5 differences of data centers of the future from modern DC

Clouds and virtualization - something that has long become modern, although recently it looked like the future, and very distant. Gradually, new technologies will appear in the world of telecommunications, which in the near future will become as familiar as the virtualization. Already understand what trends will lead to a change in the modern world of telecommunications.
For example, the same cloud technologies are still far from reaching the peak of their development and popularity. According to Gartner's forecasts, GAGR (annual growth rate) in India alone will increase by 33.2% by 2017. This assessment includes the potential of all areas of cloud technology. SaaS and IaaS will show even better results: 33.4% and 39.8%, respectively. The growth of cloud services will lead (and is already leading) to the migration of traditional IT services to a cloud basis.
Naturally, the infrastructure of data centers and the technologies used in the field of telecommunications must change in order for the changes to run smoothly. The main ways of changing modern technologies are predicted as follows:
')
Software-defined data center (SDDC) . The implementation of the cloud model according to this scheme is carried out by means of intelligent software, which contributes to the abstraction of hardware resources, with their pooling and subsequent delivery to applications in the right quantity at a specific moment.
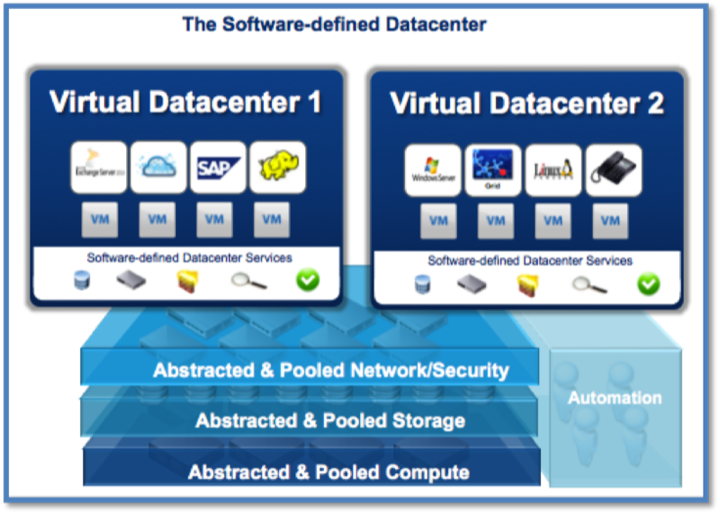
Security systems, data storage, network technologies - all this is integrated into the software-defined reality. This can be thought of as a logical layer in the data center itself. This layer allows for better and more efficient control of physical and virtual resources.
As an example, the following schemes:
- Data storage: Atlantis USX and VMware vSAN;
- Network technologies: Cisco NX-OS and VMware NSX;
- Security: Palo Alto PAN-OS and Juniper Firefly;
- Data Center: VMware SDDC and IO.OS.
All of these are robust platforms that help control many aspects of cloud computing and predetermine the way next-generation data centers work.
Multi-layered control of data centers. The data center accommodates a certain number of different systems. The control layer must be diversified. Technologies allow the integration of control over Big Data, data management and resource allocation. As an example, the latest release of OpenStack, Havana . The network component (Neutron) allows administrators to fine tune the cloud model. Now, with direct integration with OpenFlow, Neutron allows you to reach new horizons in scaling clouds and adapting various software-defined network technologies.
Data center operating systems (DCOS). When it comes to data center operating systems, it is usually not virtualization that is meant, but management of the entire data center environment. OS data center must connect the logical with the physical. There is already the first data center OS, as the creators call it (although there are already other projects). This OS IO.OS , allows you to see the relationship of all components of the system. Without such a unified management environment, many connections would simply go unnoticed. Using the OS data center, you can create a single logical cluster.
Now the Mesosphere company is developing its OS, and the program code of this product is open. This OS is called DCOS (Data Center Operation System), and is a system set of tools for data centers. The system has a graphical interface.
Infrastructure agnostic. To be completely honest, the data centers of the future should not depend on the specific server platform, hypervisor, or storage systems. Multi-layer management systems will allow for the most rational and efficient use of DC resources. This type of infrastructure will provide better scaling of all systems, with the creation of more powerful cloud platforms. Something similar is already being tested on the example of the BMC. By connecting the control panel and various APIs, you can achieve a higher level of abstraction.
Automation and robotization of data centers. The next generation DC will be tied to automation and robotization of control and monitoring systems. Resources will be dynamically distributed, administrators get effective control tools. Robotization is already involved: for example, the developer of robots like FANUC is already creating small robots for DC. In addition, IBM is discussing the possibility of using robots to monitor temperature patterns in data centers and to improve the energy efficiency of systems.

Now IBM's robots are based on iRobot Create, a customized version of Roomba's robot vacuum cleaners from iRobot. These mechanical assistants collect information about temperature and humidity in data centers.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/255085/
All Articles