OSSIM - we deploy a comprehensive open source security management system
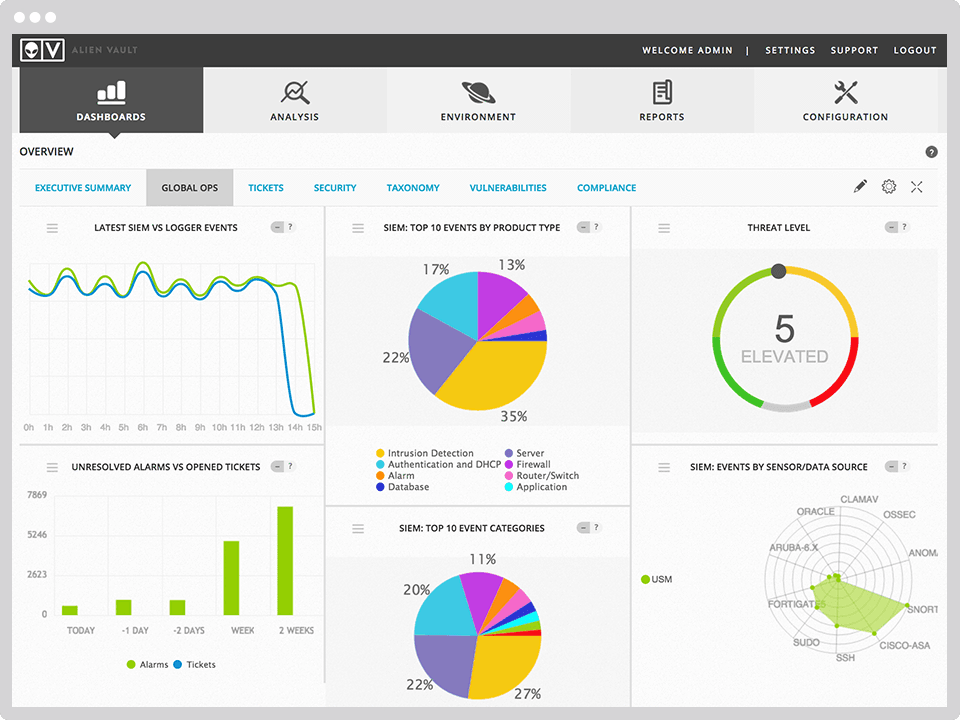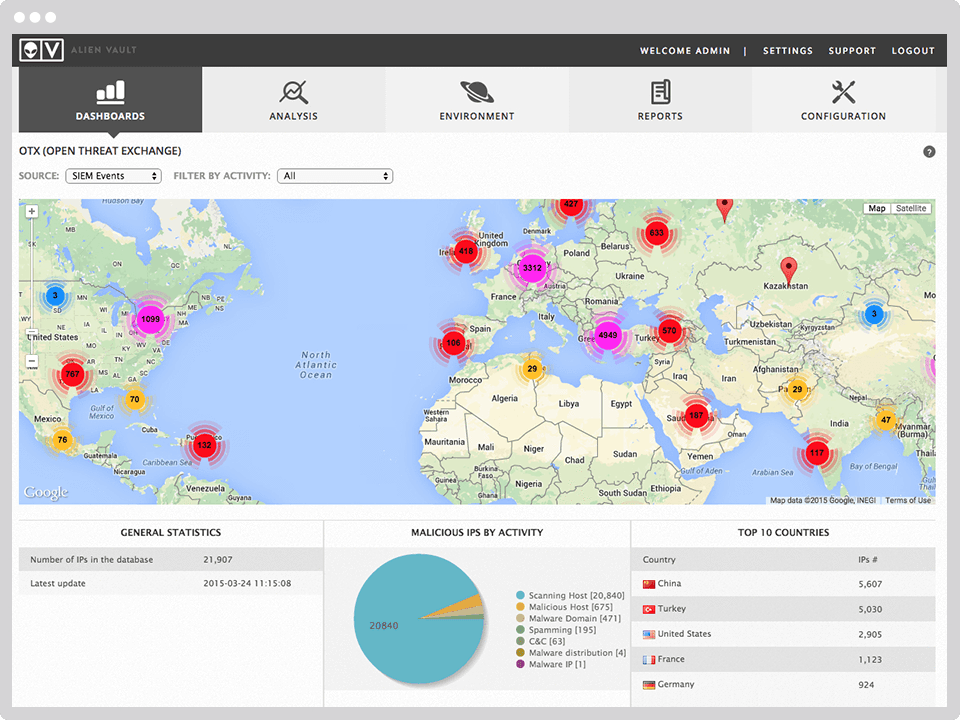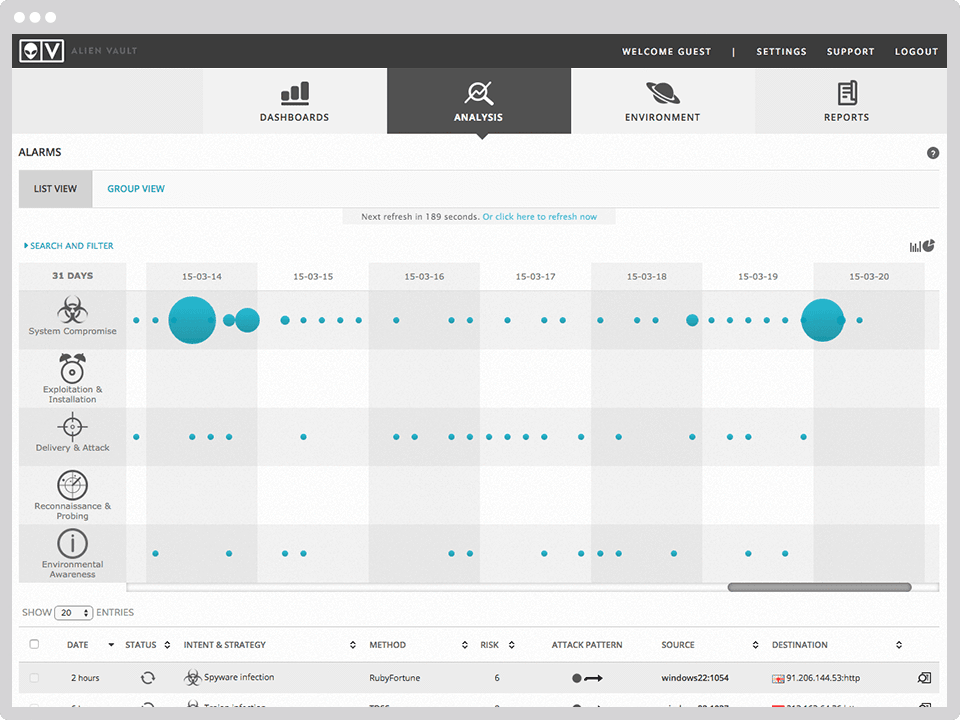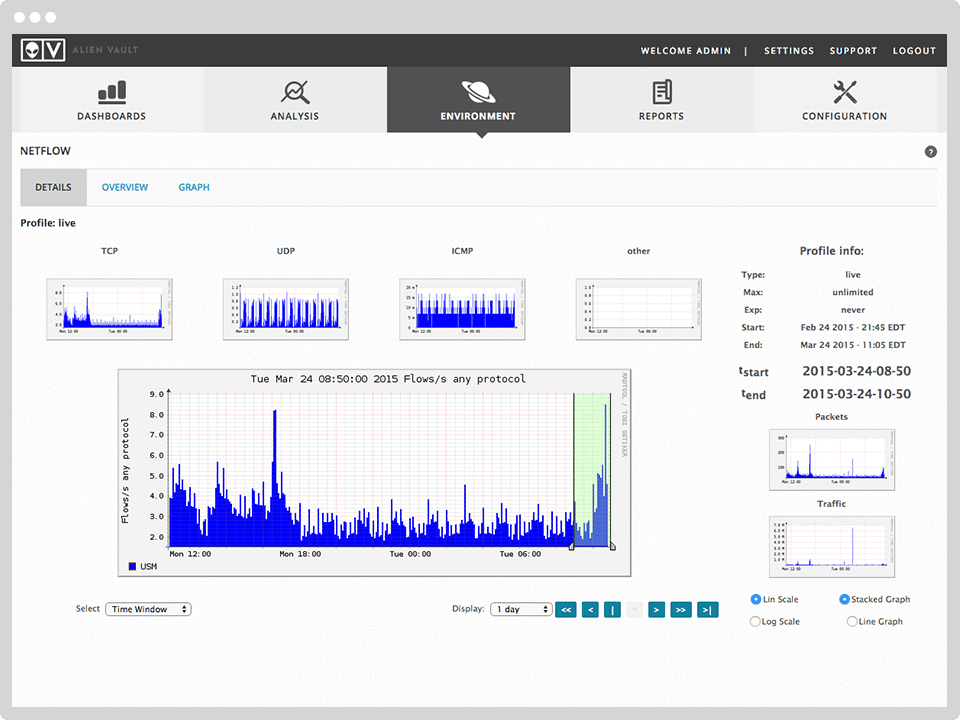
OSSIM (Open Source Security Information Management) - a system for managing, controlling and ensuring information security.
OSSIM "out of the box" includes such functionality as:
- Collecting, analyzing and correlating events - SIEM
- Host Intrusion Detection System (HIDS) - OSSEC
- Network Intrusion Detection System (NIDS) - Suricata
- Wireless Intrusion Detection System (WIDS) - Kismet
- Monitoring network nodes - Nagios
- Analysis of network anomalies - P0f , PADS , FProbe , Arpwatch , etc.
- Vulnerability Scanner - OpenVAS
- The most powerful system for the exchange of information about threats between OSSIM users - OTX
- More than 200 plugins for parsing and correlation of logs from various external devices and services
Foreword
This article will focus primarily on the installation, initial configuration and configuration of OSSIM, all the information about the features and functionality can be taken from the official site , or look in this video:
')
It is worth noting that AlienVault has 2 products, free OSSIM and a more advanced version - USM, the differences can be found at this link .
As a bonus, the last chapter of the article posted information about the integration of OSSIM with the SIEM system ArcSight .
Table of contents
Install OSSIM
OSSIM Setup
- Setup Wizard
- Configure email notifications
- HIDS setup
- WIDS setting
- Configuring the collection of system logs
- ArcSight integration
Used sources
Install OSSIM
Installing the open source SIEM system is accomplished using a ready-made installation image containing the Debian operating system and all the necessary pre-installed components and modules.
To install OSSIM, you need to open the link , and then immediately begin downloading the latest version of the OSSIM distribution.
We will be installing on VMware ESXi .
ESXi Setup
First you need to configure ESXi itself, namely to configure the interface that works in "promiscuous" mode (Promiscuous mode) . We need this mode to configure network monitoring. In OSSIM, this role is performed by Suricata .
To do this, open the host settings, and do everything as in the animation below:
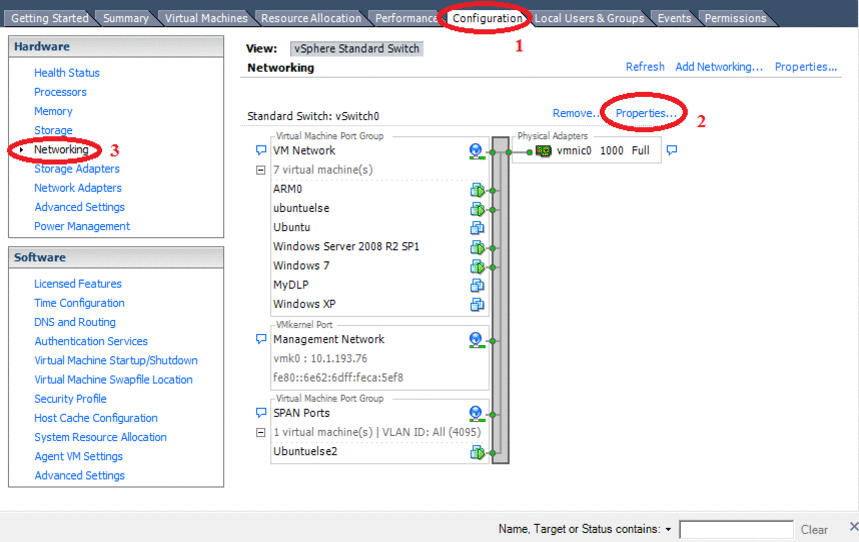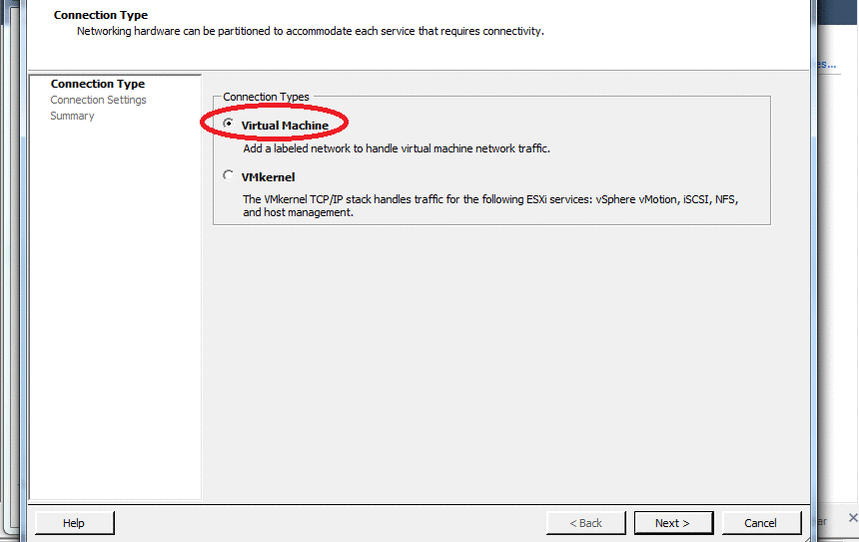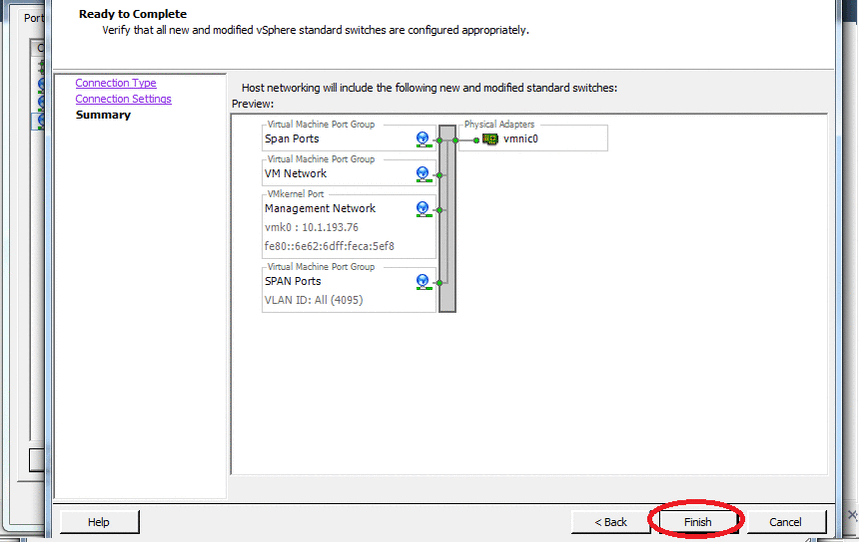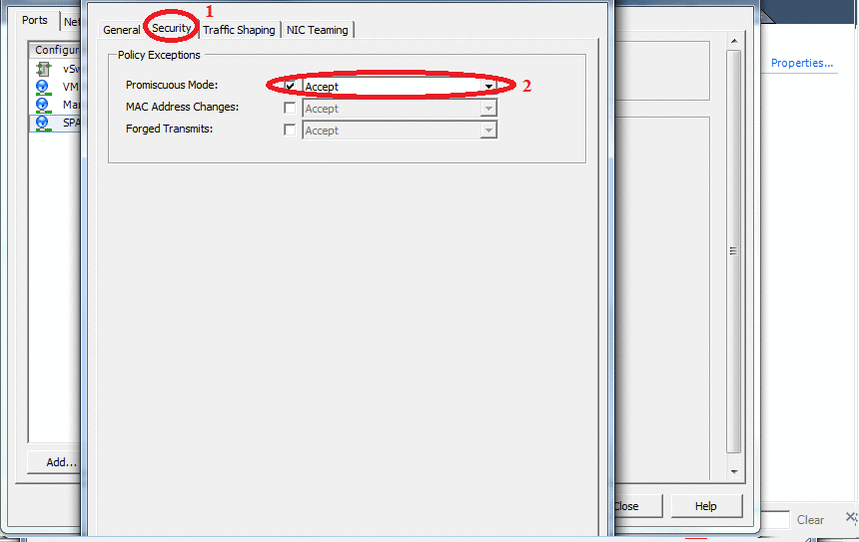
At this setting is completed, now add a virtual machine. In the screenshots below, only those settings that we change.

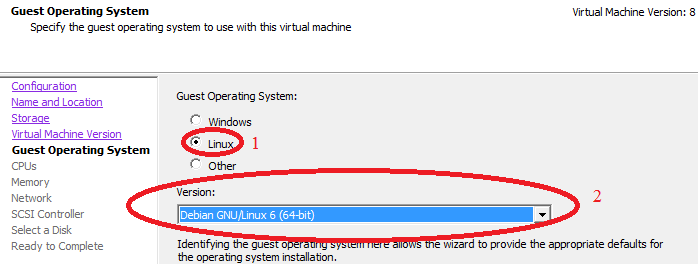
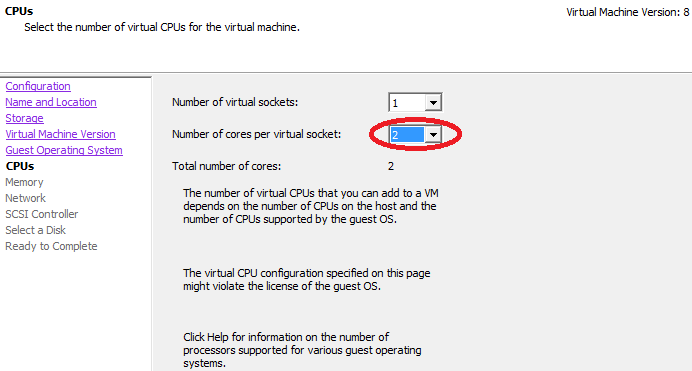
Many services in OSSIM can work in multi-threaded mode, so it is desirable to install multiple cores.

RAM, it is desirable to put more. The minimum size to which everything works is more or less stable and without slowdowns - 3GB.
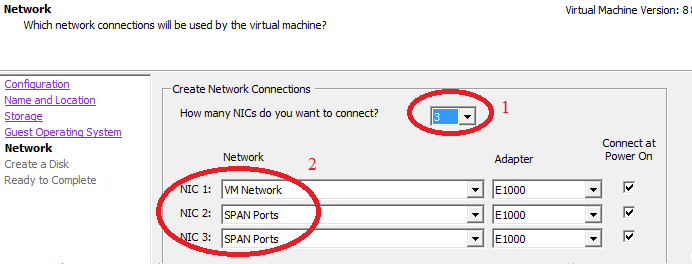
1 interface for managing OSSIM, 1 for Network IDS Suricata, one for OpenVAS (optional).

This completes the virtual machine configuration.
Installation
Let's turn on the virtual machine and connect to it, the previously downloaded OSSIM installation image.
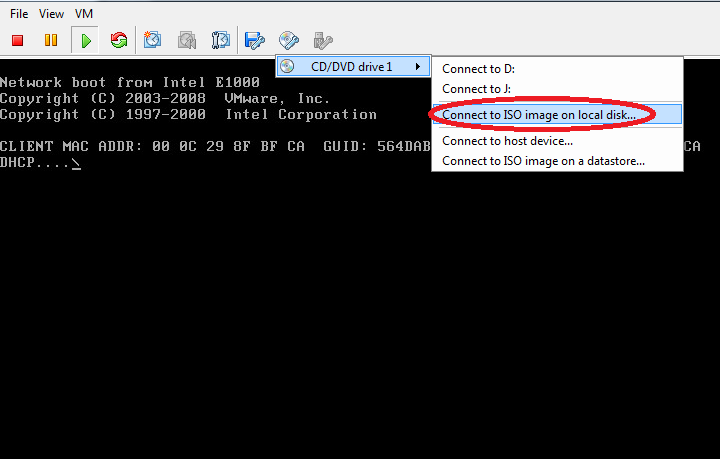
Now install OSSIM. Installation is no different than installing Debian, only the items in the installation are much smaller.
Setting is very simple, so for brevity, some screenshots in the animation are omitted.
After entering all the settings, the installation will begin.

At the “Running cdsetup ...” stage, the installation may hang for a while, as it should be.
At the end, the console will appear:
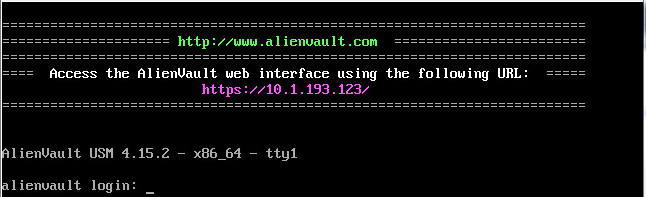
Go to the link specified in the console and enter the credentials:

This completes the installation.
OSSIM Setup
To configure OSSIM, 3 operating systems were configured: Windows server 2008 R2, Windows 7 SP1, Ubuntu 14.04 LTS, which we will directly connect to the monitoring. In addition, we will configure a wireless IDS system based on Kismet , using a host with a pre-installed Debian 6 OS as a “sensor”.
Setup Wizard
Enter the credentials specified in the previous configuration item:

And the wizard window opens before us:
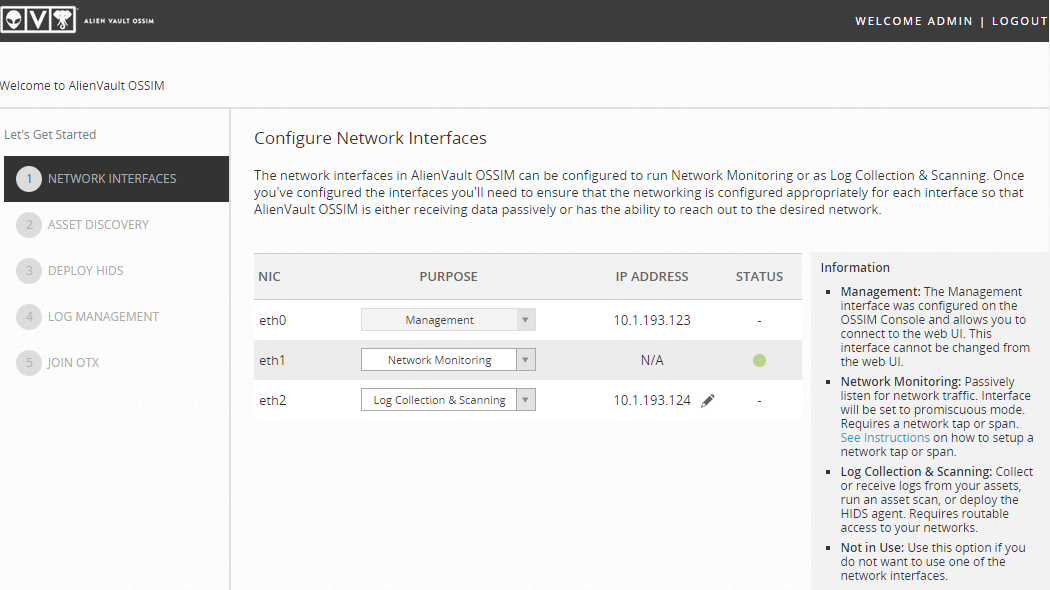
Configuring interfaces:
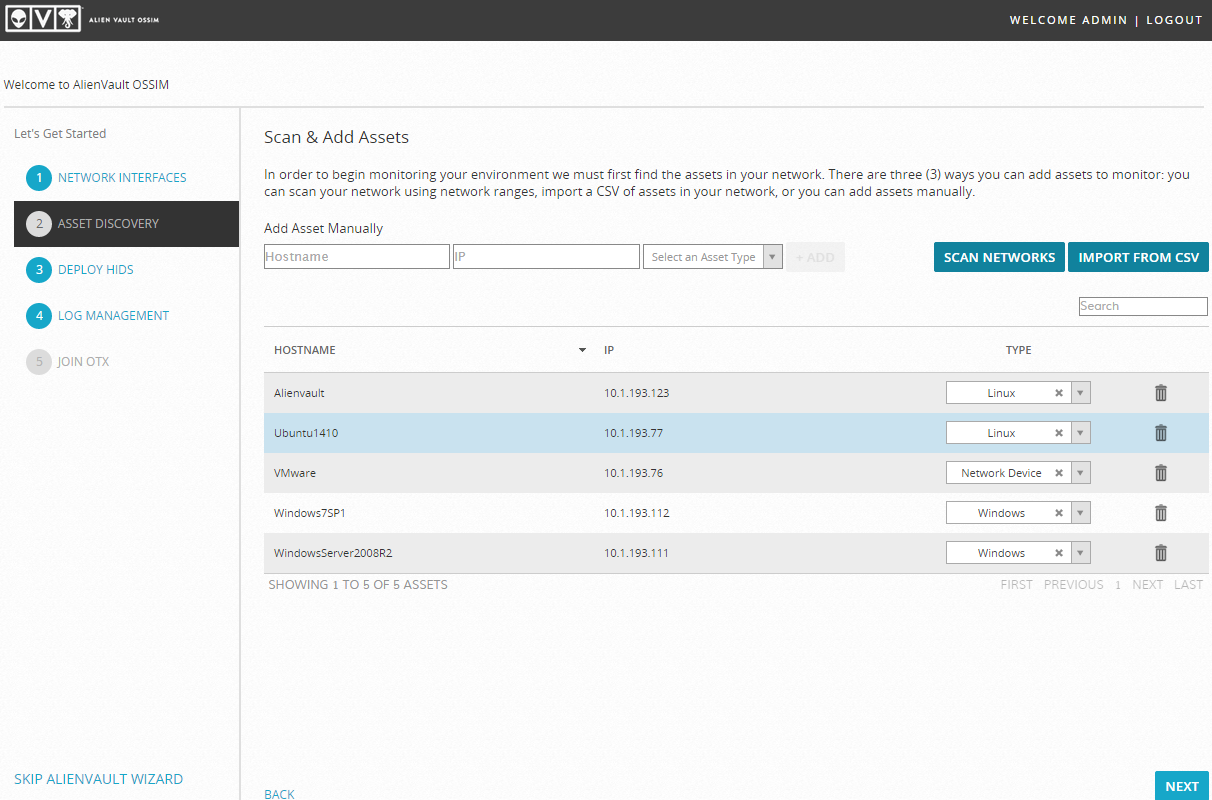
On the next paragraph, OSSIM will automatically scan the network and prompt you to specify the type of nodes found, in our case everything that does not belong to the test bench is deleted:
In the next step, you can automatically install a host intrusion detection system (OSSEC). Let's try to install it for Windows Server. Enter your credentials and click "DEPLOY":
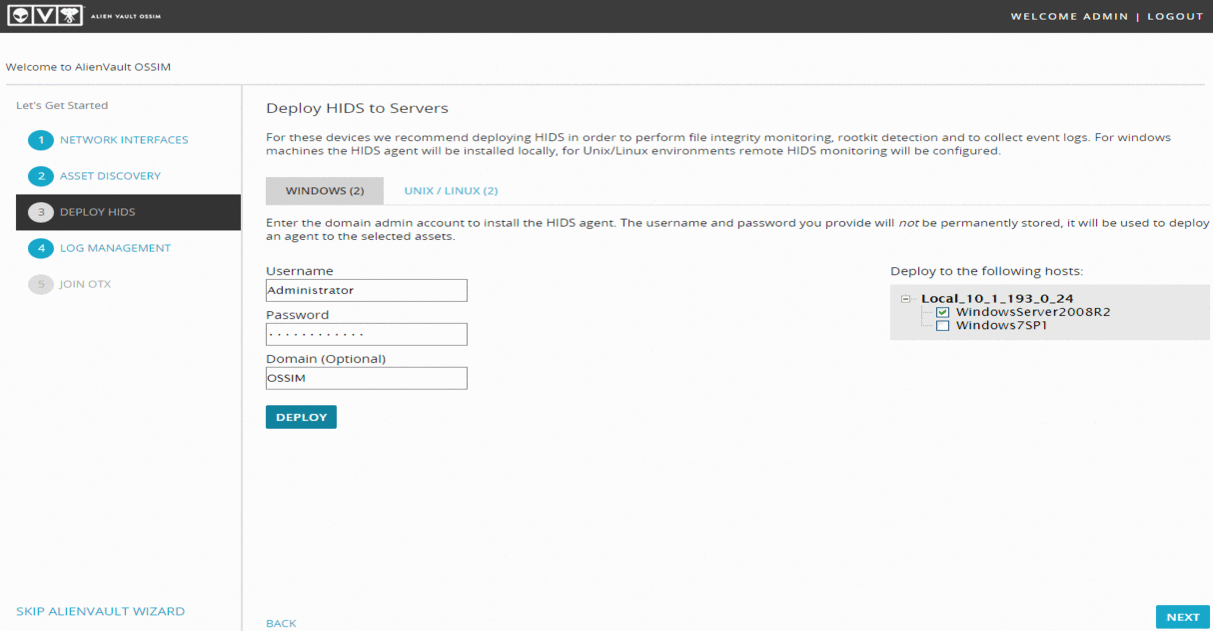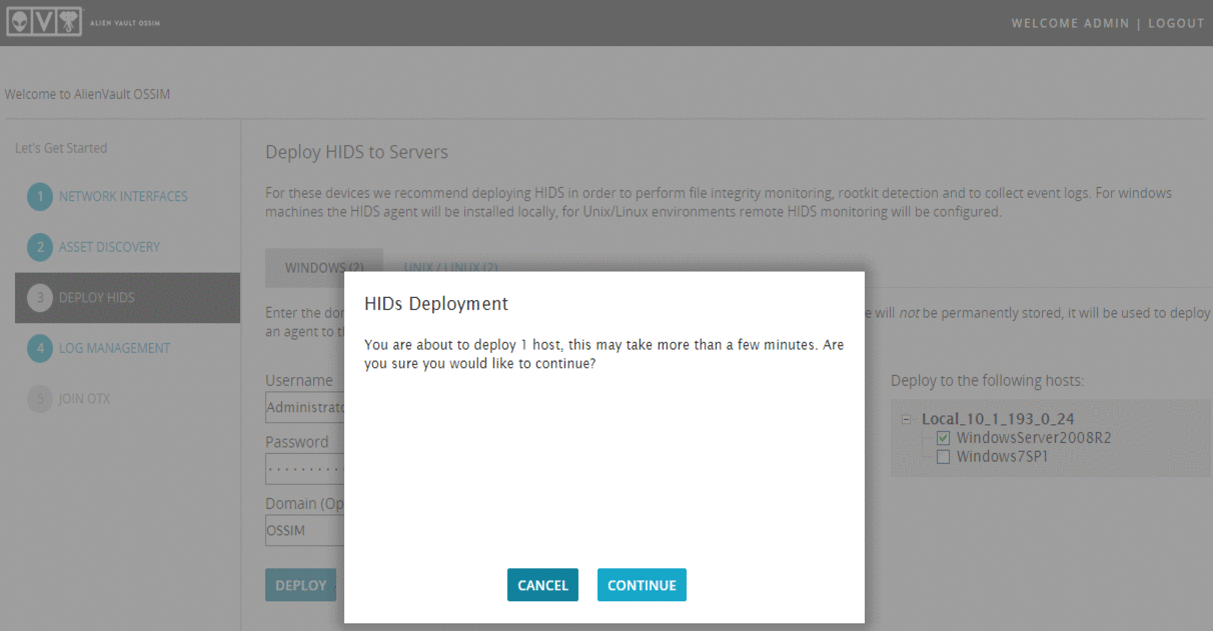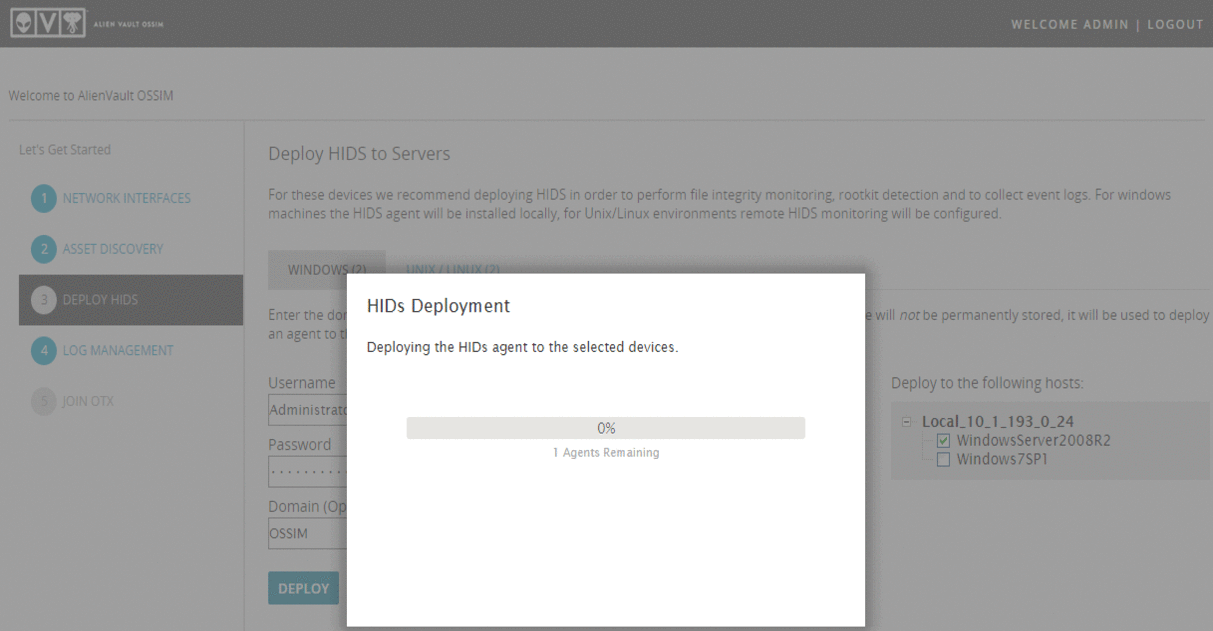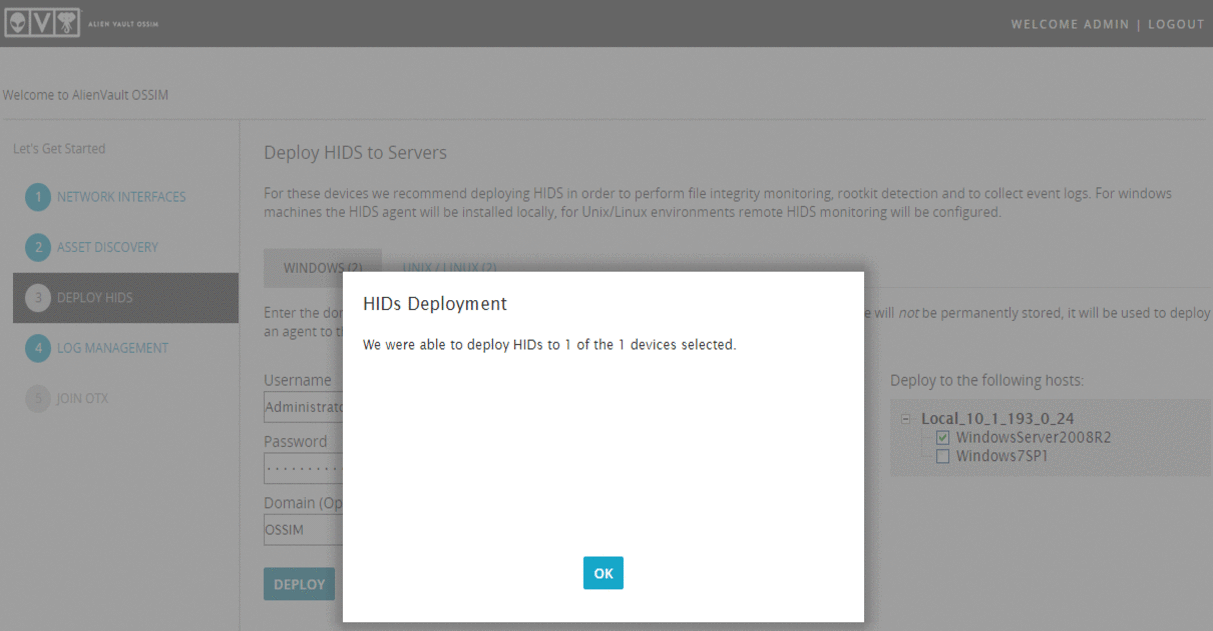
I do not recommend doing the same for Linux, since in this case, OSSEC will work without an agent ( Agentless ).
At the next stage, we are offered to set up monitoring of logs, we skip this point and return to it later, in the relevant chapter:
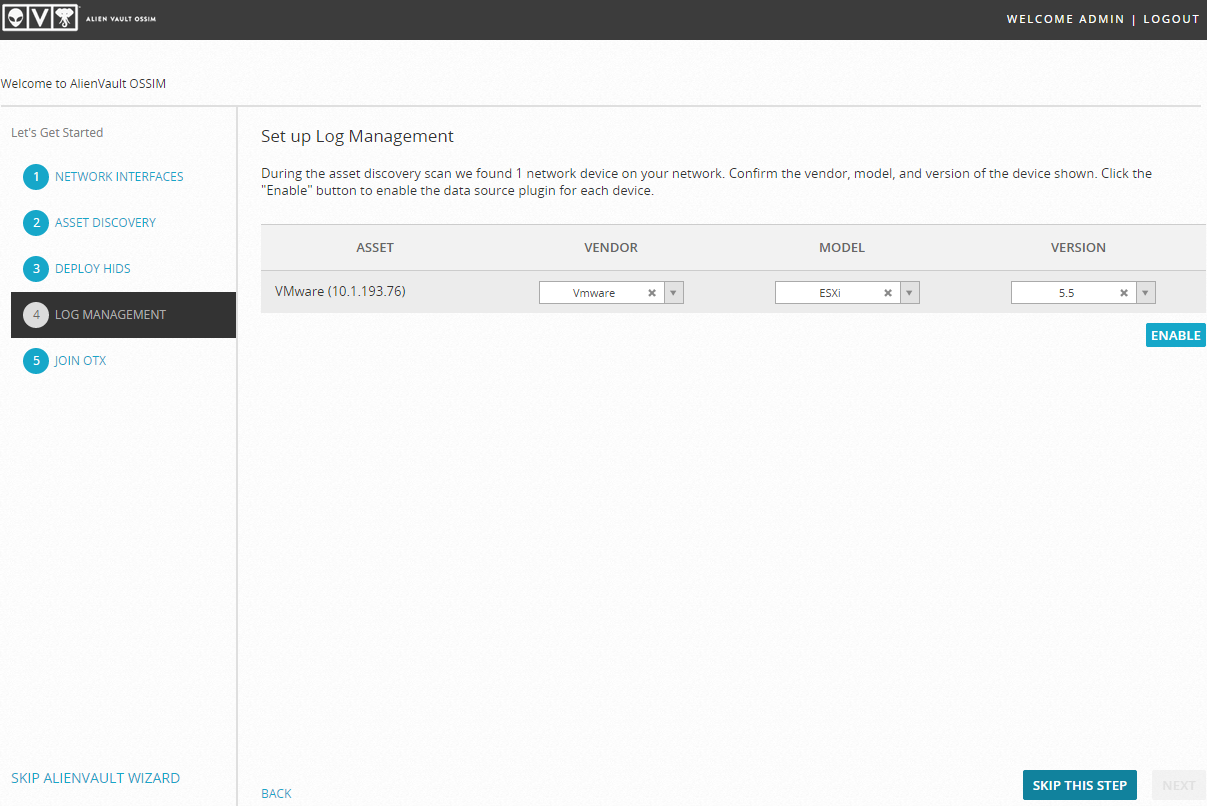
On the last paragraph, we will be offered to join the OTX, if you wish, register via the link www.alienvault.com/my-account/customer/signup and enter the token:
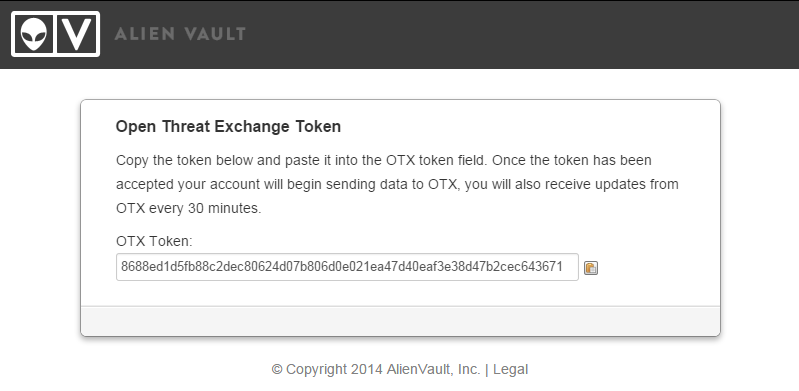
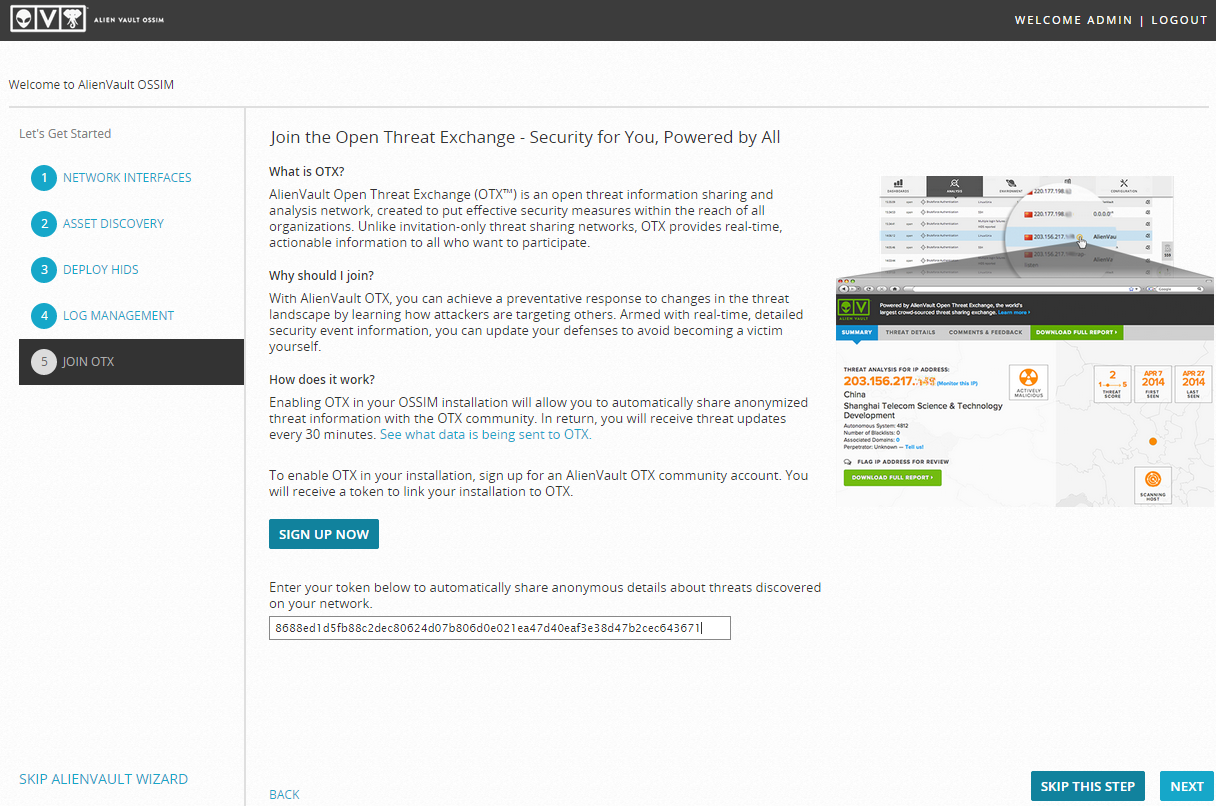
Further we see a pop-up window with the following content:
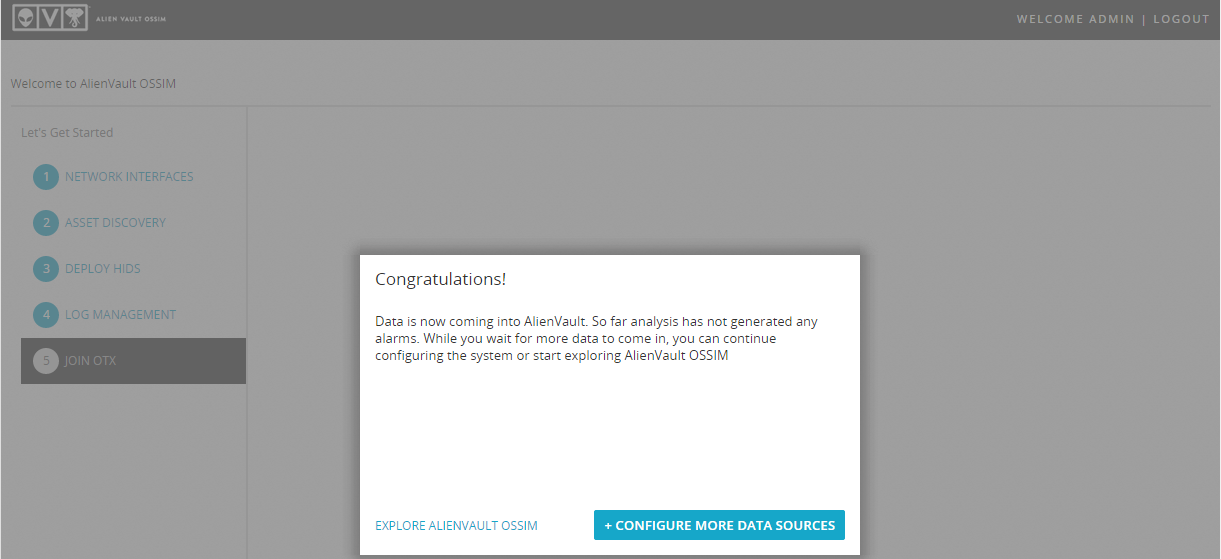
Click Explore Alienvault OSSIM and this is the end of the configuration manager.
Configure email notifications
OSSIM has an “Alarm” section in which correlated security events are displayed, however, no notification will be received for such events. But in the system there is a section “Tickets” in which for each event or events you can open a task.
“Tickets” can be created manually by a specialist or automatically when events from the “Security Events (SIEM)” log in “Alarms”, in case of an automatic opening of the “ticket”, OSSIM can automatically send notifications, which we will now configure.
Setting up email notifications takes place in 2 stages, first you need to configure postfix, and secondly, enable sending notifications.
Open SSH and connect to OSSIM:
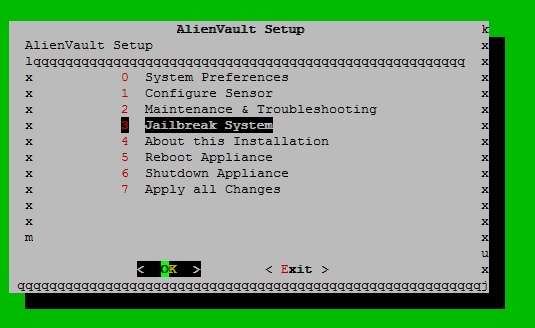
Select the item Jailbreak System and get into the console, enter:
sed -i -e "s@mailserver_relay=no@mailserver_relay=my.corporate.mail.server@" /etc/ossim/ossim_setup.conf echo relayhost = my.corporate.mail.server:25 >> /etc/postfix/main.cf service postfix restart Note: instead of my.corporate.mail.server, specify your mail server, if necessary, configure any other postfix parameters (authorization, secure connection, etc.) - see the documentation on postfix .
Now we open the settings and in the administration section we enable automatic sending of notifications:
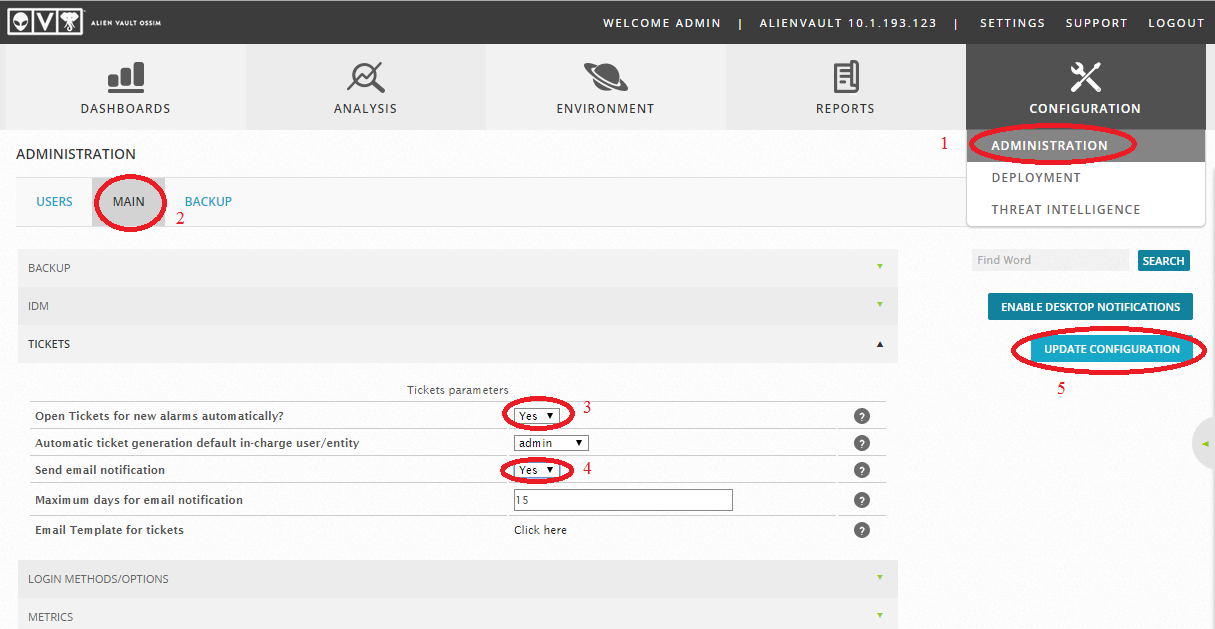
After this manipulation, any correlated event will automatically create a ticket and notify the administrator.
HIDS setup
The role of the host intrusion prevention system in OSSIM is not unknown OSSEC , the configuration of which we will examine further.
To configure HIDS, go to Environment -> Detection -> HIDS -> Agents and see 2 hosts, the first is directly AlienVault itself, the second is the Windows Server, which we installed on the “Deploy HIDS” item in the “Configuration Wizard” section. Go to the HIDS agent menu:
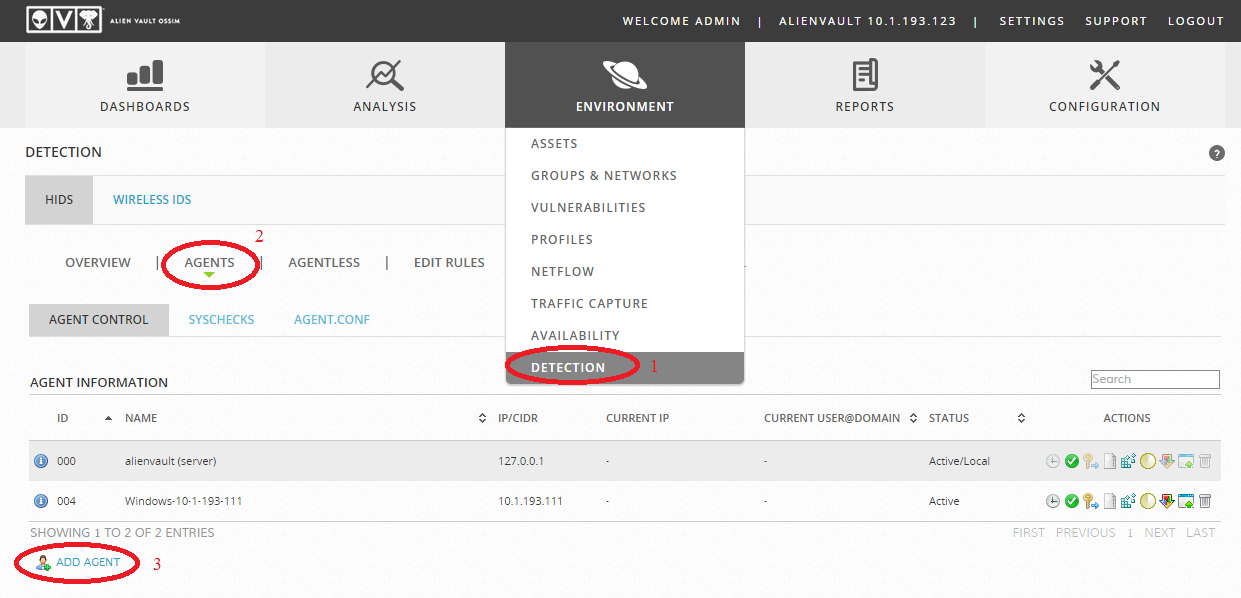
Add Windows 7 and Ubuntu:

Windows
To install HIDS, you can use the automatic installation mode.
 or download the finished exe file
or download the finished exe file  .
.Installation in automatic mode is no different from what we have already done:

When installing in manual mode, using the exe file, the OSSEC agent is set to “1 click”, without entering any additional parameters:

If successful, we will see:

Ubuntu
Now we will configure Ubuntu, connect via SSH and install OSSEC:
sudo -s apt-get install curl curl --header 'Host: www.ossec.net' --header 'User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Ubuntu; Linux x86_64; rv:31.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/31.0' --header 'Accept: text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,*/*;q=0.8' --header 'Accept-Language: en-US,en;q=0.5' --header 'DNT: 1' --header 'Referer: http://www.ossec.net/?page_id=19' --header 'Connection: keep-alive' 'http://www.ossec.net/files/ossec-hids-2.8.tar.gz' -o 'ossec-hids-2.8.1.tar.gz' –L Note: loading does not work through wget, on the server side ossec.net is checked by the User-Agent.
tar xzf ossec-hids-2.8.1.tar.gz cd ossec-hids-2.8/ /bin/bash ./install.sh 
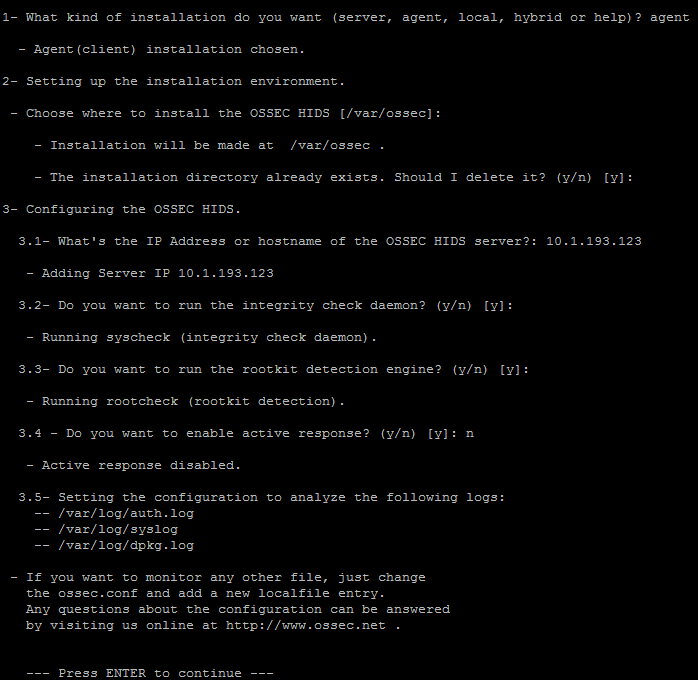
Note: clause 3.4, active protection mode (IPS instead of IDS) turn on carefully, in this case we use only the detection mode, so it leaves “n” instead of “y”.
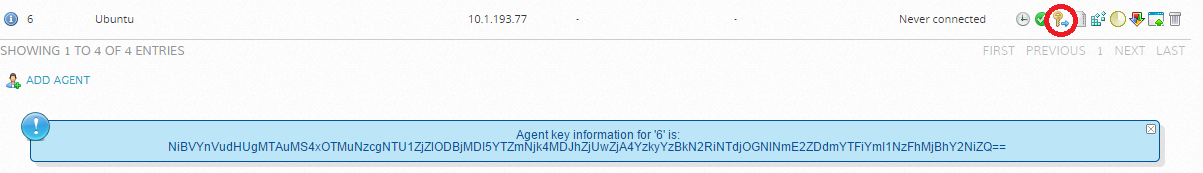
Now we will get the key, to do this, go back to the HIDS agent menu and click on
 :
:
Run the configuration using the / var / ossec / bin / manage_agents utility, press I, enter the key and exit (Q):
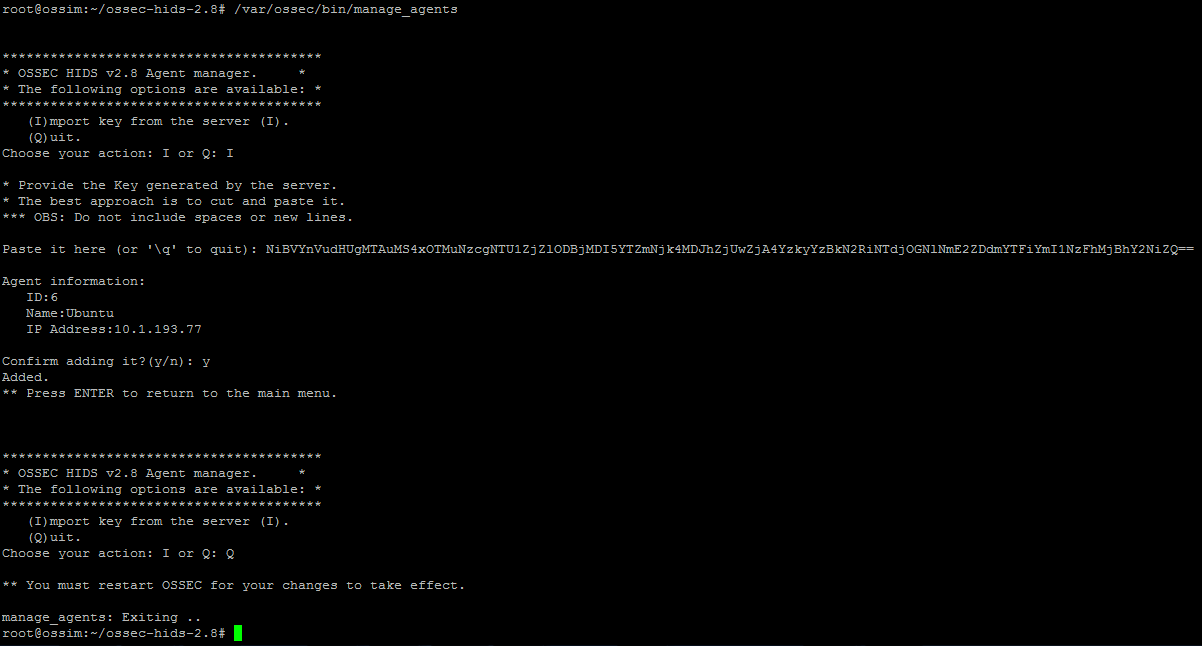
Reboot OSSEC:
service ossec restart If successful, we will see "Active" in front of the host:

If any agent does not appear as active in the list, you can restart OSSEC, for this we connect via SSH to OSSIM and perform the following actions:
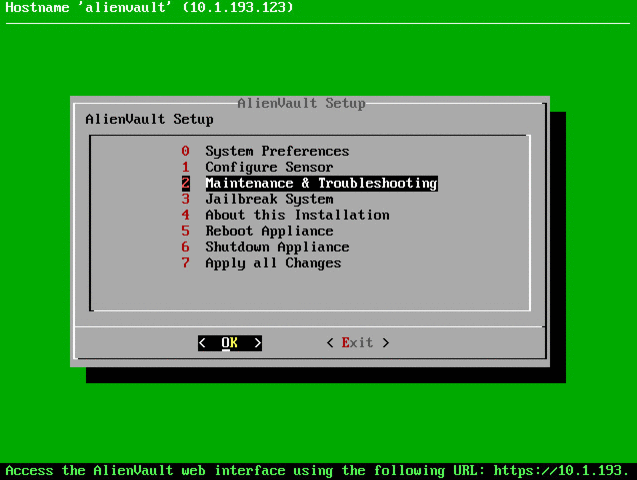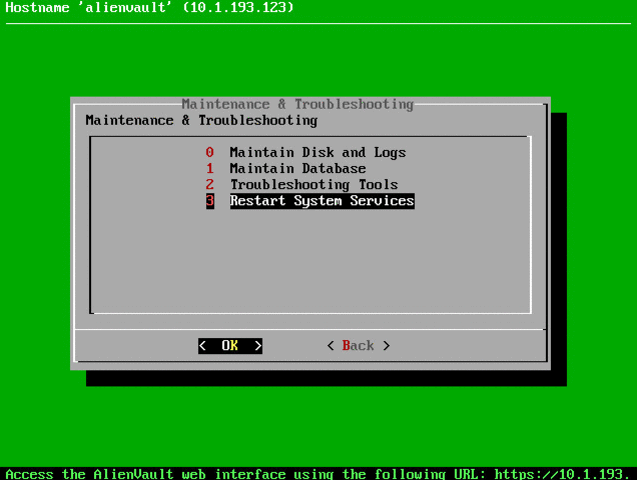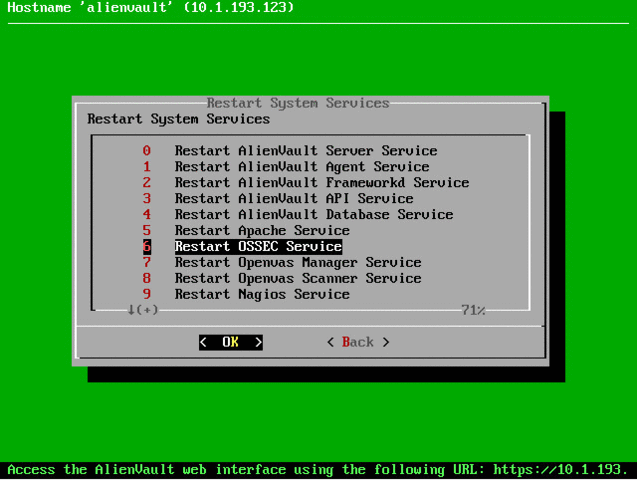
This completes the HIDS installation, now on the Environment -> Detection tab you can see the OSSEC logs:

WIDS setting
We will install WIDS as follows:
- Let's create a host with Debian 6 OS
- Connect to it and configure the Wi-Fi card
- Install and configure kismet
- Configure on OSSIM OpenVPN server
- Configure the connection between OSSIM and Debian 6
- Configure sending and writing logs to rsyslog
- Enable the kismet plugin
- Set up crown import logs in XML format from kismet
- Add a new sensor to OSSIM
- Check the performance of the solution
Virtual Machine Configuration
To install a wireless IDS system, we need a host with Debian 6 preinstalled.
Create a new virtual machine on ESXi and add a USB controller and a USB Wi-Fi card:
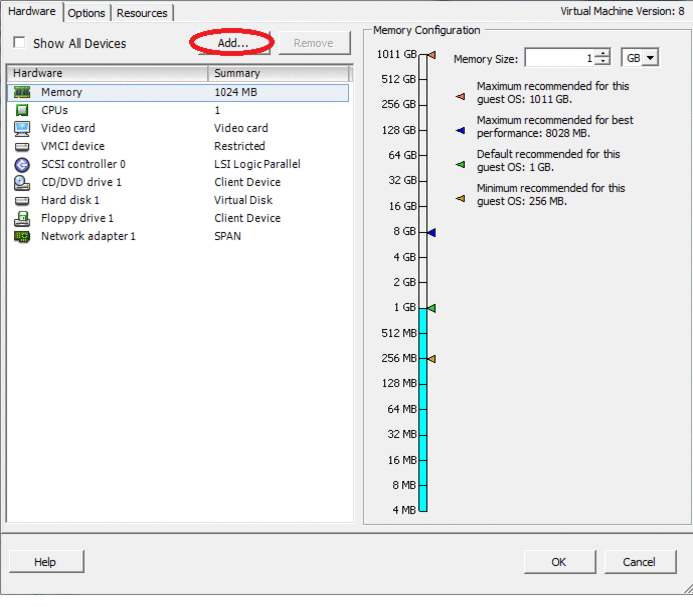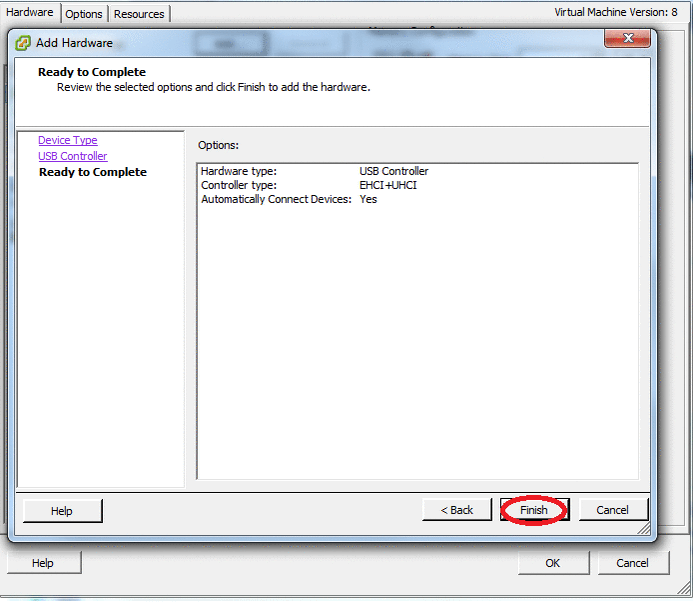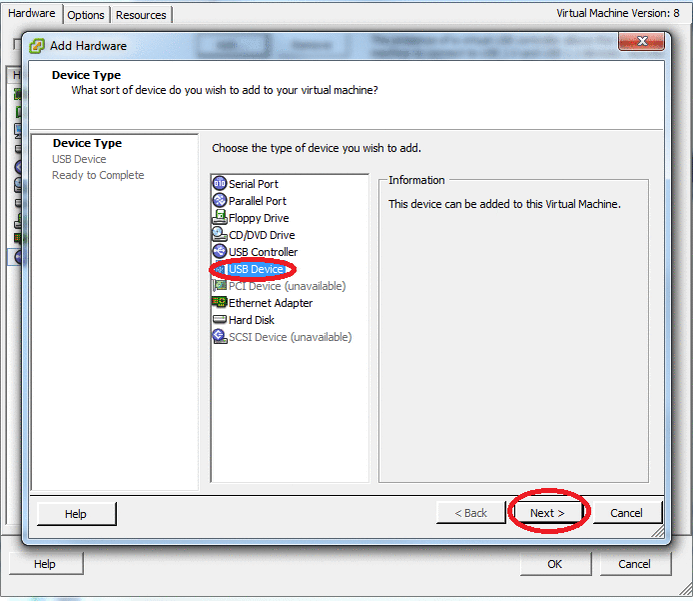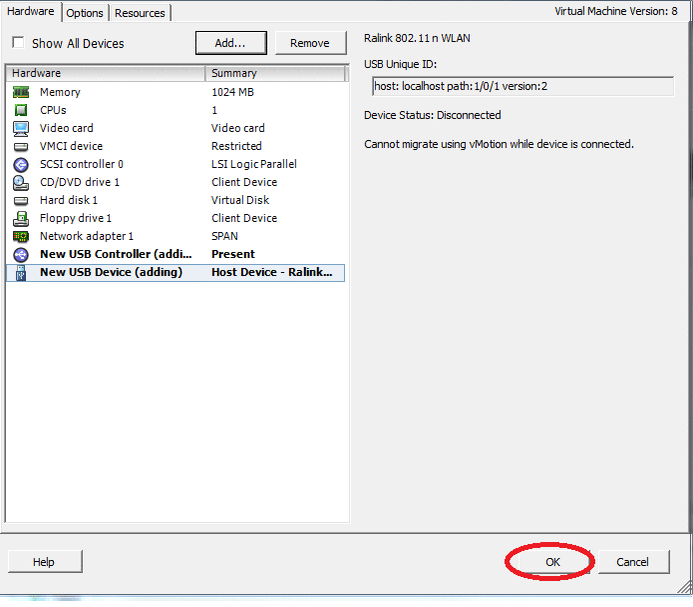
This example uses a USB Wi-Fi TOTOLink N500UD card.
Install and configure Debian
Install Debian 6 . All settings are at your discretion, the Debian installation is standard, so this tutorial is omitted.
After installing the OS, connect to SSH and install the network card drivers:
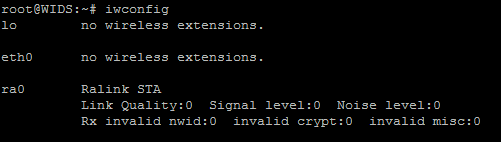
wget http://totolink.ru/files/soft/N500UD_Linux_V2.6.1.3.zip apt-get install unzip unzip N500UD_Linux_V2.6.1.3.zip apt-get install build-essential apt-get install linux-headers-$(uname -r) make make install aptitude install wireless-tools apt-get install ssh openvpn kismet ntp reboot After that, we check the availability of a new interface in iwconfig:
Set up logging from Debian to OSSIM:
echo "*.* @10.67.68.1" > /etc/rsyslog.d/wids_alienvault.conf Do not change the IP address, it should be so. This is the IP address of the OpenVPN server, which will be subsequently raised in OSSIM.
Now create a script /etc/init.d/wids_alienvault.sh with the following content:
#!/bin/sh /usr/bin/kismet_server -l xml -t kismet -f /etc/kismet/kismet.conf 2>&1 | logger -t kismet -p local7.1 Give him the right to run:
chmod 755 /etc/init.d/wids_alienvault.sh And we will enter it on autoload in /etc/rc.local to exit 0:

Now let's set up kismet.
In the /etc/kismet/kismet.conf file
First, configure the adapter:
source=rt2500,ra0,ra0-wids The name of the chipset can be viewed with the command:
lsmod | grep ^usbcore Set up the time for creating the XML report:
logexpiry=3600 Configure the name of the generated logs in order for OSSIM to correctly determine which files to import and clean:
logdefault=10.67.68.10 logtemplate=/var/log/kismet/%n_%D-%i.%l After reboot:
reboot OpenVPN setup
Connect to OSSIM via SSH, select “Jailbreak system” and enter the command:
alienvault-reconfig --add_vpnnode=WIDS-Sensor Go back to Debian and copy the configured OpenVPN archive with the settings:
scp root@10.1.193.123:/etc/openvpn/nodes/WIDS-Sensor.tar.gz ~ Apply config:
tar xzf WIDS-Sensor.tar.gz rm -f WIDS-Sensor.tar.gz mv * /etc/openvpn/ Check OpenVPN:
/etc/init.d/openvpn restart Ifconfig tun0 
Kismet setup
Go back to OSSIM.
Configure rsyslog:
echo if \$programname contains \'ismet\' then /var/log/kismet.log >> /etc/rsyslog.d/kismet.conf echo \& \~ >> /etc/rsyslog.d/kismet.conf service rsyslog restart Change the path to the file from which the plugin will take logs:
sed –i –e "s@/var/log/syslog@/var/log/kismet.log@" /etc/ossim/agent/plugins/kismet.cfg Now we will turn on the plugin that will process the kismet logs, for this we use the exit command to exit to the OSSIM menu and turn on the plugin:
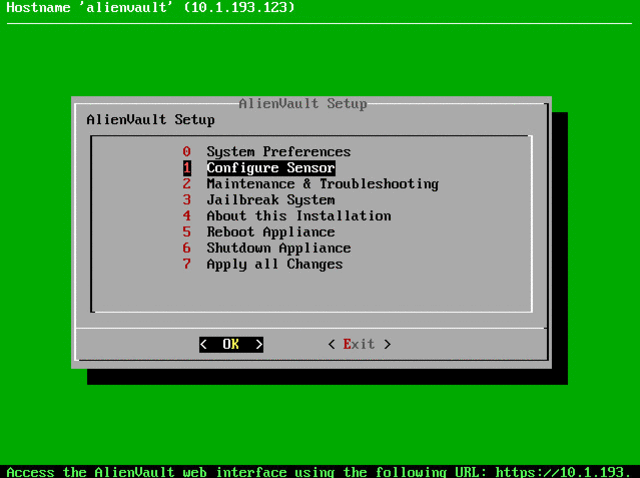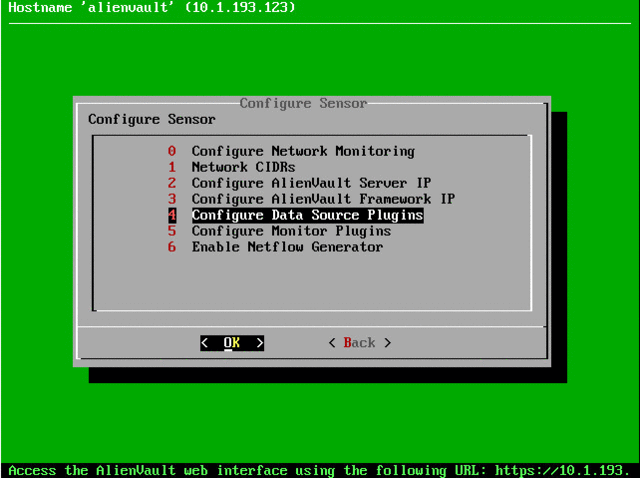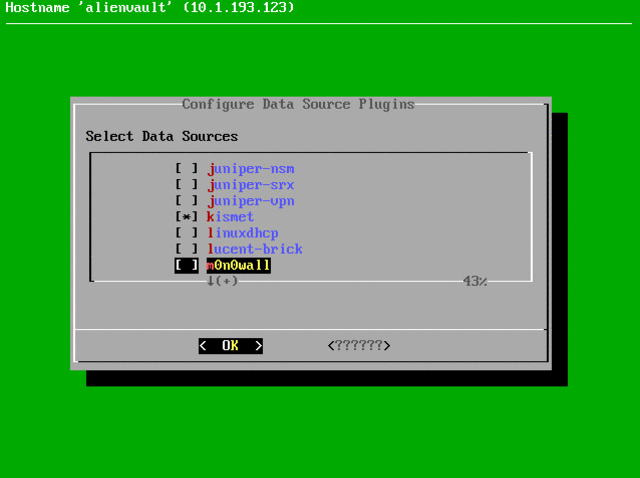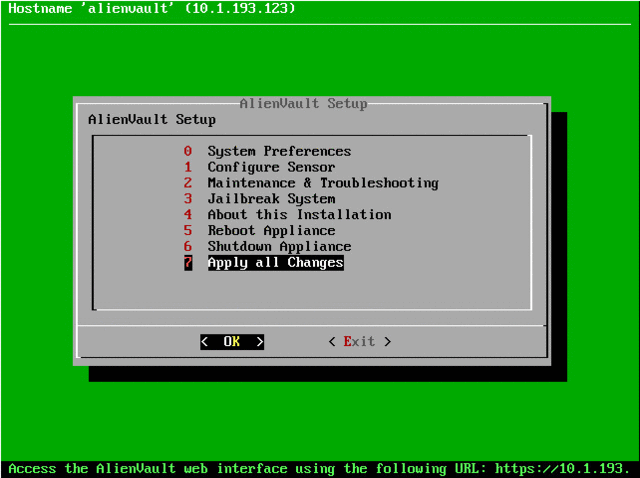
If everything is done correctly, we will see logs in “Analysis -> Security Events (SIEM)”:
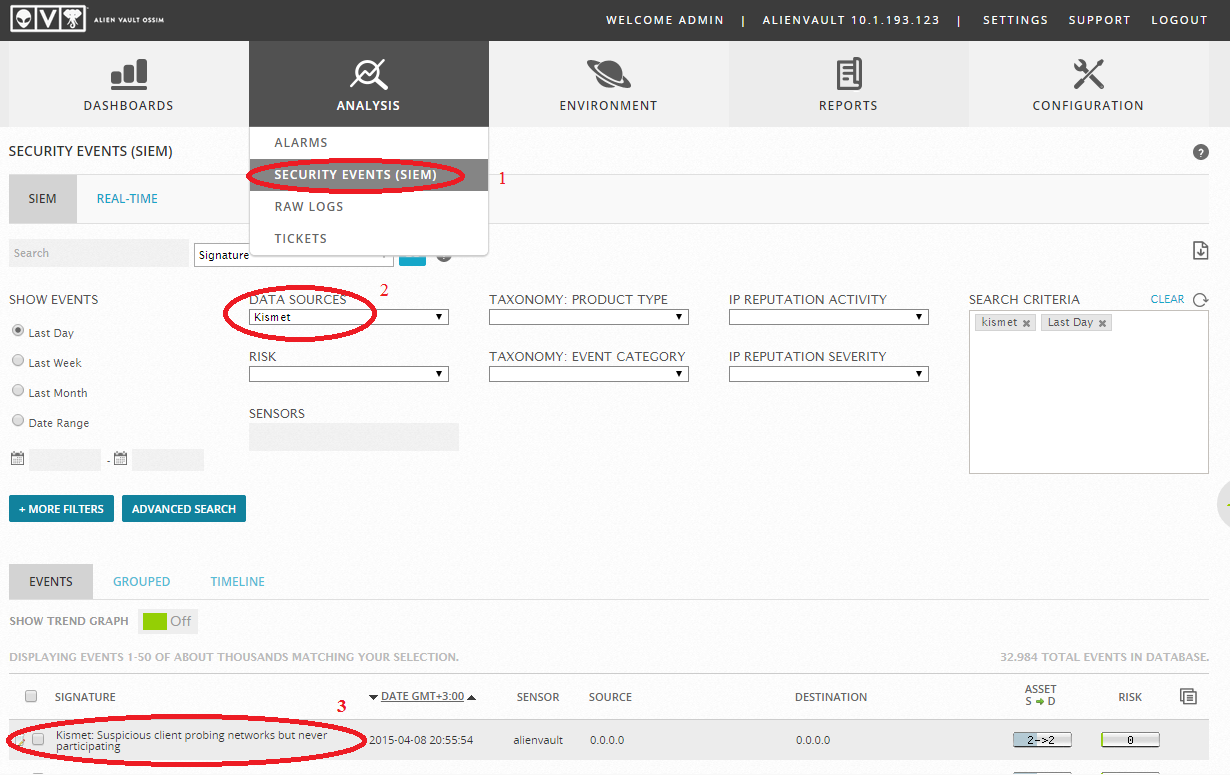
Setting up import XML logs
Now it remains to set up importing XML logs from Debian.
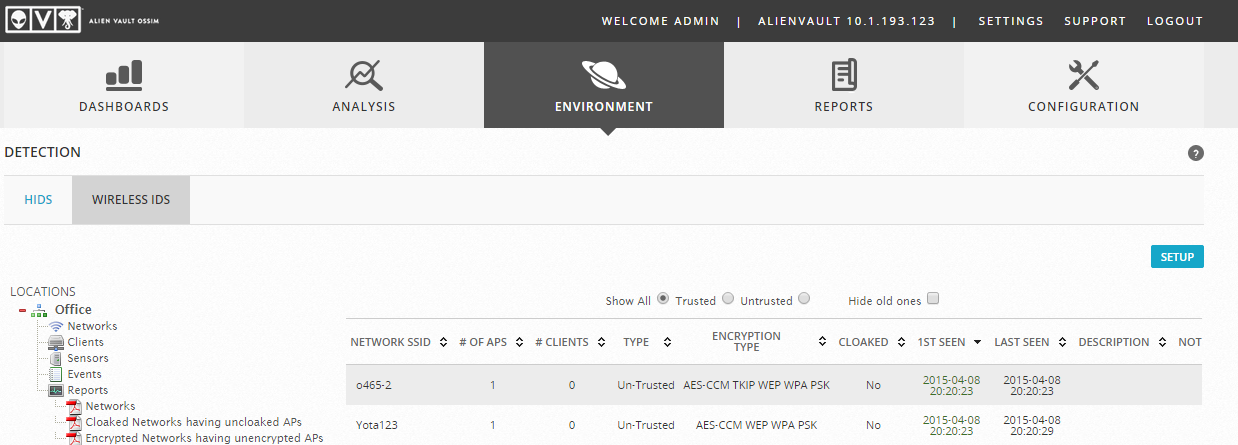
This is necessary so that OSSIM can receive not only alerts, but all available data on Wi-Fi clients and networks in the vicinity, which will subsequently be reflected in Environment -> Detection -> Wireless IDS.
Configure SSH authentication without a password so that the script that receives XML reports and cleans them from the sensor works correctly.
In OSSIM we will execute:
ssh-keygen ssh-copy-id root@10.67.68.10 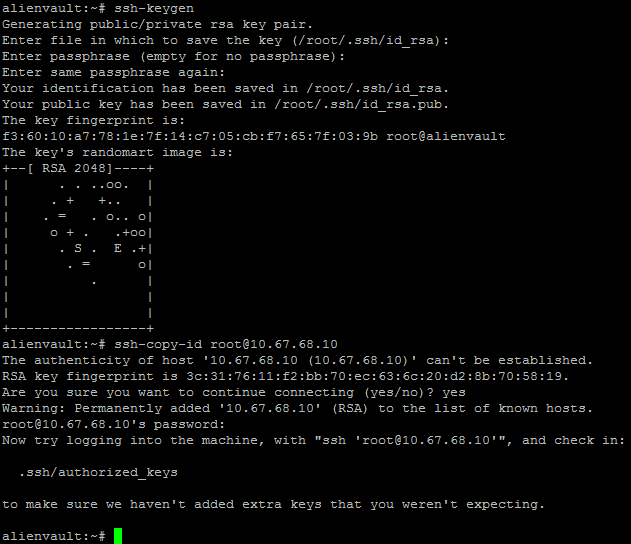
Now we will create the /etc/cron.hourly/kismet file with the following content:
#!/bin/bash /usr/bin/perl /usr/share/ossim/www/wireless/fetch_kismet.pl Copy the script itself:
cp /usr/share/ossim/www/wireless/kismet_sites.pl /var/ossim/kismet/kismet_sites.pl And correct the address in it:
echo \$sites{\'10.67.68.10\'}=\'/var/log/kismet\'\; >> /var/ossim/kismet/kismet_sites.pl Sensor Setup
Now let's go to the web interface:
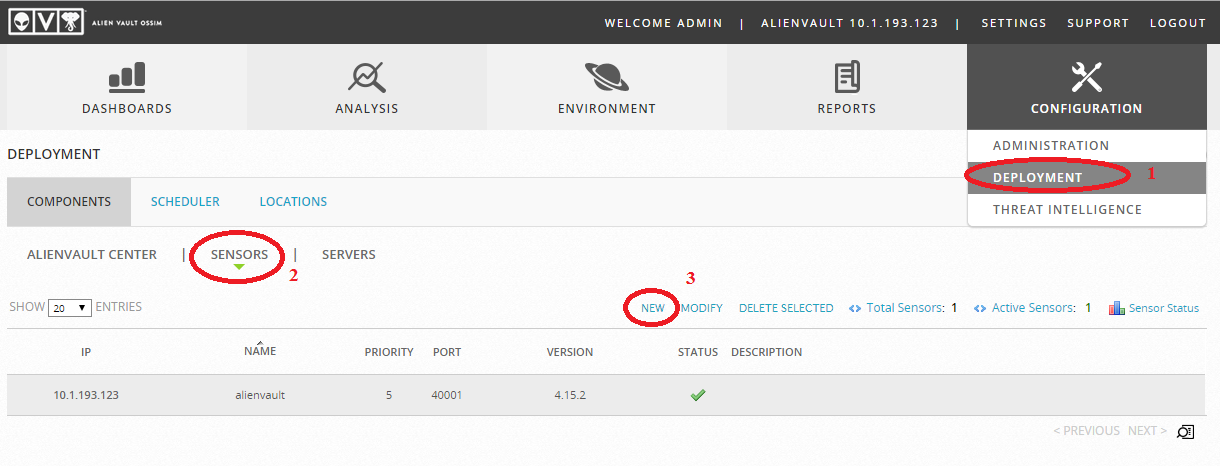
Add a new sensor:
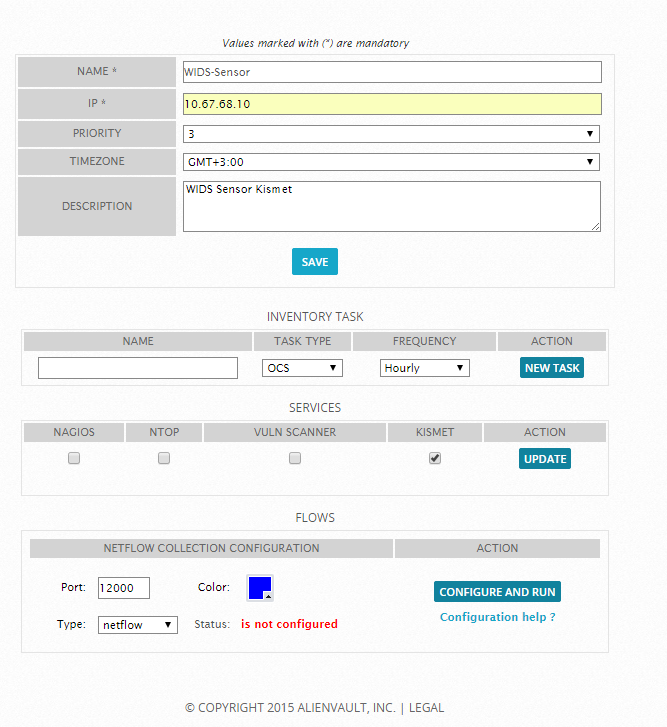
Sensor status will be with a red cross, and it should be:
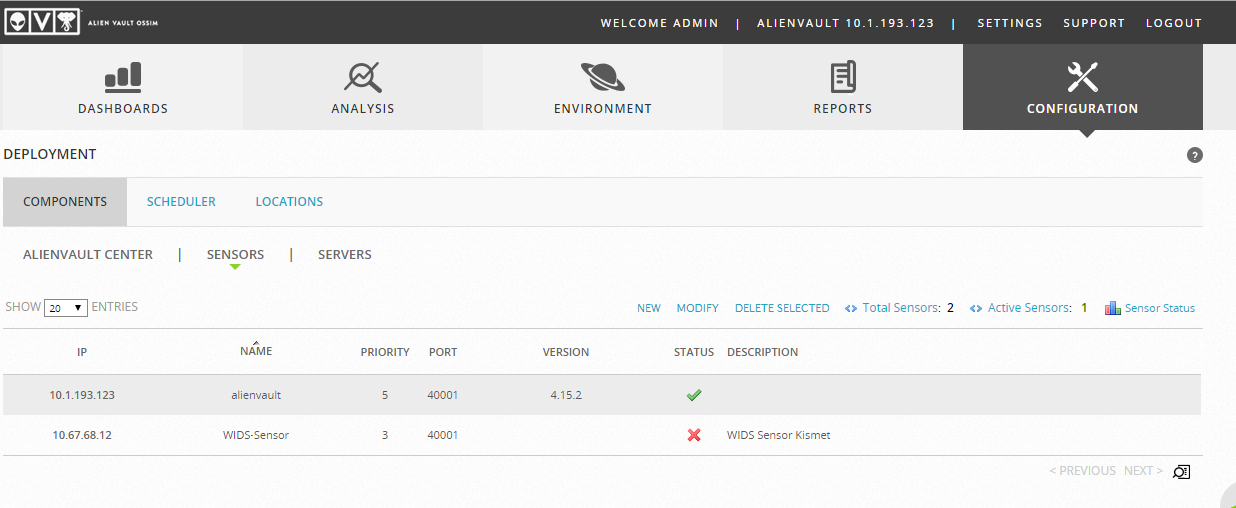
Now go to Environment -> Detection -> Wireless IDS and add the location and sensor:

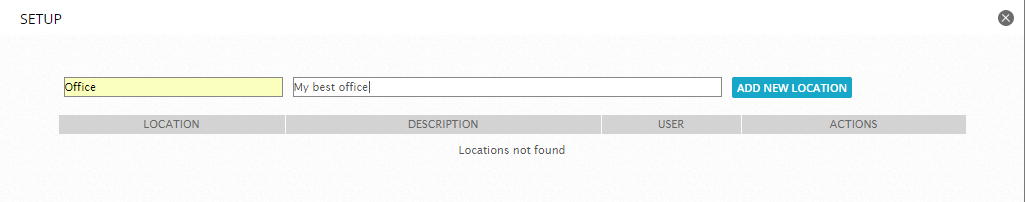
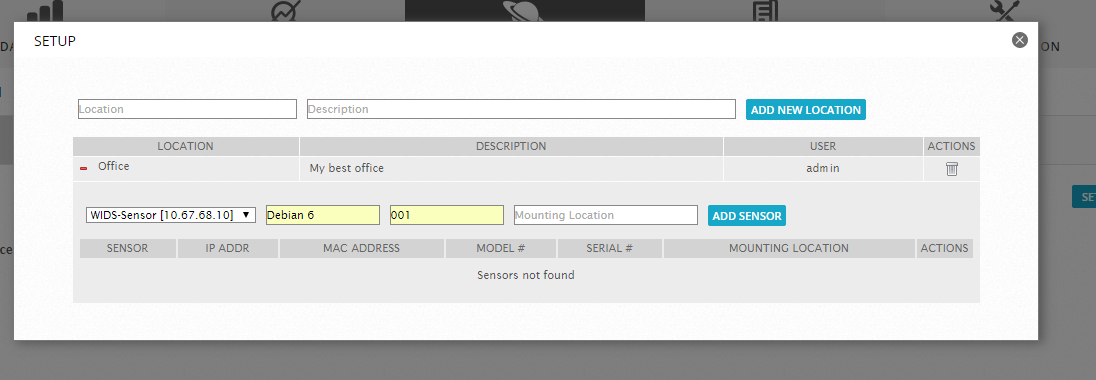
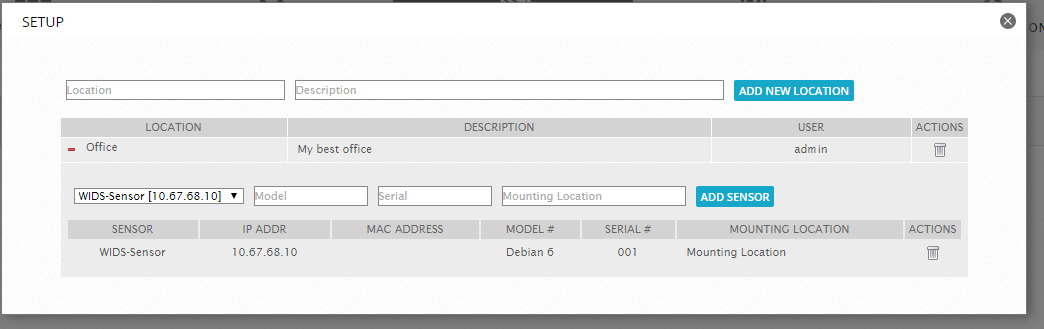
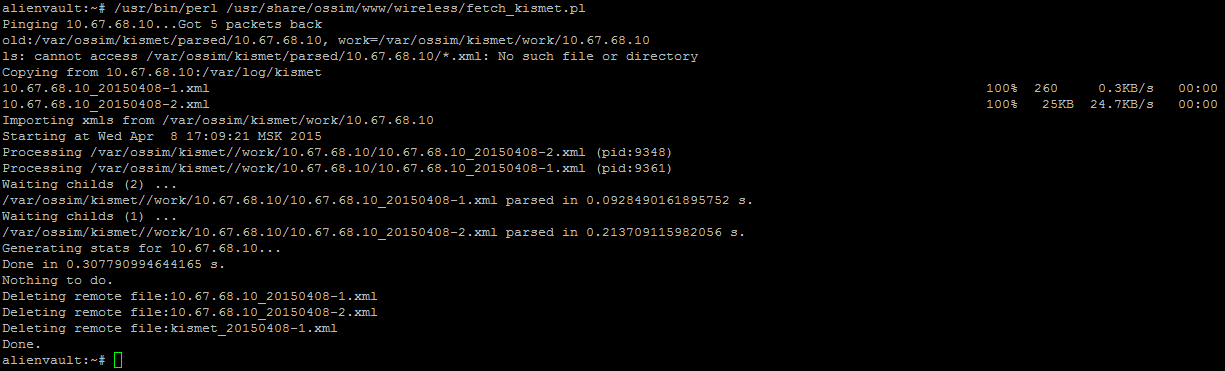
After we execute the command:
/usr/bin/perl /usr/share/ossim/www/wireless/fetch_kismet.pl And if successful, we get:
And after this action in the Environment -> Detection -> Wireless IDS item, the following data will appear:
Configuring the collection of system logs
Configure log collection from VMware ESXi, Windows server and Ubuntu.
To collect logs, we need to do the following:
- Configure sending logs from hosts to OSSIM
- See from which file the OSSIM plugin that handles events reads logs
- Configure logging from hosts to separate files through the rsyslog configuration
- Enable plugin
- Check the performance
VMware
First, we configure sending logs to ESXi, for this we open advanced settings:
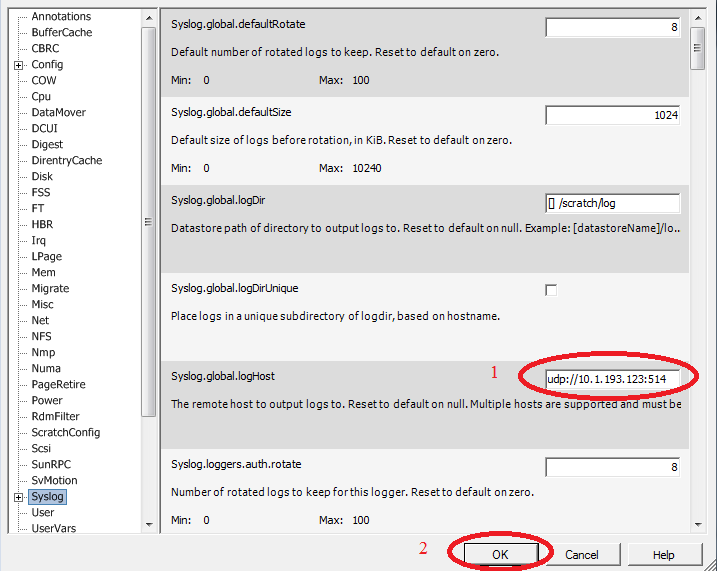
And turn on sending logs via UDP:
After that, see where the ESXi plugin will pick up logs.
cat /etc/ossim/agent/plugins/vmware-esxi.cfg | grep location 
Configure rsyslog:
echo if \$fromhost-ip == \'10.1.193.76\' then -/var/log/vmware-esxi.log >> /etc/rsyslog.d/esxi.conf service rsyslog restart Now turn on the plugin, connect via SSH to OSSIM:
Open Analysis -> Security Events (SIEM) and check:

Windows server
To send logs from Windows, we need the Snare program, which allows you to send system logs in syslog format.
Download and run:
Enable web access:
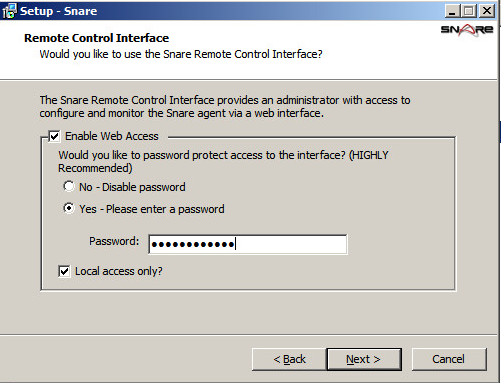
Finish the installation:
We open in the browser the address: localhost : 6161
Enter the login snare, the password that was specified during the installation, go to the "Network configuration" and specify:
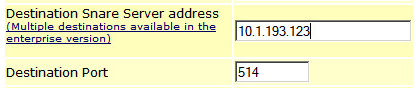
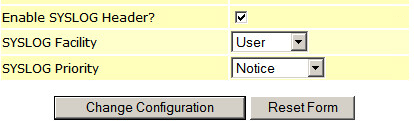
After saving the settings, open the console and reboot snare:
net stop snare net start snare 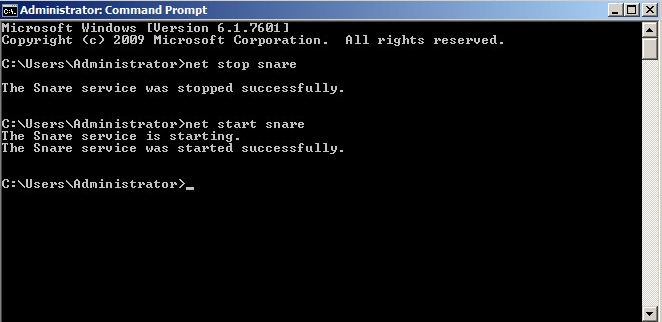
Check where the plugin gets the logs:
cat /etc/ossim/agent/plugins/snare.cfg | grep location 
Now configure rsyslog. In the rsyslog settings, there is already a pre-installed snare config (zzzzz_snare.conf), which we will now correct a little, following the OSSIM forum , replacing only 1 parameter:
sed -i -e "s@msg@rawmsg@" /etc/rsyslog.d/zzzzz_snare.conf service rsyslog restart Now we will configure the plugin, by analogy with the VMware configuration, except for the choice of the plugin itself:
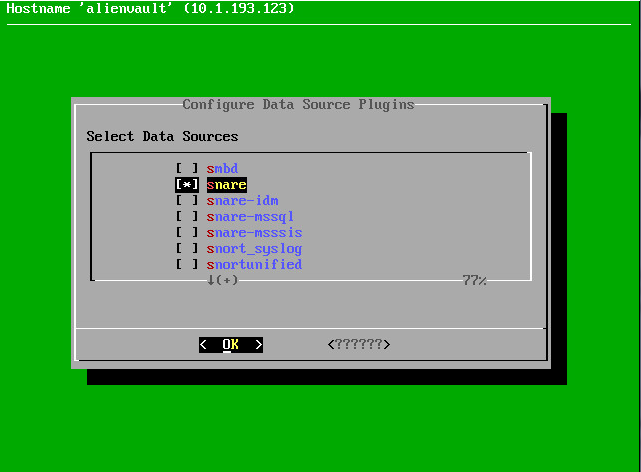
After restarting, check in Analysis -> Security Events (SIEM):
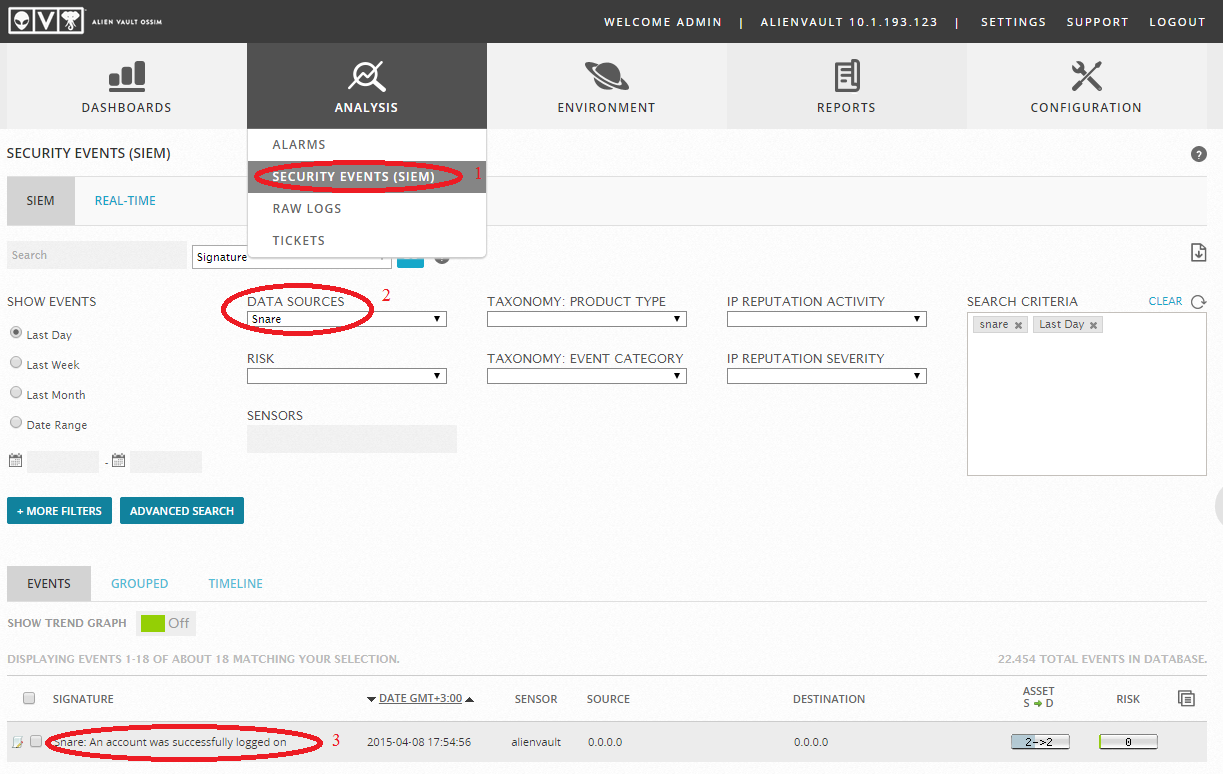
Ubuntu
To configure Ubuntu, we will use rsyslog. Connect to Ubuntu via SSH and configure sending logs to OSSIM:
echo *.* @10.1.193.123 > /etc/rsyslog.d/alienvault.conf service rsyslog restart Check where the plugin takes the logs:

cat /etc/ossim/agent/plugins/syslog.cfg Change the path to the log file:
sed –i –e "s@/var/log/syslog@/var/log/ubuntusyslog.log@" /etc/ossim/agent/plugins/syslog.cfg Now configure rsyslog in OSSIM:
echo if \$fromhost-ip == \'10.1.193.77\' then -/var/log/ubuntusyslog.log >> /etc/rsyslog.d/ubuntu.conf service rsyslog restart We include the plugin, by analogy with the previous paragraphs , only in the list of plug-ins we choose the right one:
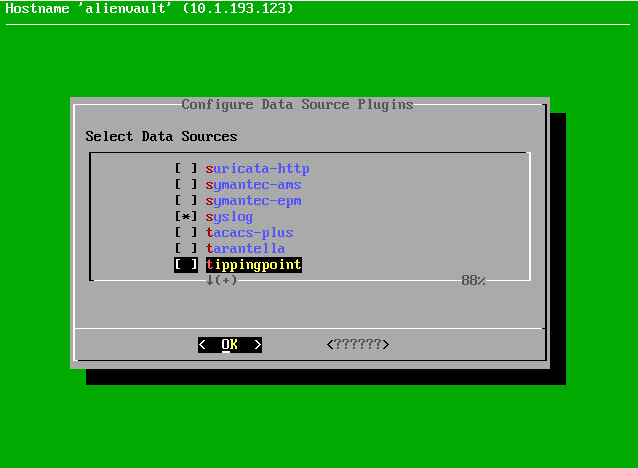
We apply and check:
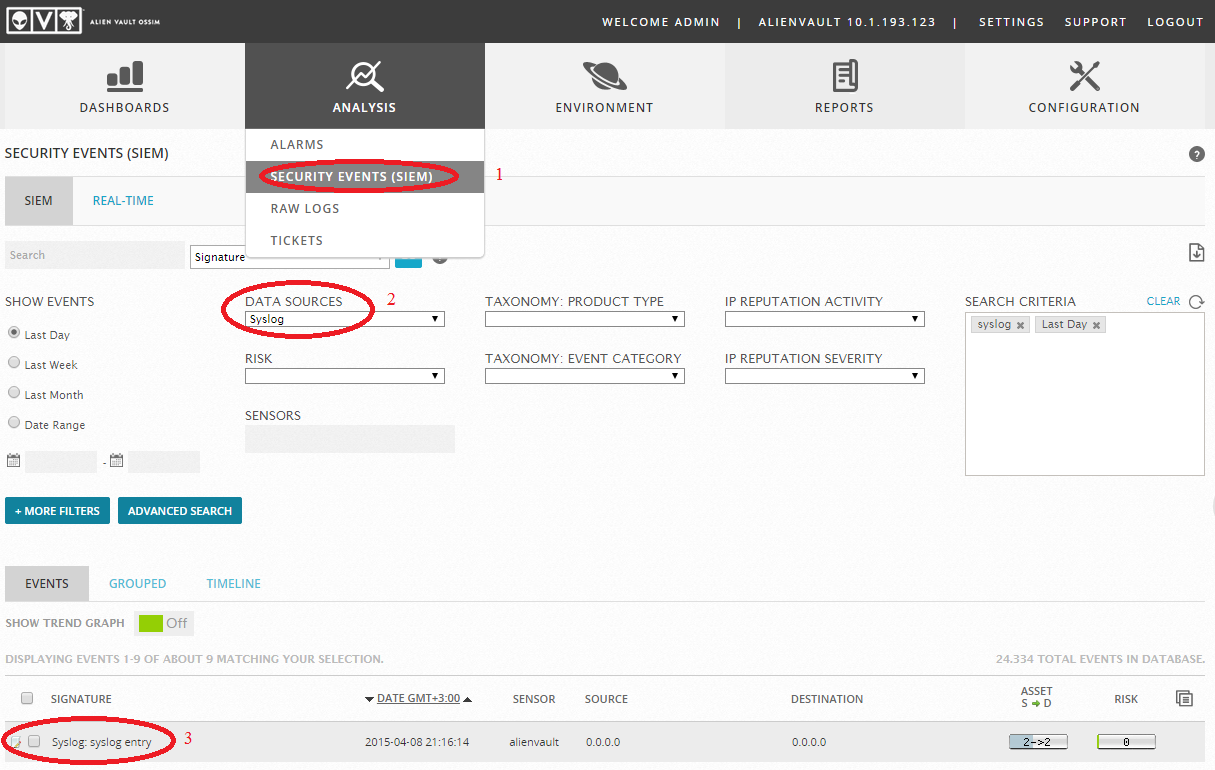
Note
If you didn’t see the AlienVault Reconfig window after selecting “Apply changes”
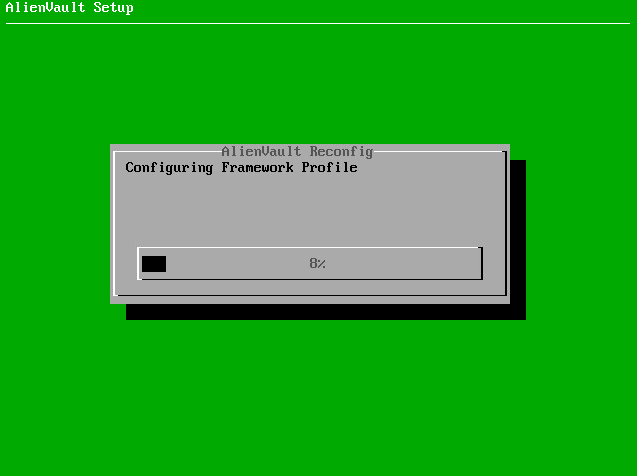
Reboot OSSIM (in the latest version 4.15.2, such a bug periodically appears)
To solve problems with parsing logs in cp1251 (Cyrillic) encoding, you need to do the following:
In the /usr/share/alienvault/ossim-agent/ParserDatabase.py file at line 288 after:
if len(ret) > 0: #We have to think about event order when processing cVal = ret[len(ret) - 1][ref] for e in ret: Paste:
e=list(e) x=[x.decode('cp1251').encode('utf8') if isinstance(x, basestring) else x for x in e] ## change for encoding cp1251 e=x e=tuple(e) In the /usr/share/alienvault/ossim-agent/TailFollowBookmark.py file on line 163 after:
def _open_file(self, fromrotate=False): """ Opens the file and seeks to the specified position based on the keyword arguments: offset and whence. Furthermore, the _current_file attribute is set as a side-effect. fromrotate: Indicates if the file is opened when a log rotation is detected """ Paste:
if «alerts.log» in self.filename: self.encode='cp1251' else: self.encode='utf8' Link to the forum , where there was a discussion of the problem with the encoding.
For information about solving this bug, many thanks to dolph2005
ArcSight integration
Now we will try to configure the integration of OSSIM with the SIEM system ArcSight .
Such a bundle can save tens of millions on ArcSight licenses if, in addition to the main office, the company has dozens of small branches that need to be protected and monitored.
The purpose of this section is to send already correlated OSSIM logs to ArcSight, and not to correlate them on the ArcSight side, increasing the load.
To do this, you need to install a connector (Syslog connector type), add the following FlexAgent:
# FlexAgent Regex Configuration File do.unparsed.events=true regex=\\D+ AV-FREE-FEED (\\D+) DST_IP -- SRC_IP: (\\d{1,3}\\.\\d{1,3}\\.\\d{1,3}\\.\\d{1,3}) , DST_IP: (\\d{1,3}\\.\\d{1,3}\\.\\d{1,3}\\.\\d{1,3}), Alarm: directive_event: AV-FREE-FEED \\D+ (\\d) (.*) token.count=5 token[0].name=Event_Name token[0].type=String token[1].name=SRC_IP token[1].type=IPAddress token[2].name=DST_IP token[2].type=IPAddress token[3].name=Dev_Severity token[3].type=String token[4].name=Event_Message token[4].type=String event.name=Event_Name event.sourceAddress=SRC_IP event.destinationAddress=DST_IP event.deviceSeverity=Dev_Severity event.message=Event_Message event.deviceVendor=__getVendor(AlienVault) event.deviceProduct=__stringConstant(OSSIM) In the folder of the connector and then in the " user \ agent \ flexagent \ syslog ". File name to make " ossim.sdkrfilereader.properties "
In the agent.properties file, change the line of agents [0] .customsubagentlist, adding “ossim” there, for example:
agents [0] .customsubagentlist = ossim | ciscopix_syslog | netscreen_syslog | ...
And the line of agents [0] .usecustomsubagentlist put true.
Next, go to the OSSIM settings:
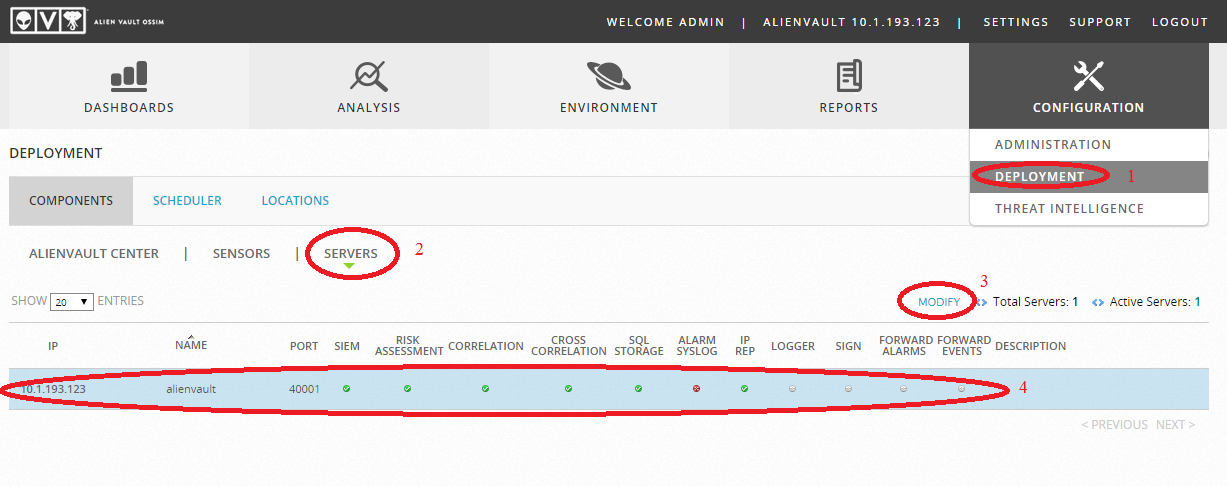
And enable sending alarm to syslog:
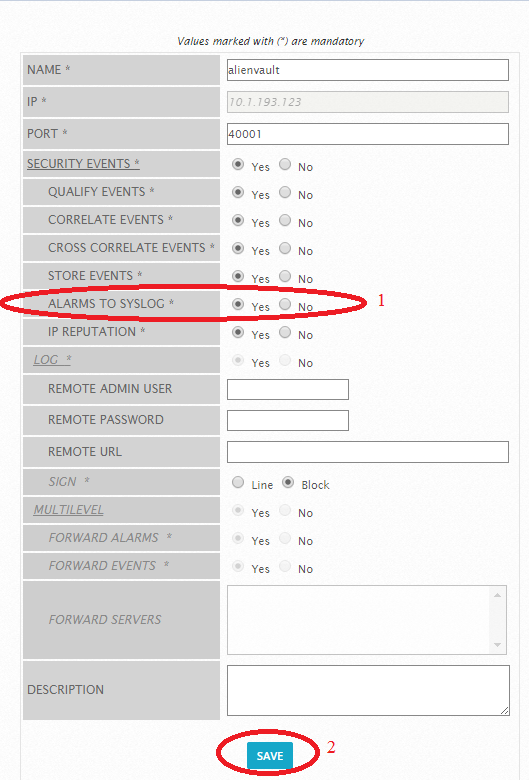
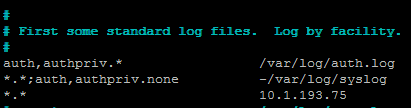
After you configure send logs to rsyslog OSSIM.
Add the line in the /etc/rsyslog.conf file:
*. * ip.your.Flex.agent
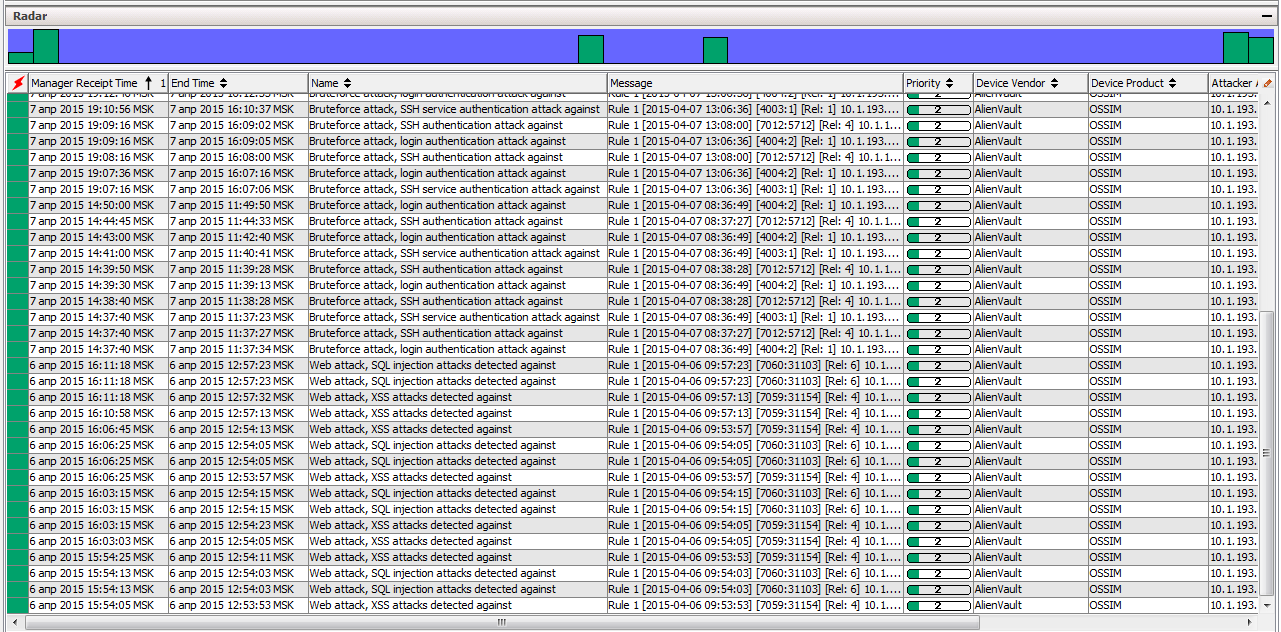
After that, the already correlated logs will appear in the ArcSight connector:
Used sources
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/255433/
All Articles