Research on IT leadership factors
A week ago, I created a survey aimed at identifying leadership factors. It turned out only 261 answers, which, of course, is not enough for a full study, but already enough to reveal some regularities.
Especially interesting are the comments of survey participants:
Or, for example, such:
And even such:
But this is all theorizing, and what will the survey results tell us?
I am not a professional researcher and I have no idea what the Chi-Square and Student Criteria differ in, and also how the confidence intervals are considered. So I took Excel Data Mining Add-in ( https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dn282373.aspx ). This tool connects to SQL Server Analysis Services Multidimensional and uses its Data Mining mechanisms to analyze data in Excel.
It looks like this:
')

And for analyzing the tables there are ready-made tools:
For a start I will use the tool Explore Data , for construction of diagrams
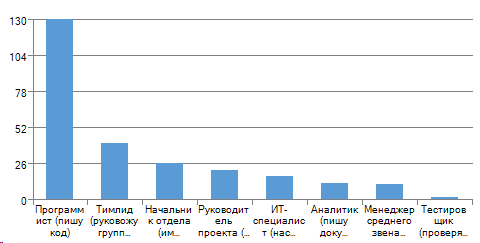
The distribution of the respondents to the question by posts:
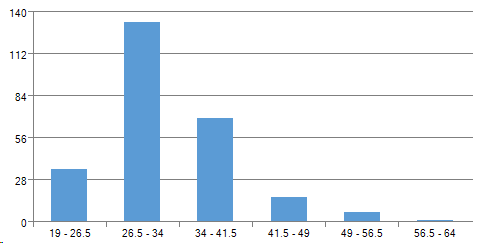
According to the age:
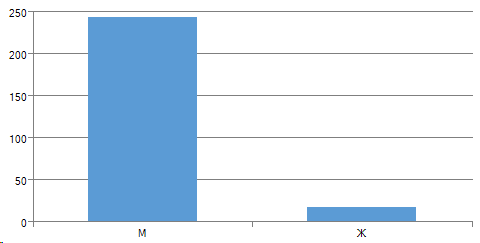
By gender:
By experience in last place:
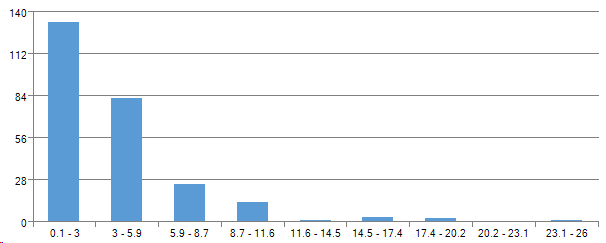
It turns out that the “average” survey participant is a programmer, age up to 35, a man, with work experience at the last place less than 3 years.
Let's try to make an analysis.
Use the Analyze Key Influencers tool to determine which columns have the most impact on the ones we need to explore.
The main question was - “Do you consider your leader a leader,” let's see what influences him.
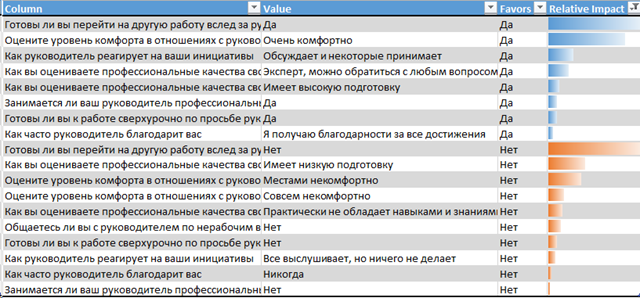
Analyze Key Influencers uses a Bayesian algorithm to identify a connection. Obviously, if the answer is “Are you ready to move to another job after the manager = Yes?” The person in charge considers his leader to be the leader, the reverse is also true. Actually this was the “validating” question in the survey itself.
The second key factor is the level of comfort. If a person answers that he is very comfortable with the leader, then with a high degree of probability he considers him a leader. The reverse is also true, but the influence is less.
The third key factor - professional qualities of a manager, a manager with higher professional qualities (in the field in which the employee is involved) will be called a leader more often than a leader with lower qualities.
Now let's analyze the impact on the level of comfort, for this I will again launch Analyze Key Influencers .

As you can see, people more often assess the level of relationships as “very comfortable” when the manager gives feedback, regularly communicates on informal issues, accepts initiatives, does not criticize, and is interested in the work of subordinates.
Also, the influence of the parameters “Are you ready to move to another job after the manager” and “Do you consider your leader as the leader” are indicated as strong factors, since the Bayesian algorithm cannot take into account the direction of influence with a high correlation between the factors.
Decision trees hide under the Classify button in the Ribbon. But due to the small amount of data and high correlation between the columns “Are you ready to move to another job after the manager , ” “Do you consider your leader as the leader” and “Evaluate the level of comfort in relations with the manager,” the tree is not built right away.
Let's try a little pochamanit:
It turned out this picture:
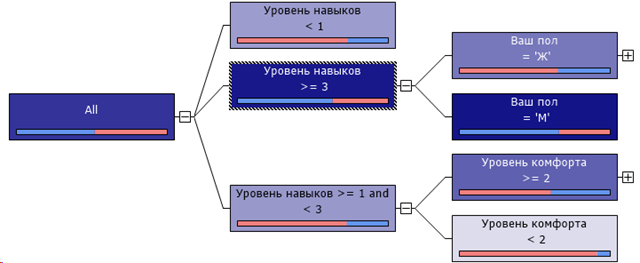
A more saturated color is more likely to be considered a leader. That is, if you are a manager and an expert (in the eyes of subordinates), and your subordinates are men, then two thirds of them will consider you a leader. Otherwise, you should try to make your subordinates comfortable, but in this case only a third will consider you a leader.
Use the Detect Categories tool. It uses a clustering algorithm. I ran the algorithm on sampled values and it revealed 4 categories to me.
Below is a list of categories with the most significant signs, the names I came up with.
And now the schedule “Do you consider your leader a leader”
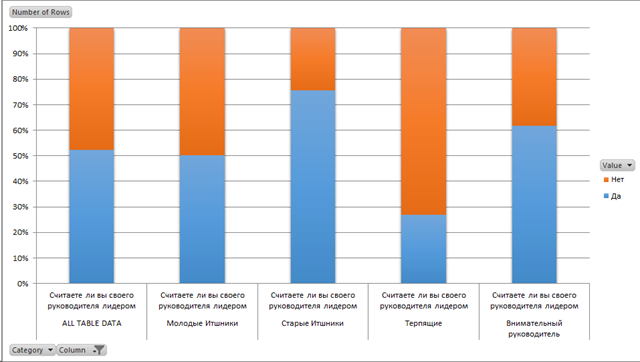
According to the schedule, it is clear that leaders-leaders are more often found in old IT staff, but this is more likely a consequence. But the category of “attentive manager” tells us that those who are more attentive to subordinates will be recognized as a leader rather than vice versa.
It is quite possible that some leadership factors remained unaccounted for in this survey, but it became quite clear that the IT manager needed to understand what the subordinates were doing, position themselves as an expert in this matter, and pay attention to their work.
I will clarify - it is important not to have a lot of knowledge \ skills \ certificates, but to be an expert for subordinates. There are many factors - how to position yourself, communicate, make decisions, and so on.
I expected a noticeable influence of the factors of independence of decision making and one-on-one communication, but they are almost imperceptible.
Link to the file with the survey data and results - 1drv.ms/1GcAuNj , you can conduct the analysis you are interested in.
Especially interesting are the comments of survey participants:
type in the search for "leadership", "leadership". Having some super knowledge is the last thing you see there. The topic of leadership trampled a huge number of psychologists. It would probably be interesting to refute their theories, but I see no point in proving their correctness.
Or, for example, such:
I think that for a leader other qualities are much more important:
Initiative - he constantly has to do something without waiting for instructions from the boss.
Openness to people - the desire to help them with their problems (but without fanaticism).
Charisma is trivial, a person who is noisy telling jokes that cheer up everyone is more likely to be a leader than a person who is learning the next PL at the computer and does not communicate with anyone.
And even such:
In essence, this is “authority”. What would they need to be two factors:
- To be able to be convincing, to convince. Developed speech and argumentation system, life experience (there is something to tell)
- Maintain justice within the team, a system of concepts ;-)
The result is a person with whom you are comfortable, on whom you can rely, who never panics and is not lost. To such people inside the team, the rest are pulled, and that’s the leader.
But this is all theorizing, and what will the survey results tell us?
I am not a professional researcher and I have no idea what the Chi-Square and Student Criteria differ in, and also how the confidence intervals are considered. So I took Excel Data Mining Add-in ( https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dn282373.aspx ). This tool connects to SQL Server Analysis Services Multidimensional and uses its Data Mining mechanisms to analyze data in Excel.
It looks like this:
')

And for analyzing the tables there are ready-made tools:

Demography
For a start I will use the tool Explore Data , for construction of diagrams
The distribution of the respondents to the question by posts:

According to the age:

By gender:

By experience in last place:

It turns out that the “average” survey participant is a programmer, age up to 35, a man, with work experience at the last place less than 3 years.
Key factors
Let's try to make an analysis.
Use the Analyze Key Influencers tool to determine which columns have the most impact on the ones we need to explore.
The main question was - “Do you consider your leader a leader,” let's see what influences him.

Analyze Key Influencers uses a Bayesian algorithm to identify a connection. Obviously, if the answer is “Are you ready to move to another job after the manager = Yes?” The person in charge considers his leader to be the leader, the reverse is also true. Actually this was the “validating” question in the survey itself.
The second key factor is the level of comfort. If a person answers that he is very comfortable with the leader, then with a high degree of probability he considers him a leader. The reverse is also true, but the influence is less.
The third key factor - professional qualities of a manager, a manager with higher professional qualities (in the field in which the employee is involved) will be called a leader more often than a leader with lower qualities.
Now let's analyze the impact on the level of comfort, for this I will again launch Analyze Key Influencers .

As you can see, people more often assess the level of relationships as “very comfortable” when the manager gives feedback, regularly communicates on informal issues, accepts initiatives, does not criticize, and is interested in the work of subordinates.
Also, the influence of the parameters “Are you ready to move to another job after the manager” and “Do you consider your leader as the leader” are indicated as strong factors, since the Bayesian algorithm cannot take into account the direction of influence with a high correlation between the factors.
Decision tree
Decision trees hide under the Classify button in the Ribbon. But due to the small amount of data and high correlation between the columns “Are you ready to move to another job after the manager , ” “Do you consider your leader as the leader” and “Evaluate the level of comfort in relations with the manager,” the tree is not built right away.
Let's try a little pochamanit:
- Discretize all text values so that algorithms can identify ranges.
- Correct the parameters that slow down the “growth” of the tree.
It turned out this picture:

A more saturated color is more likely to be considered a leader. That is, if you are a manager and an expert (in the eyes of subordinates), and your subordinates are men, then two thirds of them will consider you a leader. Otherwise, you should try to make your subordinates comfortable, but in this case only a third will consider you a leader.
Identify categories
Use the Detect Categories tool. It uses a clustering algorithm. I ran the algorithm on sampled values and it revealed 4 categories to me.
Below is a list of categories with the most significant signs, the names I came up with.
- Young IT students
- Less than 3 years on the last job.
- Do not occupy leadership positions.
- Most often, they changed jobs.
- The largest category is 129 people, about half of all respondents.
- Old ITshniki
- Age 41-49 years.
- Experience - 22-26 years.
- With the current leader working from 3.5 to 10 years.
- Work has not changed for a long time.
- About half of them are managers (department heads and above).
- 44 respondents fell into this category.
- Tolerant
- Assess the level comfortably as "very uncomfortable" and "sometimes uncomfortable."
- At the same time, they changed jobs least of all and have an experience of 8-11 years.
- The leader on them “scores”.
- Often work on orders.
- 42 respondents fell into this category.
- “Attentive Manager”
- The manager knows about the plans of the employee.
- The head gives feedback.
- Leader - expert.
- Leader thanks for achievements.
- The leader is engaged in the development of subordinates.
- Most often they make their own decisions.
- This group included 45 respondents.
- This group has the largest number of Project Managers.
And now the schedule “Do you consider your leader a leader”

According to the schedule, it is clear that leaders-leaders are more often found in old IT staff, but this is more likely a consequence. But the category of “attentive manager” tells us that those who are more attentive to subordinates will be recognized as a leader rather than vice versa.
findings
It is quite possible that some leadership factors remained unaccounted for in this survey, but it became quite clear that the IT manager needed to understand what the subordinates were doing, position themselves as an expert in this matter, and pay attention to their work.
I will clarify - it is important not to have a lot of knowledge \ skills \ certificates, but to be an expert for subordinates. There are many factors - how to position yourself, communicate, make decisions, and so on.
I expected a noticeable influence of the factors of independence of decision making and one-on-one communication, but they are almost imperceptible.
Link to the file with the survey data and results - 1drv.ms/1GcAuNj , you can conduct the analysis you are interested in.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/254543/
All Articles