Video surveillance through 3 / 4G (part 1)
Access to devices connected to the Internet via the mobile operator’s network is currently possible only using reverse VPN technology. Therefore, for the organization of remote video surveillance via 3G / 4G networks, we need two components:
In this article we will look at the settings of the router on the side of the webcam (DVR). First, a small picture illustrating the general connection of a webcam (DVR):

Attention! The material is designed for trained users who are ready to “flash” the firmware DD-WRT. If you do not have knowledge in this area, you should contact a specialist.
As routers, we will use a device with DD-WRT firmware. First, we configure the VPN link “Services -> VPN-> OpenVPN Client” . It is assumed that the 3 / 4G modem is already connected to the router and there is Internet access. Enable the OpenVPN client software:
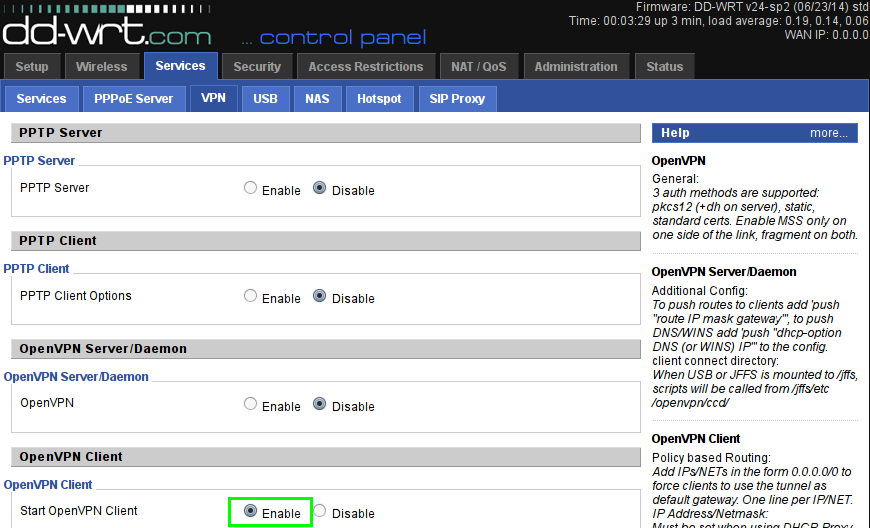
Configure VPN settings:

Let's set OpenVPN certificates:
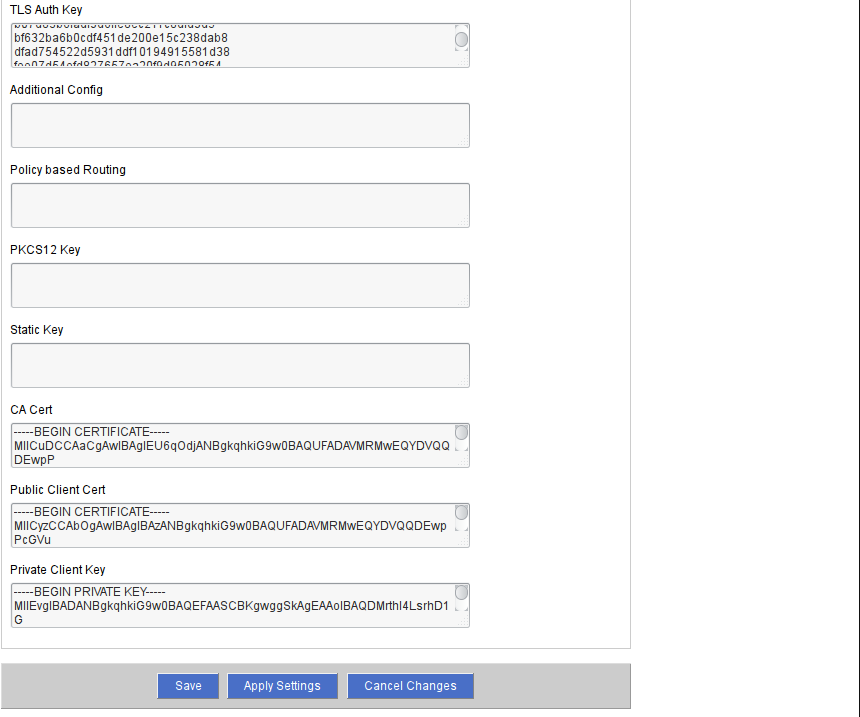
We need the following certificates and keys:
All these parameters are generated on the server side and given to you by the administrator of the VPN server.
Check it out. To do this, let's go, for example, to the “Status-> Bandwidth” page of the router settings. If the VPN connection was successful, you should see that a new tun1 interface has been added:

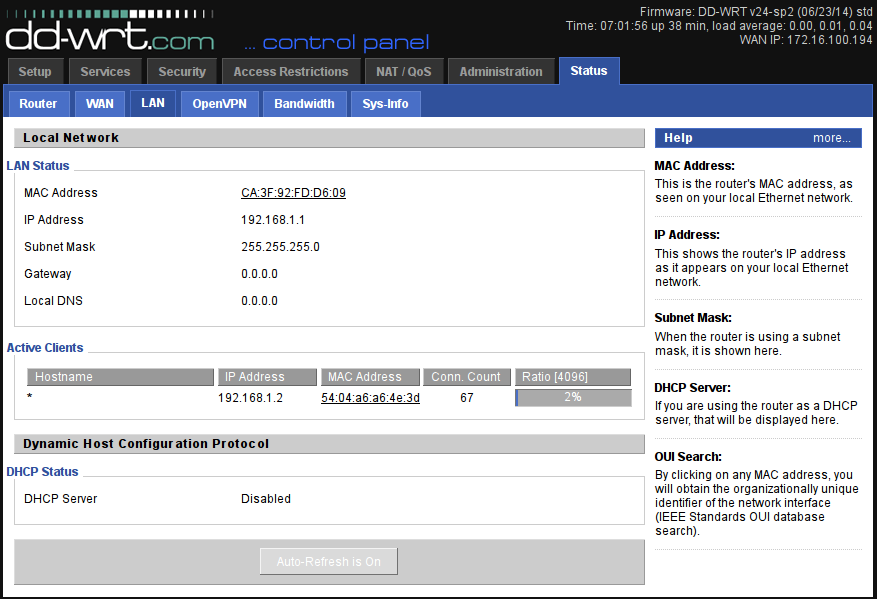
Set up access to the camcorder. We define the IP address of the camera. Ways can be different. You can, for example, go to the “Status-> LAN” page of the router and select the desired IP in the “Active Clients” list by its MAC address (which is usually printed on the webcam case).
It is better to “fix” the IP address provided by the video camera so that during further work it will not change and we would not have to reconfigure everything. This can be done in the router's “Services-> Services-> Static Leases” menu by adding the MAC and IP addresses obtained in the previous step to this list.
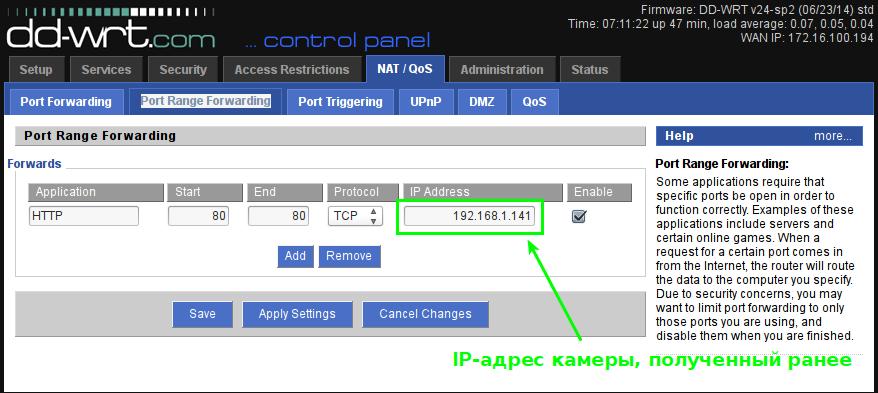
Set up port forwarding. We will configure in two places. First, the general port forwarding "NAT / QoS-> Port Range Forwarding" :
If we used a “normal” connection with a real IP, then we could stop at that. The router and camera would be “visible” from the Internet by name or by IP. But we use VPN, so we need the webcam to be visible through the interface tun1 - “Administration-> Commands-> Save-> Firewall” :
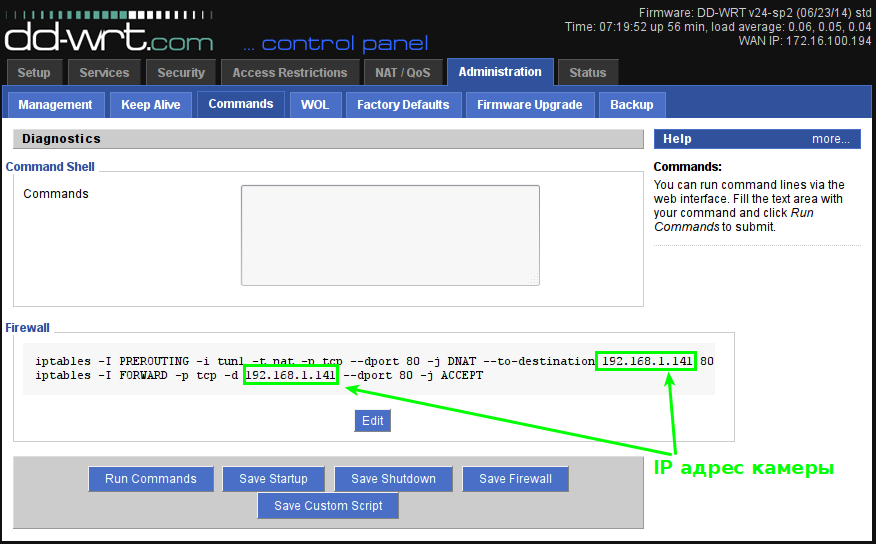
Attention! Since many webcams (DVRs) use port 80 (HTTP) for default access, we recommend that you leave only HTTPS to manage later problems with the router’s control panel to fix possible problems:

Restart the router - “Administration-> Management-> Reboot router” .
Check again that the VPN is connected (see above).
This completes the client-side (webcam) setup.
To be continued…
- A router with tunneling protocol support. In our version this is VPN - OpenVPN.
- A server that will accept connections from remote 3 / 4G and provide access to them for clients from the Internet.
In this article we will look at the settings of the router on the side of the webcam (DVR). First, a small picture illustrating the general connection of a webcam (DVR):

Attention! The material is designed for trained users who are ready to “flash” the firmware DD-WRT. If you do not have knowledge in this area, you should contact a specialist.
As routers, we will use a device with DD-WRT firmware. First, we configure the VPN link “Services -> VPN-> OpenVPN Client” . It is assumed that the 3 / 4G modem is already connected to the router and there is Internet access. Enable the OpenVPN client software:

Configure VPN settings:

Let's set OpenVPN certificates:

We need the following certificates and keys:
- "CA Cert" - the root certificate of the VPN server;
- “Public Client Cert” - a public certificate issued to the client by the server (server administrator) VPN;
- "Private Client Key" - the client's private key issued by the VPN server (server administrator) to the client;
- "TA Auth Key" is the VPN server pre-authentication key.
All these parameters are generated on the server side and given to you by the administrator of the VPN server.
Check it out. To do this, let's go, for example, to the “Status-> Bandwidth” page of the router settings. If the VPN connection was successful, you should see that a new tun1 interface has been added:

Set up access to the camcorder. We define the IP address of the camera. Ways can be different. You can, for example, go to the “Status-> LAN” page of the router and select the desired IP in the “Active Clients” list by its MAC address (which is usually printed on the webcam case).

It is better to “fix” the IP address provided by the video camera so that during further work it will not change and we would not have to reconfigure everything. This can be done in the router's “Services-> Services-> Static Leases” menu by adding the MAC and IP addresses obtained in the previous step to this list.
Set up port forwarding. We will configure in two places. First, the general port forwarding "NAT / QoS-> Port Range Forwarding" :

If we used a “normal” connection with a real IP, then we could stop at that. The router and camera would be “visible” from the Internet by name or by IP. But we use VPN, so we need the webcam to be visible through the interface tun1 - “Administration-> Commands-> Save-> Firewall” :

Attention! Since many webcams (DVRs) use port 80 (HTTP) for default access, we recommend that you leave only HTTPS to manage later problems with the router’s control panel to fix possible problems:

Restart the router - “Administration-> Management-> Reboot router” .
Check again that the VPN is connected (see above).
This completes the client-side (webcam) setup.
To be continued…
')
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/255655/
All Articles