The main vulnerabilities of corporate information systems in 2014: web applications, passwords and employees
Attack Vectors to Overcome the Network Perimeter
The complexity of the attacks in 2014 was noticeably lower than in previous years, and it was possible to overcome the network perimeter in 60% of the systems through the vulnerabilities of web applications. Also in 2014, the level of awareness of employees of companies about security issues significantly decreased: they began to follow more unfamiliar links many times and open files attached to letters. Such observations are contained in a study of Positive Technologies based on penetration tests conducted in 2014 and comparing the data with last year's results. In this article we will share some of the results of the study.
')
Overall results
For the study, 18 information systems of large state and commercial companies, both Russian and foreign (including those included in the ranking of the world's largest Fortune Global 500 companies) were selected. More than half of the enterprises had many subsidiaries and branches located in different cities and countries. In most systems, the number of active nodes available on the network perimeter was in the hundreds. The largest number of projects related to industry, banking and IT.
94% of the systems studied contained vulnerabilities that allowed for complete control over certain critical resources - Active Directory, ERP, e-mail, and network equipment management systems. At the same time, in 67% of cases, obtaining full control over the most important resource was possible on behalf of any external attacker , in 27% of cases it was enough to have access to the user segment of the internal network.
Almost all of the systems studied were exposed to high-risk vulnerabilities; in particular, almost all contained critical vulnerabilities associated with configuration flaws. Virtually every information system ( 89% ) revealed vulnerabilities associated with errors in the code of web applications . In more than half of the companies ( 61% ), these were high-risk vulnerabilities.
Most of the systems ( 78% ) studied in 2014 contained critical vulnerabilities associated with the use of outdated software versions , which is significantly worse than the results of the previous year, when such systems were slightly more than half. The average age of the most outdated unspecified updates is 73 months (in 2013, it was two times lower — 32 months).
Disadvantages of network perimeter protection
In 73% of systems, an external intruder acting from the Internet is able to access nodes on the internal network without using social engineering methods. If the attacker uses social engineering, then access to the network from the outside can be obtained in 87% of cases. At the same time, 61% of systems can successfully attack an unskilled malefactor (in 2013, this figure was 46%).

The difficulty of overcoming the perimeter
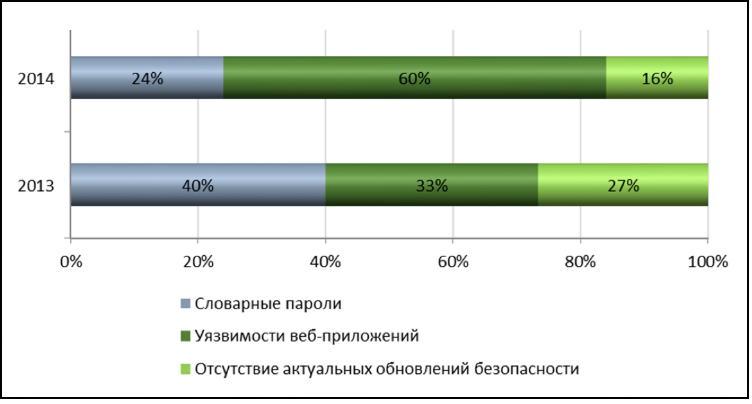
Overcoming the perimeter in 2014, as in the previous year, on average, requires only two vulnerabilities to be exploited. However, in more than half of the systems, where in 2014 they managed to overcome the perimeter (6 out of 11), this was done as a result of the exploitation of only one vulnerability. Moreover, in 60% of cases, the intrusion vector into the internal network is based on vulnerabilities in the code of web applications . Thus, the vulnerability of the type "Implementation of SQL statements" is found in 67% of systems, and "Download arbitrary files" - in 40%.
The most common vulnerabilities on the network perimeter are the network equipment and server management interfaces accessible from the Internet (their share increased from 82 % to 93% over the past year), as well as the use of dictionary passwords , including the default and empty passwords , 87% .

Statistics on the use of various protocols, including remote access interfaces, on the network perimeter (share of systems)
Disadvantages of internal network protection
When testing on behalf of an internal attacker (for example, an ordinary employee located in the user segment of the network), in all cases it was possible to obtain unauthorized privileged access to critical resources - banking systems, ERP systems and other business-relevant components of the network. In 78% of cases, the intruder can gain complete control over the organization’s entire information infrastructure.
In more than half of the cases (56%), the internal attacker is of sufficiently low skill to gain access to critical resources. And the complex attacks that require high qualification were not needed at all in 2014 (in 2013 they were required for penetration into 17% of the systems). On average, an internal attacker needs to exploit three different vulnerabilities in order to gain control over critical resources, which is worse than the previous year, when the attack consisted of an average of 5 stages.

The difficulty of accessing critical resources from the insider
The most common vulnerability of intranet resources is still the use of weak passwords that were found in all the systems studied . At the same time, simple passwords of administrators were revealed in each system: more than half of them are up to 6 characters long.

Share systems with dictionary passwords. Red color - passwords of administrators, blue - user passwords
The next most common vulnerability of internal networks is an insufficient level of protection of privileged accounts (88% of systems). Particular attention should be paid to the introduction of two-factor authentication for Active Directory domain administrators in connection with the appearance of the Kerberos Golden Ticket attack in 2014. This attack allows, once having obtained high privileges in the domain, to subsequently access it with the maximum level of access on behalf of an arbitrary account — by exploiting the flaws in the architecture of the Kerberos protocol, while tracking the actions of the attacker is extremely difficult.
Lack of employee awareness
In 2014, employee awareness was rated significantly lower compared to the previous year, when it was acceptable in every third tested system. In 2014, no company reached an acceptable level: 67% of the systems showed an extremely low or low level , while the rest were rated “below average”.
In particular, in 2014, the share of user transitions by the link provided in the letter almost doubled (from 11% to 20%). It was also recorded 4 times more facts of launching attached files or entering credentials in fake forms (15%).

A full version of this study with a detailed analysis of the main vulnerabilities of the year, including a realistic assessment of the spread of Heartbleed and Shellshock, will be published later. However, everyone can find out these details at the webinar, which will be conducted by the authors of the study on the nearest Thursday, April 16 at 14:00 The webinar is free, but you must register for participation:
www.ptsecurity.ru/lab/webinars/#40020
In addition, a record of the previous Positive Technologies webinar of experts has already been published - this report is devoted to statistics of vulnerabilities of web applications and remote banking systems in 2014: my.webinar.ru/record/480993
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/255681/
All Articles