Principles of Web Animation
Translator’s Note : The material presented below contains a significant number of technical terms that may cause inaccuracies in the translation. If you notice a typo, mistake or inaccuracy of the translation - write to us and we will fix everything promptly.
In addition, in the continuation of the topic of today's publication for one week will be open advanced course of the Academy on CSS-animations , which is usually available by subscription. His description is posted at the end of the topic.

')
Front-end designers and developers use CSS to create styles, position elements - in general, to make websites look beautiful. Often, CSS is also used to add motion to web pages, although it usually does not go beyond smooth transitions or animations.
In fact, animation can be a powerful tool that allows site visitors and customers to more easily interact with the product interface and achieve their goals faster. This can be achieved if you follow some fundamental principles in your work.
The Disney company has been engaged in animation for many years and has developed such recommendations - back in 1981, the book “ The Illusion of Life: Disney Animation ” (“ The Illusion of Life: Disney Animation ”) was published, which listed 12 animation principles (they were written on Habré) . They describe how to use animation to create a sense of the real world with viewers looking at the screen.
In today's article we will look at each of the twelve of these principles and discuss their possible use in creating web pages. All CSS and HTML sources can be downloaded on Codepen .
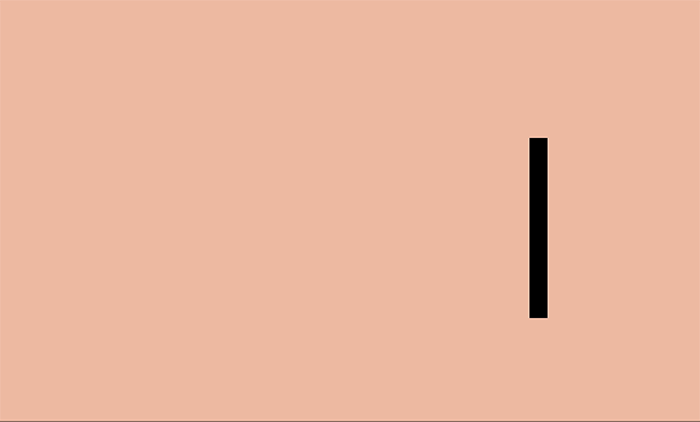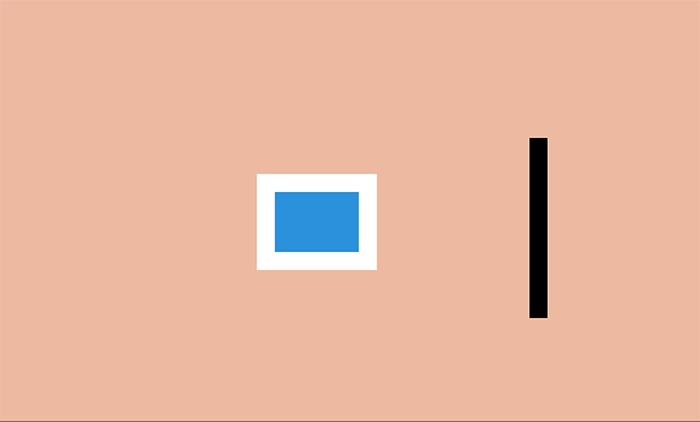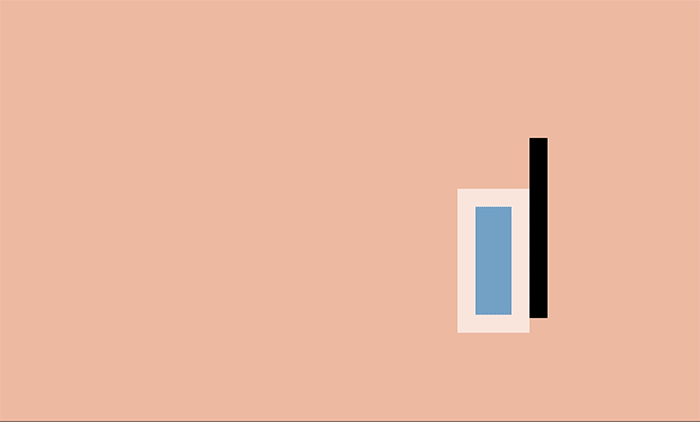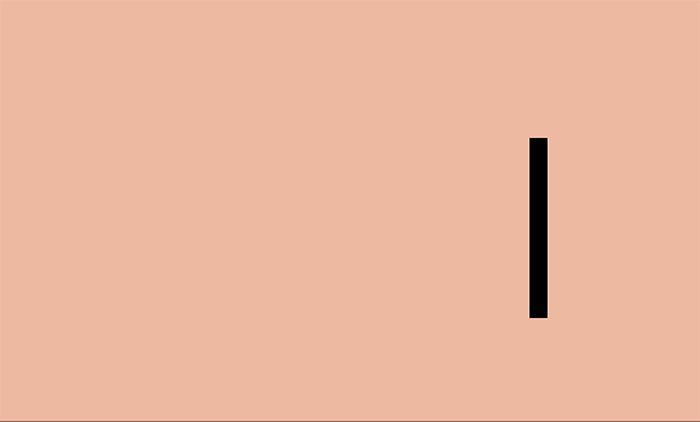
In the world there is the concept of "body mass" - and when an object moves, its mass remains unchanged. When the ball hits the ground, it will become slightly wider and flatten, because during physical contact the mass of the object is redistributed.
This effect is most useful when creating physical objects (for example, people, watches, or bouncing balls).
Of course, in the case of web pages, this property can also be ignored - DOM elements are not necessarily associated with physical objects and can grow and shrink in size on the screen. For example, a button can grow and transform into an information window, and error messages appear and disappear.
Despite this, the technique of “flattening and expanding” can be used to create a sense of the physical element on the page. Even small changes can create a subtle, but eye-catching effect.
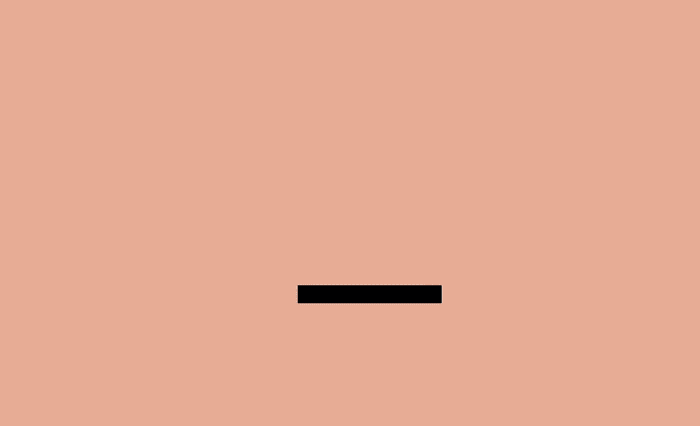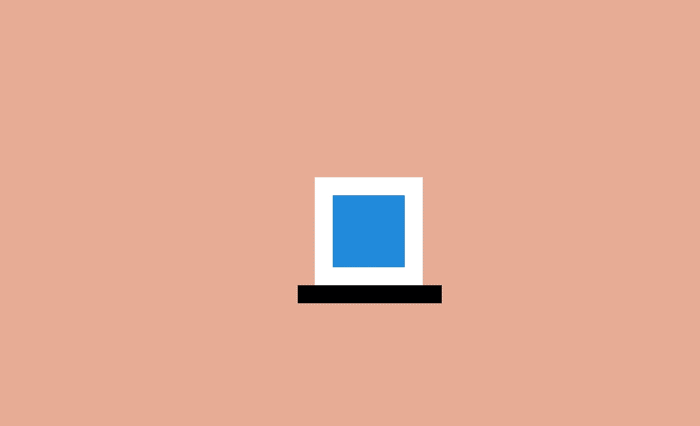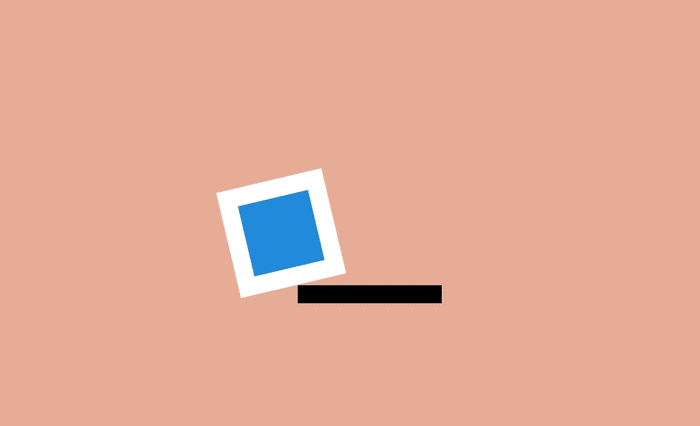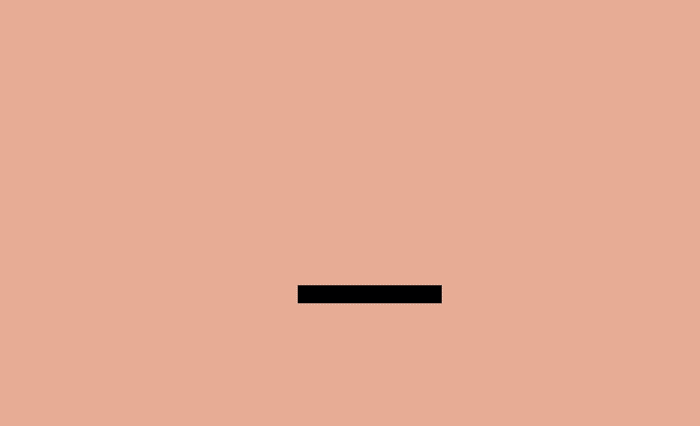
Movement does not occur suddenly. In ordinary life, any action is preceded by some kind of preparation, be it a ball slowing down before falling from the steps or a person bending the knees before jumping.
This effect can be used to make the movement of objects on a web page more realistic. The wait itself can be implemented, for example, as a light wiggle, which allows users to understand what is happening and helps them to more easily follow the movement of an object across the screen.
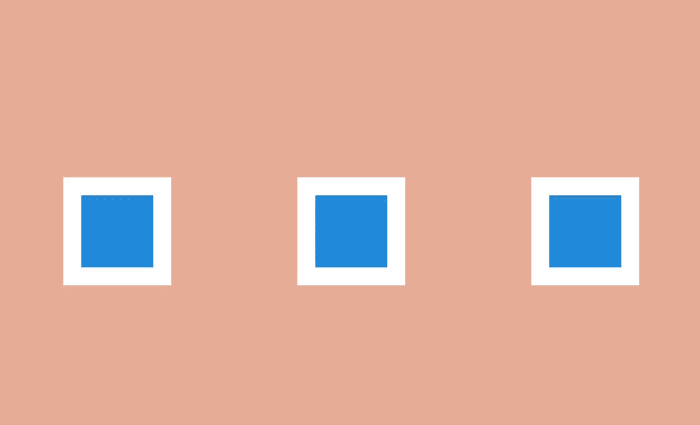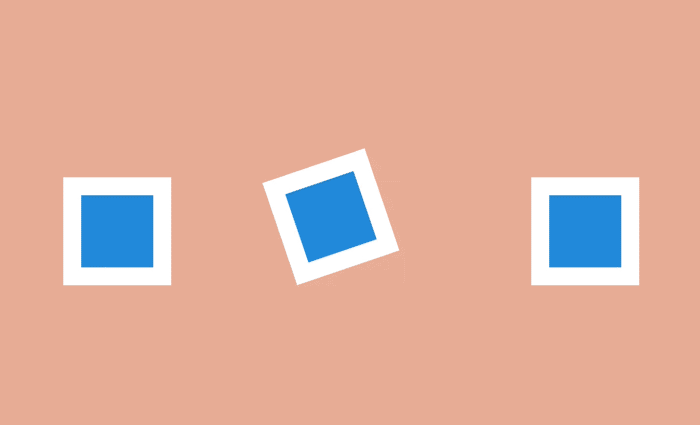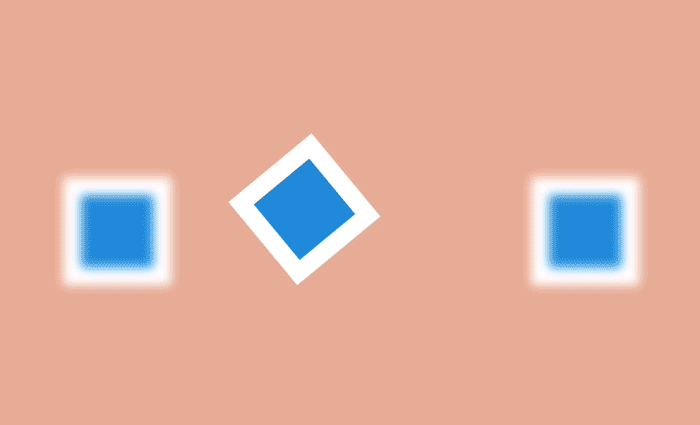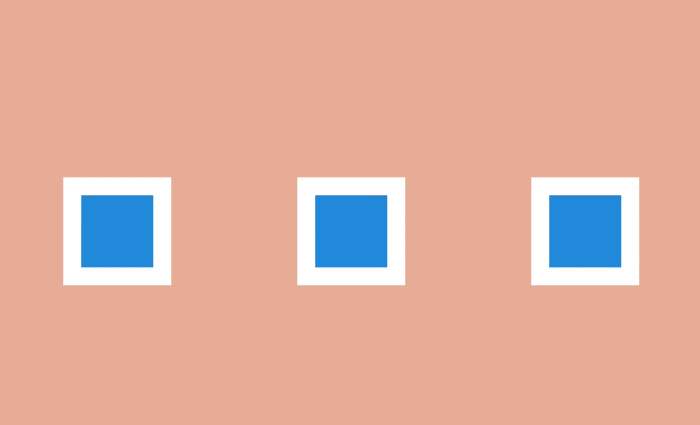
This effect is to define the object as the focus of the scene, while other objects make room for the main action. To create such an effect, the desired object is appropriately brought to the fore or masked by the accompanying elements in order to focus the user's view on what he should see.
In web terms, this means using translucent obscuring for certain content. The imposition of a darker layer on an existing page and the subsequent placement of content in the foreground focuses all the attention of users on it.
Another approach is to use movements. When several objects simultaneously move on the page, it is rather difficult to understand which of them is really worth looking at. If in such a situation you stop all objects, except for one “necessary” one, then all attention will automatically be focused on it.
Movement can be used in a different way. For example, if a user is working with a document, a slight jitter and the flashing of the “Save” button may prompt a person to click on it. When there is no activity on the screen, even a small movement is very prominent.
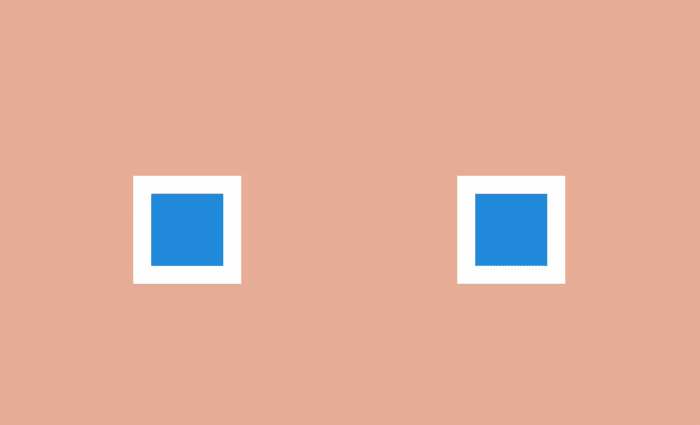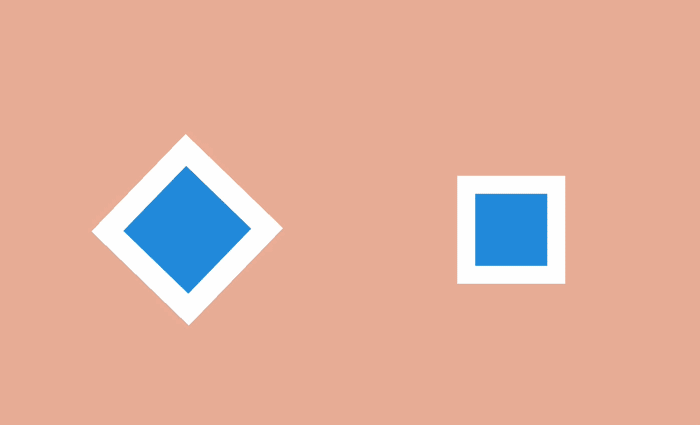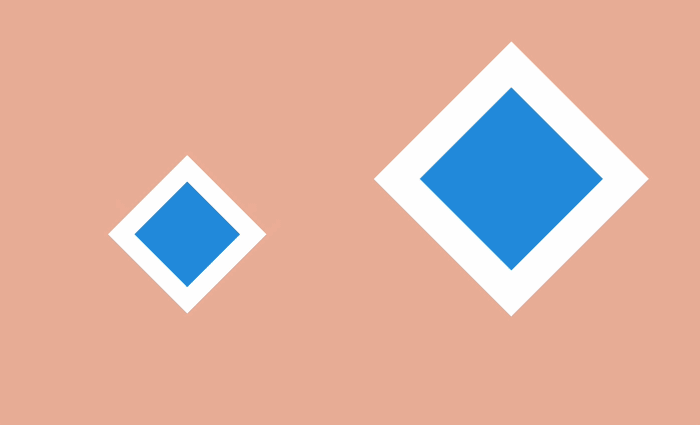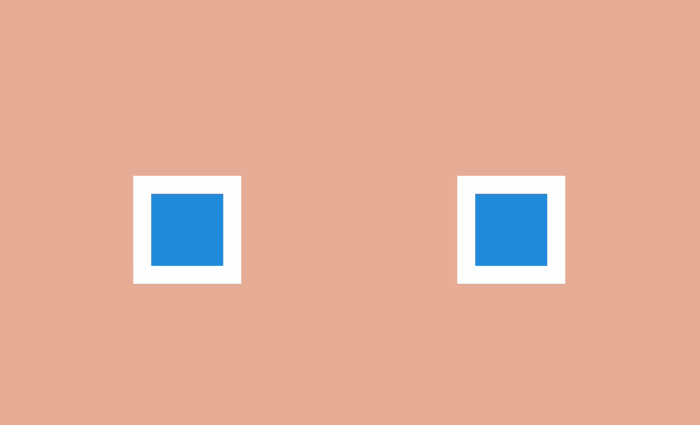
Direct movement is characterized by the complete rendering of all frames of the animation. In turn, a step change is characterized by the creation of a sequence of key frames, the intervals between which are filled later, usually with the help of auxiliary means.
The second approach is used in most web animations: the transitions between the main frames are implemented by the browser, which interpolates the difference between each of them and draws as many intermediate frames as needed to make the final animation smooth.
An exception is the “Steps” function. When using it, the browser “strides” for a given number of discrete frames. In this way, you can create a sequence of images, and then play them in the browser one by one using the “Straight Ahead Action” style.

Actions do not always occur simultaneously. When a moving car slows down sharply, with the smoke of the tires, it nods, and the driver inside continues to move until the final stop occurs.
This effect is achieved with the help of the movements of following and choking - they are needed to signal that the object has stopped. For example, an item placed in the list may slightly move the desired position, and then return to the correct position.
The effect of overruns is created by giving objects a different rate of movement. This approach is used in transitions in iOS — some buttons and elements move at different speeds, as a result of which movements become more realistic than they would be if they move at the same speed. The combination of movements gives the user time to realize the changes taking place.
In the web, this is usually achieved by combining smooth transitions or CSS animations with different playback speeds.

Objects rarely go instantly from a state of rest immediately to maximum speed. Usually, it takes some time for them to accelerate - just as it takes to stop. Without a gradual acceleration and deceleration of movement look unnatural.
In CSS terminology, acceleration and deceleration is known as easing, or “smoothness function,” which describes the change in animation speed.
Using the functions of smoothness, you can create accelerating and slowing animations and even more complex effects (using the

Slowing and acceleration makes objects more realistic, but there is one more thing: in life they rarely move in a straight line, as a rule, the movement goes along a curved arc.
To achieve this movement in an arc using CSS can be a couple of different ways. One is to combine several animations. For example, the animation of a bouncing ball can be made with the help of object movements up and down, and the second movement is combined with the movement also to the right. Thus it turns out that the ball jumps on the screen.
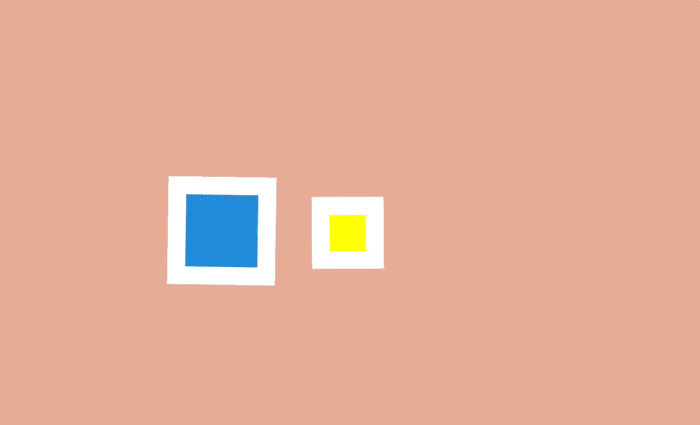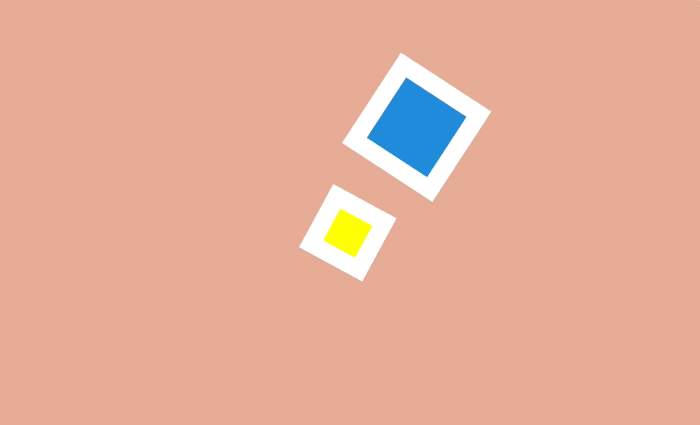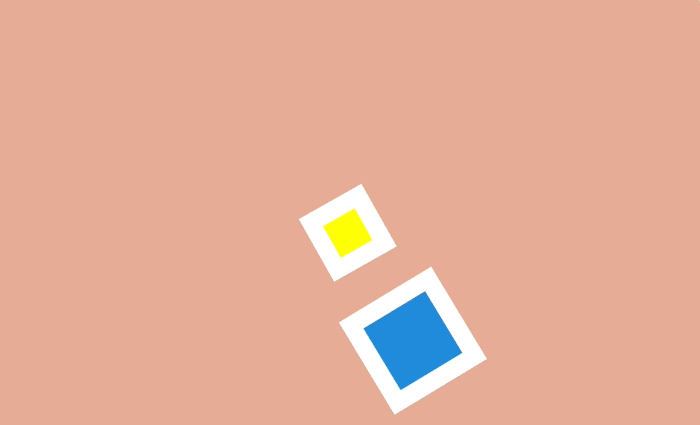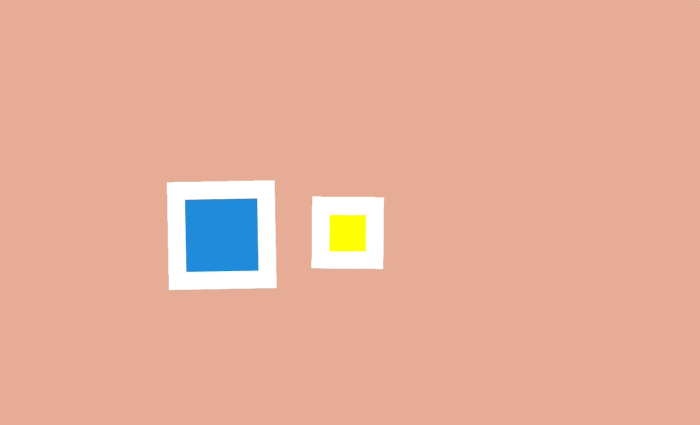
The second way is to rotate the element. By changing the center of rotation and moving it beyond the limits of the original object, an arc can also be formed.
The main action that takes place on the screen can be emphasized with “secondary” animation. This may be the movement of a person’s hands when walking or shaking his head with each step. Or dust rising from the ground with each blow of the ball.
In the case of websites, secondary elements can “drive apart” in order to highlight what the user really needs to pay attention to (for example, dragging an element to insert it in the middle of the list).
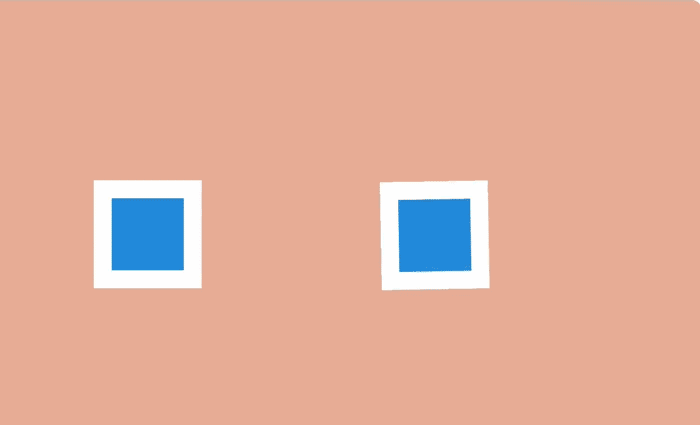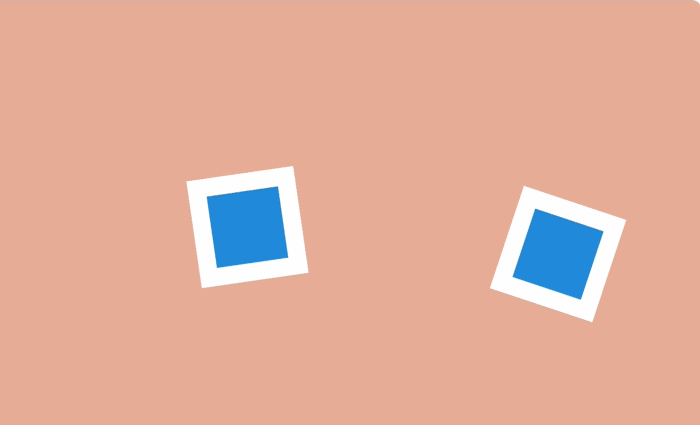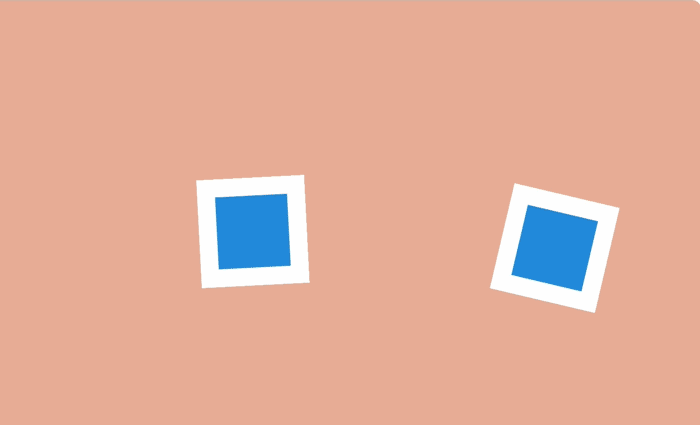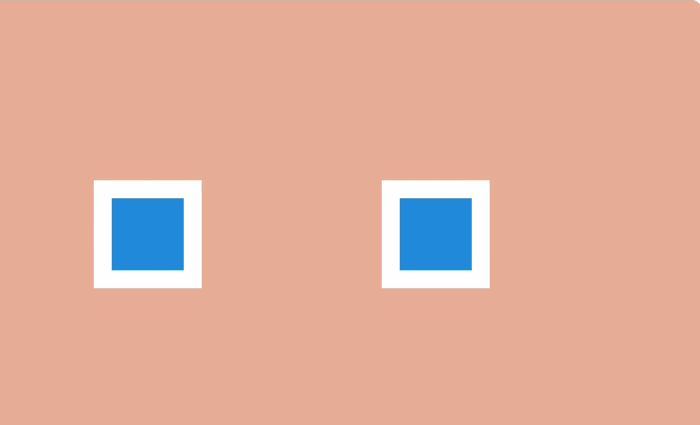
Using the manipulation of the duration of the animation can be done so that large objects seem heavy, and small - light.
On the Web, this can be achieved by simply changing the values of
By changing the duration of the animation, you can select it among the content of the web page or during interaction with the user.
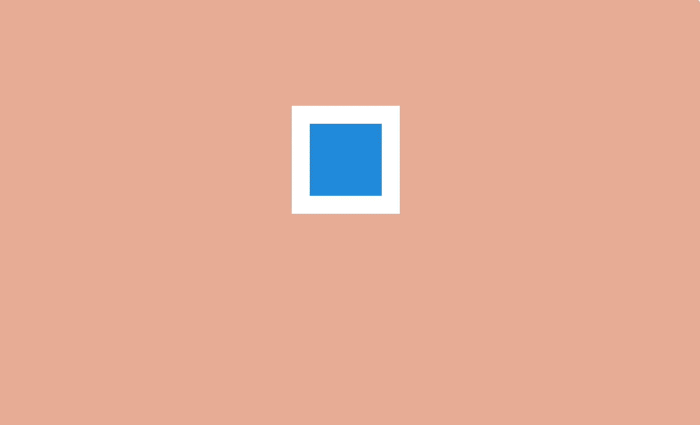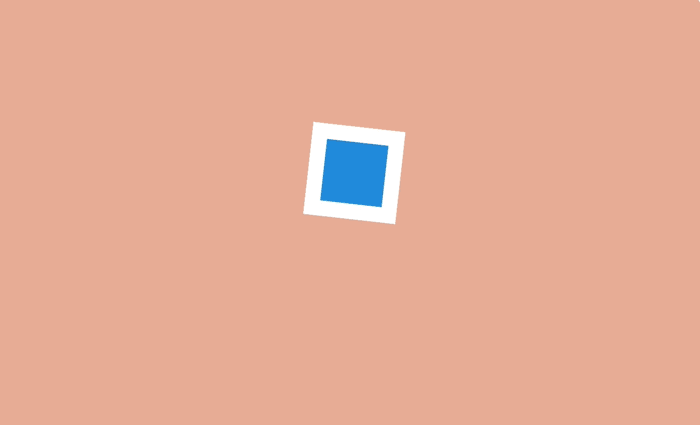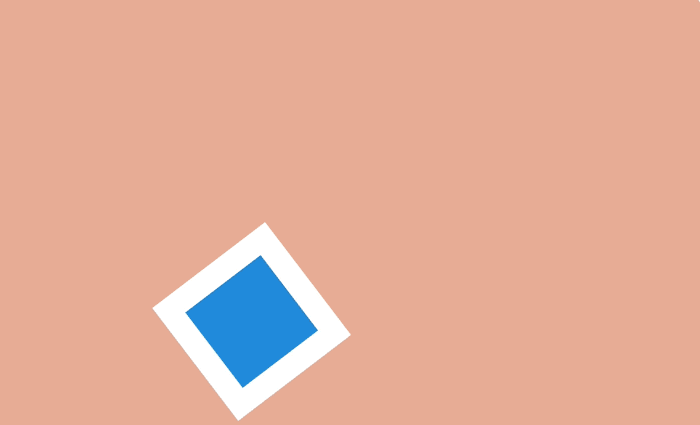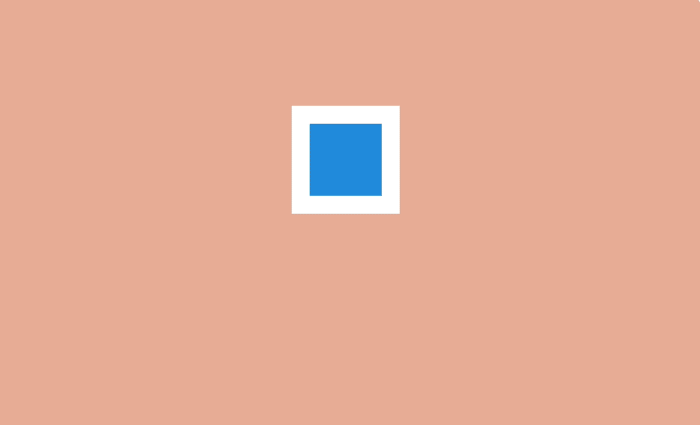
This technique is often used to draw attention to certain actions and make them more dramatic in cartoons. A wolf who is trying to bite someone opens his mouth much wider than usual - so much worse and more impressive.
On a web page, objects can be enlarged and reduced to highlight them and attract the user's attention. For example, when filling in a form, the active field makes sense to do more, and inactive at the moment, on the contrary, decrease.

When working with volumetric objects, it is necessary to take into account the rules of perspective - people live in a three-dimensional world, so if something looks different from what they expect, it seems wrong.
Modern browsers have good support for 3D transformations. This means that the developer can create an animation that will rotate objects and move them around the screen, and the browser itself will create smooth transitions between states.

In the world of art, attention to detail can create a special atmosphere - arising, for example, when looking at a picture. Similarly, in the world of the web, high-quality and well-chosen animations make the site look more attractive and authoritative. Great strides in this kind of work were achieved, for example, by the Stripe service team.
Using the principles described above will allow web developers to create better and more enjoyable looking animations. If the animation takes into account the physical weight of the object, highlights the changes, it uses secondary movements, and its execution time is meticulously calculated - this will significantly improve the overall user experience of the page.
As we said at the beginning of the article, in the continuation of the topic of publication, we open one of the advanced HTML Academy courses on animation for free access.
The Animation course covers the basics of animation on CSS. You will move, rotate and modify objects, simultaneously mastering the techniques of animation work in CSS.
All tasks are developed in the framework of a single storyline (legend), according to which you can help humanity to go the way of the development of civilization up to flights into space.
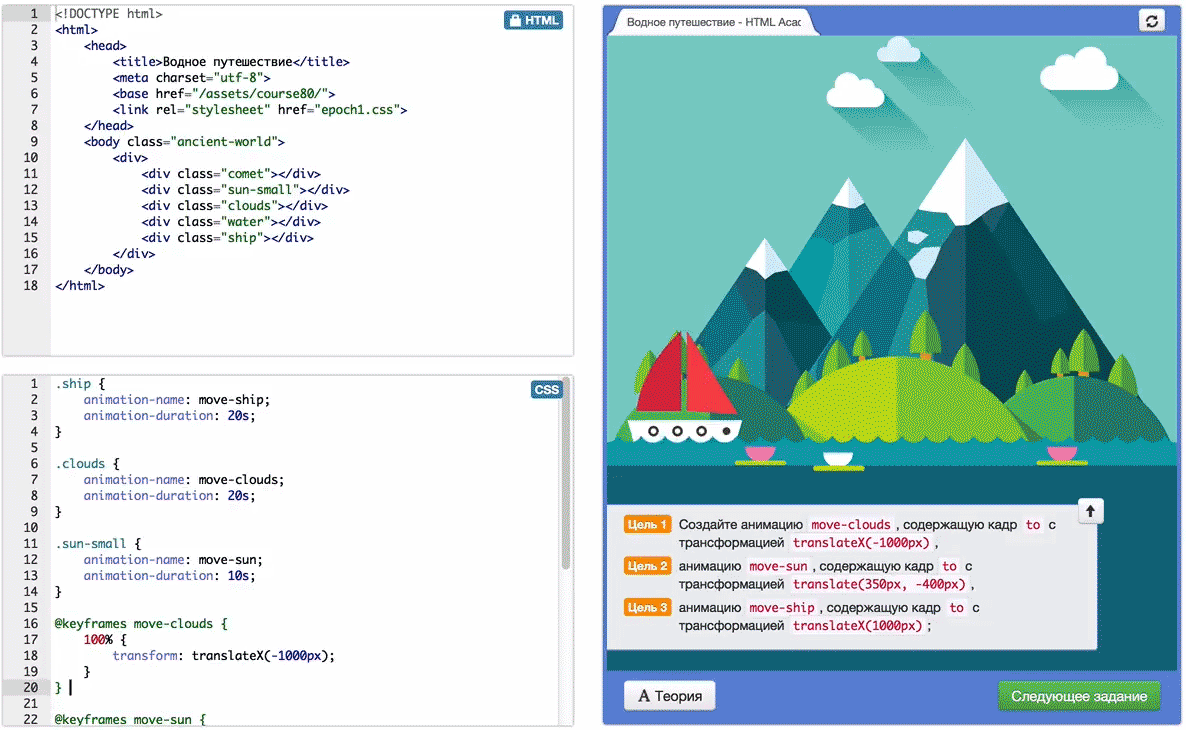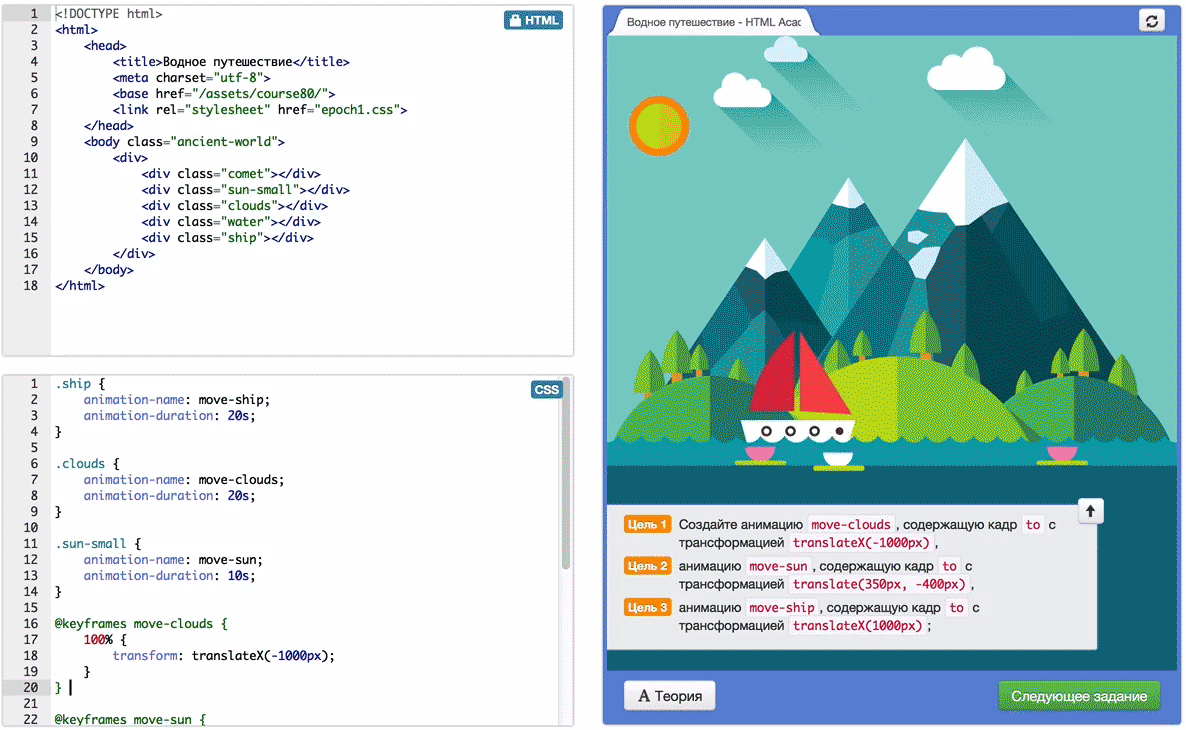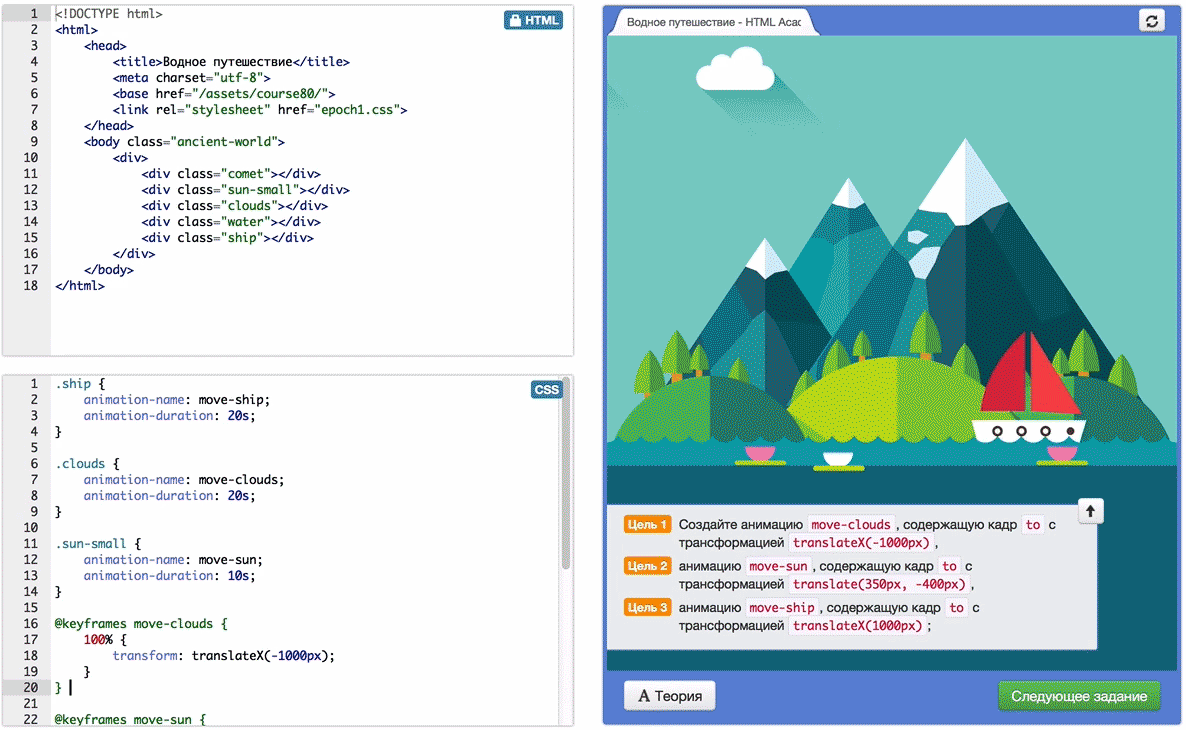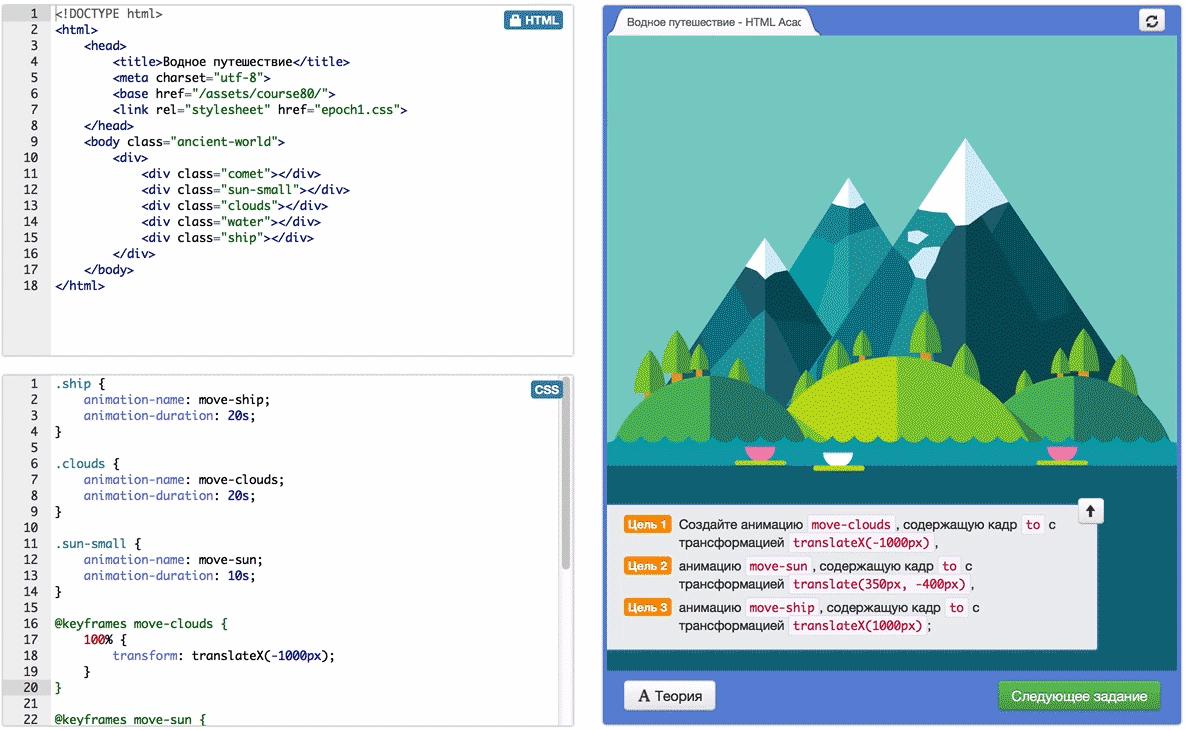
See you at the Academy!
In addition, in the continuation of the topic of today's publication for one week will be open advanced course of the Academy on CSS-animations , which is usually available by subscription. His description is posted at the end of the topic.

')
Front-end designers and developers use CSS to create styles, position elements - in general, to make websites look beautiful. Often, CSS is also used to add motion to web pages, although it usually does not go beyond smooth transitions or animations.
In fact, animation can be a powerful tool that allows site visitors and customers to more easily interact with the product interface and achieve their goals faster. This can be achieved if you follow some fundamental principles in your work.
The Disney company has been engaged in animation for many years and has developed such recommendations - back in 1981, the book “ The Illusion of Life: Disney Animation ” (“ The Illusion of Life: Disney Animation ”) was published, which listed 12 animation principles (they were written on Habré) . They describe how to use animation to create a sense of the real world with viewers looking at the screen.
In today's article we will look at each of the twelve of these principles and discuss their possible use in creating web pages. All CSS and HTML sources can be downloaded on Codepen .
Flattening and stretching
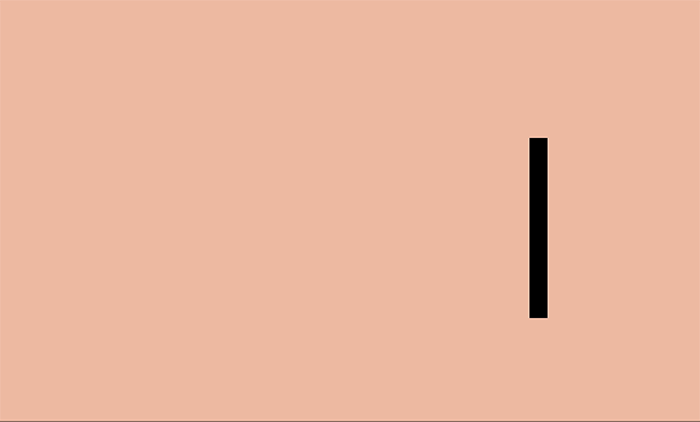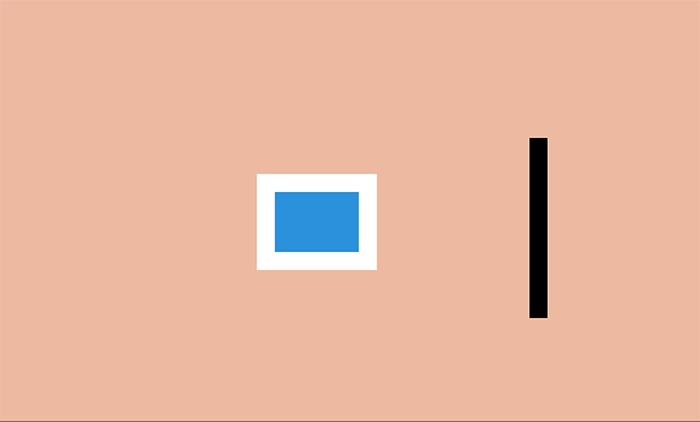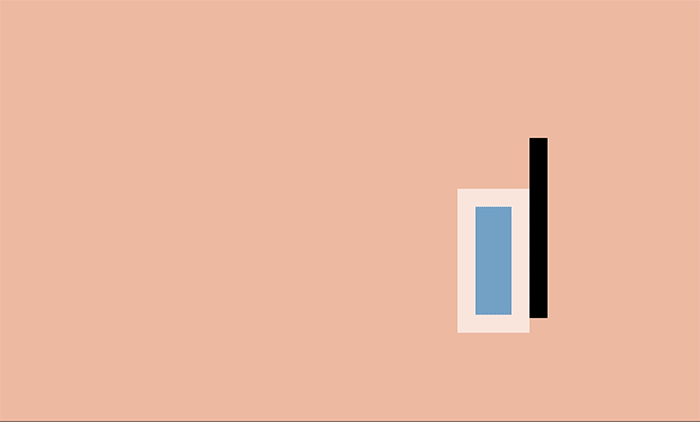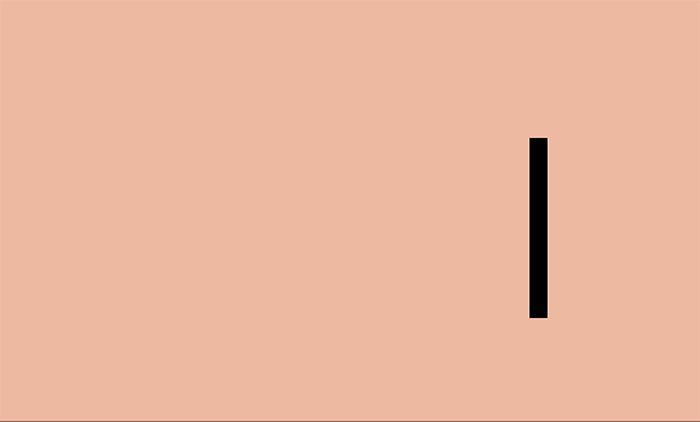
In the world there is the concept of "body mass" - and when an object moves, its mass remains unchanged. When the ball hits the ground, it will become slightly wider and flatten, because during physical contact the mass of the object is redistributed.
This effect is most useful when creating physical objects (for example, people, watches, or bouncing balls).
Of course, in the case of web pages, this property can also be ignored - DOM elements are not necessarily associated with physical objects and can grow and shrink in size on the screen. For example, a button can grow and transform into an information window, and error messages appear and disappear.
Despite this, the technique of “flattening and expanding” can be used to create a sense of the physical element on the page. Even small changes can create a subtle, but eye-catching effect.
Expectation

Movement does not occur suddenly. In ordinary life, any action is preceded by some kind of preparation, be it a ball slowing down before falling from the steps or a person bending the knees before jumping.
This effect can be used to make the movement of objects on a web page more realistic. The wait itself can be implemented, for example, as a light wiggle, which allows users to understand what is happening and helps them to more easily follow the movement of an object across the screen.
Focusing

This effect is to define the object as the focus of the scene, while other objects make room for the main action. To create such an effect, the desired object is appropriately brought to the fore or masked by the accompanying elements in order to focus the user's view on what he should see.
In web terms, this means using translucent obscuring for certain content. The imposition of a darker layer on an existing page and the subsequent placement of content in the foreground focuses all the attention of users on it.
Another approach is to use movements. When several objects simultaneously move on the page, it is rather difficult to understand which of them is really worth looking at. If in such a situation you stop all objects, except for one “necessary” one, then all attention will automatically be focused on it.
Movement can be used in a different way. For example, if a user is working with a document, a slight jitter and the flashing of the “Save” button may prompt a person to click on it. When there is no activity on the screen, even a small movement is very prominent.
Movement "full speed ahead" and "step change"

Direct movement is characterized by the complete rendering of all frames of the animation. In turn, a step change is characterized by the creation of a sequence of key frames, the intervals between which are filled later, usually with the help of auxiliary means.
The second approach is used in most web animations: the transitions between the main frames are implemented by the browser, which interpolates the difference between each of them and draws as many intermediate frames as needed to make the final animation smooth.
An exception is the “Steps” function. When using it, the browser “strides” for a given number of discrete frames. In this way, you can create a sequence of images, and then play them in the browser one by one using the “Straight Ahead Action” style.
Following and choking

Actions do not always occur simultaneously. When a moving car slows down sharply, with the smoke of the tires, it nods, and the driver inside continues to move until the final stop occurs.
This effect is achieved with the help of the movements of following and choking - they are needed to signal that the object has stopped. For example, an item placed in the list may slightly move the desired position, and then return to the correct position.
The effect of overruns is created by giving objects a different rate of movement. This approach is used in transitions in iOS — some buttons and elements move at different speeds, as a result of which movements become more realistic than they would be if they move at the same speed. The combination of movements gives the user time to realize the changes taking place.
In the web, this is usually achieved by combining smooth transitions or CSS animations with different playback speeds.
Smooth acceleration and deceleration

Objects rarely go instantly from a state of rest immediately to maximum speed. Usually, it takes some time for them to accelerate - just as it takes to stop. Without a gradual acceleration and deceleration of movement look unnatural.
In CSS terminology, acceleration and deceleration is known as easing, or “smoothness function,” which describes the change in animation speed.
Using the functions of smoothness, you can create accelerating and slowing animations and even more complex effects (using the
cubic-bezier function).Dougie

Slowing and acceleration makes objects more realistic, but there is one more thing: in life they rarely move in a straight line, as a rule, the movement goes along a curved arc.
To achieve this movement in an arc using CSS can be a couple of different ways. One is to combine several animations. For example, the animation of a bouncing ball can be made with the help of object movements up and down, and the second movement is combined with the movement also to the right. Thus it turns out that the ball jumps on the screen.

The second way is to rotate the element. By changing the center of rotation and moving it beyond the limits of the original object, an arc can also be formed.
Secondary action

The main action that takes place on the screen can be emphasized with “secondary” animation. This may be the movement of a person’s hands when walking or shaking his head with each step. Or dust rising from the ground with each blow of the ball.
In the case of websites, secondary elements can “drive apart” in order to highlight what the user really needs to pay attention to (for example, dragging an element to insert it in the middle of the list).
lead time

Using the manipulation of the duration of the animation can be done so that large objects seem heavy, and small - light.
On the Web, this can be achieved by simply changing the values of
animation-duration and transition-duration .By changing the duration of the animation, you can select it among the content of the web page or during interaction with the user.
Exaggeration

This technique is often used to draw attention to certain actions and make them more dramatic in cartoons. A wolf who is trying to bite someone opens his mouth much wider than usual - so much worse and more impressive.
On a web page, objects can be enlarged and reduced to highlight them and attract the user's attention. For example, when filling in a form, the active field makes sense to do more, and inactive at the moment, on the contrary, decrease.
Volume

When working with volumetric objects, it is necessary to take into account the rules of perspective - people live in a three-dimensional world, so if something looks different from what they expect, it seems wrong.
Modern browsers have good support for 3D transformations. This means that the developer can create an animation that will rotate objects and move them around the screen, and the browser itself will create smooth transitions between states.
Attractiveness

In the world of art, attention to detail can create a special atmosphere - arising, for example, when looking at a picture. Similarly, in the world of the web, high-quality and well-chosen animations make the site look more attractive and authoritative. Great strides in this kind of work were achieved, for example, by the Stripe service team.
Conclusion
Using the principles described above will allow web developers to create better and more enjoyable looking animations. If the animation takes into account the physical weight of the object, highlights the changes, it uses secondary movements, and its execution time is meticulously calculated - this will significantly improve the overall user experience of the page.
And now about the course on animation
As we said at the beginning of the article, in the continuation of the topic of publication, we open one of the advanced HTML Academy courses on animation for free access.
The Animation course covers the basics of animation on CSS. You will move, rotate and modify objects, simultaneously mastering the techniques of animation work in CSS.
All tasks are developed in the framework of a single storyline (legend), according to which you can help humanity to go the way of the development of civilization up to flights into space.

See you at the Academy!
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/255583/
All Articles