A little about the HL7 EHR-System Functional Model (Functional Model of the EMC system)
Among the standards of Health Level 7 (HL7), despite the name of the organization, there are those that do not relate directly to the transfer of medical data. The standard “ HL7 EHR-System Functional Model ” or “HL7 Functional Model of the EHR System”, the second version of which with significant additions was published in April 2014, refers specifically to such standards. This standard is normative, not advisory, approved by ANSI in 2007, in 2009 the first version of the standard, after the revision of ISO and CEN, was published as ISO / HL7 10781. The standard can be downloaded for free on the HL7.org website called HL7 EHR-System Functional Model, Release 2 . The standard includes a description of the standard and how to use it, and an application with a list of functions.
Before one of you runs to download it, just a minute of attention. This standard is somewhat difficult to understand, since it is focused not on programmers, or even on business analysts, but on a slightly higher level. The following picture conditionally shows the place of this standard among all other published HL7.
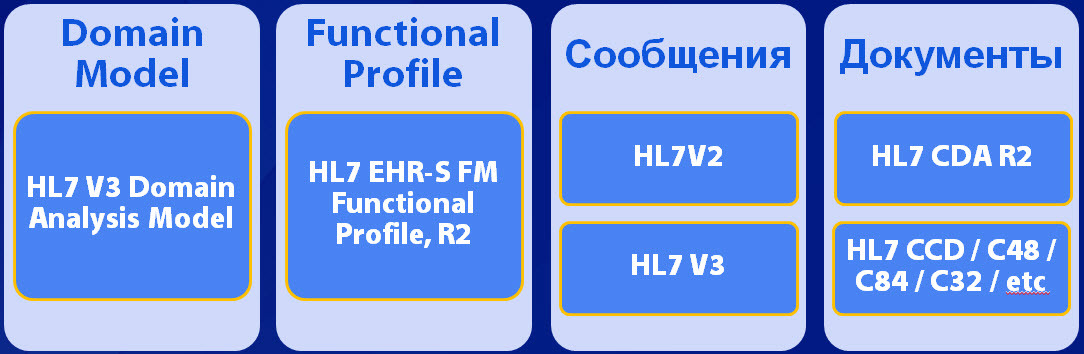
')
That is, before starting to get acquainted with the functional model, it would be nice to look at the HL7V3 Domain Analysis Model for your chosen medical field, for example, HL7 Version 3 Domain Analysis Model: Emergency Medical Services . The HL7 Domain Analysis Model standard contains a large number of Use Case, Activity and other types of UML diagrams for a particular area of medical services (in this case, emergency medical care) and probably reflects the best practice collected by numerous experts in this area. The standard, again in relation to Emergency Medical Services, helps to figure out who, how and to whom transmits medical information in the case of emergency medical care and transportation of the patient. Similar models exist for other areas.
Now that we know what the main components of the system will need to be implemented, we can use the following standard, which is described in this article to find out what functions these components of the system should perform in the ideal case.
To begin, consider the typical (hypothetical) scenarios in which, according to the compilers of the HL7 EHR-S FM standard, it can be used. (Chapter 5 Anticipated Uses of the Standard) The above scenarios, of course, reflect the overseas realities.
And so, the first scenario: A group of doctors who own a private clinic uses a certain medical system for financial operations: billing, planning, etc., but does not store patients' EHC in it. For some reason, this system must be updated or replaced over the next 2 years. The group of doctors takes the HL7 EHR-S FM standard and, having a lot of practical experience, begin to see which functions from the section of the Function of the Medical Process best fit their ideal EHR system. At this time, the administrative staff of the clinic examines the list of functions from the Auxiliary Functions section, and the technical staff from the information infrastructure. Next, they create a Functional Profile that combines all these requirements.
Scenario 2: A large hospital medical information system was recently updated to comply with HIPAA requirements. However, this update did not include support for clinical decisions, monitoring system performance, reporting, etc. The director of information technologies at the hospital asks the group of doctors to consider the functions of the treatment process and the functions of providing the treatment process. At this time, the IT team is exploring information support functions. The list was then consolidated and sent to the hospital information system provider to add the required functions.
Scenario Three: A certain supplier of medical systems has in its development various EHR support systems targeted at large hospitals and similar organizations. At the same time, the company would like to enter the market for private practices and small clinics, but in this case they need to meet Medicare requirements. In addition to Medicare requirements, the company would also like to add a number of features to compete successfully with existing systems in this market. Having reviewed the list of functions in various sections of the HL7 EHR-S FM standard, company representatives concluded that they needed very small changes in existing systems for successful competition.
As you can see, in all three cases we are talking about a certain list of functions that everyone learns. And indeed it is. In the first version of the standard there were three sections (or groups), in the second version there are already 7. Accordingly, the number of functions recommended for a typical medical system also increased from 140 to 322, and the criteria for testing them from 972 to 2310. The picture below shows how These sections (groups of functions) are organized:
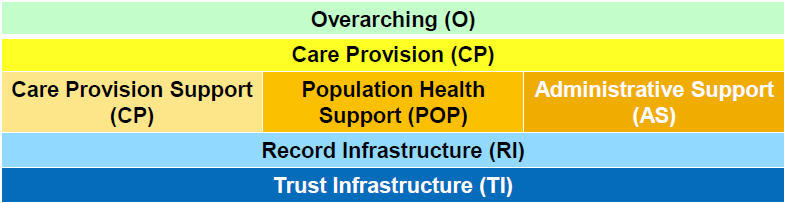
Each section consists of a set of functions, each of which, in turn, can have clarifying subfunctions and the corresponding verification criteria for this function. Chapter 4, Overview and Definition of the Functional Model , describes how the functions are presented in the standard.
For example, Overarching (General Section) contains only one function - OV.1 - which states that the criteria for testing this section apply to all EHR systems and, therefore, should be included in all functional profiles.
The Care Provision section has several functions, one of which CP.1.1 Manage Patient History has 14 subfunctions, for example, CP.1.1.2 - the system SHALL elements according to the scope of practice, organizational policy, and / or jurisdictional law .
And so on. Obviously, there is no point in listing all the functions. Sections and functions that are interesting for IT departments are, as always, located in the basement, namely, Record Infrastructure and Trust Infrastructure . Maybe someone wants to get to know them better.
As described in the scenarios above, the standard does not imply that all the listed functions are required to be implemented in a typical EHR system, so the user of the standard can create his own Functional Profile by selecting only what is necessary in the context of applying a particular honey system. The following picture conventionally shows such a profile covering all 7 sections.
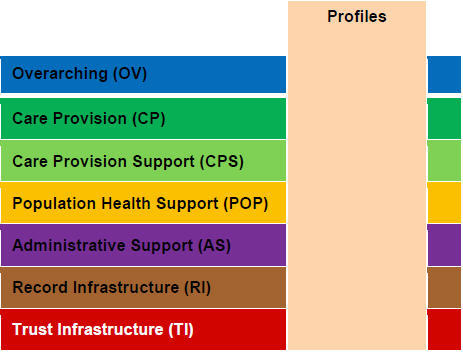
In general, a real EHR system, as the drafters of the standard claim, can correspond to more than one Functional Profile (although I don’t quite understand how that prevents them from being combined). The largest chapter in the standard, chapter 6 of the Conformance Clause, describes how to create profiles, what structure they have, how to add functions, how to choose verification conditions, how they should be correctly recorded in English and so on.
In order not to start from scratch, on the site HL7.org, in the Standards > EHR Profiles section, besides the standard itself, you can also download ready-made profiles for various areas, for example, HL7 EHR Pharmacist / Pharmacy Provider Functional Profile or HL7 EHR Child Health Functional Profile .
Although the standard itself is somewhat broader than just the listing of sections and functions, some of its parts are applicable only for English-speaking countries. For example, as mentioned above, the requirements for the descriptions of the verification requirements. What words can be used, what words are not allowed, what they mean and so on. So, it is not recommended to use reconcile (harmonize), but harmonize (harmonization) is possible, although the first one is found very often, and the second is unlikely to be remembered by anyone in the documentation for information systems.
Returning to the first picture in this article. After the system functions have been defined, the remaining two right-hand columns, Messages and Documents, find the HL7 technical standards for interfacing (transmitting data) with other systems and presenting medical data.
I deliberately did not make a review of the chapters of the standard, this makes little sense. The most interesting thing, in my opinion, is to go through the functions and see how your system meets the requirements of HL7. This is if you are a supplier of honey systems. And if the consumer is a medical system, then the same set of functions will probably help prepare for the tender.
Before one of you runs to download it, just a minute of attention. This standard is somewhat difficult to understand, since it is focused not on programmers, or even on business analysts, but on a slightly higher level. The following picture conditionally shows the place of this standard among all other published HL7.

')
That is, before starting to get acquainted with the functional model, it would be nice to look at the HL7V3 Domain Analysis Model for your chosen medical field, for example, HL7 Version 3 Domain Analysis Model: Emergency Medical Services . The HL7 Domain Analysis Model standard contains a large number of Use Case, Activity and other types of UML diagrams for a particular area of medical services (in this case, emergency medical care) and probably reflects the best practice collected by numerous experts in this area. The standard, again in relation to Emergency Medical Services, helps to figure out who, how and to whom transmits medical information in the case of emergency medical care and transportation of the patient. Similar models exist for other areas.
Now that we know what the main components of the system will need to be implemented, we can use the following standard, which is described in this article to find out what functions these components of the system should perform in the ideal case.
To begin, consider the typical (hypothetical) scenarios in which, according to the compilers of the HL7 EHR-S FM standard, it can be used. (Chapter 5 Anticipated Uses of the Standard) The above scenarios, of course, reflect the overseas realities.
And so, the first scenario: A group of doctors who own a private clinic uses a certain medical system for financial operations: billing, planning, etc., but does not store patients' EHC in it. For some reason, this system must be updated or replaced over the next 2 years. The group of doctors takes the HL7 EHR-S FM standard and, having a lot of practical experience, begin to see which functions from the section of the Function of the Medical Process best fit their ideal EHR system. At this time, the administrative staff of the clinic examines the list of functions from the Auxiliary Functions section, and the technical staff from the information infrastructure. Next, they create a Functional Profile that combines all these requirements.
Scenario 2: A large hospital medical information system was recently updated to comply with HIPAA requirements. However, this update did not include support for clinical decisions, monitoring system performance, reporting, etc. The director of information technologies at the hospital asks the group of doctors to consider the functions of the treatment process and the functions of providing the treatment process. At this time, the IT team is exploring information support functions. The list was then consolidated and sent to the hospital information system provider to add the required functions.
Scenario Three: A certain supplier of medical systems has in its development various EHR support systems targeted at large hospitals and similar organizations. At the same time, the company would like to enter the market for private practices and small clinics, but in this case they need to meet Medicare requirements. In addition to Medicare requirements, the company would also like to add a number of features to compete successfully with existing systems in this market. Having reviewed the list of functions in various sections of the HL7 EHR-S FM standard, company representatives concluded that they needed very small changes in existing systems for successful competition.
As you can see, in all three cases we are talking about a certain list of functions that everyone learns. And indeed it is. In the first version of the standard there were three sections (or groups), in the second version there are already 7. Accordingly, the number of functions recommended for a typical medical system also increased from 140 to 322, and the criteria for testing them from 972 to 2310. The picture below shows how These sections (groups of functions) are organized:

Each section consists of a set of functions, each of which, in turn, can have clarifying subfunctions and the corresponding verification criteria for this function. Chapter 4, Overview and Definition of the Functional Model , describes how the functions are presented in the standard.
For example, Overarching (General Section) contains only one function - OV.1 - which states that the criteria for testing this section apply to all EHR systems and, therefore, should be included in all functional profiles.
The Care Provision section has several functions, one of which CP.1.1 Manage Patient History has 14 subfunctions, for example, CP.1.1.2 - the system SHALL elements according to the scope of practice, organizational policy, and / or jurisdictional law .
And so on. Obviously, there is no point in listing all the functions. Sections and functions that are interesting for IT departments are, as always, located in the basement, namely, Record Infrastructure and Trust Infrastructure . Maybe someone wants to get to know them better.
As described in the scenarios above, the standard does not imply that all the listed functions are required to be implemented in a typical EHR system, so the user of the standard can create his own Functional Profile by selecting only what is necessary in the context of applying a particular honey system. The following picture conventionally shows such a profile covering all 7 sections.

In general, a real EHR system, as the drafters of the standard claim, can correspond to more than one Functional Profile (although I don’t quite understand how that prevents them from being combined). The largest chapter in the standard, chapter 6 of the Conformance Clause, describes how to create profiles, what structure they have, how to add functions, how to choose verification conditions, how they should be correctly recorded in English and so on.
In order not to start from scratch, on the site HL7.org, in the Standards > EHR Profiles section, besides the standard itself, you can also download ready-made profiles for various areas, for example, HL7 EHR Pharmacist / Pharmacy Provider Functional Profile or HL7 EHR Child Health Functional Profile .
Although the standard itself is somewhat broader than just the listing of sections and functions, some of its parts are applicable only for English-speaking countries. For example, as mentioned above, the requirements for the descriptions of the verification requirements. What words can be used, what words are not allowed, what they mean and so on. So, it is not recommended to use reconcile (harmonize), but harmonize (harmonization) is possible, although the first one is found very often, and the second is unlikely to be remembered by anyone in the documentation for information systems.
Returning to the first picture in this article. After the system functions have been defined, the remaining two right-hand columns, Messages and Documents, find the HL7 technical standards for interfacing (transmitting data) with other systems and presenting medical data.
I deliberately did not make a review of the chapters of the standard, this makes little sense. The most interesting thing, in my opinion, is to go through the functions and see how your system meets the requirements of HL7. This is if you are a supplier of honey systems. And if the consumer is a medical system, then the same set of functions will probably help prepare for the tender.
Homework
In the English-language literature, there are three types of medical systems - EHR , EMR and PHR - which can be translated into Russian as EHR. Because of this, the meaning and functionality of the systems is lost. Even some English-speaking colleagues are sometimes confused in these terminologies. I suggest that you yourself look for and understand what their similarities and differences.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/256609/
All Articles