections
, Multimap map, .
.
, — ,
— , JDK
JDK .
: , .
| Order | Order | - - | - | Guava | Apache Commons Collections | GS Collections | JDK | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
- | Yes | HashMap | ArrayList | ArrayList- Multimap | MultiValueMap | FastList- Multimap | HashMap<K, ArrayList<V>> | |
| not | HashMap | HashSet | HashMultimap | MultiValueMap. multiValueMap( new HashMap<K, Set>(), HashSet.class); | UnifiedSet- Multimap | HashMap<K, HashSet<V>> | ||
| - | not | HashMap | TreeSet | Multimaps. newMultimap( HashMap, Supplier <TreeSet>) | MultiValueMap. multiValueMap( new HashMap<K, Set>(), TreeSet.class); | TreeSortedSet- Multimap | HashMap<K, TreeSet<V>> | |
- | - | Yes | Linked HashMap | ArrayList | LinkedList- Multimap | MultiValueMap. multiValueMap(new LinkedHashMap<K, List>(), ArrayList.class); | LinkedHashMap< K, ArrayList<V>> | |
- | - | not | LinkedHash- Multimap | Linked- HashSet | LinkedHash- Multimap | MultiValueMap. multiValueMap(new LinkedHashMap<K, Set>(), LinkedHashSet.class); | LinkedHashMap<K, LinkedHashSet<V>> | |
| - | - | not | TreeMap | TreeSet | TreeMultimap | MultiValueMap. multiValueMap( new TreeMap<K, Set>(),TreeSet.class); | TreeMap<K, TreeSet<V>> |
, Apache Commons Collections ,
. guava ,
map' . GS Collections
multimap Bag (HashBagMultimap), . multiset multimap.
Multimap
: «Hello World! Hello All! Hi World!»,
,
, Hello ..
1. Multimap Guava:
HashMultimap guava
, , (
HashMap, HashSet). .
HashMap, HashSet). .
String INPUT_TEXT = "Hello World! Hello All! Hi World!"; // List <String> words = Arrays.asList(INPUT_TEXT.split(" ")); // Multimap Multimap<String, Integer> multiMap = HashMultimap.create(); // Multimap int i = 0; for(String word: words) { multiMap.put(word, i); i++; } // System.out.println(multiMap); // {Hi=[4], Hello=[0, 2], World!=[1, 5], All!=[3]} - // System.out.println(multiMap.keySet()); // [Hi, Hello, World!, All!] - // System.out.println("Hello = " + multiMap.get("Hello")); // [0, 2] System.out.println("World = " + multiMap.get("World!")); // [1, 5] System.out.println("All = " + multiMap.get("All!")); // [3] System.out.println("Hi = " + multiMap.get("Hi")); // [4] System.out.println("Empty = " + multiMap.get("Empty")); // [] // System.out.println(multiMap.size()); // 6 // System.out.println(multiMap.keySet().size()); // 4 ArrayListMultimapTest guava
, ,
( HashMap, ArrayList).
.
( HashMap, ArrayList).
.
String INPUT_TEXT = "Hello World! Hello All! Hi World!"; // List <String> words = Arrays.asList(INPUT_TEXT.split(" ")); // Multimap Multimap<String, Integer> multiMap = ArrayListMultimap.create(); // Multimap int i = 0; for(String word: words) { multiMap.put(word, i); i++; } // System.out.println(multiMap); // {Hi=[4], Hello=[0, 2], World!=[1, 5], All!=[3]} - , // System.out.println(multiMap.keySet()); // [Hello, World!, All!, Hi]- // System.out.println("Hello = " + multiMap.get("Hello")); // [0, 2] System.out.println("World = " + multiMap.get("World!")); // [1, 5] System.out.println("All = " + multiMap.get("All!")); // [3] System.out.println("Hi = " + multiMap.get("Hi")); // [4] System.out.println("Empty = " + multiMap.get("Empty")); // [] // System.out.println(multiMap.size()); // 6 // System.out.println(multiMap.keySet().size()); // 4 LinkedHashMultimapTest guava
, (
LinkedHashMap, LinkedHashSet).
.
LinkedHashMap, LinkedHashSet).
.
String INPUT_TEXT = "Hello World! Hello All! Hi World!"; // List <String> words = Arrays.asList(INPUT_TEXT.split(" ")); // Multimap Multimap<String, Integer> multiMap = LinkedHashMultimap.create(); // Multimap int i = 0; for(String word: words) { multiMap.put(word, i); i++; } // System.out.println(multiMap); // {Hello=[0, 2], World!=[1, 5], All!=[3], Hi=[4]}- // System.out.println(multiMap.keySet()); // [Hello, World!, All!, Hi]- // System.out.println("Hello = " + multiMap.get("Hello")); // [0, 2] System.out.println("World = " + multiMap.get("World!")); // [1, 5] System.out.println("All = " + multiMap.get("All!")); // [3] System.out.println("Hi = " + multiMap.get("Hi")); // [4] System.out.println("Empty = " + multiMap.get("Empty")); // [] // System.out.println(multiMap.size()); // 6 // System.out.println(multiMap.keySet().size()); // 4 LinkedListMultimapTest guava
, (
LinkedHashMap, LinkedList).
.
LinkedHashMap, LinkedList).
.
String INPUT_TEXT = "Hello World! Hello All! Hi World!"; // List <String> words = Arrays.asList(INPUT_TEXT.split(" ")); // Multimap Multimap<String, Integer> multiMap = LinkedListMultimap.create(); // Multimap int i = 0; for(String word: words) { multiMap.put(word, i); i++; } // System.out.println(multiMap); // {Hello=[0, 2], World!=[1, 5], All!=[3], Hi=[4]}- // System.out.println(multiMap.keySet()); // [Hello, World!, All!, Hi]- // System.out.println("Hello = " + multiMap.get("Hello")); // [0, 2] System.out.println("World = " + multiMap.get("World!")); // [1, 5] System.out.println("All = " + multiMap.get("All!")); // [3] System.out.println("Hi = " + multiMap.get("Hi")); // [4] System.out.println("Empty = " + multiMap.get("Empty")); // [] // System.out.println(multiMap.size()); // 6 // System.out.println(multiMap.keySet().size()); // 4 TreeMultimapTest guava
, (
TreeMap, TreeSet).
TreeMap, TreeSet).
String INPUT_TEXT = "Hello World! Hello All! Hi World!"; // List<String> words = Arrays.asList(INPUT_TEXT.split(" ")); // Multimap Multimap<String, Integer> multiMap = TreeMultimap.create(); // Multimap int i = 0; for(String word: words) { multiMap.put(word, i); i++; } // System.out.println(multiMap); // {Hello=[0, 2], World!=[1, 5], All!=[3], Hi=[4]}- // System.out.println(multiMap.keySet()); // [Hello, World!, All!, Hi]- // System.out.println("Hello = " + multiMap.get("Hello")); // [0, 2] System.out.println("World = " + multiMap.get("World!")); // [1, 5] System.out.println("All = " + multiMap.get("All!")); // [3] System.out.println("Hi = " + multiMap.get("Hi")); // [4] System.out.println("Empty = " + multiMap.get("Empty")); // [] // System.out.println(multiMap.size()); // 6 // System.out.println(multiMap.keySet().size()); // 4 2. MultiValueMap Apache Commons Collections:
MultiValueMap Apache Commons Collections
, ( HashMap
ArrayList )
ArrayList )
String INPUT_TEXT = "Hello World! Hello All! Hi World!"; // List<String> words = Arrays.asList(INPUT_TEXT.split(" ")); // Multimap MultiMap<String, Integer> multiMap = new MultiValueMap<String, Integer>(); // Multimap int i = 0; for(String word: words) { multiMap.put(word, i); i++; } // System.out.println(multiMap); // {Hi=[4], Hello=[0, 2], World!=[1, 5], All!=[3]} - // System.out.println(multiMap.keySet()); // [Hi, Hello, World!, All!] - // System.out.println("Hello = " + multiMap.get("Hello")); // [0, 2] System.out.println("World = " + multiMap.get("World!")); // [1, 5] System.out.println("All = " + multiMap.get("All!")); // [3] System.out.println("Hi = " + multiMap.get("Hi")); // [4] System.out.println("Empty = " + multiMap.get("Empty")); // null // System.out.println(multiMap.keySet().size()); // 4 MultiValueMap, TreeMap<String, TreeSet>()
,
String INPUT_TEXT = "Hello World! Hello All! Hi World!"; // List<String> words = Arrays.asList(INPUT_TEXT.split(" ")); // Multimap MultiMap<String, Integer> multiMap = MultiValueMap.multiValueMap(new TreeMap<String, Set>(), TreeSet.class); // Multimap int i = 0; for(String word: words) { multiMap.put(word, i); i++; } // System.out.println(multiMap); // {All!=[3], Hello=[0, 2], Hi=[4], World!=[1, 5]} - // System.out.println(multiMap.keySet()); // [All!, Hello, Hi, World!] // System.out.println("Hello = " + multiMap.get("Hello")); // [0, 2] System.out.println("World = " + multiMap.get("World!")); // [1, 5] System.out.println("All = " + multiMap.get("All!")); // [3] System.out.println("Hi = " + multiMap.get("Hi")); // [4] System.out.println("Empty = " + multiMap.get("Empty")); // null // System.out.println(multiMap.keySet().size()); // 4 MultiValueMap, LinkedHashMap<String, LinkedHashSet>()
,
String INPUT_TEXT = "Hello World! Hello All! Hi World!"; // List<String> words = Arrays.asList(INPUT_TEXT.split(" ")); // Multimap MultiMap<String, Integer> multiMap = MultiValueMap.multiValueMap(new LinkedHashMap<String, Set>(), LinkedHashSet.class); // Multimap int i = 0; for(String word: words) { multiMap.put(word, i); i++; } // System.out.println(multiMap); // {Hello=[0, 2], World!=[1, 5], All!=[3], Hi=[4]} - // System.out.println(multiMap.keySet()); // [Hello, World!, All!, Hi] - // System.out.println("Hello = " + multiMap.get("Hello")); // [0, 2] System.out.println("World = " + multiMap.get("World!")); // [1, 5] System.out.println("All = " + multiMap.get("All!")); // [3] System.out.println("Hi = " + multiMap.get("Hi")); // [4] System.out.println("Empty = " + multiMap.get("Empty")); // null // System.out.println(multiMap.keySet().size()); // 4 3. Multimap GS Collections:
FastListMultimap
String INPUT_TEXT = "Hello World! Hello All! Hi World!"; // List<String> words = Arrays.asList(INPUT_TEXT.split(" ")); // Multimap MutableListMultimap<String, Integer> multiMap = new FastListMultimap<String, Integer>(); // Multimap int i = 0; for(String word: words) { multiMap.put(word, i); i++; } // System.out.println(multiMap); // {Hi=[4], World!=[1, 5], Hello=[0, 2], All!=[3]}- // System.out.println(multiMap.keysView()); // [Hi, Hello, World!, All!] - // System.out.println("Hello = " + multiMap.get("Hello")); // [0, 2] System.out.println("World = " + multiMap.get("World!")); // [1, 5] System.out.println("All = " + multiMap.get("All!")); // [3] System.out.println("Hi = " + multiMap.get("Hi")); // [4] System.out.println("Empty = " + multiMap.get("Empty")); // [] // System.out.println(multiMap.size()); // 6 // System.out.println(multiMap.keysView().size()); // 4 HashBagMultimap
String INPUT_TEXT = "Hello World! Hello All! Hi World!"; // List<String> words = Arrays.asList(INPUT_TEXT.split(" ")); // Multimap MutableBagMultimap<String, Integer> multiMap = new HashBagMultimap<String, Integer>(); // Multimap int i = 0; for(String word: words) { multiMap.put(word, i); i++; } // System.out.println(multiMap); // {Hi=[4], World!=[1, 5], Hello=[0, 2], All!=[3]}- // System.out.println(multiMap.keysView()); // [Hi, Hello, World!, All!] - // System.out.println("Hello = " + multiMap.get("Hello")); // [0, 2] System.out.println("World = " + multiMap.get("World!")); // [1, 5] System.out.println("All = " + multiMap.get("All!")); // [3] System.out.println("Hi = " + multiMap.get("Hi")); // [4] System.out.println("Empty = " + multiMap.get("Empty")); // [] // System.out.println(multiMap.size()); // 6 // System.out.println(multiMap.keysView().size()); // 4 TreeSortedSetMultimap
String INPUT_TEXT = "Hello World! Hello All! Hi World!"; // List<String> words = Arrays.asList(INPUT_TEXT.split(" ")); // Multimap MutableSortedSetMultimap<String, Integer> multiMap = new TreeSortedSetMultimap<String, Integer>(); // Multimap int i = 0; for(String word: words) { multiMap.put(word, i); i++; } // System.out.println(multiMap); // {Hi=[4], World!=[1, 5], Hello=[0, 2], All!=[3]}- // System.out.println(multiMap.keysView()); // [Hi, Hello, World!, All!] - // System.out.println("Hello = " + multiMap.get("Hello")); // [0, 2] System.out.println("World = " + multiMap.get("World!")); // [1, 5] System.out.println("All = " + multiMap.get("All!")); // [3] System.out.println("Hi = " + multiMap.get("Hi")); // [4] System.out.println("Empty = " + multiMap.get("Empty")); // [] // System.out.println(multiMap.size()); // 6 // System.out.println(multiMap.keysView().size()); // 4 4. , JDK multiMap HashMap
multiMap HashMap
final int LIST_INDEXES_CAPACITY = 50; String INPUT_TEXT = "Hello World! Hello All! Hi World!"; // List<String> words = Arrays.asList(INPUT_TEXT.split(" ")); // Multimap Map<String, List<Integer>> fakeMultiMap = new HashMap<String, List<Integer>>(words.size()); // map int i = 0; for(String word: words) { List<Integer> indexes = fakeMultiMap.get(word); if(indexes == null) { indexes = new ArrayList<Integer>(LIST_INDEXES_CAPACITY); fakeMultiMap.put(word, indexes); } indexes.add(i); i++; } // System.out.println(fakeMultiMap); // {Hi=[4], Hello=[0, 2], World!=[1, 5], All!=[3]} - // System.out.println(fakeMultiMap.keySet()); // [Hi, Hello, World!, All!] - // System.out.println("Hello = " + fakeMultiMap.get("Hello")); // [0, 2] System.out.println("World = " + fakeMultiMap.get("World!")); // [1, 5] System.out.println("All = " + fakeMultiMap.get("All!")); // [3] System.out.println("Hi = " + fakeMultiMap.get("Hi")); // [4] System.out.println("Empty = " + fakeMultiMap.get("Empty")); // null // int cnt = 0; for(List<Integer> lists: fakeMultiMap.values()) { cnt += lists.size(); } System.out.println(cnt); // 6 // System.out.println(fakeMultiMap.keySet().size()); // 4 4.3 BiMap guava, Apache Commons Collections GS Collections
BiMap , HashBiMap guava GS Collections
BidiMap Apache Commons Collections. HashBiMap, guava Enum
, EnumHashBiMap EnumBiMap, Apache Commons Collections
, .
BiMap - «»,
: ,
- , .
1. BiMap Guava:
BiMap guava
String[] englishWords = {"one", "two", "three","ball","snow"}; String[] russianWords = {"", "", "","","c"}; // Multiset BiMap<String, String> biMap = HashBiMap.create(englishWords.length); // - int i = 0; for(String englishWord: englishWords) { biMap.put(englishWord, russianWords[i]); i++; } // - System.out.println(biMap); // {two=, three=, snow=c, ball=, one=} - // System.out.println(biMap.keySet()); // [two, three, snow, ball, one] - System.out.println(biMap.values()); // [, , c, , ]- // System.out.println("one = " + biMap.get("one")); // one = System.out.println("two = " + biMap.get("two")); // two = System.out.println(" = " + biMap.inverse().get("")); // = ball System.out.println(" = " + biMap.inverse().get("c")); // = snow System.out.println("empty = " + biMap.get("empty")); // empty = null // System.out.println(biMap.size()); // 5 EnumBiMap guava
enum ENGLISH_WORD { ONE, TWO, THREE, BALL, SNOW } enum POLISH_WORD { JEDEN, DWA, TRZY, KULA, SNIEG } // - , public static void main(String[] args) { ENGLISH_WORD[] englishWords = ENGLISH_WORD.values(); POLISH_WORD[] polishWords = POLISH_WORD.values(); // Multiset BiMap<ENGLISH_WORD, POLISH_WORD> biMap = EnumBiMap.create(ENGLISH_WORD.class, POLISH_WORD.class); // - int i = 0; for(ENGLISH_WORD englishWord: englishWords) { biMap.put(englishWord, polishWords[i]); i++; } // - System.out.println(biMap); // {ONE=JEDEN, TWO=DWA, THREE=TRZY, BALL=KULA, SNOW=SNIEG} // System.out.println(biMap.keySet()); // [ONE, TWO, THREE, BALL, SNOW] System.out.println(biMap.values()); // [JEDEN, DWA, TRZY, KULA, SNIEG] // System.out.println("one = " + biMap.get(ENGLISH_WORD.ONE)); // one = JEDEN System.out.println("two = " + biMap.get(ENGLISH_WORD.TWO)); // two = DWA System.out.println("kula = " + biMap.inverse().get(POLISH_WORD.KULA)); // kula = BALL System.out.println("snieg = " + biMap.inverse().get(POLISH_WORD.SNIEG)); // snieg = SNOW System.out.println("empty = " + biMap.get("empty")); // empty = null // System.out.println(biMap.size()); // 5 } EnumHashBiMap guava
enum ENGLISH_WORD { ONE, TWO, THREE, BALL, SNOW } // - , public static void main(String[] args) { ENGLISH_WORD[] englishWords = ENGLISH_WORD.values(); String[] russianWords = {"", "", "","","c"}; // Multiset BiMap<ENGLISH_WORD, String> biMap = EnumHashBiMap.create(ENGLISH_WORD.class); // - int i = 0; for(ENGLISH_WORD englishWord: englishWords) { biMap.put(englishWord, russianWords[i]); i++; } // - System.out.println(biMap); // {ONE=, TWO=, THREE=, BALL=, SNOW=c} // System.out.println(biMap.keySet()); // [ONE, TWO, THREE, BALL, SNOW] System.out.println(biMap.values()); // [, , , , c] // System.out.println("one = " + biMap.get(ENGLISH_WORD.ONE)); // one = System.out.println("two = " + biMap.get(ENGLISH_WORD.TWO)); // two = System.out.println(" = " + biMap.inverse().get("")); // = BALL System.out.println(" = " + biMap.inverse().get("c")); // = SNOW System.out.println("empty = " + biMap.get("empty")); // empty = null // System.out.println(biMap.size()); // 5 } 2. C BidiMap Apache Commons Collections:
DualHashBidiMap Apache Commons Collections
String[] englishWords = {"one", "two", "three","ball","snow"}; String[] russianWords = {"", "", "","","c"}; // Multiset BidiMap<String, String> biMap = new DualHashBidiMap(); // - int i = 0; for(String englishWord: englishWords) { biMap.put(englishWord, russianWords[i]); i++; } // - System.out.println(biMap); // {ball=, snow=c, one=, two=, three=}- // System.out.println(biMap.keySet()); // [ball, snow, one, two, three]- System.out.println(biMap.values()); // [, c, , , ]- // System.out.println("one = " + biMap.get("one")); // one = System.out.println("two = " + biMap.get("two")); // two = System.out.println(" = " + biMap.getKey("")); // = ball System.out.println(" = " + biMap.getKey("c")); // = snow System.out.println("empty = " + biMap.get("empty")); // empty = null // System.out.println(biMap.size()); // 5 3. C HashBiMap GS Collections:
HashBiMap GS Collections
String[] englishWords = {"one", "two", "three","ball","snow"}; String[] russianWords = {"", "", "","","c"}; // Multiset MutableBiMap<String, String> biMap = new HashBiMap(englishWords.length); // - int i = 0; for(String englishWord: englishWords) { biMap.put(englishWord, russianWords[i]); i++; } // - System.out.println(biMap); // {two=, ball=, one=, snow=c, three=} - // System.out.println(biMap.keySet()); // [snow, two, one, three, ball] - System.out.println(biMap.values()); // [, , , c, ] - // System.out.println("one = " + biMap.get("one")); // one = System.out.println("two = " + biMap.get("two")); // two = System.out.println(" = " + biMap.inverse().get("")); // = ball System.out.println(" = " + biMap.inverse().get("c")); // = snow System.out.println("empty = " + biMap.get("empty")); // empty = null // System.out.println(biMap.size()); // 5 4. , JDK
HashMap BiMap
String[] englishWords = {"one", "two", "three","ball","snow"}; String[] russianWords = {"", "", "","","c"}; // BiMap Map<String, String> biMapKeys = new HashMap(englishWords.length); Map<String, String> biMapValues = new HashMap(russianWords.length); // - int i = 0; for(String englishWord: englishWords) { biMapKeys.put(englishWord, russianWords[i]); biMapValues.put(russianWords[i], englishWord); i++; } // - System.out.println(biMapKeys); // {ball=, two=, three=, snow=c, one=}- // System.out.println(biMapKeys.keySet()); // [ball, two, three, snow, one] - System.out.println(biMapValues.keySet()); // [, , , c, ] - // System.out.println("one = " + biMapKeys.get("one")); // one = System.out.println("two = " + biMapKeys.get("two")); // two = System.out.println(" = " + biMapValues.get("")); // = ball System.out.println(" = " + biMapValues.get("c")); // = snow System.out.println("empty = " + biMapValues.get("empty")); // empty = null // System.out.println(biMapKeys.size()); // 5 V.
, JDK. , , ( ), , .
5.1 .
Guava gs-collections new, jdk.
5.1.1) (List)
| Title | JDK | guava | gs-collections |
|---|---|---|---|
| new ArrayList<>() | Lists.newArrayList() | FastList.newList() | |
| Arrays.asList(«1», «2», «3») | Lists.newArrayList(«1», «2», «3») | FastList.newListWith(«1», «2», «3») | |
capacity | new ArrayList<>(100) | Lists.newArrayListWithCapacity(100) | FastList.newList(100) |
| new ArrayList<>(collection) | Lists.newArrayList(collection) | FastList.newList(collection) | |
Iterable | - | Lists.newArrayList(iterable) | FastList.newList(iterable) |
Iterator' | - | Lists.newArrayList(iterator) | - |
| Arrays.asList(array) | Lists.newArrayList(array) | FastList.newListWith(array) | |
c | - | - | FastList.newWithNValues(10, () -> «1») |
// List<String> emptyGuava = Lists.newArrayList(); // c guava List<String> emptyJDK = new ArrayList<>(); // JDK MutableList<String> emptyGS = FastList.newList(); // c gs // 100 List < String > exactly100 = Lists.newArrayListWithCapacity(100); // c guava List<String> exactly100JDK = new ArrayList<>(100); // JDK MutableList<String> empty100GS = FastList.newList(100); // c gs // 100 ( 100) List<String> approx100 = Lists.newArrayListWithExpectedSize(100); // c guava List<String> approx100JDK = new ArrayList<>(115); // JDK MutableList<String> approx100GS = FastList.newList(115); // c gs // List<String> withElements = Lists.newArrayList("alpha", "beta", "gamma"); // c guava List<String> withElementsJDK = Arrays.asList("alpha", "beta", "gamma"); // JDK MutableList<String> withElementsGS = FastList.newListWith("alpha", "beta", "gamma"); // c gs System.out.println(withElements); System.out.println(withElementsJDK); System.out.println(withElementsGS); // Iterable ( ) Collection<String> collection = new HashSet<>(3); collection.add("1"); collection.add("2"); collection.add("3"); List<String> fromIterable = Lists.newArrayList(collection); // c guava List<String> fromIterableJDK = new ArrayList<>(collection); // JDK MutableList<String> fromIterableGS = FastList.newList(collection); // c gs System.out.println(fromIterable); System.out.println(fromIterableJDK); System.out.println(fromIterableGS); /* JDK Collection , guava gs Iterable */ // Iterator' Iterator<String> iterator = collection.iterator(); List<String> fromIterator = Lists.newArrayList(iterator); // c guava, JDK System.out.println(fromIterator); // String[] array = {"4", "5", "6"}; List<String> fromArray = Lists.newArrayList(array); // c guava List<String> fromArrayJDK = Arrays.asList(array); // JDK MutableList<String> fromArrayGS = FastList.newListWith(array); // c gs System.out.println(fromArray); System.out.println(fromArrayJDK); System.out.println(fromArrayGS); // c MutableList<String> fromFabricGS = FastList.newWithNValues(10, () -> String.valueOf(Math.random())); // c gs System.out.println(fromFabricGS); 5.1.2) (set)
| Title | JDK | guava | gs-collections |
|---|---|---|---|
| new HashSet<>() | Sets.newHashSet() | UnifiedSet.newSet() | |
| new HashSet<>(Arrays.asList(«alpha», «beta», «gamma»)) | Sets.newHashSet(«alpha», «beta», «gamma») | UnifiedSet.newSetWith(«alpha», «beta», «gamma») | |
| new HashSet<>(collection) | Sets.newHashSet(collection) | UnifiedSet.newSet(collection) | |
Iterable | - | Sets.newHashSet(iterable) | UnifiedSet.newSet(iterable) |
Iterator' | - | Sets.newHashSet(iterator); | - |
| new HashSet<>(Arrays.asList(array)) | Sets.newHashSet(array) | UnifiedSet.newSetWith(array) |
// Set<String> emptyGuava = Sets.newHashSet(); // c guava Set<String> emptyJDK = new HashSet<>(); // JDK Set<String> emptyGS = UnifiedSet.newSet(); // c gs // 100 ( 100) Set<String> approx100 = Sets.newHashSetWithExpectedSize(100); // c guava Set<String> approx100JDK = new HashSet<>(130); // JDK Set<String> approx100GS = UnifiedSet.newSet(130); // c gs // Set<String> withElements = Sets.newHashSet("alpha", "beta", "gamma"); // c guava Set<String> withElementsJDK = new HashSet<>(Arrays.asList("alpha", "beta", "gamma")); // JDK Set<String> withElementsGS = UnifiedSet.newSetWith("alpha", "beta", "gamma"); // c gs System.out.println(withElements); System.out.println(withElementsJDK); System.out.println(withElementsGS); // Iterable ( ) Collection<String> collection = new ArrayList<>(3); collection.add("1"); collection.add("2"); collection.add("3"); Set<String> fromIterable = Sets.newHashSet(collection); // c guava Set<String> fromIterableJDK = new HashSet<>(collection); // JDK Set<String> fromIterableGS = UnifiedSet.newSet(collection); // c gs System.out.println(fromIterable); System.out.println(fromIterableJDK); System.out.println(fromIterableGS); /* JDK Collection , guava Iterable */ // Iterator' Iterator<String> iterator = collection.iterator(); Set<String> fromIterator = Sets.newHashSet(iterator); // c guava, JDK System.out.println(fromIterator); // String[] array = {"4", "5", "6"}; Set<String> fromArray = Sets.newHashSet(array); // c guava Set<String> fromArrayJDK = new HashSet<>(Arrays.asList(array)); // JDK Set<String> fromArrayGS = UnifiedSet.newSetWith(array); // c gs System.out.println(fromArray); System.out.println(fromArrayJDK); System.out.println(fromArrayGS); 5.1.3) Map
| Title | JDK | guava | gs-collections |
|---|---|---|---|
| map' | new HashMap<>() | Maps.newHashMap() | UnifiedMap.newMap() |
| map' c capacity | new HashMap<>(130) | Maps.newHashMapWithExpectedSize(100) | UnifiedMap.newMap(130) |
| map' map' | new HashMap<>(map) | Maps.newHashMap(map) | UnifiedMap.newMap(map) |
| map' | - | - | UnifiedMap.newWithKeysValues(«1», «a», «2», «b») |
map
//
Map<String, String> emptyGuava = Maps.newHashMap(); // c guava
Map<String, String> emptyJDK = new HashMap<>(); // JDK
Map<String, String> emptyGS = UnifiedMap.newMap(); // c gs
// map' 100 ( 100)
Map<String, String> approx100 = Maps.newHashMapWithExpectedSize(100); // c guava
Map<String, String> approx100JDK = new HashMap<>(130); // JDK
Map<String, String> approx100GS = UnifiedMap.newMap(130); // c gs
// map' map'
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>(3);
map.put(«k1»,«v1»);
map.put(«k2»,«v2»);
Map<String, String> withMap = Maps.newHashMap(map); // c guava
Map<String, String> withMapJDK = new HashMap<>(map); // JDK
Map<String, String> withMapGS = UnifiedMap.newMap(map); // c gs
System.out.println(withMap);
System.out.println(withMapJDK);
System.out.println(withMapGS);
// map'
Map<String, String> withKeys = UnifiedMap.newWithKeysValues(«1», «a», «2», «b»);
System.out.println(withKeys);
Map<String, String> emptyGuava = Maps.newHashMap(); // c guava
Map<String, String> emptyJDK = new HashMap<>(); // JDK
Map<String, String> emptyGS = UnifiedMap.newMap(); // c gs
// map' 100 ( 100)
Map<String, String> approx100 = Maps.newHashMapWithExpectedSize(100); // c guava
Map<String, String> approx100JDK = new HashMap<>(130); // JDK
Map<String, String> approx100GS = UnifiedMap.newMap(130); // c gs
// map' map'
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>(3);
map.put(«k1»,«v1»);
map.put(«k2»,«v2»);
Map<String, String> withMap = Maps.newHashMap(map); // c guava
Map<String, String> withMapJDK = new HashMap<>(map); // JDK
Map<String, String> withMapGS = UnifiedMap.newMap(map); // c gs
System.out.println(withMap);
System.out.println(withMapJDK);
System.out.println(withMapGS);
// map'
Map<String, String> withKeys = UnifiedMap.newWithKeysValues(«1», «a», «2», «b»);
System.out.println(withKeys);
5.2 .
| Title | JDK | guava | apache | gs-collections |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Collections.frequency(collection, «1») | Iterables.frequency(iterable, «1») | CollectionUtils.cardinality(«1», iterable) | mutableCollection.count((each) -> «a1».equals(each)) | |
| collection.stream().findFirst().orElse(«1») | Iterables.getFirst(iterable, «1») | CollectionUtils.get(iterable, 0) | orderedIterable.getFirst() | |
| collection.stream().skip(collection.size()-1).findFirst().orElse(«1»); | Iterables.getLast(iterable, «1») | CollectionUtils.get(collection, collection.size()-1) | orderedIterable.getLast() | |
| Collections.max(collection) | Ordering.natural().max(iterable) | - | orderedIterable.max() | |
| Collections.min(collection) | Ordering.natural().min(iterable) | - | orderedIterable.min() | |
| Iterables.getOnlyElement(iterable) | CollectionUtils.extractSingleton(collection) | |||
| Collections.binarySearch(list, «13») | Ordering.natural().binarySearch(list, «13») | mutableList.binarySearch(«13») | ||
| collection.stream().filter(«13»::equals).findFirst().get() | Iterables.find(iterable, «13»::equals) | CollectionUtils.find(iterable, «13»::equals) | mutableList.select(«13»::equals).get(0) | |
| collection.stream().filter((s) -> s.contains(«1»)).collect(Collectors.toList()) | Iterables.filter(iterable, (s) -> s.contains(«1»)) | CollectionUtils.select(iterable, (s) -> s.contains(«1»)) | mutableCollection.select((s) -> s.contains(«1»)) |
:
1)
Collection<String> collection = Lists.newArrayList("a1", "a2", "a3", "a1"); Iterable<String> iterable = collection; MutableCollection<String> collectionGS = FastList.newListWith("a1", "a2", "a3", "a1"); // int i1 = Iterables.frequency(iterable, "a1"); // guava int i2 = Collections.frequency(collection, "a1"); // c JDK int i3 = CollectionUtils.cardinality("a1", iterable); // c Apache int i4 = collectionGS.count((s) -> "a1".equals(s)); long i5 = collection.stream().filter((s) -> "a1".equals(s)).count(); // c stream JDK System.out.println("count = " + i1 + ":" + i2 + ":" + i3 + ":" + i4 + ":" + i5); // count = 2:2:2:2:2 2)
Collection<String> collection = Lists.newArrayList("a1", "a2", "a3", "a1"); OrderedIterable<String> orderedIterable = FastList.newListWith("a1", "a2", "a3", "a1"); Iterable<String> iterable = collection; // Iterator<String> iterator = collection.iterator(); // c JDK String jdk = iterator.hasNext() ? iterator.next(): "1"; String guava = Iterables.getFirst(iterable, "1"); // guava String apache = CollectionUtils.get(iterable, 0); // c Apache String gs = orderedIterable.getFirst(); // c GS String stream = collection.stream().findFirst().orElse("1"); // c Stream API System.out.println("first = " + jdk + ":" + guava + ":" + apache + ":" + gs + ":" + stream); // first = a1:a1:a1:a1:a1 3)
Collection<String> collection = Lists.newArrayList("a1", "a2", "a3", "a8"); OrderedIterable<String> orderedIterable = FastList.newListWith("a1", "a2", "a3", "a8"); Iterable<String> iterable = collection; // Iterator<String> iterator = collection.iterator(); // c JDK String jdk = "1"; while(iterator.hasNext()) { jdk = iterator.next(); } String guava = Iterables.getLast(iterable, "1"); // guava String apache = CollectionUtils.get(collection, collection.size()-1); // c Apache String gs = orderedIterable.getLast(); // c GS String stream = collection.stream().skip(collection.size()-1).findFirst().orElse("1"); // c Stream API System.out.println("last = " + jdk + ":" + guava + ":" + apache + ":" + gs + ":" + stream); // last = a8:a8:a8:a8:a8 4)
Collection<String> collection = Lists.newArrayList("5", "1", "3", "8", "4"); OrderedIterable<String> orderedIterable = FastList.newListWith("5", "1", "3", "8", "4"); Iterable<String> iterable = collection; // String jdk = Collections.max(collection); // c JDK String gs = orderedIterable.max(); // c GS String guava = Ordering.natural().max(iterable); // guava System.out.println("max = " + jdk + ":" + guava + ":" + gs); // max = 8:8:8 5)
Collection<String> collection = Lists.newArrayList("5", "1", "3", "8", "4"); OrderedIterable<String> orderedIterable = FastList.newListWith("5", "1", "3", "8", "4"); Iterable<String> iterable = collection; // String jdk = Collections.min(collection); // c JDK String gs = orderedIterable.min(); // c GS String guava = Ordering.natural().min(iterable); // guava System.out.println("min = " + jdk + ":" + guava + ":" + gs); // min = 1:1:1 6)
Collection<String> collection = Lists.newArrayList("a3"); OrderedIterable<String> orderedIterable = FastList.newListWith("a3"); Iterable<String> iterable = collection; // String guava = Iterables.getOnlyElement(iterable); // guava String jdk = collection.iterator().next(); // c JDK String apache = CollectionUtils.extractSingleton(collection); // c Apache assert(orderedIterable.size() > 1);// c GS String gs = orderedIterable.getFirst(); System.out.println("single = " + jdk + ":" + guava + ":" + apache + ":" + gs); // single = a3:a3:a3:a3 7)
List<String> list = Lists.newArrayList("2", "4", "13", "31", "43"); MutableList<String> mutableList = FastList.newListWith("2", "4","13", "31", "43"); // int jdk = Collections.binarySearch(list, "13"); int guava = Ordering.natural().binarySearch(list, "13"); int gs = mutableList.binarySearch("13"); System.out.println("find = " + jdk + ":" + guava + ":" + gs); // find = 2:2:2 8)
Collection<String> collection = Lists.newArrayList("a1", "a2", "a3", "a1"); MutableCollection<String> orderedIterable = FastList.newListWith("a1", "a2", "a3", "a1"); Iterable<String> iterable = collection; // String jdk = collection.stream().skip(2).findFirst().get(); // c JDK String guava = Iterables.get(iterable, 2); // guava String apache = CollectionUtils.get(iterable, 2); // c Apache System.out.println("third = " + jdk + ":" + guava + ":" + apache); // third = a3:a3:a3 9)
Collection<String> collection = Lists.newArrayList("2", "14", "3", "13", "43"); MutableCollection<String> mutableCollection = FastList.newListWith("2", "14", "3", "13", "43"); Iterable<String> iterable = collection; // List<String> jdk = collection.stream().filter((s) -> s.contains("1")).collect(Collectors.toList()); // c JDK Iterable<String> guava = Iterables.filter(iterable, (s) -> s.contains("1")); // guava Collection<String> apache = CollectionUtils.select(iterable, (s) -> s.contains("1")); // c Apache MutableCollection<String> gs = mutableCollection.select((s) -> s.contains("1")); // c GS System.out.println("select = " + jdk + ":" + guava + ":" + apache + ":" + gs); // select = [14, 13]:[14, 13]:[14, 13]:[14, 13] 5.3 ,
| Title | JDK | guava | apache | gs-collections |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| collection1.containsAll(collection2) | Iterables.elementsEqual(iterable1, iterable2) | CollectionUtils.containsAll(collection1, collection2) | mutableCollection1.containsAll(mutableCollection2) | |
| !Collections.disjoint(collection1, collection2) | !Sets.intersection(set1, set2).isEmpty() | CollectionUtils.containsAny(collection1, collection2) | !mutableSet1.intersect(mutableSet2).isEmpty() | |
| () | Set<T> result = new HashSet<>(set1); result.retainAll(set2) | Sets.intersection(set1, set2) | CollectionUtils.intersection(collection1, collection2) | mutableSet1.intersect(mutableSet2) |
| Collections.disjoint(collection1, collection2) | Sets.intersection(set1, set2).isEmpty() | !CollectionUtils.containsAny(collection1, collection2) | mutableSet1.intersect(mutableSet2).isEmpty() | |
| , (difference) | Set<T> result = new HashSet<>(set1); result.removeAll(set2) | Sets.difference(set1, set2) | CollectionUtils.removeAll(collection1, collection2) | mutableSet1.difference(mutableSet2) |
| (symmetric difference) | Sets.symmetricDifference(set1, set2) | CollectionUtils.disjunction(collection1, collection2) | mutableSet1.symmetricDifference(mutableSet2) | |
| Set<T> result = new HashSet<>(set1); result.addAll(set2) | Sets.union(set1, set2) | CollectionUtils.union(collection1, collection2) | mutableSet1.union(mutableSet2) |
:
1)
Collection<String> collection1 = Lists.newArrayList("a1", "a2", "a3", "a1"); Collection<String> collection2 = Lists.newArrayList("a1", "a2", "a3", "a1"); Iterable<String> iterable1 = collection1; Iterable<String> iterable2 = collection2; MutableCollection<String> mutableCollection1 = FastList.newListWith("a1", "a2", "a3", "a1"); MutableCollection<String> mutableCollection2 = FastList.newListWith("a1", "a2", "a3", "a1"); // boolean jdk = collection1.containsAll(collection2); // c JDK boolean guava = Iterables.elementsEqual(iterable1, iterable2); // guava boolean apache = CollectionUtils.containsAll(collection1, collection2); // c Apache boolean gs = mutableCollection1.containsAll(mutableCollection2); // c GS System.out.println("containsAll = " + jdk + ":" + guava + ":" + apache + ":" + gs); // containsAll = true:true:true:true 2)
Collection<String> collection1 = Lists.newArrayList("a1", "a2", "a3", "a1"); Collection<String> collection2 = Lists.newArrayList("a4", "a8", "a3", "a5"); Set<String> set1 = Sets.newHashSet("a1", "a2", "a3", "a1"); Set<String> set2 = Sets.newHashSet("a4", "a8", "a3", "a5"); MutableSet<String> mutableSet1 = UnifiedSet.newSetWith("a1", "a2", "a3", "a1"); MutableSet<String> mutableSet2 = UnifiedSet.newSetWith("a4", "a8", "a3", "a5"); // boolean jdk = !Collections.disjoint(collection1, collection2); // c JDK boolean guava = !Sets.intersection(set1, set2).isEmpty(); // guava boolean apache = CollectionUtils.containsAny(collection1, collection2); // c Apache boolean gs = !mutableSet1.intersect(mutableSet2).isEmpty(); // c GS System.out.println("containsAny = " + jdk + ":" + guava + ":" + apache + ":" + gs); // containsAny = true:true:true:true 3) ()
Collection<String> collection1 = Lists.newArrayList("a1", "a2", "a3", "a1"); Collection<String> collection2 = Lists.newArrayList("a4", "a8", "a3", "a5"); Set<String> set1 = Sets.newHashSet("a1", "a2", "a3", "a1"); Set<String> set2 = Sets.newHashSet("a4", "a8", "a3", "a5"); MutableSet<String> mutableSet1 = UnifiedSet.newSetWith("a1", "a2", "a3", "a1"); MutableSet<String> mutableSet2 = UnifiedSet.newSetWith("a4", "a8", "a3", "a5"); // Set<String> jdk = new HashSet<>(set1); // c JDK jdk.retainAll(set2); Set<String> guava = Sets.intersection(set1, set2); // guava Collection<String> apache = CollectionUtils.intersection(collection1, collection2); // c Apache Set<String> gs = mutableSet1.intersect(mutableSet2); // c GS System.out.println("intersect = " + jdk + ":" + guava + ":" + apache + ":" + gs); // intersect = [a3]:[a3]:[a3]:[a3] 4) , (difference)
Collection<String> collection1 = Lists.newArrayList("a2", "a3"); Collection<String> collection2 = Lists.newArrayList("a8", "a3", "a5"); Set<String> set1 = Sets.newHashSet("a2", "a3"); Set<String> set2 = Sets.newHashSet("a8", "a3", "a5"); MutableSet<String> mutableSet1 = UnifiedSet.newSetWith("a2", "a3"); MutableSet<String> mutableSet2 = UnifiedSet.newSetWith("a8", "a3", "a5"); // , (difference) Set<String> jdk = new HashSet<>(set1); // c JDK jdk.removeAll(set2); Set<String> guava = Sets.difference(set1, set2); // guava Collection<String> apache = CollectionUtils.removeAll(collection1, collection2); // c Apache Set<String> gs = mutableSet1.difference(mutableSet2); // c GS System.out.println("difference = " + jdk + ":" + guava + ":" + apache + ":" + gs); // difference = [a2]:[a2]:[a2]:[a2] 5) (symmetric difference)
Collection<String> collection1 = Lists.newArrayList("a2", "a3"); Collection<String> collection2 = Lists.newArrayList("a8", "a3", "a5"); Set<String> set1 = Sets.newHashSet("a2", "a3"); Set<String> set2 = Sets.newHashSet("a8", "a3", "a5"); MutableSet<String> mutableSet1 = UnifiedSet.newSetWith("a2", "a3"); MutableSet<String> mutableSet2 = UnifiedSet.newSetWith("a8", "a3", "a5"); // (symmetric difference) Set<String> intersect = new HashSet<>(set1); // c JDK intersect.retainAll(set2); Set<String> jdk = new HashSet<>(set1); jdk.addAll(set2); jdk.removeAll(intersect); Set<String> guava = Sets.symmetricDifference(set1, set2); // guava Collection<String> apache = CollectionUtils.disjunction(collection1, collection2); // c Apache Set<String> gs = mutableSet1.symmetricDifference(mutableSet2); // c GS System.out.println("symmetricDifference = " + jdk + ":" + guava + ":" + apache + ":" + gs); // symmetricDifference = [a2, a5, a8]:[a2, a5, a8]:[a2, a5, a8]:[a2, a5, a8] 6)
Set<String> set1 = Sets.newHashSet("a1", "a2"); Set<String> set2 = Sets.newHashSet("a4"); MutableSet<String> mutableSet1 = UnifiedSet.newSetWith("a1", "a2"); MutableSet<String> mutableSet2 = UnifiedSet.newSetWith("a4"); Collection<String> collection1 = set1; Collection<String> collection2 = set2; // Set<String> jdk = new HashSet<>(set1); // c JDK jdk.addAll(set2); Set<String> guava = Sets.union(set1, set2); // guava Collection<String> apache = CollectionUtils.union(collection1, collection2); // c Apache Set<String> gs = mutableSet1.union(mutableSet2); // c GS System.out.println("union = " + jdk + ":" + guava + ":" + apache + ":" + gs); // union = [a1, a2, a4]:[a1, a2, a4]:[a1, a2, a4]:[a1, a2, a4] 5.4
| Title | JDK | guava | apache | gs-collections |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Collections.sort(list); | Ordering.natural().sortedCopy(iterable) | mutableList.sortThis() | ||
| collection.removeIf((s) -> s.contains(«1»)) | Iterables.removeIf(iterable, (s) -> s.contains(«1»)) | CollectionUtils.filter(iterable, (s) -> !s.contains(«1»)) | mutableCollection.removeIf((Predicate<String>) (s) -> s.contains(«1»)) | |
| collection.removeIf((s) -> !s.contains(«1»)) | Iterables.removeIf(iterable, (s) -> !s.contains(«1»)) | CollectionUtils.filter(iterable, (s) -> s.contains(«1»)) | mutableCollection.removeIf((Predicate<String>) (s) -> !s.contains(«1»)) | |
| collection.stream().map((s) -> s + "_1").collect(Collectors.toList()) | Iterables.transform(iterable, (s) -> s + "_1") | CollectionUtils.transform(collection, (s) -> s + "_1") | mutableCollection.collect((s) -> s + "_1") | |
| collection.stream().forEach((s) -> s.append("_1")) | Iterables.transform(iterable, (s) -> s.append("_1")) | CollectionUtils.transform(collection, (s) -> s.append("_1")) | mutableCollection.forEach((Procedure<StringBuilder>) (s) -> s.append("_1")) |
1)
List<String> jdk = Lists.newArrayList("a1", "a2", "a3", "a1"); Iterable<String> iterable = jdk; MutableList<String> gs = FastList.newList(jdk); // Collections.sort(jdk); // jdk List<String> guava = Ordering.natural().sortedCopy(iterable); // guava gs.sortThis(); // c gs System.out.println("sort = " + jdk + ":" + guava + ":" + gs); // sort = [a1, a1, a2, a3]:[a1, a1, a2, a3]:[a1, a1, a2, a3] 2)
Collection<String> jdk = Lists.newArrayList("a1", "a2", "a3", "a1"); Iterable<String> guava = Lists.newArrayList(jdk); Iterable<String> apache = Lists.newArrayList(jdk); MutableCollection<String> gs = FastList.newList(jdk); // jdk.removeIf((s) -> s.contains("1")); // jdk Iterables.removeIf(guava, (s) -> s.contains("1")); // guava CollectionUtils.filter(apache, (s) -> !s.contains("1")); // apache gs.removeIf((Predicate<String>) (s) -> s.contains("1")); // c gs System.out.println("removeIf = " + jdk + ":" + guava + ":" + apache + ":" + gs); // removeIf = [a2, a3]:[a2, a3]:[a2, a3]:[a2, a3] 3)
Collection<String> jdk = Lists.newArrayList("a1", "a2", "a3", "a1"); Iterable<String> guava = Lists.newArrayList(jdk); Iterable<String> apache = Lists.newArrayList(jdk); MutableCollection<String> gs = FastList.newList(jdk); // jdk.removeIf((s) -> !s.contains("1")); // jdk Iterables.removeIf(guava, (s) -> !s.contains("1")); // guava CollectionUtils.filter(apache, (s) -> s.contains("1")); // apache gs.removeIf((Predicate<String>) (s) -> !s.contains("1")); // c gs System.out.println("retainIf = " + jdk + ":" + guava + ":" + apache + ":" + gs); // retainIf = [a1, a1]:[a1, a1]:[a1, a1]:[a1, a1] 4)
Collection<String> collection = Lists.newArrayList("a1", "a2", "a3", "a1"); Iterable<String> iterable = collection; Collection<String> apache = Lists.newArrayList(collection); MutableCollection<String> mutableCollection = FastList.newList(collection); // List<String> jdk = collection.stream().map((s) -> s + "_1").collect(Collectors.toList()); // jdk Iterable<String> guava = Iterables.transform(iterable, (s) -> s + "_1"); // guava CollectionUtils.transform(apache, (s) -> s + "_1"); // apache MutableCollection<String> gs = mutableCollection.collect((s) -> s + "_1"); // c gs System.out.println("transform = " + jdk + ":" + guava + ":" + apache + ":" + gs); // transform = [a1_1, a2_1, a3_1, a1_1]:[a1_1, a2_1, a3_1, a1_1]:[a1_1, a2_1, a3_1, a1_1]:[a1_1, a2_1, a3_1, a1_1] 5)
Collection<StringBuilder> jdk = Lists.newArrayList(new StringBuilder("a1"), new StringBuilder("a2"), new StringBuilder("a3")); Iterable<StringBuilder> iterable = Lists.newArrayList(new StringBuilder("a1"), new StringBuilder("a2"), new StringBuilder("a3"));; Collection<StringBuilder> apache = Lists.newArrayList(new StringBuilder("a1"), new StringBuilder("a2"), new StringBuilder("a3")); MutableCollection<StringBuilder> gs = FastList.newListWith(new StringBuilder("a1"), new StringBuilder("a2"), new StringBuilder("a3")); // jdk.stream().forEach((s) -> s.append("_1")); // jdk Iterable<StringBuilder> guava = Iterables.transform(iterable, (s) -> s.append("_1")); // guava CollectionUtils.transform(apache, (s) -> s.append("_1")); // apache gs.forEach((Procedure<StringBuilder>) (s) -> s.append("_1")); // c gs System.out.println("change = " + jdk + ":" + guava + ":" + apache + ":" + gs); // changeAll = [a1_1, a2_1, a3_1]:[a1_1, a2_1, a3_1]:[a1_1, a2_1, a3_1]:[a1_1, a2_1, a3_1] Vi.
5.1
( Java, ):
1) () — , ,
— — ,
— — , ,
— — ,
, ,
— —
,
2) (Stack) — , «LIFO» (« — »). AT
, /.
3) (Queue) — , «FIFO» (« — »). AT
/.
4) (Double-ended queue) — ,
.
5) (. priority queue) — ,
. ,
— (heap) — , ,
6) (), (Associative array, Dictionary) — ,
«— »
— - (hashtable) — , ,
— - (Multimap multihash) — -,
,
— - - (bi-map) — -,
, ,
— - (hashtable) — -, ,
— - (hashtable) — -, ,
7) — ,
,
— — , ,
,
— — , , ,
— — , , ,
8) — 1 0,
9) —
,
10) — , ,
11) — ,
Java :
: , .
VII. Conclusion
, , , . , ( ) , - .
github' .
, :
1. java.util.concurrent.* tutorial
2. Trove library: using primitive collections for performance
3. Java performance tuning tips
4. Large HashMap overview
5. Memory consumption of popular Java data types
6. , , , javadoc
PPS I also advise you to look at my opensource project [useful-java-links] (https://github.com/Vedenin/useful-java-links/tree/master/link-rus) - perhaps the most comprehensive collection of useful Java libraries, frameworks and Russian-language instructional videos. There is also a similar [English version] (https://github.com/Vedenin/useful-java-links/) of this project and start the opensource subproject [Hello world] (https://github.com/Vedenin/useful-java -links / tree / master / helloworlds) for preparing a collection of simple examples for different Java libraries in one maven project (I will be grateful for any help).
General table of contents 'cheat sheets'
1. JPA and Hibernate in questions and answers
2. Three hundred fifty most popular non-mobile Java opensource projects on github
3. Collections in Java (standard, guava, apache, trove, gs-collections, and others
4. Java Stream API
5. Two hundred and fifty Russian-language teaching videos of lectures and reports on Java.
6. List of useful links for Java programmer
7 Typical tasks
7.1 Optimum way to convert an InputStream to a string
7.2 The most productive way to bypass the Map, count the number of occurrences of the substring
8. Libraries for working with Json (Gson, Fastjson, LoganSquare, Jackson, JsonPath and others)
2. Three hundred fifty most popular non-mobile Java opensource projects on github
3. Collections in Java (standard, guava, apache, trove, gs-collections, and others
4. Java Stream API
5. Two hundred and fifty Russian-language teaching videos of lectures and reports on Java.
6. List of useful links for Java programmer
7 Typical tasks
7.1 Optimum way to convert an InputStream to a string
7.2 The most productive way to bypass the Map, count the number of occurrences of the substring
8. Libraries for working with Json (Gson, Fastjson, LoganSquare, Jackson, JsonPath and others)
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/256877/
All Articles